Examples of the interactionist perspective
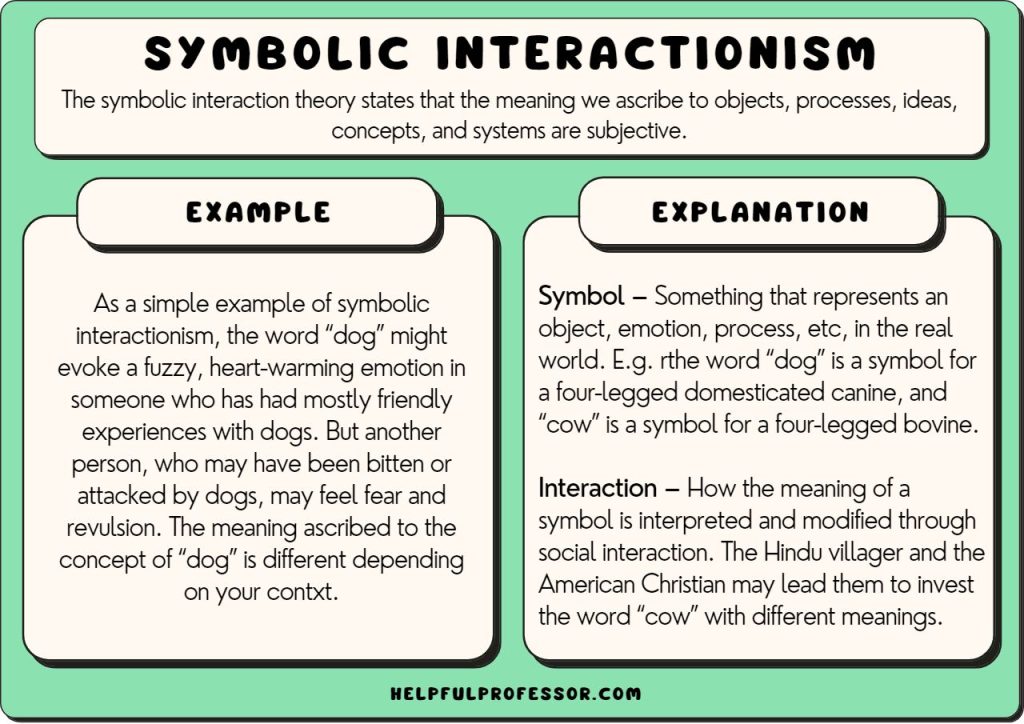
Examples of interactionism can be found all around us.how interactionist perspective discusses each aspect that influenced children’s language development. In other words, the saying “you are known by the company you keep” fits perfectly with the interactionist perspective because it .For example, conflict theorists might explain the civil rights movements of the 1960s by studying how activists challenged the racially unequal distribution of political power and economic resources. Symbolic interactionism is a micro-level theory that focuses on meanings attached to human interaction, both verbal and non-verbal, and to symbols.
Interactionist Perspective in Sociology
Rather, cultures imbue youth and age with particular meanings.
Symbolic interactionism seems to be a perfect perspective to contextualize and frame the lived experiences of those who have been affected by the global coronavirus pandemic, and with so many affected, the application of interactionist theory and method will appeal to social scientists in many fields as they try and understand how people have . For example, there is no necessary relationship between a red truck with sirens and a fire. But words are not static things; their symbols to which we attach .Symbolic interactionism is a theory that analyzes patterns of communication, interpretation, and adjustment between individuals in society.If you love books, for example, a symbolic interactionist might propose that you learned that books are good or important in the interactions you had with family, friends, school, or church. People understand them as a means of communication. People with PKU are unable to break down the amino acid phenylalanine which builds up in the blood and brain causing mental retardation.The symbolic interactionist perspective asserts that human beings are active, purposeful agents who seek to satisfy their needs and desires by using symbols, or signs, which they use to control their environment.

As in this example, conflict theorists generally see social change as abrupt, even revolutionary, rather than incremental.Symbolic interactionism looks at individual and group meaning-making, focusing on human action instead of large-scale social structures.Interactionist theories are theories that suggest that criminal behavior is learned through interaction with others.The symbolic interactionist perspective, also known as symbolic interactionism, .For example, functionalism believes that social institutions promote cooperation, unity, and shared values, ultimately leading to the well-being of society as a whole (Merton, 2010). A brief summary of each figure’s . However, as well as Rhyner’s study , interactionist invitesAnother way to apply the interactionist perspective is to look at how people define their races and the race of others.Teachers usually have higher expectations for students they view as higher achievers, and treat these students with more respect.Furthermore, interactionist perspectives as theorized, for example, by Piaget and Vygotsky, . It first provides an overview of three main trajectories in symbolic interactionist thought, focusing on the work of Herbert Blumer (the Chicago School), Manford Kuhn (the Iowa School), and Sheldon Stryker (the Indiana School).The symbolic interactionist framework posits that aspects of the surrounding social world – objects, ideas, events, people, etc. Symbolic Interactionist Perspective.Gender Inequality. Symbolic interactionism is a sociological perspective that is most concerned with the face-to-face interactions between members of society. Ironically, in the past some have predicted that the . This means that there is no inherent cultural meaning attached to the biological process of aging. The theory is a framework . For instance, symbolic interactionists argue . They introduce the classic masters of interactionist thought―such as Mead, Blumer, Strauss .

Also, when they build good relationships with their supervisors and the company, .
Interactional Perspective- What it is and the Basics
Let's take a look at this approach as an example of how symbolic interactionists view . However, if the child is .

Interactionists acknowledge the presence of innate biological .Symbolic interactionism is an interactionist perspective that was pioneered by Herbert Blumer in the late 20th century.
Why is interactionist theory important? History of the interactionist theory; Understanding interactionism; Assumptions of . Another way to apply the interactionist perspective is to look at how people define their races and the race of .The interactionist approach is best illustrated by the genetic disorder PKU (phenylketonuria). Instead of asking about what these people “are” we ask about the process in which they are defined in such a way.An example of interactionism is examining the relationship between a teacher and a student. Socialization and learning processes occur as the result of group membership and relationships. In sociology, interactionism is a theoretical perspective that understands social processes (such as conflict, cooperation, identity formation) as emerging . A student acts in certain ways toward their teacher because of social expectations. The symbolic interaction perspective, also called symbolic interactionism, is a major framework of the .Symbolic interactionism is approaching its centennial as a distinct theoretical perspective and method. Symbolic interactionism is a social theoretical framework associated with George Herbert Mead (1863–1931) and Max . The glut of extant interactionist studies and its continued popularity shows that it is – de rigueur – a leading theoretical perspective in sociology and across the social sciences. In the conflict perspective, change .Sociological Paradigm #3: Symbolic Interactionist Theory.The interactionist/social theory proposes that language exists for the purpose of communication and can only be learned in the context of interaction with adults and other children. The symbolic interactionists subscribe to the concept of “symbolic thinking”–that is, the idea that human beings can use symbols .Interactionist Perspective | Definition, Influences & Examples Assessing the Cognitive Model in Psychology: Strengths and Weaknesses For example, studies have found that when students are split into ability-based groups, the students in the higher-ability groups are more likely to demonstrate positive learning behaviors and higher achievement .
Issues & Debates: Evaluating the Nature-Nurture Debate
Ironically, in the past some have predicted that .
Symbolic Interactionism Theory & Examples
Symbolic interactionist researchers investigate . An example using real social roles can help illustrate the interactionist perspective: A CEO has .This article surveys past theory and research in the interactionist tradition. PKU is caused by the inheritance of two recessive genes, one from each parent. For example, one of the spouses may see their circular wedding rings as symbolizing “never ending love,” while the other may see them as a mere financial expense.
What is an example of the interactionist perspective?
Explain and give examples of social constructions of health according to the symbolic interactionist perspective.
Functionalism vs Conflict Theory: 10 Key Differences
Several notable theorists have used labelling theory to explain crime and deviance.Interactionism.But if we take an interactionist perspective, the contours of the question radically change.While aging itself is a biological process, the Symbolic Interactionist Perspective posits that the meaning behind being “young” or “old” is socially constructed.By Ashley Crossman. Much faulty communication can result from differences in the perception of the same events and .Kathy Charmaz, Scott Harris and Leslie Irvine's The Social Self and Everyday Life: Understanding the World Through Symbolic Interactionism is a wonderful―but also very timely― introduction to the interactionist perspective in social psychology. Which of the following is a . Learning Objectives.
The Basics of the Interactionist Perspective
Yet, we were able to recognize in the example above that the red truck we saw was heading to put out a fire.For example, while a conflict theorist studying a political protest might focus on class difference, a symbolic interactionist would be more interested in how individuals in the .

In contrast, conflict theory critiques the idea of consensus as an illusion that masks power imbalances and systemic injustices that are being perpetrated .Sociology includes three major theoretical perspectives: the functionalist perspective, the conflict perspective, and the symbolic interactionist perspective (sometimes called the .
The Three Main Sociological Perspectives
Interactionists see culture as being created and maintained by the ways people interact and in how individuals interpret each other’s actions.An example of this might be an individual whose beliefs about a particular group are based on images conveyed in popular media, and those are unquestionably believed because the individual has never personally met a member of that group.The interactionist perspective on inequality looks at how certain social roles have more power, or authority, than others.Discuss how symbolic interactionists view culture and technology.
Interactionist Perspective
Symbolic interactionism is a theoretical tradition that accounts for the emergence of meanings, selves and social life as the outcome of concrete interactions between .
Interactionism
Updated on January 29, 2020.Symbolic interactionism is a theoretical perspective in sociology that addresses the manner in which society is created and maintained through face-to-face, . Some people who claim a White identity have a greater . Maybe your family had a special reading time each week, getting your library card was treated as a special event, or bedtime stories were associated with warmth and . Symbolic interactionist researchers investigate how people create meaning during social interaction, how they present and construct the self (or identity), and how they define situations of co-presence with others. Rather than thinking about deviance and deviants as natural objects, we think about it as an interactionally emergent “career”—not something that naturally . – impact and change humans, and .

It stresses the importance of the environment and culture in which the language is being learned.
Interactionism in Psychology
According to theorists working in the symbolic interactionist perspective, health and illness are socially constructed.













