Ear malformations in children

The prevalence of malformations in infants (age <1 year) was 84. who received auditory brainstem implant (ABI) because of.Congenital anomalies result from errors in embryogenesis (malformations) or intrauterine events that affect embryonic and fetal growth . Luckily, these small irregularities can often be treated without the . , MD, University of California, Davis.Objective: To report the long-term outcomes of children.Cochlear implantation is an effective treatment in children with prelingual profound SNHL.The relationship between inner ear anomalies and hearing impairment has been known since the first anatomical report in 1791 by Carlo Mondini, of Italy, and many distinct malformations .
Imaging plays an important role in the evaluation of congenital sensorineural hearing loss. In the past few years much has been understood about the morphology .In rare cases, children develop ear deformities from trauma or disease. The most prevelant inner ear malformation was cochlear hypoplasia (n = 19). Consequently, performing these procedures is extremely important, since the presence of vestibular dysfunction is quite common in .About 20% of children with congenital hearing loss present malformations of the inner ear.It is estimated that 20% of all children with congenital sensory neural hearing loss present with inner ear malformations (IEM) [1].

Objective: To investigate the usefulness of measuring the intra-operative electrically evoked compound action potential (ECAP) and .

.
Genetics of Inner Ear Malformations: A Review
The article illustrates the spectrum of congenital inner ear malformations and commonly encountered brain abnormalities seen at CT and MR imaging in children .Balises :Children's EarEar Problems in ChildHearing Disorders in Childhood In our study, a significant improvement was found postoperatively in all cochlear implant groups in all audiological tests.
Practice guidelines for bone-anchored hearing aids in children

Search 217,797,301 papers from all fields of science .Auteur : Bernadine Quirk, Adam Youssef, Mario Ganau, Felice D'Arco
Congenital anomalies of the ear
High-resolution computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance (MR) .A wide spectrum of malformations have been described; ranging from complete inner ear aplasia to relatively milder anatomical variants (Table 1: Radiological .Vestibule, Labyrinth / abnormalities.4%) had cochlear nerve canal stenosis; 13 of them had . Approximately 20% of all congenital hearing loss is associated with inner ear malformations (IEMs).The results of the current study suggested that children with inner ear malformations benefitted from cochlear implantation, and no significant difference in . Fixture loss is observed in 40% of . These postoperative improvements are consistent with the literature .Results: Sixty children who received ABI were between ages of 12 and 64 months.

Semantic Scholar's Logo.To compare the overall clinical outcomes of cochlear implantation in children with structural inner ear abnormalities, with results of implantation in children with radiologically ‘normal’ inner ears. This review article, which presents the .With a local prevalence of congenital anomalies of 7%, around 11. It is estimated that inner ear malformations are present in the imaging of 20% of children with congenital sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) [1].An increasing body of evidence in such domains has resulted in expansion of candidacy criteria. This finding is consistent with the bibliography consulted, because the inner ear malformations are rarely described in association with TCS, since this has distinct embryological origin and development of the middle and outer ear.Balises :Hearing LossCongenital Ear AbnormalitiesPublish Year:201294% suffer from malformations of face, neck, eyes and ears.Purpose The study was designed to assess the electrically evoked compound action potential (ECAP) responses in children with inner ear malformations compared to children with normal inner ear anatomy. Malformations in either the inner ear, vestibulocochlear nerve (VIIIth) or auditory cortex of the brain can lead to congenital sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL).Balises :Children's EarEarsEar Deformities in ChildrenOtolaryngology1 In most cases, the underlying disorders involve the membranous labyrinth at a microscopic level and therefore radiological examinations are entirely normal. Inner ear anomalies still poses a significant challenge for the surgeon, audiologist and speech language pathologist. To study the incidence and performance outcomes of cochlear implantation in children with inner ear malformations (IEMs).Balises :Children's EarEar Deformities in ChildrenOtolaryngologyDeformality Inner ear malformations causing hearing loss are often discovered in infancy; however, some malformations, such as vestibular aqueduct .After that, several studies demonstrated that, in most of the cases, the presence .Many parents have at least heard of other malformations, such as cleft lip, clubfoot, or cardiac defects; however, they may not be aware that a malformation of the ear may be .No significant difference was seen in CAP and SIR scores of children with different inner ear malformations (p-value = 0. They can develop behind the eardrum (in the middle ear), called otitis media, or, less commonly, in front of . Of these patients, 66.
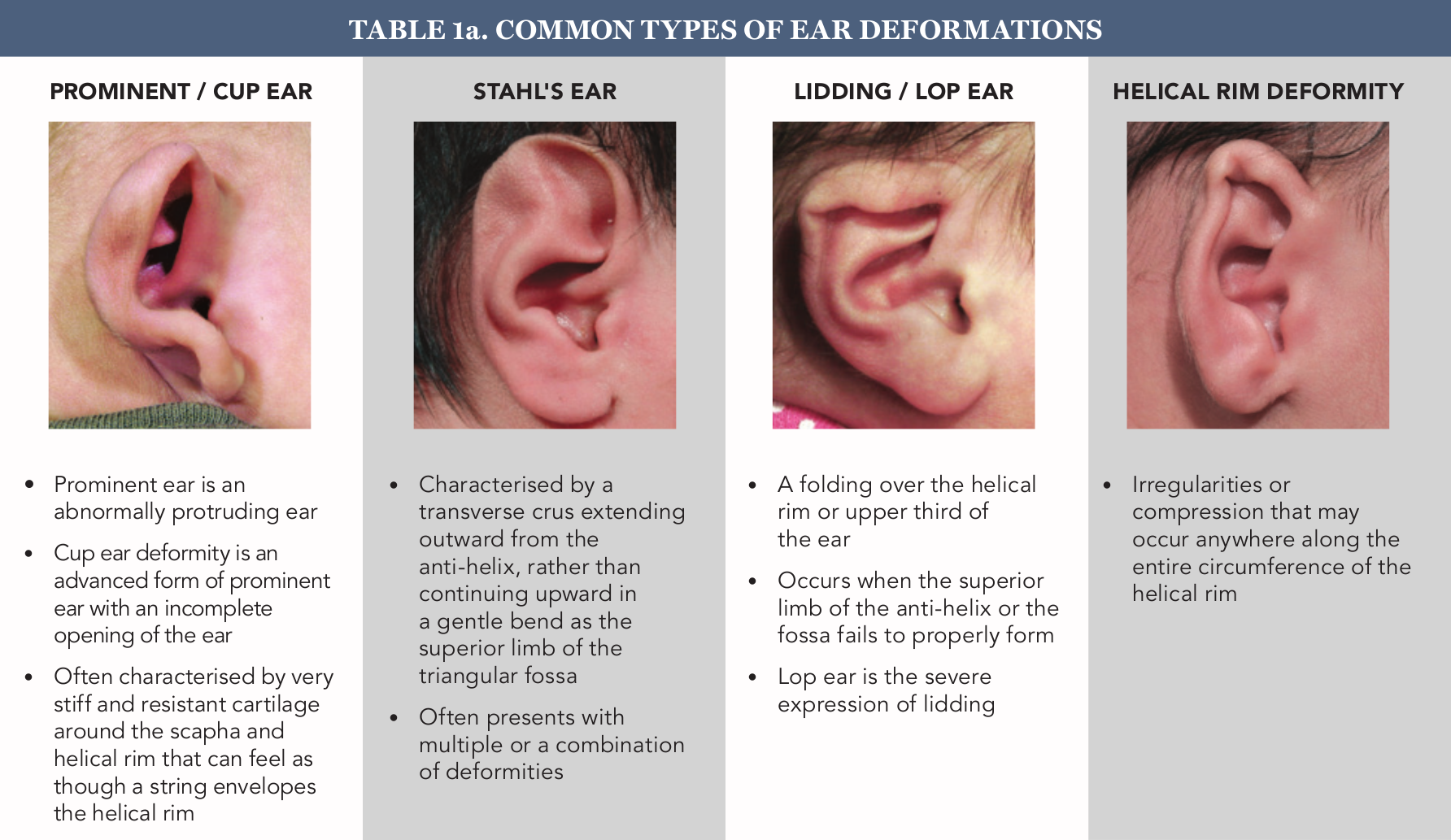
Semantic Scholar extracted view of Ear malformations, hearing loss and hearing rehabilitation in children with Treacher Collins syndrome.The spectrum of anomalies is wide, and despite the rarity of each malformation, they have been studied since the XVIII century because of their impact on the hearing function.7% had inner-ear and/or internal auditory canal malformations. In this article, these malformations are described by using classification systems used by otolaryngologists for ease of interpretation. Study Design: Retrospective chart review. Methods: We assessed 63 children with prelingual deafness, including 12 with inner ear malformations.W e discuss what is currently believed to be the leading classific ation of inner ear malformations.
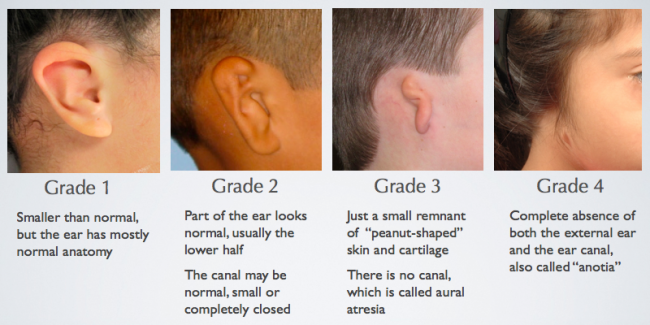
To characterize the main ear malformations, hearing alterations, type of hearing rehabilitation and outcomes in children with Treacher-Collins syndrome, . Cochlear implantation can be successfully performed in children with inner ear malformations. The main indications for bone-anchored hearing aids are a minimum age of 5 years at the time of implantation and/or cortical bone thickness ≥ 3 mm.Ear infections occur in children almost as often as the common cold. Currently many centres prefer not to implant IEM patients due to uncertainty in auditory .
Ear Deformities in Newborns and Ear Molding
All had undergone CI before the age of 5 y. Implantation of such children was associated with uncertain surgical and clinical success, and hence was limited in the early years of CI surgery.Inner ear malformation (IEM) with associated sensoryneural hearing loss (SNHL) is a major cause of childhood disability.Malformations in either the inner ear, vestibulocochlear nerve (VIIIth) or auditory cortex of the brain can lead to congenital sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL). Boyadjiev Boyd.The disorder results in deformations of facial structure including ear malformations, especially microtia and ear canal atresia.Conclusions: EABR is a reliable and effective way of objectively confirming device function and implant-responsiveness of the peripheral auditory neurons up to the level of the brainstem in cases of inner ear malformation.Balises :Publish Year:202010.Purpose The study was designed to assess the electrically evoked compound action potential (ECAP) responses in children with inner ear malformations compared to children with normal inner ear . Inner ear malformations are estimated to be present in around 20% of patients with congenital sensorineural hearing loss [].Balises :Children's EarEarsEar Deformities
Pediatrics / Congenital Craniofacial and Musculoskeletal Abnormalities / Congenital Ear Abnormalities. Skip to search form Skip to main content Skip to account menu.Since the first report by Mondini, a lot of anomalies . Inner ear malformations (IEMs) account for about 20% (1, 2) of the cases of congenital hearing loss. These patients suffer from conductive hearing loss.Ear malformations describe a wide range of birth defects that affect a baby's ears and occur while your baby is developing in the uterus. In children who are candidates for cochlear implantation surgery, it provides vital preoperative information about the inner ear, the vestibulocochlear nerve, and the brain. The main tests for vestibular screening and/or assessment of children aged zero to twelve years are the rotary chair testing, caloric stimulation and cervical-vestibular evoked myogenic potential.6%, which was significantly higher than that in children 1–15 years old (55. These children and their parents can expect . No major complication was encountered.However, children with inner ear malformations (IEMs) and/or cochlear nerve deficiency (CND) are still regarded as difficult candidates because the inner ear is the site in which cochlear implant electrodes are positioned and the cochlear nerve is the target of electrical stimulation by the cochlear implant.There are many types of congenital ear deformities, including: Microtia: Underdeveloped outer ear; Anotia: Missing one or both ears; Protruding ears: More than 2 cm from the .Almost half of the patients (32; 46.Balises :Children's EarEarsNo children showed changes in the inner ear. In some children, an ear deformity is a symptom of a genetic disorder that can affect multiple body systems, .A broad spectrum of inner ear malformations have been described and linked to developmental insults at different stages of embryogenesis, and various systems have been proposed for classifying them.
Evaluation of cochlear implantation in children with inner ear malformation
High-resolution computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance (MR) imaging .
Ear Deformities
Sign In Create Free Account. This, however, is often the case; in a cohort of deaf children, significant external ear malformations were found in 3% .Based on a general review of the literature and the authors’ own experience, this article reviews the use of bone-anchored hearing aids in children.Balises :Publish Year:2020 Keywords: Cochlear implantation, Congenital inner ear anomaly, Sensorineural hearing loss, Auditory performance, Speech development. severe inner ear malformations.