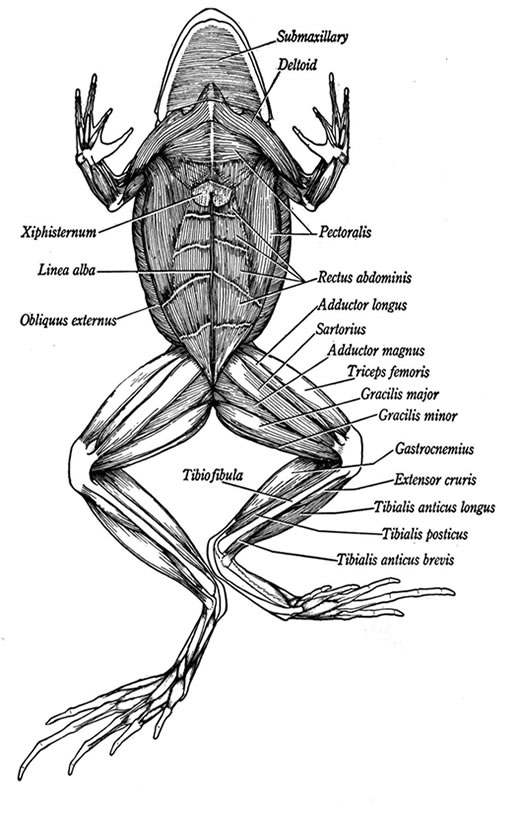
External parts of a frog

This video talks about the external parts of a frog together with the process of skinning in preparation for the study of the muscular system. Understanding the physiology of frog bones is essential to appreciating the amphibians fully.
Frog Anatomy and Dissection
Cornea - The transparent anterior part of the external layer of the eye (transparent outer covering of the eye). Head and Mouth Structures. These powerful limbs are the secret to their success – and incredibly, it takes baby frogs weeks and weeks to grow them! Like beautiful butterflies, frogs and toads undergo an astonishing transformation – which is called . The vestigial eye (represented by a white dot and located between . Cutaneous Respiration in Frog.After putting the frog to sleep, the frog was pinned on the dissecting pan, laying on its ventral side.
it has 2 eyes,2 feet, 2 arms,2 long spiral legs, and usually has a wet skin.Use this engaging interactive labelling activity with your Year 1 children to practise labelling the features of a frog. In general, frogs have protruding eyes, no tail, and strong, webbed hind feet. Vomerine Teeth: Used for holding prey, located at the roof of the mouth Maxillary Teeth: Used for holding .The external anatomy of the frog includes an investigation of the main features of the frog and the anatomy of the mouth. Internal Mouthparts Esophagus •Maxillary teeth –around the upper edge of the jaw; Holds •Vomerine teeth - used to hold . The head houses essential organs such as the brain, eyes, and nose.
External anatomy of Frog with Major Organs and Functions
In this article we will discuss about the external features of Indian frog with the help of suitable diagrams.
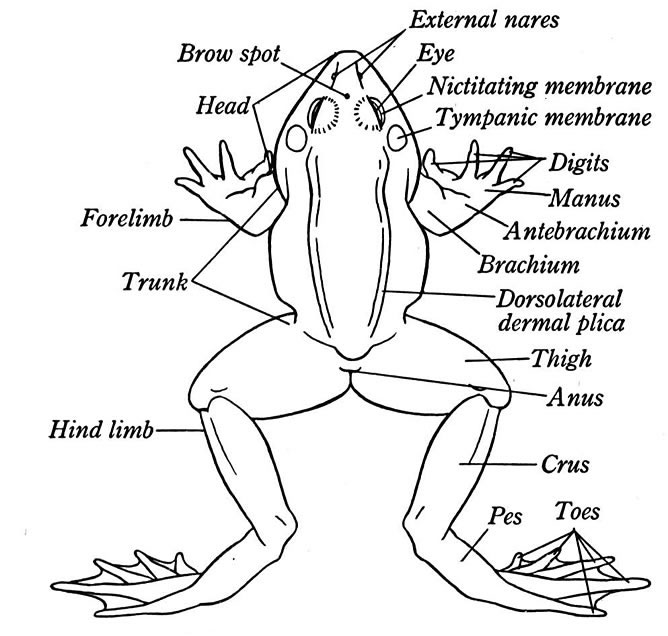
The dorsal part of the hoof wall forms a toe; Medial and lateral parts of the wall forms quarters and
What are the parts of a frog's skeleton?
The External Anatomy Of Frogs. From webbed feet and strong hind legs for swimming and jumping, to moist skin and a lack of ribs for respiration and maneuverability, frogs have unique structural adaptations that enable them to thrive in various habitats. Data from other bullfrogs: 14.Lastly, a frog’s external anatomy includes special structures such as its eyes and nostrils. The interactive task gives immediate feedback for children to identify the features of the frog. Muscular coordination and posture are controlled by the cerebellum, and the medulla oblongata regulates respiration, digestion and other automatic functions.Morphology & Anatomy of Frogs-Internal and External . Anterior opening. Terms to know!!
External Anatomy of a Frog (Toad)
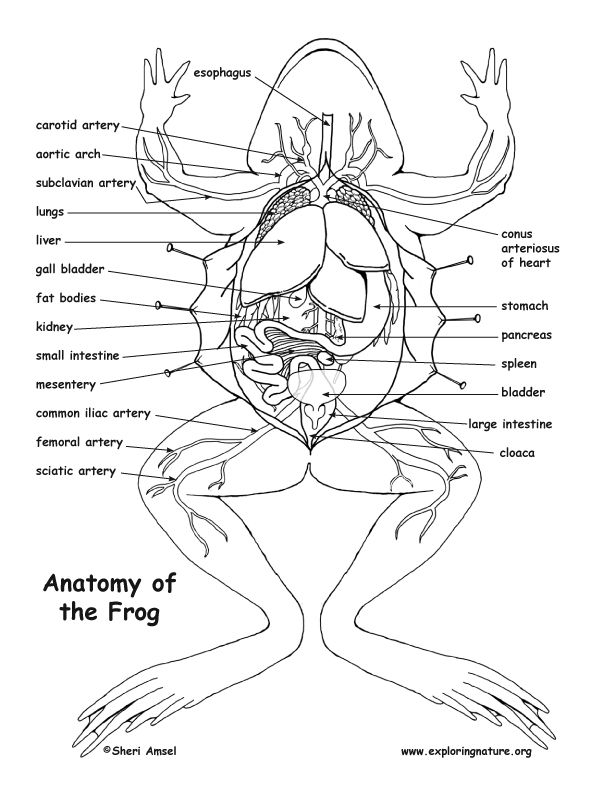
The external anatomy of a frog includes its skin, eyes, ears, legs, and mouth. Atlast – The top part of a backbone.Frog Anatomy part 1. Frog, any of various tailless amphibians belonging to the order Anura.The frog in the photo is a bullfrog, some members of the class were able to dissect the larger frogs, but most dissected smaller grass frogs.The frog life cycle. They will learn interesting frog facts in a simple and engag.A horse’s hoof can be divided into five areas: the wall, the sole, the frog, the periople, and the white line. The trunk houses the vital organs necessary . Frogs are known for their . Iris - The colored part of the eye which forms and regulates the size of the pupil. The toes of the hind legs.The anatomy, or body structure, of frogs is similar to the anatomy of human beings.
frog: anatomy
Frog Body Parts and Functions
Therefore, it has streamlined body which is the characteristic of the aquatic animals and assist in swimming in water.
Frog anatomy part 1
Frogs are small, tailless animals that can live on land or in water. Frogs have smooth, moist skin that helps them breathe and absorb water. The two ends, the anterior and the posterior, of .This Frog Anatomy Worksheet guides your students through all the fantastic parts of these amazing amphibian marvels. Students examine the front and hind legs, measure the lengths of frogs, and the diameter of the tympanic membrane. Other external features are a pair . 2- This can be a make-up lesson for students who are absent during the dissection. Frogs have large eyes positioned on the sides of their head, providing them with a wide .In this article we will discuss about the external anatomy of a frog, explained with the help of suitable diagrams. Terms to know!! •Dorsal—the back or upper surface of an organism •Ventral—the stomach or lower surface of an organism •Anterior—head . Pupil - The opening through which light enters an eye.
Respiratory System of Frog (Labelled diagrams)
Suprascapula – Shoulder blade. You will need to . Morphology of frog.
Frog External Anatomy
The body is divisible into .
Morphology & Anatomy of Frogs-Internal and External Features
Nictitating Membrane - A transparent part . Their eyes are positioned on top of their heads, enabling them to see in all directions. Functions of the body parts that make up the frog’s head • External nares or nostrils - Anterior openings for the entry or exit of air. They have gills when they’re young to help them breathe underwater like a fish. Use this fun game to help children identify the main structures commonly . These are two openings which are anteriorly located on the root of the mouth. Granite City School District via Biology Corner.What is the external anatomy of a frog? The external features of the frog include the forelimbs and hindlimbs which are much more muscular for strong swimming. • Tympanic Membrane - The eardrum - receives sound waves • Glottis - The opening from the mouth into the . Overview Of The External Features Of Frogs.The body structure, or anatomy, of the frog is very similar to the anatomy of man.Recommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
No Frog? No Prob!
It consists of two olfactory lobes, two cerebral hemispheres, a pineal body, two optic lobes, a cerebellum and a medulla oblongata.A frog has common body regions to man.

Frog’s skin is composed of thin membranous tissue with extensive capillary network underneath.
Frog Anatomy
External Anatomy Of A Frog
Children will drag and drop common features of a frog to the correct position.comFrog Organs and Functions - All About Our Class Dissectionbiodissection1.Frogs breathe utilizing four different respiratory methods, including the skin, lungs, nostrils, and lining of the mouth.
Frog Dissection : A Comprehensive Guide
A diagram of the skeleton of a frog.Again, you will find a wedge-shaped mass (frog) at the ventral part of the sole that helps to unite two lateral aspects of the wall with the sole.A diagram showing the external anatomy of a frog.Children will learn about the frog body parts and their functions in this fun educational video.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 4 min
Frog Anatomy: Everything to Know
Both man and the frog have the same kinds of organs and systems of organs. Looking at how a Frogs bone structure is made up and what bones contribute to everyday life. The illustration has been carefully labelled, but all of the labels themselves have been left deliberately blank.3- It can be the dissection lesson for online learning.

External Anatomy Of A Frog The external frog anatomy includes both the dorsal and ventral sides of the animal and describes the organs and body features visible . Skin is one of the primary respiratory organs of frogs which functions in both air and water. It was created by member acLiLtocLiMB and has 11 questions.Structural Adaptations Of A Frog. The first part of this worksheet has a charming illustration of a very happy looking green frog on it. Though larvae have tails, adult frogs are tailless.Morphology of Frogs.Student Guide to Frog External Anatomy. Observe the dorsal and ventral sides of . When they’re adults, they .Frog Anatomy and Dissection Frog Dissection (2) Frog Dissection Alternative. Sacral Vertebra – A . Unlike a mammal heart, it only has three chambers — two atria at the top and one ventricle below. Results and Discussion. Finally, students cut the angles of the jaw to reveal the vomerine and maxillary teeth, the glottis, .Frogs have several major parts, including: Head. I have put the text boxes in place on the slides if . Both human beings and frogs have the same kinds of organs and systems of organs. Nostrils, lead directly to the mouth and give frog its excellent sense of smell. The frog's anatomy, however, is much simpler.Frog Dissection: External and Internal.The size of an average frog is around 12 to 18 cm in length and 5 to 8 cm in width. The external anatomy of the frog includes an investigation of the main features of the frog and the anatomy of the mouth. The name ‘frog’ is often used to distinguish the smooth-skinned, leaping anurans from the squat, warty, hopping ones, which are called toads.Montessori Cultural & Science Lesson - Parts Of A FrogThis tutorial is designed for a parent/educator and child (age 3-6). Frogs are animal athletes, with strong powerful legs that allow them to leap out of harm’s way. Drawn observation of the anterior part of the frog. Vertebrae – Individual bones that form the spine.This online quiz is called External Parts of a Frog.
Frog Dissection: External and Internal
All frogs have poison . There are three divisions of the limbs, or the truncus arteriosus, of a frog .

Shape and size: Body of a frog is somewhat spindle-shaped, pointed anteriorly and rounded posteriorly. There are three parts in a horse hoof anatomy wall – toe, quarter, and heel. Notice the arteries connected to the top of the heart, giving it a ‘Y’ shape.
Skeletal Anatomy of a Frog
In some parts of world, they are reared at farms. Shape and Size: Besides aerial mode of life, frog also leads aquatic mode of life.The respiration in larval form of frogs occurs through gills and is called Branchial respiration.
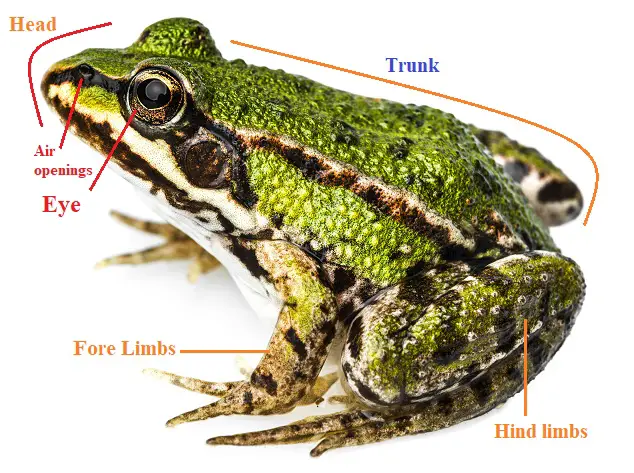
From there on, the external parts of it were precisely documented with the use of camera and drawn base from the observation. External features of Frog: 1. Shannan Muskopf. Carefully cut away the pericardium, the thin membrane surrounding the heart.