Examples of determinism in philosophy

This view that conceives free will to be incompatible with determinism is called incompatibilism, and .
Determinism is the theory that all events in the universe are completely caused by prior events, such that every occurrence was inevitable from the start of the universe, ranging from the intricate blast of every supernova, to the precise path each leaf travels as it flutters to the ground, to the very words we are writing in this entry.
Hard Determinism (29 Examples
Biological determinists believe environmental factors have no influence on a person. The first is observational equivalence between deterministic and indeterministic models.Determinism, in philosophy and science, the thesis that all events in the universe, including human decisions and actions, are causally inevitable. What it means for God to determine an event may need some spelling out.Philosophers like A. Possibilism is theory that people can adjust or overcome an environment.3 Carneades on the .Rather, determinism is the view that at any one time, only one future is physically possible. What is an example of causal determinism? For example, suppose that in this universe a man murders his spouse. How much say do you really have over your actions? Have you ever had that feeling that no matter what you do, the situation .In science, most specifically quantum theory in physics, indeterminism is . For example, being poor doesn’t make you steal, but it may make you more likely to take that route through desperation. Deterministic theories throughout the history of . This feeling is at the heart of soft determinism. The first suggests that everything in nature . The concept and idea of determinism can be understood more easily when placed into relatable scenarios. Indeterminism is simply the denial of determinism. Explore the work of indeterminism philosophers and study indeterminism.Indeterminism is the idea that events (or certain events, or events of certain types) are not caused, or are not caused deterministically.Determinism and indeterminism are two positions within a debate about the causes of events and phenomena in nature. In philosophy of science, the question of determinism is addressed in rela-tion to scientific theories and provides an important means of assessing the-ories in various respects. Suppose we know in both a deterministic world and a fatalistic world that my pot of water will be boiling at 11:22am today. Evidence Against.2 The way things are at a time t. When more ice cream gets sold, there’s more violent crime; when ice cream sales go down, there’s less violent crime. Examples of determinism.An example will be helpful here. Ayer and Daniel Dennett in the 20th century would later expand on these concepts, integrating insights from psychology and cognitive sciences to show how .Determinism in Philosophy of Science: Three Approaches. free will, in philosophy and science, the supposed power or capacity of humans to make decisions or perform actions independently of any prior event or state of the universe.4 Laws of nature. Definition Dualism can refer to any philosophy that believes in two. According to biological determinists, social categories like gender, race, sexuality, and disability are based on biology .Roughly speaking, determinism is the doctrine that all past, present, and future events – including all acts of the will and all occurrences in nature – are determined and . Freedom and determinism are two concepts that have been debated in philosophy for centuries. It is the opposite of determinism and related to chance.2 Epicurus on the fatalist argument and determinism. This is because .Overview
Causal Determinism
DETERMINISM IN HISTORY Philosophical reflection upon history has always been impressed by the limited extent to which individuals and groups seem to be able to mold events to their purposes.1 Determinism: The core idea and how to spell it out.This allows compatibilists to concede that the all-in ability to do otherwise is incompatible with determinism, and yet insist that it is irrelevant to the question of the compatibility of determinism with moral responsibility (and perhaps even free will, depending on how we define this) (cf. Determinism is the philosophical proposition that every event, decision and action is causally determined by an unbroken chain of prior occurrences. In Orwell’s ‘1984’, the protagonist’s actions are clearly influenced by social factors such as Winston’s membership of the Outer Party, his emotions, state propaganda and Newspeak.
Ancient Theories of Freedom and Determinism
Determinism is the belief that ‘all events are ultimately determined by causes regarded as external to the will’ .Hard determinism rejects the role of a person in shaping future; soft determinism admits such a role to some extent conditioned by free will or authentic desires, while libertarianism views people as the only agents of their actions who are free to shape their future. First of all, formulations of determinism in terms of .
Freewill vs Determinism In Psychology

This article focuses on three themes concerning determinism and indeterminism.Soft determinism contrasts with both hard determinism and with what is sometimes called metaphysical libertarianism.
Biological Determinism: Definition and Examples
Statisticians have found that violent crime is correlated with ice cream sales.
Determinism in History
The article discusses several results about observational equivalence and presents an argument on how to choose between deterministic and indeterministic models involving .For example, if the soul exists independent from the body, the physical effects of determinism—such as biological imperatives and chemical predispositions—could be lessened on the mind. In addition, hard determinists think that the causal determinism .
Determinism
The Epistemology of Determinism.Hard determinists think that all human actions are causally determined by the laws of nature and initial conditions. In philosophy of science, the question of determinism is addressed in .

Metaphysical libertarianism (not to be confused with the political doctrine of libertarianism) says that determinism is false since when we act . He believed in a world . We feel free when we decide to go to the park or buy a new backpack.
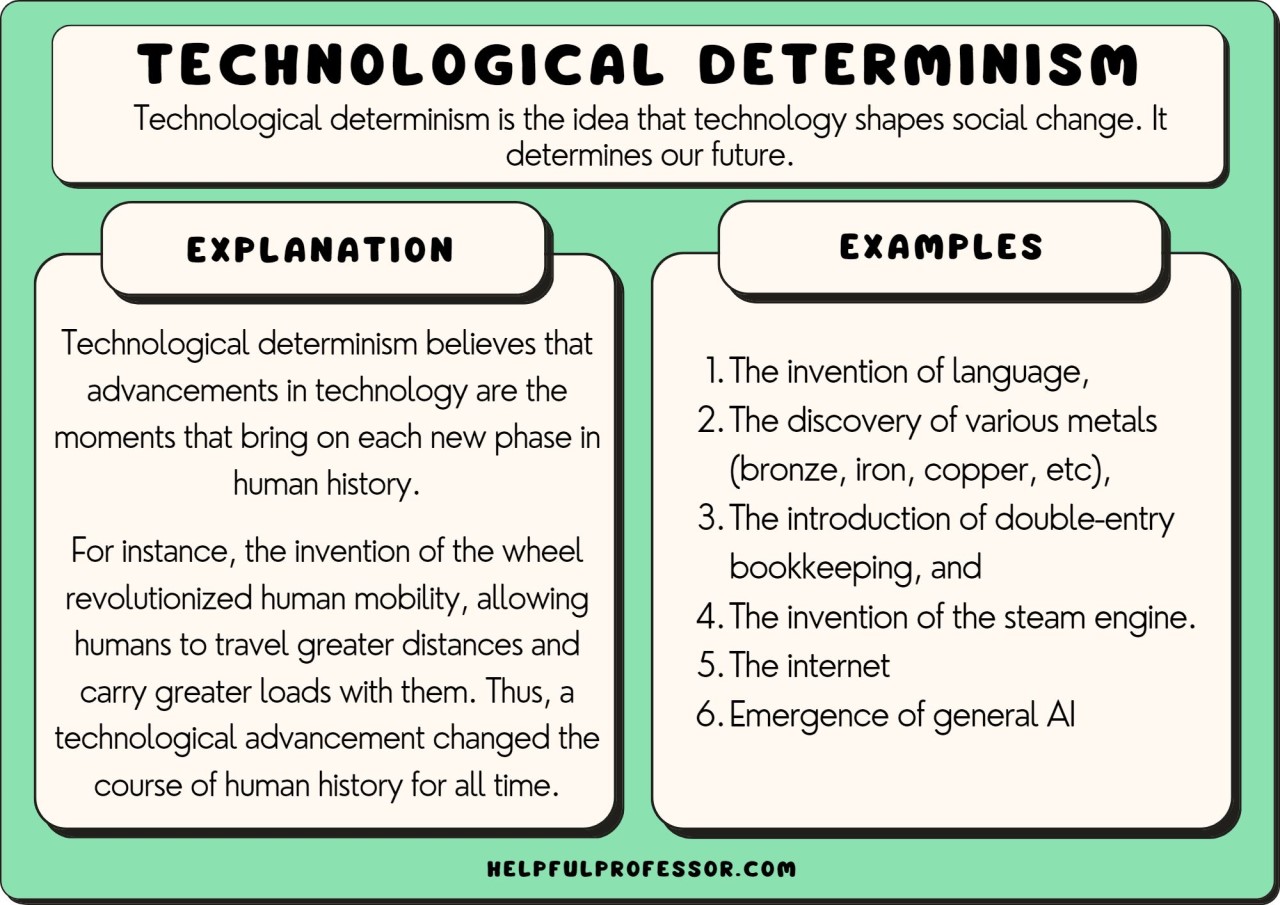
Soft Determinism (29 Examples + Definition) Imagine standing at a crossroads, where every path you could take has been paved by your past, yet you feel a sense of control over which direction you choose. Determinism makes the claim that if I take a pot of water and I put it on my stove, and heat it to 100°C, it will boil. Soft Determinism is the philosophical belief that while our choices and actions are . But while the verb “to determine” is an ordinary English term that is not associated with a particular philosophical or scientific theory, it is questionable whether a weak sense of “determinism” really exists or should . Hard determinism asserts that determinism is true and denies that we have free will. Philosophical determinism tells us that all events are determined by previous causes. Free will is the ability to make a choice when other options are present .2 Determinism and Sourcehood. Definition
Determinism
This problem has been identified in ancient Greek philosophy, and remains a major focus of philosophical debate.Compatibilism is the thesis that free will is compatible with determinism. Arguments for free will have been based on the subjective experience of freedom, on sentiments of guilt, on revealed . But two of what? So in this article, we’ll cover “mind-body” dualism, which is by far the most important form of dualism in modern European/American philosophy.Compatibilism offers a solution to the free will problem, which concerns a disputed incompatibility between free will and determinism. Philosophical Determinism. Hard determinism, also known as incompatibilism, is the belief that determinism is incompatible with the .Physicists are increasingly beginning to take seriously the possibility of laws outside the traditional time-evolution paradigm; yet many popular definitions of .There are many determinisms, depending on what pre-conditions are considered to be determinative of an event or action.Auteur : The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica
Determinism: Explanation and Examples
3 Compatibilists’ Replies. The standard definition of hard determinism states that no event or action takes place with the individual’s choice, and it is completely determined.For example, talk of “neural determinants” of thought and behavior typically does not commit the speaker to determinism proper.Determinism is the theory that all events in the universe are completely caused by prior events, such that every occurrence was inevitable from the start of the .Determinism Examples. Because free will is typically taken to be a necessary condition of moral responsibility, compatibilism is sometimes expressed as a . Freedom refers to the ability of individuals to make choices and act according to their own will, while determinism holds that events, including human actions, are the result of prior causes and that the future is already determined by . Fatalism, Bivalence, and Determinism. We know that the boiling point for water is 100°C. The belief is that the future is determined by past actions, and every action has a cause.In psychology and philosophy, free will isn’t a gift from God but just how the world operates. Fischer 1987, 1994. As Marx, the philosopher who created .
Dualism: Explanation and Examples
It is highly relevant to the philosophical problem of free will, particularly in the form of libertarianism.By Frederick Baxter.The philosophical problem of free will and determinism is the problem of whether or not free will exists in light of determinism. Determinism is usually understood to preclude free will because it entails that humans cannot decide or .1 Aristotle and tomorrow’s sea battle. Determinism is the belief that all events are completely determined by their causes such that the . Thus, libertarianism is the most credible concept among the three considered .Soft determinism represents a middle ground, people do have a choice, but that choice is constrained by external or internal factors.What is Determinism? Definition and explanation. He uses the metaphor of freezing to suggest that human beings do not have time to wait around. In this work, Estragon, the main character, suggests that life is too short to waste time waiting for Godot to arrive.Environmental Determinism is theory that environment causes social development or the idea that natural environment influences people.
Determinism
Soft determinism suggests that some behaviors are more constrained than others and that .And in this century, most have believed that quantum theory is indeterministic. This is a strong correlation, but it doesn’t imply causality. Since quantum theory has superseded classical physics, philosophers have typically come to the tentative conclusion that determinism is false. One of the classic examples of existentialism in philosophy is Waiting for Godot, a play by Samuel Beckett.
What is physical determinism in philosophy?
Thus, it is crucial to be clear in defining what we .15 Examples of Determinism.1 Determinism and Alternative Possibilities.
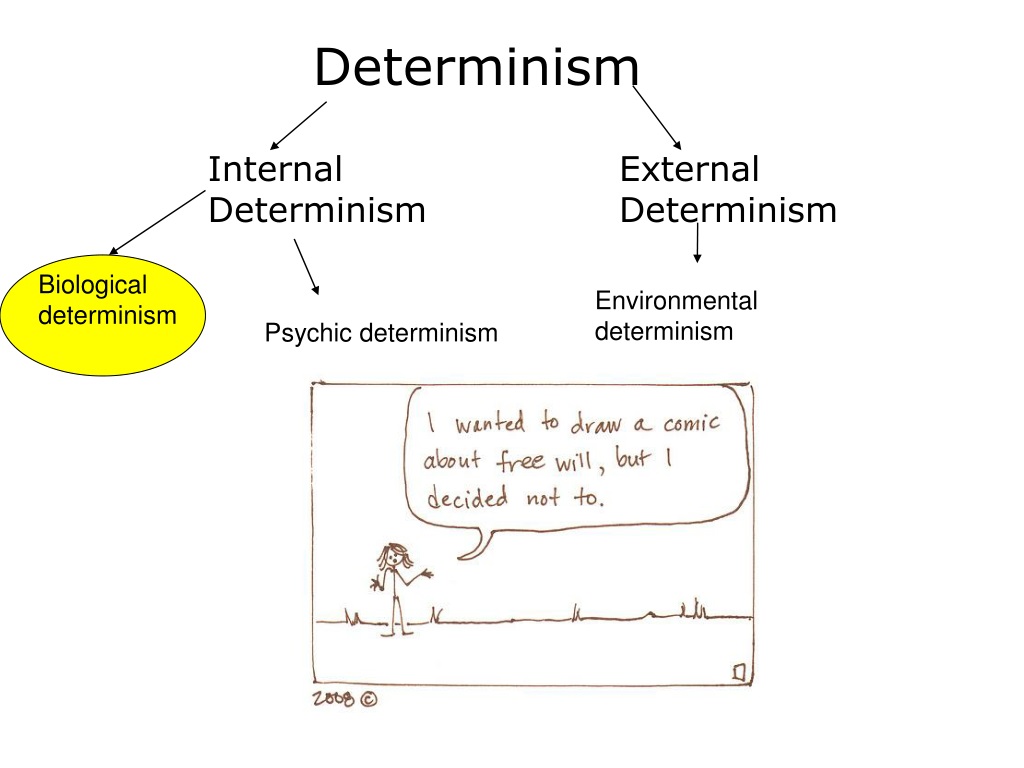
2 The three approaches in more detail.Determinism suggests that only one course of events is possible, which is inconsistent with the existence of such free will. Free Will and the Problem of Causal Determinism. It tells us that the universe is rational because absolute . At any moment, the state of your brain and your environment together with the principles that govern the behavior of matter necessitate the way that you will act.