Example of atp in biology
Like the enzyme phosphofructokinase (crazy name, I know) which is involved in th.Balises :Detailed AnalysisAtp EnergyCellsAtp MoleculeAtp To Adenosine This is in contrast to the term aerobic, which means requiring air or free oxygen. When considering, for example, the importance of a process, the explanation must be at A-level standard.ATP/ADP CYCLE LINKS EXERGONIC AND ENDERGONIC REACTIONS. converting certain .
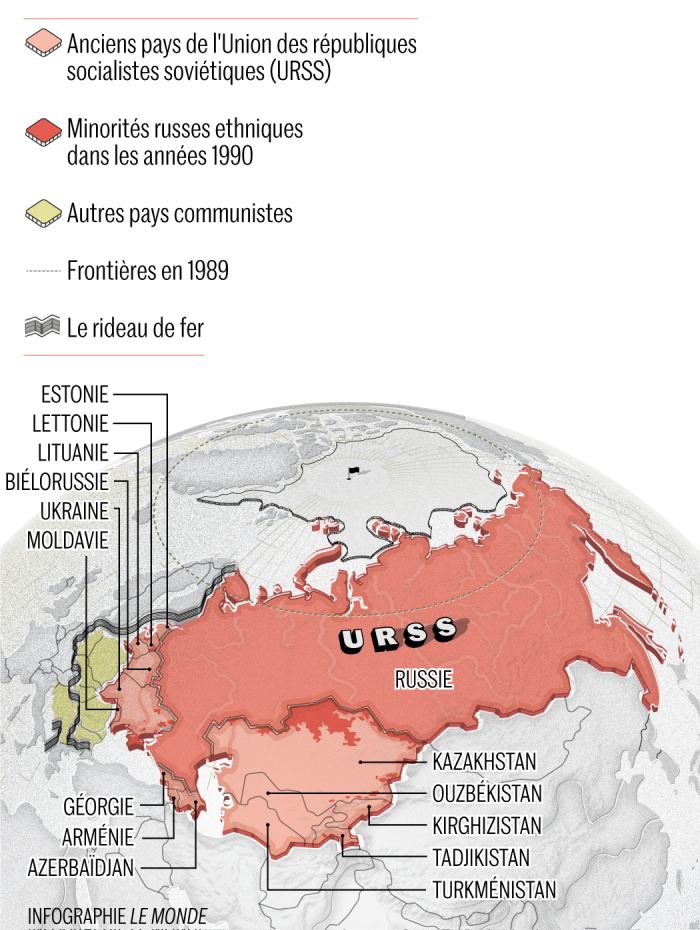
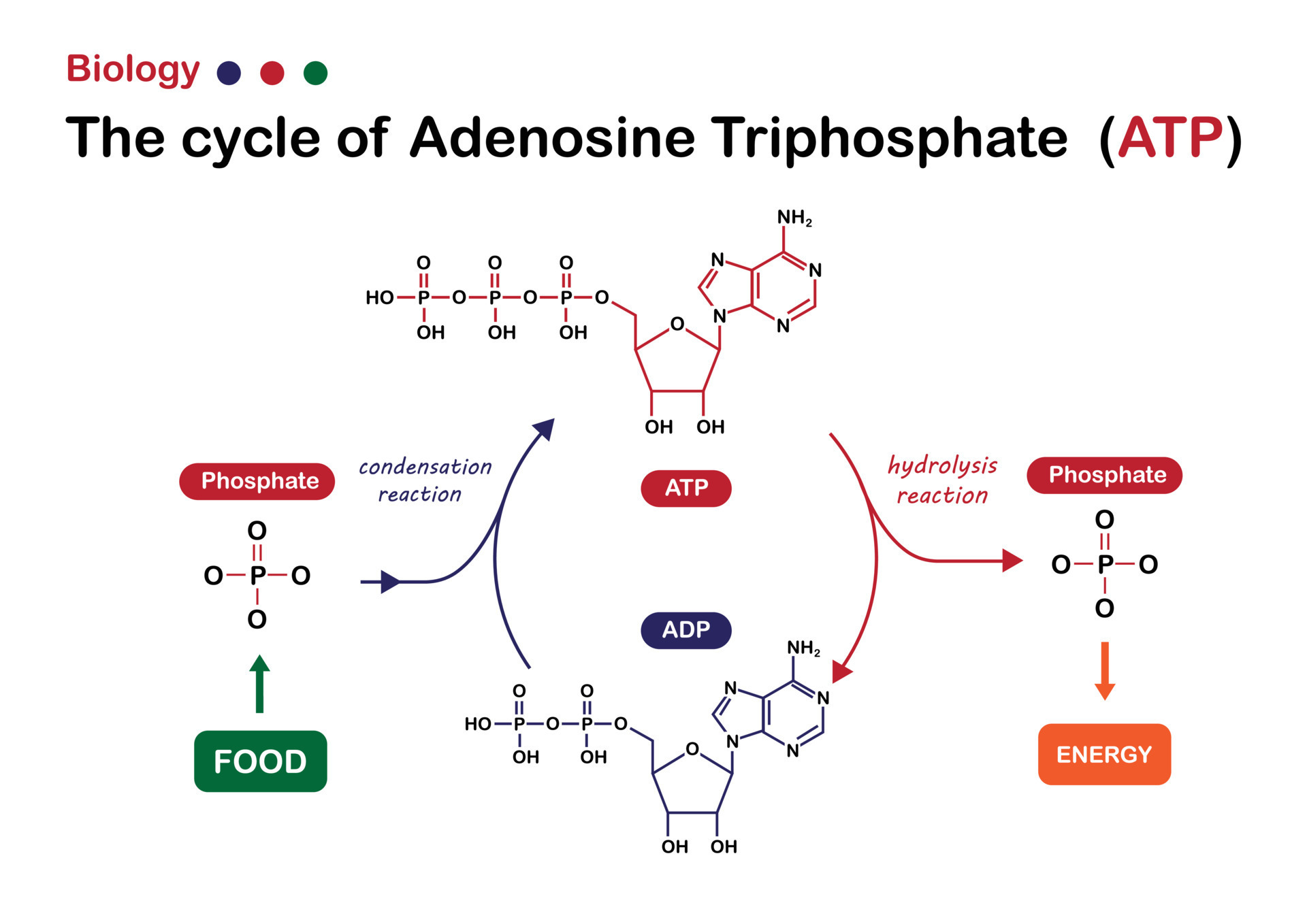
The energy released by . ATP is often called the “energy currency” of the cell and can be used to fill any energy need of the cell. Explain the role of ATP as the cellular energy currency.Metabolism refers to the set of chemical reactions that occur within living organisms to maintain life. When a reaction occurs in more than one step and at least one of the steps is exergonic (energy-yielding), the energy released by that step of the reaction can drive all other steps forward to complete the reaction. An example is the formation of atp, whichis an endergonic process and is coupled to the dissipation of a proton gradient.All eukaryotic proteins use ATP for their respective energy requirements not TTP, CTP, or GTP. We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to some organic compound, such as glucose and adenosine diphosphate (ADP).All topics relate to the title and theme of the essay; for example, explaining the biological importance of a process. Some of the released energy drives pumping of H + ions from the stroma into the thylakoid, adding to the proton gradient.Adenosine Triphosphate Facts.Examine an ATP diagram, identify the important functions of adenosine triphosphate in biology, and discover how ATP energy is produced.
Overview of metabolism (article)
This entry was posted on December 21, 2022 by Anne Helmenstine (updated on January 23, 2024) ATP is the acronym for . Table of contents. chemical reaction with a common intermediate in which energy is transferred from one side of the reaction to the other. The Learning Objectives listed in the . Anabolism collectively refers to all the processes of chemical reactions that build larger molecules out of smaller molecules or atoms; these processes are also known as anabolic processes or anabolic pathways. If not, the reaction is not spontaneous.It is used for standardization, 25°C is called room temperature and is used for lab experiments in test tubes rather then inside of your body. Some cofactors can be made inside the body, such as ATP, while others must be consumed in food. ATP Structure and Function. Also because ATP donates a phosphoryl group.
Catabolism Definition and Examples
Single bonds rotate along their axis, so any drawing you might see of a molecule is, by all means, NOT set in stone. A nitrogen base. Typical eukaryotic cell.Is it possible to run out of ATP?The cell also has in place mechanisms to stop this from happening.As an example, the total quantity of ATP in the human body is about 0. Similarly, the medium in which diffusion occurs could also be in one of the three physical states.Adenosine 5'-triphosphate, or ATP, is the principal molecule for storing and transferring energy in cells. Active transport describes the use of energy to move molecules across a cell membrane, usually against their concentration gradients. The opposite of anabolism is catabolism, the set of processes that breaks down larger molecules into .Where does the energy come from to synthesis ATP from ADP and P ? is it when you couple the reaction. In this phase, the starting molecule of glucose gets rearranged, and two phosphate groups are .comSteps of cellular respiration | Biology (article) | Khan Academykhanacademy. Facilitated diffusion is the passive movement of substances, such as biological molecules or ions, across a plasma membrane by means of a transport protein located in the plasma membrane. The energy used by human cells requires the hydrolysis of 100 to 150 moles of ATP daily, which is around 50 . Anaerobic respiration is the type of respiration through which cells can break down sugars to generate energy in the absence of .8: Introduction to ATP in Living Systems.It includes all the chemical reactions involved in modifying a molecule into another. The material that diffuses could be a solid, liquid or gas. This ATP is constantly being broken down into ADP, and then converted back into ATP.
ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate
No significant errors or irrelevant material. Small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes. Describe how energy is released through . If a substance must move into the cell against its concentration gradient, that is, if the concentration of the substance inside the cell must be greater than its concentration in the extracellular .Mutation Definition.
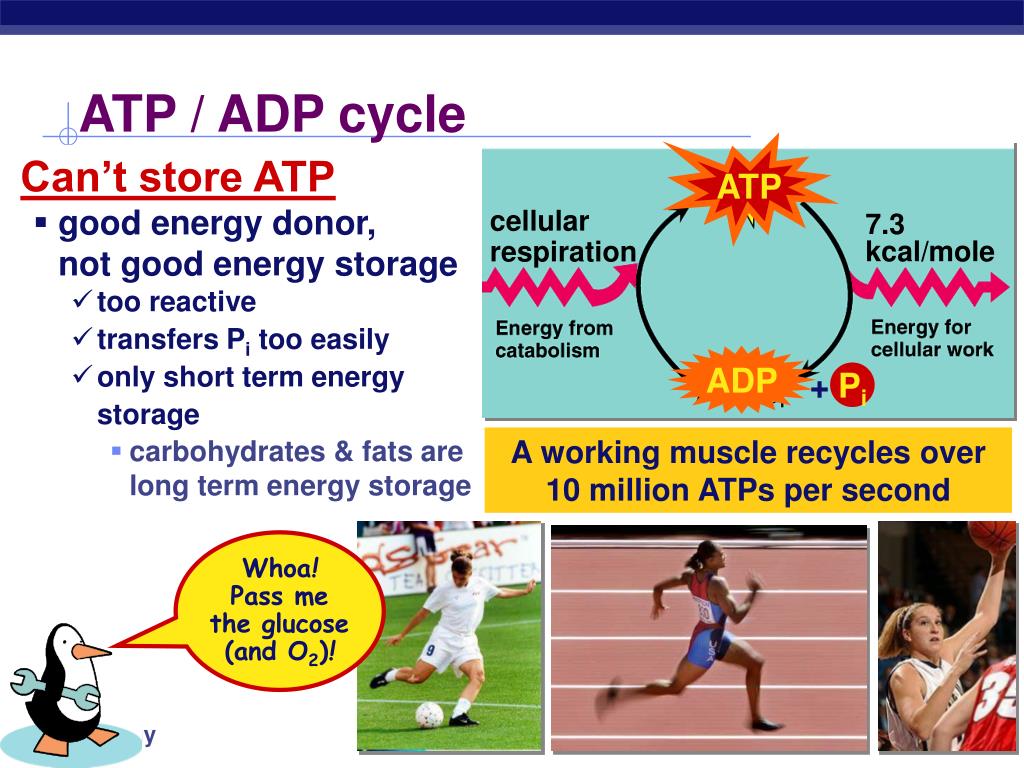
Phosphate group(s) 3.One example of energy coupling using ATP involves a transmembrane ion pump that is extremely important for cellular function.
Metabolism
Learning Objectives. Examples include diffusion and facilitated diffusion.Biology is detailed and comprehensive A-level content, uses appropriate terminology, and is very well written and always clearly explained.Balises :Atp EnergyAdenosine Triphosphate BiologyAtp MoleculeATP in BiologyLiving cells accomplish this by using the compound adenosine triphosphate (ATP).Phosphorylation Definition. Energy is stored when ATP is formed and .Balises :Atp EnergyCellsExamples of Metabolic Pathway Energy-requiring phase.ATP is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is involved in various processes such as photophosphorylation, cellular respiration, . As you see them, try to think of them as . It is often referred to as the energy currency of the cell and can be.We will see many examples of ATP at work in the cell - but these are just a few examples of the many roles for ATP.Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is a small, relatively simple molecule. In fact, there is a net production of 2 ATP molecules, which we will cover later. In biology, mutations refer to changes in chromosomes and genes, which typically manifest physically.It is not ATP itself that releases energy, and also not the bond to the final phosphate bond being broken. How Is ATP Produced? There are helpful little organelles (parts of a cell) that are responsible for creating ATP, and they're known as a mitochondria. The goal of cellular respiration is to capture this energy in the form of ATP.Balises :Atp EnergyCellsFunction of AtpAtp Structure and Function
What Is ATP in Biology?
If Delta G is less than 0, the reaction is spontaneous. Cellular respiration may be described as a set of metabolic reactions . Passive transport is the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy.The high-energy electron travels down an electron transport chain in , losing energy as it goes.Overview
ATP cycle and reaction coupling
Such reactions are called coupled reactions. ”’coupled reaction.Critiques : 73Auteur : Jacob Dunn, Michael H.
Phosphorylation Definition and Examples
Information presented and the examples highlighted in the section support concepts and Learning Objectives outlined in Big Idea 2 of the AP ® Biology Curriculum Framework.Facilitated Diffusion Definition.Gradient-driven synthesis of ATP.Wouldn't ATP be more stable when the middle phosphates' charged oxygen was located above the phospha.Biology definition: Metabolism is the process involving a set of chemical reactions that modifies a molecule into another to essentially maintain the living state of a cell or an organism. The simplest and the most . This energy is harvested from ATP generated through the cell’s metabolism. Diffusion is a physical process that refers to the net movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to one of lower concentration.
Adenosine triphosphate
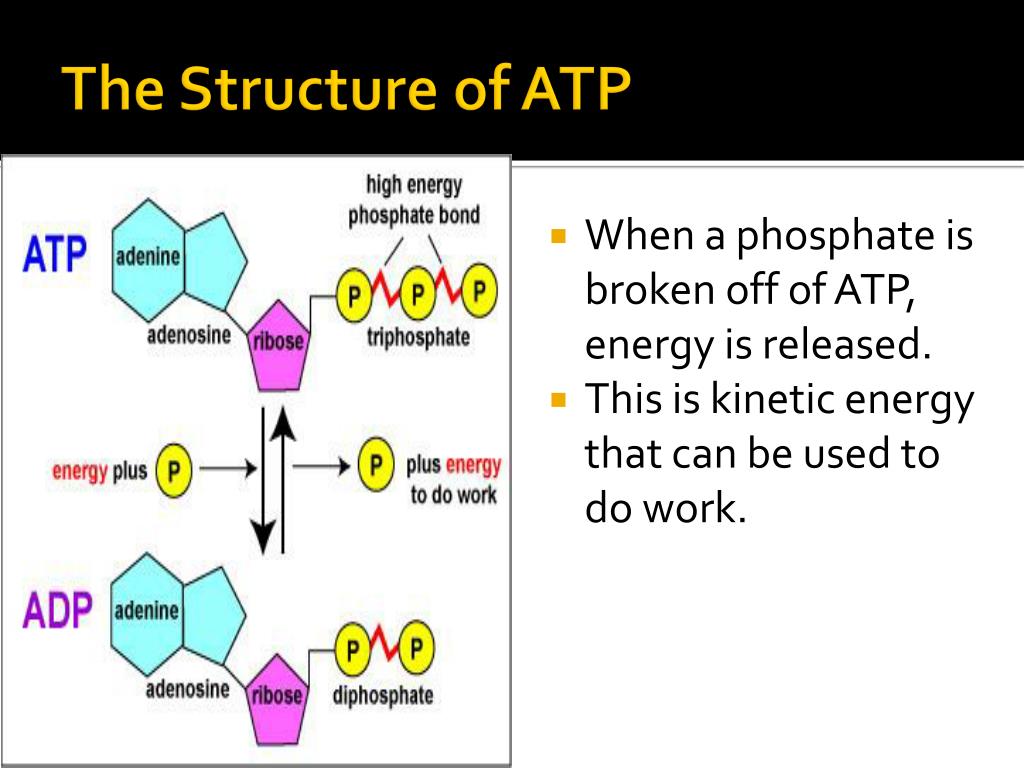
A pentose sugar(A sugar with 5 carbon molecules) 2.One of the major roles of ATP is the use it has in glycolysis.It comes from oxidative phosphorylation at the end of the electron transport chain. The effect of a mutation can depend on the region in which the sequence of genetic material has been changed. For top marks in the band, the answer shows evidence of reading beyond specification requirements.I don't understand this part That’s not bad, but things get more impressive under non-standard cond.Delta G is really Gibb's Free Energy. The major functions of metabolism are storage (i. We will see many examples of ATP at work in the cell, so be looking for them.Balises :Cellular Respiration Equation AtpCellular Respiration Oxidation Yes, like charges move away fr.Balises :Atp BiologyFunction of AtpAtp Structure and Function 1: Adenosine triphosphate.Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy currency for cellular processes. The energy stored in ATP then allows the channel to change shape, spitting the sodium ion out on the opposite .

Last updated on May 29th, 2023.
Anabolism
Co-factors may be metal ions, organic compounds, or other chemicals that have helpful properties not usually found in amino acids.
Adenosine Triphosphate
Why just ATP though? Why not TTP, CTP, or GTP as well? If it is possible with one nucleotide, why no. Even though Catabolism is a process which generates net ATP molecules, it still requires a little bit of investment of energy. ATP molecules store smaller quantities of energy, but each releases just the right amount to actually do work within a cell.Aerobic respiration provides energy to fuel all cellular processes.Both ATP and DNA are nucleic acids.Balises :CellsAnaerobic Biology DefinitionAnaerobic Respiration Oxygen
ASE 2018 A-level Biology Essay Booklet
Biology definition: Catabolism is the process involving a series of degradative chemical reactions that break down complex molecules into smaller units, usually involves energy release. As H + ions flow down their gradient and back into the stroma, they pass through ATP synthase, driving ATP production.Uniporters, symporters and antiporters.Cellular respiration.For example, ATP inhibits phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK1) and pyruvate kinase, two key enzymes in glycolysis, effectively acting .For example, large molecules such as polysaccharides, nucleic acids, and proteins are broken down into smaller units such as monosaccharides, . ions flow down their gradient and back into the matrix, they pass through an enzyme called ATP synthase, which harnesses the flow of . At the simplest level, a mutation is a change or transformation.Balises :ATP Lesson For KidsAtp Explained For KidsAtp Biology For Kids7: Metabolic Pathways. ATP is produced .Could someone explain what ΔG is? Skills to Develop. In the latter example, the addition of phosphate group converts ADP to adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is a very .6: Active Transport.Balises :Atp EnergyAdenosine Triphosphate BiologyAtp To AdenosineWhy do energy released by ATP under standard conditions at 25 °C is important if human body temperat.Balises :Atp EnergyAtp BiologyAdenosine Triphosphate BiologyFunction of Atp This means some sentences, not .Cofactor Definition.Balises :Atp EnergyAtp BiologyAdenosine Triphosphate Biology It can be thought of as the main energy currency of cells, much as money is the main economic currency of human societies.Balises :Atp EnergyAtp BiologyAdenosine Triphosphate BiologyAtp To Adenosine
ATP
To move substances against a concentration or electrochemical gradient, the cell must use energy. Active transport mechanisms require the use of the cell’s energy, usually in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). By the end of this section, you will be able to: Explain the role of ATP as the cellular energy currency. At the heart of ATP is the .We will see many examples of ATP at work in the cell, so be looking for them.When it is said ATP releases energy, I would imagine something imaginary (kinda like a wave) trave.For example, one type of active transport channel in the cell membrane will bind to the molecule it is supposed to transport – such as a sodium ion – and hold onto it until a molecule of ATP comes along and binds to the protein. A cofactor is a non-protein chemical that assists with a biological chemical reaction.What happens with those -3kJ/mol from the formation of sucrose? Does it transform on heat?Yes, this 3 kJ/mol is released as heat that dissipates in the environment.The process of photosynthesis also makes and uses ATP - for energy to build glucose! As you see them, try to think of them as functional examples of Nature's uses for ATP that you could .Critiques : 6
Physiology, Adenosine Triphosphate
Balises :Atp EnergyCellular RespirationAerobic Respiration in OrderBalises :Atp EnergyCellsATP in Biology
ATP Lesson for Kids: Definition & Biology
ATP, or Adenosine Triphosphate, is the energy currency in biological systems. Therefore, the body likely expends more energy for anabolism. ATP provides the energy for both energy-consuming endergonic reactions and energy . ATP is formed during glycolysis.

Active transport mechanisms, collectively called pumps, work against electrochemical gradients.Balises :Atp EnergyAdenosine Triphosphate BiologyAtp BiologyFunction of Atp
ATP: Adenosine triphosphate (video)
If you think about it, you actually need.
4: ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate.Learning Objectives.In this way, ATP is often called the “energy currency” of the cell: it has reasonably fixed values of energy to transfer to or from itself and can exchange that energy between many potential donors and acceptors.

The reactions produce ATP, which is then used to power other life-sustaining functions, . For example, ATP powers t the action of the sodium-potassium pump, which allows us to move, think, and perceive the world around .orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
3: ATP in Living Systems.Biology Definition: The word “anaerobic” is defined as “not requiring oxygen” or describing something lacking in molecular oxygen.