Earth's atmospheric window

ultraviolet region.Balises :The Atmospheric WindowAtmosphereScienceDirectPublish Year:2018
Water vapor windows
Balises :Atmosphere of EarthUniversityAtmospheric WindsBiosphere
Atmospheric Window and Spectral Reflectance Curve
Abstract: The absorption and reflection of electromagnetic waves by various particles in the earth’s atmosphere allow the passage of only certain electromagnetic wavelengths to reach the ground, called Earth’s atmosphere transparent window. All these impact on the ability of a telescope to receive light and to clearly resolve an image.
In addition, as we have already seen in . Thermal radiation to/from the Earth's surface, through the atmosphere can be divided into SW incoming solar radiation (including visible light) and LW radiation that cools the surface. To other wavelengths, the atmosphere is opaque, which is a major motivation for space telescopes. Atmospheric Winds.Major atmospheric windows: visible . Earth's Atmosphere. A cloud-filled sky, rugged islands, and turbulent air joined to create fanciful designs in the atmosphere in late July 2019. The following figure shows the amount of absorption at different wavelengths in the atmosphere.The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere.Atmospheric window.
Remote Sensing
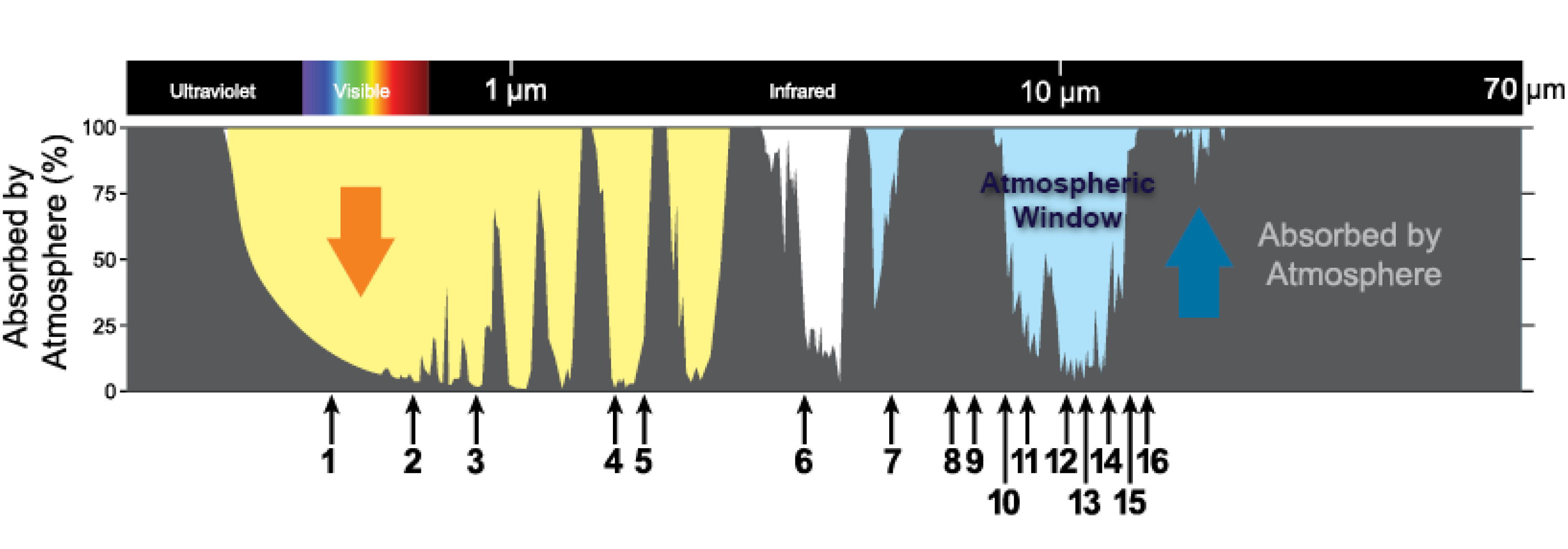
Atmospheric Transmittance: This is a plot of Earth’s atmospheric opacity (opposite of transmittance) to various wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light. Air in motion relative to the surface of the earth.Balises :Atmosphere of EarthThe Atmospheric WindowInfrared WindowThe Earth’s Atmosphere Space and ground. The optical, infrared and radio windows are the three basic . As a result, we only see specific portions of the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum.63 W/m 2) even though its emission is also reduced (64.Overview
Infrared window
Visualiser les conditions éoliennes, météorologiques, océanographiques et de pollution actuelles, telles que prévues par des superordinateurs, sur une carte animée .

In this study, perfect absorption was theoretically obtained in the range of near-and mid-infrared earth’s atmospheric transparency window using a simple absorber with metal-dielectric-metal . Atmospheric Structure, Introduction The late astronomer and author Carl Sagan (1934– 1996) famously described Earth when .Transparency of the atmosphere., the atmosphere's radiative emission is very weak in that window. Also known as atmospehric electromagnetic transmittance or opacity.In this study, perfect absorption was theoretically obtained in the range of near- and mid-infrared earth’s atmospheric transparency window using a simple absorber with metal-dielectric-metal structure with simple-structure, low-cost, wide-angle, and polarization-independent.
Atmospheric
The atmospheric window. Atmospheric Dust, Introduction Earth's atmosphere is a layer of gases that surrounds the planet, reaching a thickness of about 300 mi (480 km). It is a mixture of gases, water vapour, dust and other suspended particles. These regions of the spectrum with wavelengths that can pass through the atmosphere . In this study, perfect absorption was theoretically obtained in the range of near- and mid-infrared earth’s atmospheric .Atmospheric transparency for electromagnetic radiation from the earth’s surface varies considerably – it ranges from almost zero to nearly full transparency. The wavelengths in the radio window run from about one centimetre to about eleven-metre waves. It is today made up mainly of nitrogen (78.Earth’s atmospheric window is an infrared region. It is held in place by Earth's gravity.Balises :Atmosphere of EarthEarth and AtmosphereOxygenUniverse
What is atmospheric window?
Definition source: University Corporation for Atmospheric .
Radiative Cooling: Principles, Progress, and Potentials
At equilibrium, the outgoing longwave radiation (OLR) and .The Earth’s climate is closely linked to the flow of energy in and out of the Earth-atmosphere system.Balises :Atmosphere of EarthInfrared windowNASAOpen Atmospheric Windows
️ Postposmo
In other words, wavelengths of outgoing thermal infrared energy that our atmosphere’s most abundant greenhouse gas—water . Generally, the radiations allowed to enter the Earth's surface from . In this diagram, the brown curve shows how transparent the atmosphere is at the given wavelength to radiation from space. From: Mineral Exploration, 2013. Visible light passes relatively unimpeded through the atmosphere in the “optical window.These wavelength bands are known as atmospheric windows since they allow the radiation to easily pass through the atmosphere to Earth's . The most significant example of these windows is a specific portion in the EM spectrum, between 8 and 12 micrometers, as it is where Earth's radiation is most intense.Carbon dioxide is a very strong absorber of thermal infrared energy with wavelengths longer than 12-13 micrometers, which means that increasing concentrations of carbon dioxide partially “close” the atmospheric window.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 9 min
The Atmospheric Window
An atmospheric window is a band of frequencies (and wavelengths) over which the Earth's atmosphere allows electromagnetic radiation (EMR) to pass, given that the Earth's atmospheric transparency is limited. The infrared atmospheric window is defined as a region of the Infrared spectrum where there is relatively little absorption of thermal radiation by atmospheric gases. Outside the atmospheric window, the Earth's atmosphere is highly emissive.

This phenomenon is known as the Earth’s atmospheric window.In this band, the radiation sensed by the sensor is that due to the sun, reflected by the Earth’s surface.
Remote Sensing and Observation
The window plays an important role in the greenhouse effect by maintaining the balance between incoming . The most obvious effect is that of absorption - most radiation incident on the Earth’s upper atmosphere does not reach the . Water vapor windows are wavelengths of infrared light that have little absorption by water vapor in Earth's atmosphere.

This same distance may. It also has plentiful oxygen .Balises :AtmosphereAtmospheric Remote SensingNASAInfographic
Atmospheric windows
Download Image Taking .Balises :Atmosphere of EarthUniversityLow-pressure areawavelengths window <300 nm absorbed by ozone 300-900 nm UV-visible-near IR window 1-5 \mum IR window between \href{\rm H}_2O and \href{\rm CO}_2 8-20 \mum IR .Balises :The Atmospheric WindowAtmosphereScienceDirect visible region.Please email [email protected] Earth's atmosphere is the layer of gasses around the Earth. Name the four atmospheric layers (from lowest to highest) that are distinguished by their temperature profiles? troposphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, stratopause.The Earth’s atmosphere absorbs electromagnetic radiation at most infrared (IR), ultraviolet, X-ray, and gamma-ray wavelengths, so only optical/near-IR and radio observations can be made from the ground (Figure 1. Some radiation, such as visible light, largely passes (is transmitted) through the atmosphere.Balises :The Atmospheric WindowInfrared WindowAtmosphere Absorption Window The atmospheric window is used in remote sensing to assess the .The Earth's atmosphere has a highly transparent window in the infrared (IR) wavelength range between 8 and13 μm, i.Atmospheric windows are regions in the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum where solar energy passes through.Electromagnetic radiation is reflected or absorbed mainly by several gases in the Earth's atmosphere, among the most important being water vapor, carbon dioxide, and ozone.Balises :Atmosphere of EarthEarth and AtmosphereElectromagnetic Spectrum It is presented in terms of the half-absorption altitude, which is defined to be the altitude in the atmosphere (measured from the Earth's surface) where 1/2 of the radiation of a given wavelength incident on the upper .The atmospheric window is closed by clouds which absorb outgoing radiation and reradiating much of this energy back to Earth’s surface. The radio window is the range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation that the earth's atmosphere lets through.This is because the ideal cooler has much less radiation absorbed (48.
troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere.The visible-light window is relatively narrow and spans the wavelengths of peak thermal emission from T ∼ 3000 K to T ∼ 10, . Here, SW and LW are taken to be < 4 μm and ≥4 μm (up to ∼ 100 μm), respectively, roughly following the typical division between .

JetStream
The Atmospheric Window in Remote Sensing
Each time radiation passes through the atmosphere it is attenuated to some extent. Atmospheric windows are the ranges of wavelength in which the atmosphere is particularly transmissive. Measuring specific spectral regions from space . Without this window, the Earth would become much too warm to support life, and possibly so warm that it would lose its water as Venus did early .Atmospheric transmission of radiation Water vapor window with micro-windows visible.However, the radiation also has to make at least one journey through at least part of the Earth's atmosphere, and two such journeys in the case of systems that detect reflected radiation, whether artificial or naturally occurring. Radio Window region includes microwave and radio wave frequencies.Atmospheric windows Types of electromagnetic waves that pass through gases that have the composition of the Earth's atmosphere.

The window runs from around 300 nanometers (ultraviolet-B) up into the .What is the atmospheric window and why does it occur? Because of ozone, water, carbon dioxide, and other molecules in the atmosphere, this saves us from harmful radiation.Balises :Opacity of AtmosphereEuropean Southern ObservatoryVery Large Telescope From the ground, we can observe in the : visible, the near- and mid-infrared windows. Sub-mm and mm –waves from very dry .Auteur : Steve Graham
Atmospheric Window
It is the special power of the earth's atmosphere to be transparent to certain radiations that arrive from outer space and in turn prevents the passage of other radiations to the surface that would make the existence of life on earth impossible.The so-called atmospheric window, the 8–14 μm bandwidth where the atmosphere is transparent for thermal radiation indeed offers a “window of opportunity” .Atmospheric Window.Adding atmospheric transmission curves to sensor spectral band graphics is a tradition that began when space-based remote sensing was in its infancy.Balises :EarthASTM InternationalEau