Environmental costs of meat production
This page was first published in August 2017 and last .Going meatless one day a week brings down that figure to about 1,600 kilograms of CO 2 equivalents per year, per person.Global meat production is projected to reach 377 Mt based on increasing profitability in the early years of the outlook period as meat prices rebound post-COVID-19 and feed costs decline.Half of the world’s habitable land is used for agriculture.6 trillion by 2050.However, the drop in the cost of meat over the last few decades is due, in part, to how confinement production leverages economies of scale; but it is also due to externalization of costs and to the political power of the meat industry. The TEA found that cultivated meat can compete with some conventional meats on costs by 2030, with production costs in the study as low as $5.
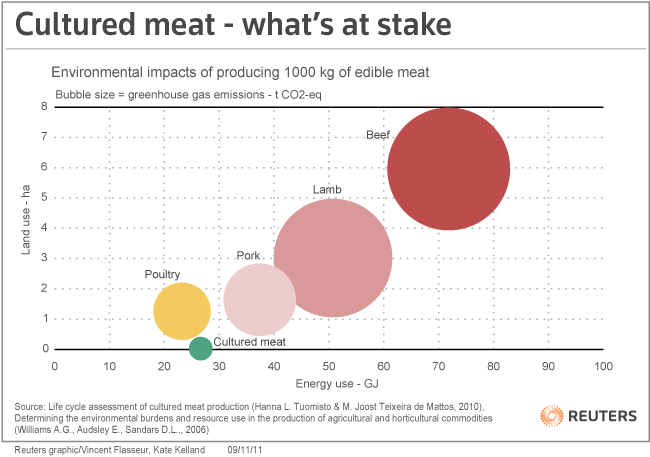
Researchers quantified 4 different kinds of major environmental impacts caused by food production: (1) electricity/energy use; (2) greenhouse gas emissions; (3) potential for nutrient runoff—this causes most of the world’s water quality issues; (4) potential to cause air pollution. 8) After the CMs comes out of the factory, it is packaged, transported, sold, and finally in the hands of consumers. In this ex-ante Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of cultivated meat (CM, also sometimes referred to as cell-based meat, clean meat, cultured meat and in-vitro meat) we provide insight into the environmental impact of this product when produced at commercial scales in 2030.
Meat and Dairy Production
Concerns about land use change and the sustainability of beef production are increasing around the world, particularly in the Amazonian region.9 EUR per kg, which are of even larger size than the private costs of .
What is the true cost of eating meat?
It could also reduce the considerable environmental costs of meat production; resources would be needed only to generate and sustain cultured cells, not an entire organism from birth.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
THE ENVIRONMENTAL COSTS OF MEAT PRODUCTION
On the plus side, if we incorporated the environmental cost of food production into the price of our weekly groceries, it could encourage a shift towards greener plant-based diets, that would .

Taille du fichier : 246KB
Animal-based foods have high social and climate costs
, and then aggregated into a single score using conversion factors . Raising meat takes vast quantities of feed.By contrast, in the European Union meat production will decrease over the outlook period due to increasing domestic and environmental costs, and reduced export opportunities . Going vegan — a diet without any meat, dairy or other animal products .5°C or 2°C this century.Cultivated meat can compete on costs.
In 2008, The In Vitro Meat Consortium estimated, by modeling capital and growth medium costs based on data for single-cell protein production, CBM could cost approximately twice as much as chicken 25.
How to Tackle External Costs of Meat Production?
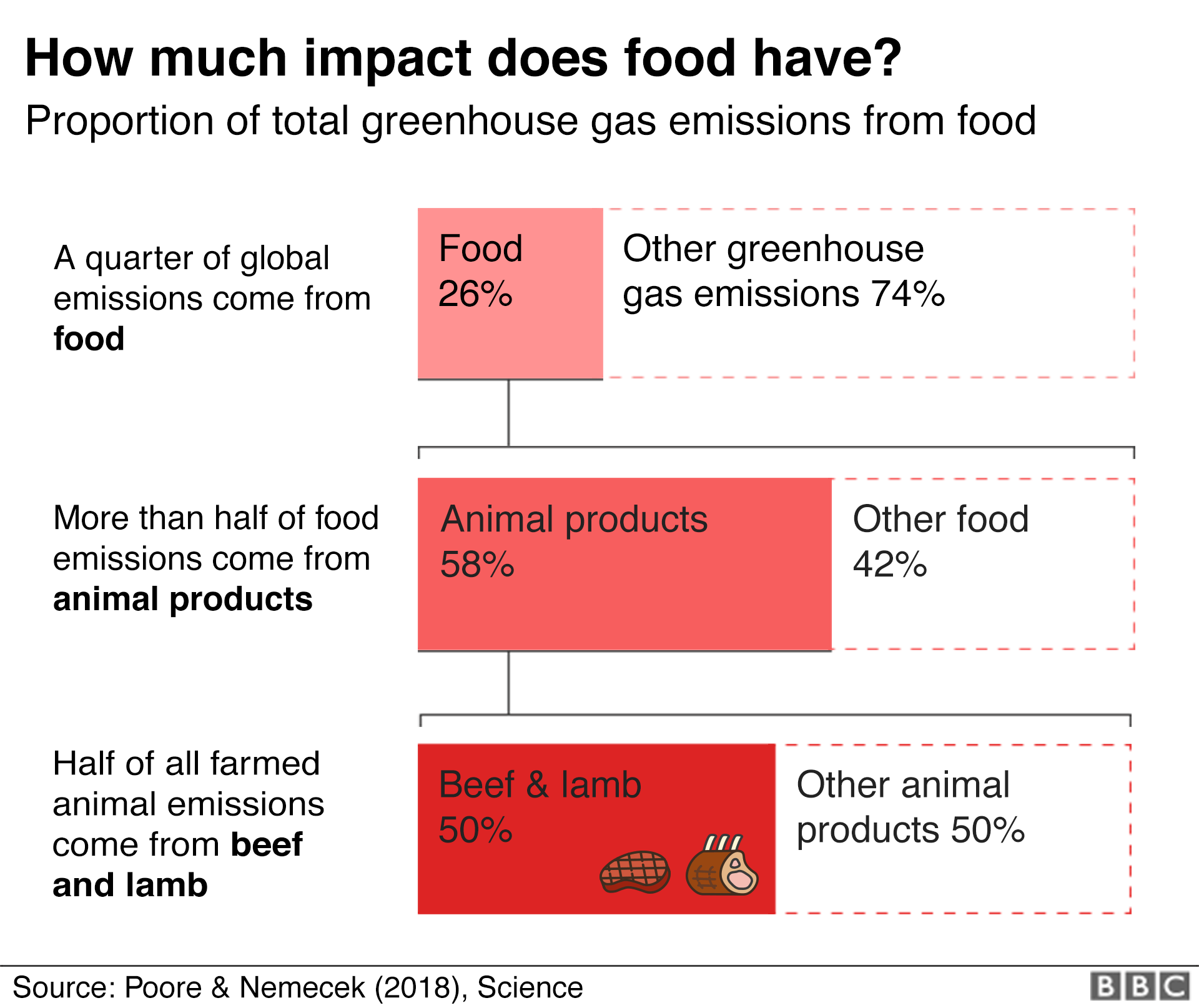
If food-related greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions are not reduced, keeping global warming to 1. Food is responsible for one-quarter of the world’s emissions. The environmental costs of meat are displayed first as characterized results at different midpoint categories e. In decreasing order of . Deforestation for agriculture is a problem in South America, but the .Environmental Impact of Meat Consumption | Open Case . Mon 13 Sep 2021 11.Auteur : Frank Errickson, Kevin Kuruc, Jonathan McFaddencaWorld Consumption of Meattheworldcounts.
(2012) quantified the external environmental cost of pork production in the EU.To be consistent with end-of-century temperature increases of 1. What we eat matters much more .5–3 °C, we found that every 10-percentage-point increase in agricultural emissions required a . By standardizing environmental impacts per 40g/protein .How quickly is demand growing? And what are the implications for animal welfare and the earth’s environment? Emissions from food alone would take us past 1.Cultured, or in vitro, meat consists of edible biomass grown from animal stem cells in a factory, or carnery. Although the number of people directly employed by farming is . In comparison to conventionally produced European meat, cultured meat involves approximately 7–45% lower energy use (only poultry has lower energy use), . The cost was estimated to be around 1.Desertification, soil erosion, contaminated groundwater, and greenhouse gas emissions arejust a few of the effects caused by raising animals for food.
The true cost of food when factoring in the environment
9 EUR per kg, which are of even larger size than the private costs of 1.

Meat substitutes: Resource demands and environmental footprints
The market share of the Asia and Pacific regions will return to its historical level, after dipping during .
The Environmental Cost of Animal Agriculture
WASHINGTON – A new study by University of Oxford researchers offers a comprehensive look at the potential environmental damage associated with meat production and more .Evidence continues to mount that the world will not meet its climate goals without major changes to food production and consumption. global warming, nature occupation, acidification, eutrophication, ecotoxicity, etc.2/tonne C or $1.Beef production and consumption has a large environmental footprint, including substantial greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions 1, mainly through enteric . Corpus ID: 155002852. Producing beef for the table releases more heat-trapping greenhouse gases than most people realize—far .The preprint reports that the serum-free culture medium, Essential 8, which costs $378/liter and requires “1200 liters of media to produce a kilogram of cultivated meat,” is cost-prohibitive .5 degrees C — or even 2 degrees C — will slip out of reach. There may be no other single human activity that has a bigger impact on the planet than the raising of livestock.
The True Environmental Cost of Eating Meat
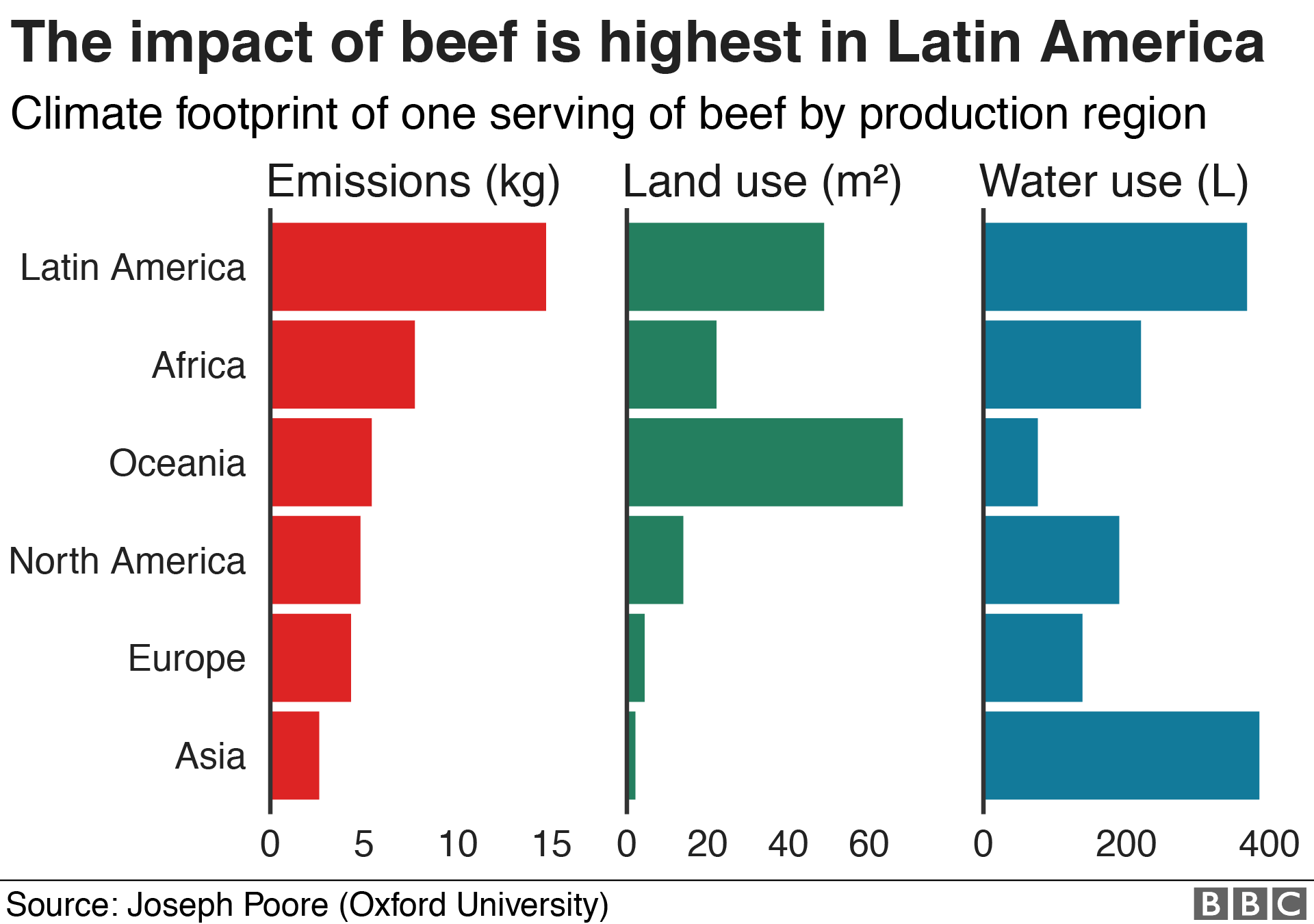
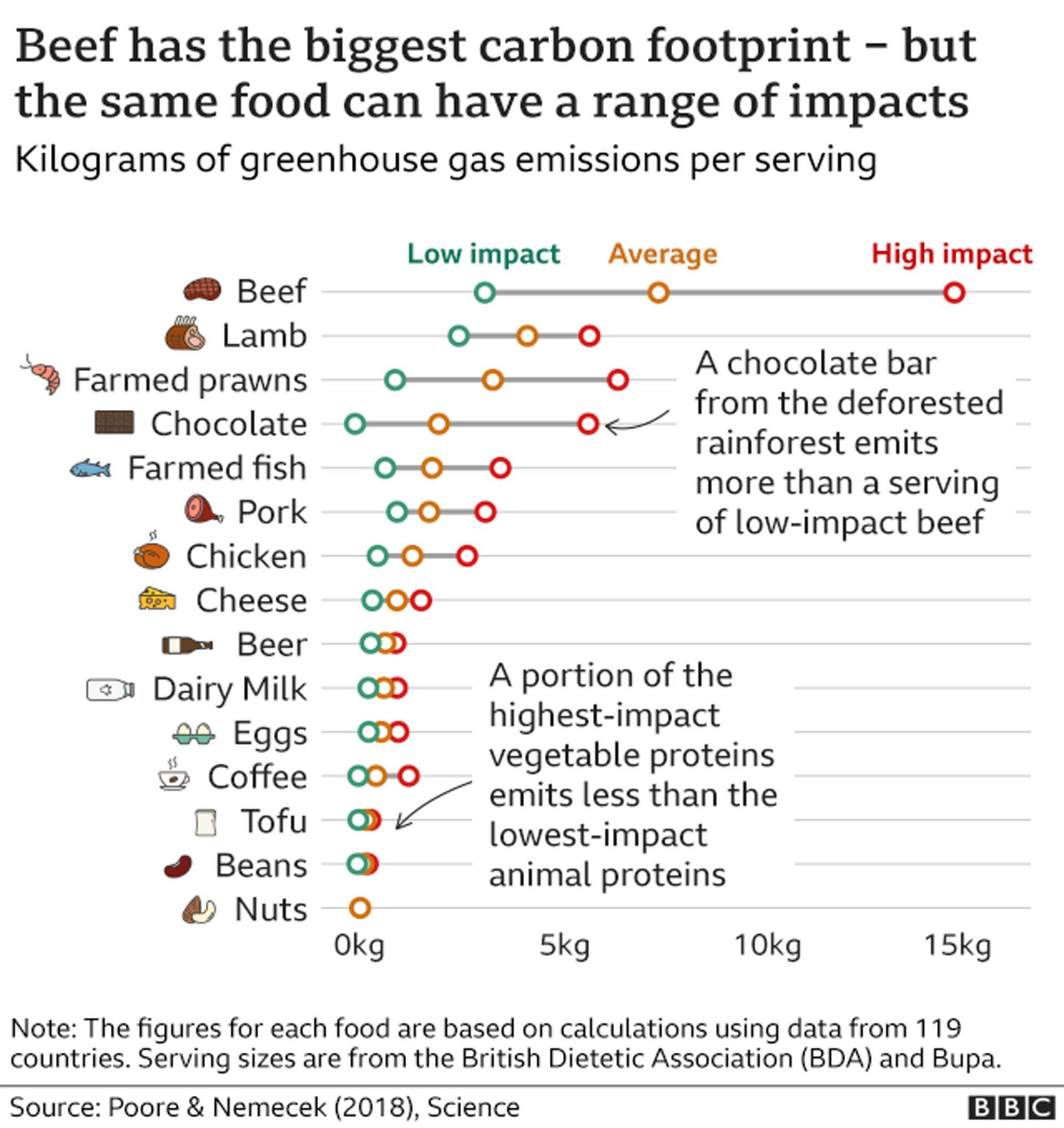
We intend to improve . Overall, most meat production growth will occur in developing regions. continued to eat meat at the same level of consumption rather than shifting to more moderate or plant-based diets, it would cost the U. Falcon received a two-year Environmental Venture Projects (EVP) grant from the Woods .If people in the U. $180 billion if people ate meat per . The global production of food is responsible for a third of all planet-heating gases emitted by human activity, with the use of animals . Beef is a luxury protein in many respects.Mooney and Stanford colleagues Rosamond L.Desertification, soil erosion, contaminated groundwater, and greenhouse gas emissions are just a few of the effects caused by raising animals for food.Despite this urgent need to reduce emissions, food . We know what we should be doing if we want to be environmentally conscious.The results showed that production of 1000 kg cultured meat requires 26–33 GJ energy, 367–521 m 3 water, 190–230 m 2 land, and emits 1900–2240 kg CO 2 -eq GHG emissions.Average cradle-to-grave carbon footprint of beef produced and consumed is 42. Beef and processed pork generate an external cost of 2€/100 g, poultry .
Expected social costs of climate change: $6. This is the first LCA study which uses primary . The Alarming Environmental Costs of Beef. Externalization of Costs.
Figures for the value of the global meat industry vary wildly from $90bn to as much as $741bn.
The Environmental Cost of Meat
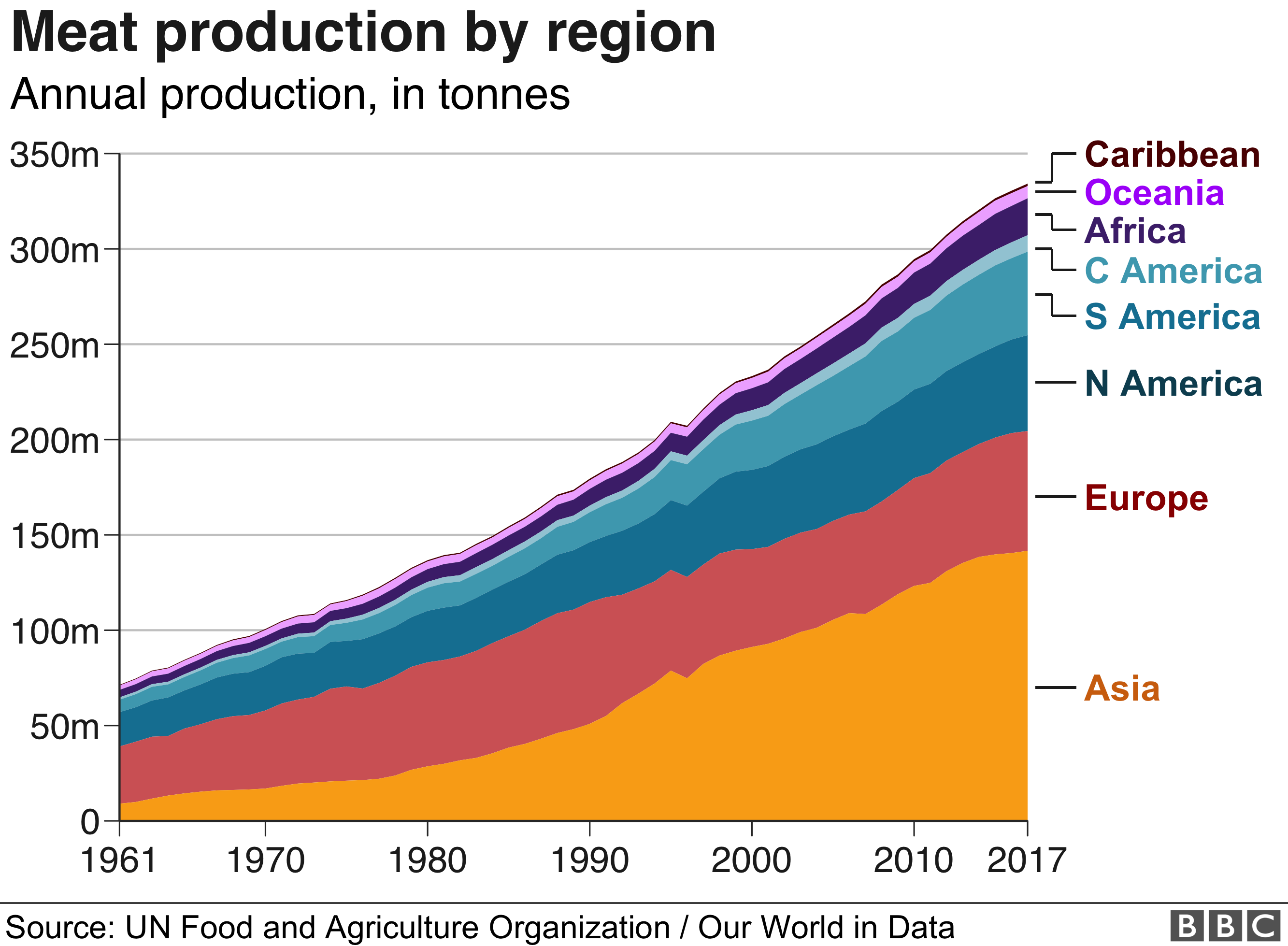
3 billion people and uses one-third of the world’s fresh water. One possible approach to accounting for the estimated global environmental impacts of beef production is to implement a tax on beef consumption.9 € per kg of pork .7 kg CO 2e /kg. The agriculture sector has many adverse environmental impacts, including .Lifecycle environmental and health-related impact of meat consumption are monetized.The Environmental Cost of Meat.Meat has become a controversial topic in public debates, as it involves multiple sustainability dimensions.Overall, the environmental costs of producing conventional pig meat are estimated to be 1. In 2017, the Food & Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) announced that livestock production uses 70% of all agricultural land; in the last two years, that .Production of meat, which spans numerous agricultural and food industries and sectors, has profound negative global impacts on the environment. Here, we review global meat consumption trends and the various sustainability dimensions involved, including economic, social, environmental, health, and animal welfare issues.The adoption of alternatives to meat proteins (insects, plants, mycoprotein, microalgae, cultured meat, etc.2 tonne CO 2 ( Fankhauser, 1994 ).7) To cultivate meat in the stage of cell culture, a clean and aseptic growth environment is required, and the environmental requirements of the production plant should be strictly monitored to ensure the quality of meat. Hybrid products that combine plant-based meats with cultivated meat as an ingredient offer a compelling near-term opportunity to further .The authors concluded that the social costs of meat and dairy could be 20 % lower if the environmental impacts were reduced.Keeping this in mind, red meat deserves particular scrutiny because of its high environmental footprint.) might potentially influence the environmental impact and human . Meat has much larger environmental and climate . price of 5€/l, to a p2 price of 1€/l, while the demand for oil increases from x1 to x2, Modern . Naylor and Walter P.Beef production includes the maintenance and production of about 31 million beef-breed cows, 3 million cull dairy cows, and 14.Meat production is the single greatest cause of deforestation globally, with about half of the world’s habitable land used for this purpose (Brown, 2022; Ritchie & Roser, 2021).
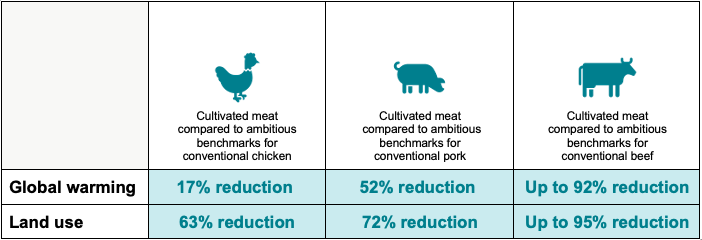
What is the environmental impact of cultivated meat?
Greenhouse gas .
Meat's Environmental Impact
Millions of acres have been plowed over for large, monoculture crop fields dedicated to feeding livestock.
Navigating sustainability trade-offs in global beef production
For beef, dairy and sheep/goat meat, our SCAP estimates are 35%, 18% and 23% of each product’s total production costs (private plus social cost) based on averages of producer price data . Recycle, compost, use public transport more, insulate better, . But widely accepted research suggests that meat consumption . Check out the infographic below to learn more . Using the same monetization method (Weidema, 2009), Nguyen et al. While the companies reap all the profit from livestock production, there are many .










:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Weill_Cornell_Medicine_48064045073-9fad88ac650941c8bb811ed0c3e8808f.jpg)
