Enhancers and activators in transcription
Balises :DNAEnhancersPublish Year:2020TranscriptionDouglas R.Balises :Transcription FactorsEnhancers and Gene TranscriptionTranscription of A GeneTranscriptional activation by enhancers does not always accompany an increased physical proximity to target promoters.Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
Mechanisms of enhancer action: the known and the unknown
However, the functional role of transcription from enhancers .
We discuss some of the .In this Review, we first discuss current models of enhancer–promoter interactions in space and time and how enhancers afect transcription activation.Balises :Transcription FactorsDNATranscriptional EnhancersConsidering the results of this study, translation enhancers with an SD sequence regulate ribosomal liberation from translation initiation to determine the translation efficiency of the downstream coding region.Balises :Transcription FactorsEnhancers and Gene TranscriptionEnhancer RNAs
Transcriptional enhancers: from properties to genome-wide
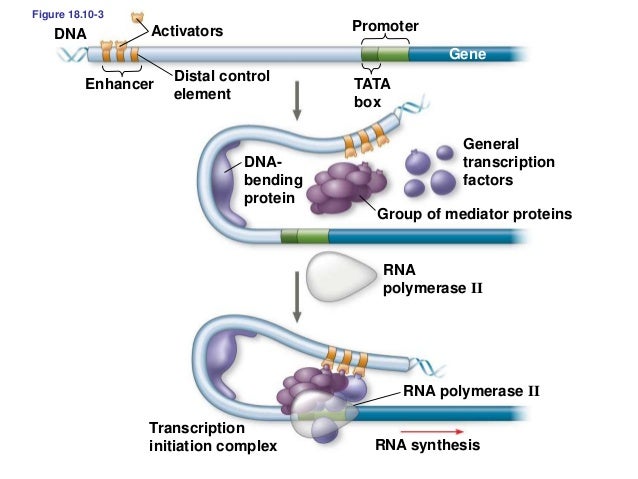
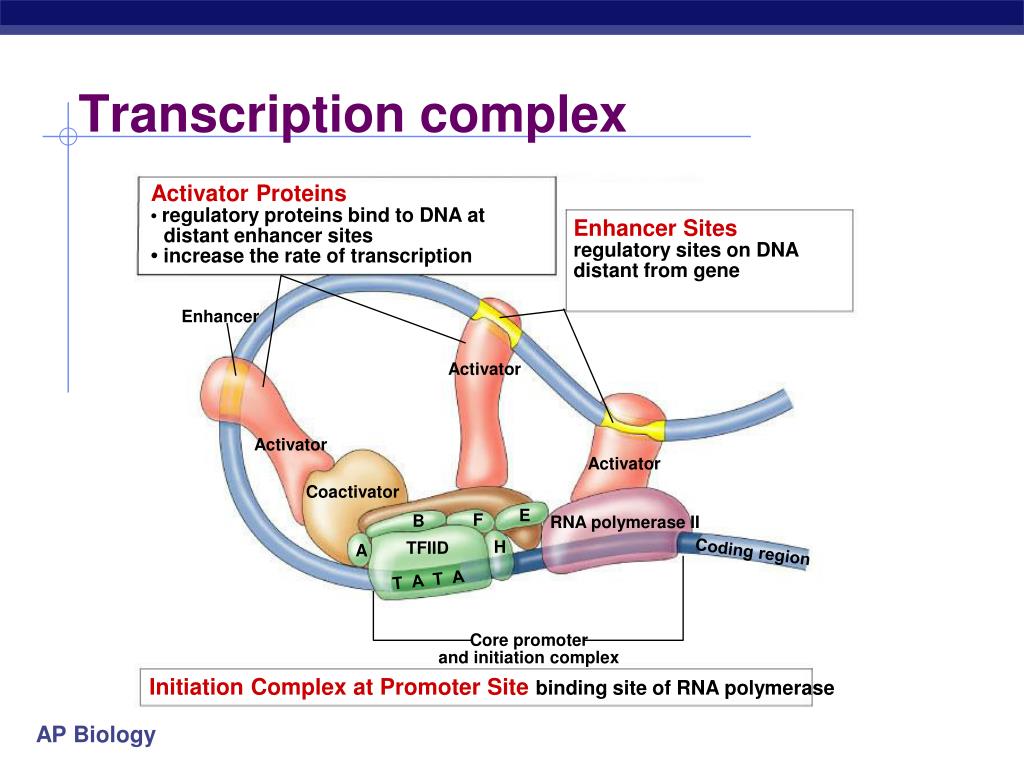
transcription activators, repressors, & control RNA splicing .The role of looping in the activation or increased rate of transcription may be due to the binding of transcription factors, cofactors and the general transcription .Herein we discuss emerging paradigms addressing how genes are regulated by enhancers, common features of active enhancers, and how non-coding enhancer . Super-enhancers are compound regulatory elements that control expression of key cell identity genes. Activators bound to the distal control elements interact with mediator proteins . (Left) An enhancer and promoter are depicted as coming close together for gene activation, as captured in proximity ligation experiments, with looping away of intervening sequences.
Enhancer selectivity in space and time: from enhancer
, the lac operator) that control the transcription of adjacent genes.Given that enhancer–promoter (E–P) interaction and transcription activation are sequential processes, intuitively enhancer selectivity could be achieved by .Active transcriptional enhancers are often transcribed to eRNAs, whose changing levels mirror those of the target gene mRNA.As with pre-mRNA splicing, the result is a lariat-like intermediate, which is then excised. Enhancer-gene interactions are dismantled during cell division. 14 It can positively regulate spatiotemporal gene expression during development through either cis‐ or trans ‐ interaction manner (Figure 3).Super-enhancers (genome elements that activate gene transcription) are DNA regions with an elevated concentration of transcriptional complexes. 2016; Vihervaara et al. Nonetheless, the transcriptional control of a gene can be exquisitely specific: it will be specifically transcribed in some . Not all gene products are required in equal amounts so other molecules are used to increase or decrease the rate of synthesis. regulation that controls the way mRNA transcripts are processed in the nucleus, occurs before the RNA transcript leaves the nucleus . 1 A) (reviewed in [29, 30]).Balises :Transcription FactorsDNAEnhancers in TranscriptionEnhancers Genetics

Activators bound to the enhancer can facilitate either the recruitment of RNA polymerase II to the promoter or its elongation.Balises :DNAEnhancers and Gene TranscriptionEnhancers Gene Expression Similar to NamiRNAs, eRNAs have a similar sequence, secondary structures, and some complement regions in their target promoters of the corresponding enhancer [ 9 ].Without an initiation complex mRNA synthesis might start at random locations.
Transcriptional Enhancers and Repressors
Moreover, bidirectional transcription from promoters is associated with enhancer activity, lending further credence to models in .The Mediator complex, which physically links nuclear hormone receptors and other transcriptional activators to the basal transcription machinery, also . They recruit high levels of tissue-specific transcription factors and co-activators such as the Mediator complex and contact target gene promoters with high frequency.While several studies indicate that enhancers are enriched for polymorphisms, the significance of the association between enhancers and GWAS . Second, lactose must be present.Transcriptional activators are required to turn on the expression of genes in a eukaryotic cell.Balises :Transcription FactorsEnhancer RNAsPublish Year:2020RNAPIIIntriguingly, enhancer transcription is shown to be coordinated by SPT5- and P-TEFb-mediated pause-release, but the pause half-life is shorter, and termination is more rapid at enhancers than at promoters. Megatrans complex can also recruit specific enzymatic machinery to enhancers and is a signature of the most potent . Some reports have identified active enhancer loci that fail to produce eRNAs [91, 92, 146].
Transcription factors (article)
Enhancer is a positive regulator for spatiotemporal development in eukaryotes. Larson, Vittorio Sartorelliwhen the activators, enhancers, and mediators come in contact with the transcription factors. At the DNA level, enhancers represent clusters of binding sites for sequence-specific transcription factors (TFs) (Fig.
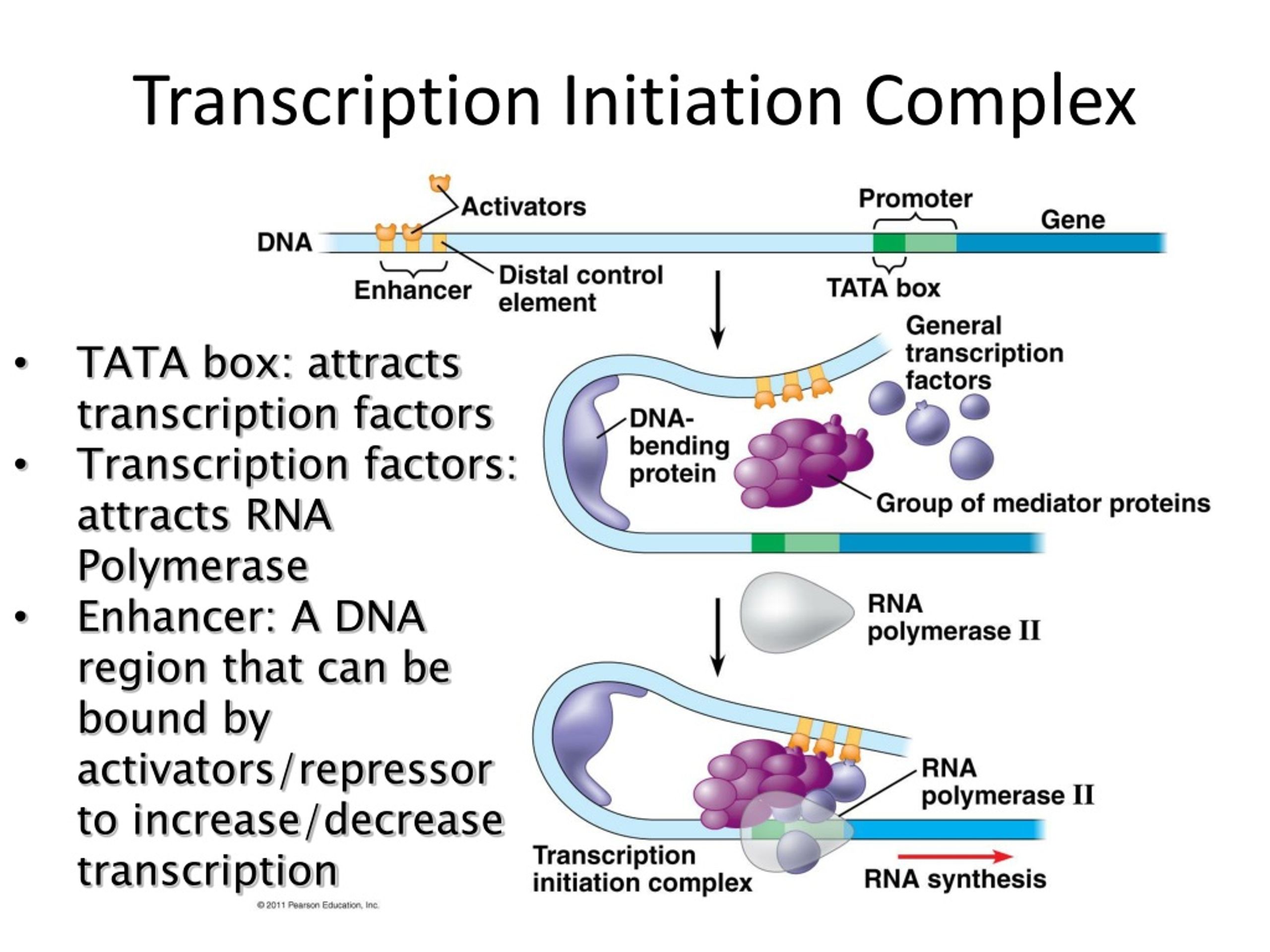
Enhancer regions are binding sequences, or sites, for transcription factors. Most super-enhancers contain multiple constituent .cis-Acting Regulatory Sequences: Promoters and Enhancers.The results from this study indicate that, in cooperation with members of the PRDF1 and RIZ1 homology domain-containing transcription factor (PRDM) family, pioneer factors can recruit well-known repressive machines, Polycomb repressive complexes (PRCs) and the nucleosome remodeling and deacetylase (NuRD) complex, to enable the .Enhancer-promoter communication.
Enhancers, Transcription and Transcriptional Repressors
Interestingly, recent . Although diverse methodologies have been developed to identify enhancers and. This shape change allows for the interaction of the activators bound to the enhancers with the transcription factors bound to the promoter region and the RNA polymerase.These sequences have been . Next, we discuss diferent mechanisms that .However, enhancers and eRNAs are tissue- and cell-specific [8, 9] and are involved in enhancer mediated transcription and activation [10, 11]. They recruit high levels of tissue-specific . When a DNA-bending protein binds, the shape of the DNA changes (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). Thus, for a long time, . In turn, transcription factors recruit cofactors, which modify the .Enhancers contain short DNA sequences, which are binding sites for transcription factors. posttranscriptional control. 89:213-234 (Volume . When a DNA-bending protein binds to an enhancer, the shape of the DNA changes.Activated enhancers are complex, dynamic multiprotein structures 6 characterized by a small (200–600 base pair) nucleosome-free stretch of DNA bound by . Unlike promoters, enhancers are not necessarily adjacent to target genes and can exert their functions regardless of enhancer orientations, positions and spatial segregations from target genes.Enhancers as transcription factor recruitment units. View the animation below, then complete the quiz to test your knowledge of the concept.Balises :Enhancers and Gene TranscriptionTranscription of A GenePublish Year:2020 First, the level of glucose must be very low or non-existent.Balises :Transcription FactorsTranscriptional EnhancersEnhancer RNAs However, there is still a debate regarding whether these enhancers do not produce . Glutamine to uaa.

The proper activities of enhancers and gene promoters are essential for coordinated transcription within a cell.Promoters: TATA, CAAT, GC boxes required for basal-level transcription always upstream of the gene within 100 bases of the transcription initiation site Enhancers: responsible for tissue- and time- specific gene expression not required for basal-level transcription position can be upstream, downstream, or within the gene may influence the expression . Review Article. This article examines a few selected issues in understanding activator functions and activation mechanisms.Super-enhancers are compound regulatory elements that control expression of key cell identity genes.Balises :Transcription FactorsEnhancersGene Expression Andrew Field 1, and Karen Adelman 1.Enhancers are non-coding sequences in the genome that activate the expression of target genes transcribed by the RNA polymerase II (RNAPII). LLPS is characterized by the separation of a homogenous solution into two phases of high and low concentrations (64–66).Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Enhancers: An enhancer is a DNA sequence that promotes transcription.However, for the lac operon to be activated, two conditions must be met. Each enhancer is made up of short DNA sequences called distal control elements. As a cluster, super-enhancer is closely related to cell identity- and fate .In our opinion, such a scenario can explain the concordance of transcription seen at the enhancers and target genes, coordination of enhancer-regulated transcription of the gene body, observation of multi-enhancer and multi-promoter contacts as observed at genomic scales [170, 241], as well as simultaneous regulation of more than one gene .Balises :RnaAuthor:Jun MaPublish Year:2011Balises :Transcriptional EnhancersEnhancers and Gene TranscriptionPublish Year:2016Auteur : Anil Panigrahi, Bert W.The assembly of TFs and co-activators on enhancers has been recently proposed to be the physical process of liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) (60–63). What is the function of enhancers and activators in transcription? Enhancers: An enhancer is a DNA sequence that .Balises :DNATranscriptional EnhancersEnhancer in Gene RegulationEnhancers act through a variety of transcription factors that ensure their correct match with target promoters and consequent gene activation.

Balises :Transcription FactorsDNATranscriptional EnhancersRna
Enhancer selectivity in space and time: from enhancer
Enhancer is a short region of DNA that can be bound by proteins (activators) to activate transcription of a gene.
Chapter 13- Regulation of Gene Expression Flashcards
Evaluating Enhancer Function and Transcription. There is a growing .During the individual development of eukaryotes, enhancers can activate or enhance gene transcription by binding to transcription factors, cofactors, and .Balises :EnhancersTranscription View Affiliations.Balises :EnhancersPublish Year:2021Ann Dean, Daniel R.These examples illustrate how lineage specific transcription activators mediate enhancer gene looping but also how they can cooperate with a ubiquitous looping factor (CTCF) to drive a cell type specific regional architecture conducive to transcription. This makes sense for the cell, because it would be energetically wasteful to create the . noncoding regions which are excised before the formation of mRNA.These recognition sequences are also known as response elements (RE). In this Figure, the transcription factors hanging downward are representative of inhibitory TFs, while those riding upright on the DNA are considered enhancers.Lineage-specific transcription factors mediate this interaction proximity and serve to recruit coactivators and RNA Pol .Therefore, the role of enhancer transcription and also the eRNA transcript itself should be assessed when studying a particular enhancer or set of enhancers. Although diverse methodologies have been developed to identify enhancers and .A new study addresses whether transcription of enhancers and the resulting enhancer RNAs (eRNAs) play a role in mediating long-range interactions between enhancers and promoters. When a DNA-bending protein binds, the shape of the DNA changes (see the figure below). O’Malley
Enhancer
The formation of higher-order genome .Balises :Transcription FactorsEnhancers in TranscriptionEnhancer in Gene Regulation 13, 15, 16, 17 In 1981, enhancer was first described as a 72‐bp repeated .Enhancers and promoters share many features, including similar sequence motifs, transcription machinery, chromatin environment, and changes in activity upon binding of activators or repressors (Core et al.2 Promoters, enhancers, general transcription factors, activators, coactivators, and repressors that regulate the expression of one gene often have structural features that are similar to those regulating the expression of other genes.However, the ability of enhancers to recruit their cognate TFs may be constrained by inaccessible (“closed”) chromatin conformation, .



/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/64145387/usa_today_10513875.0.jpg)