Extraocular muscle innervation
Eye anatomy: Muscles, arteries, nerves and lacrimal gland
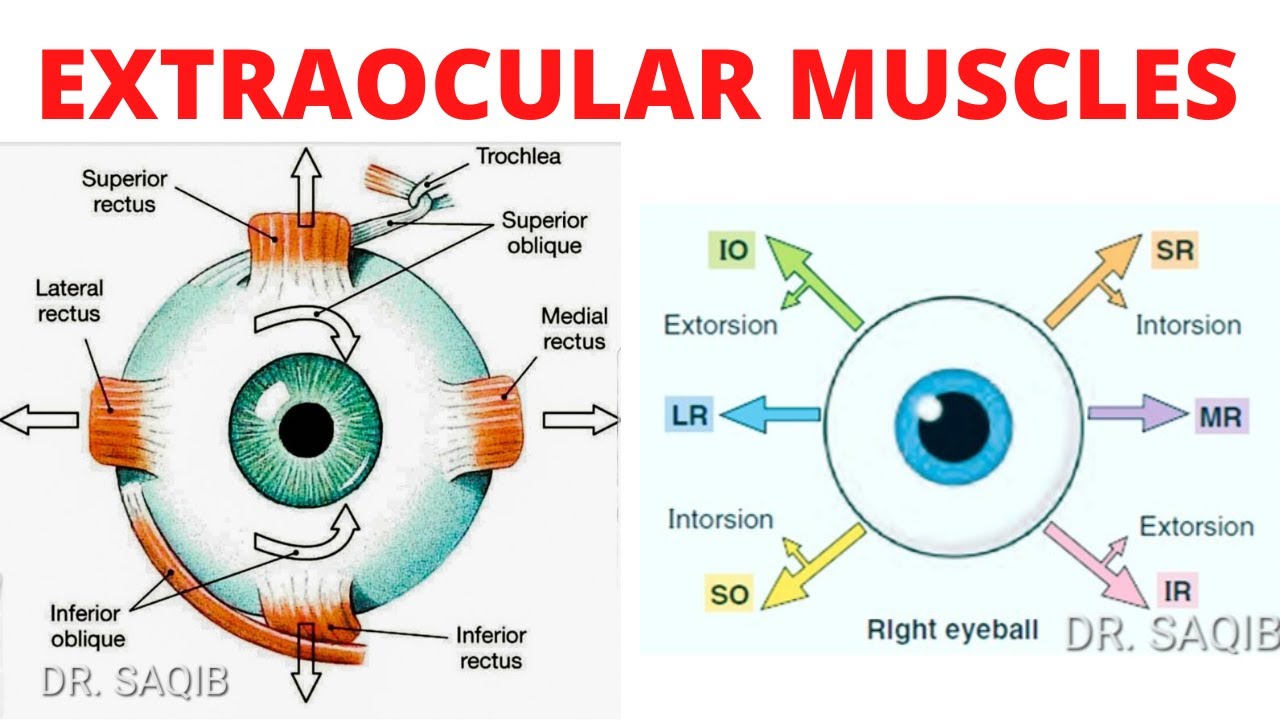
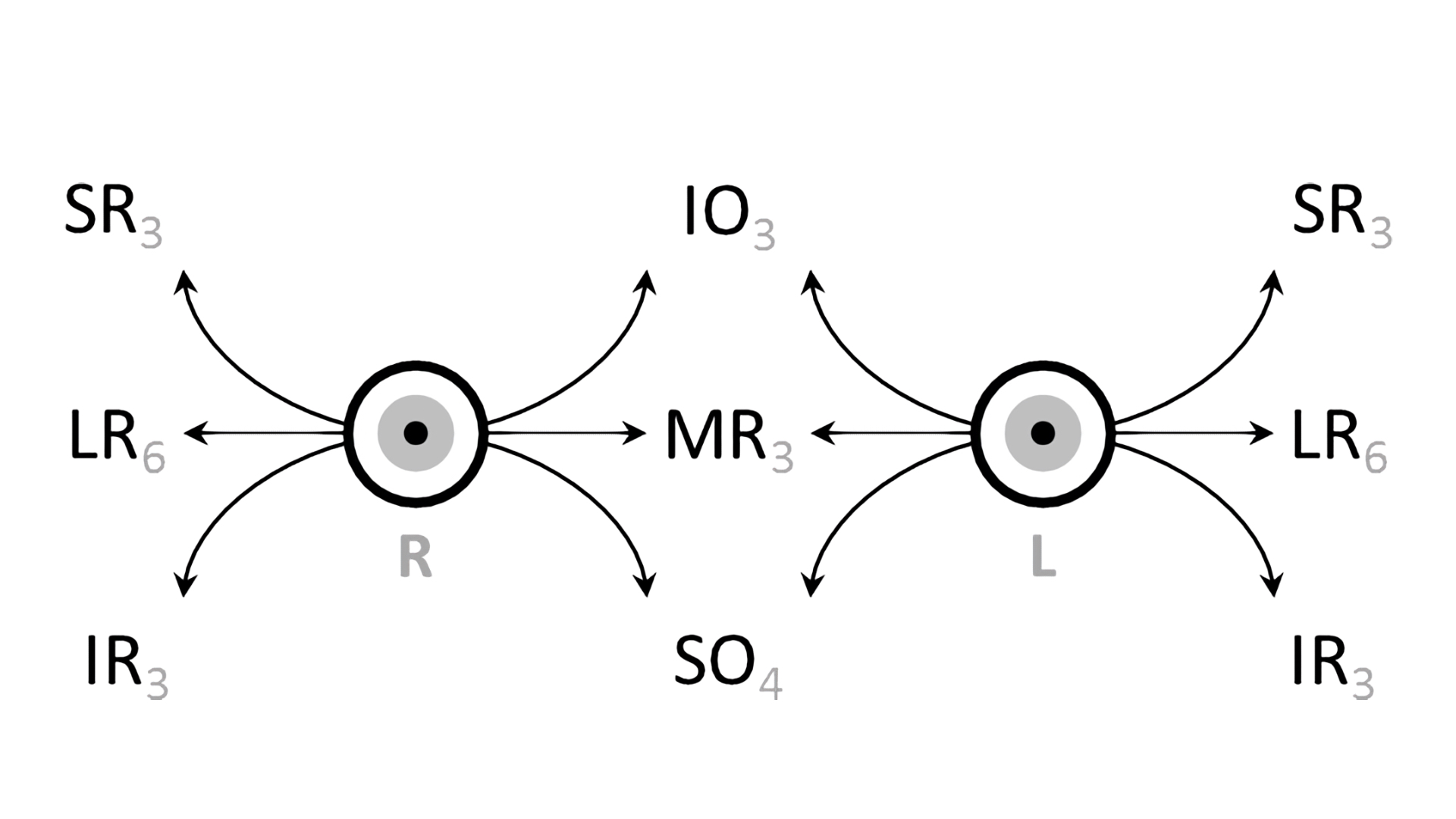
EOM fibers can be broadly divided into singly-and multiply-innervated fibers. superior oblique : internal rotation in neutral gaze, depression in adduction.Striated muscle of the leg can contain several hundred muscle fibers per motor unit 6; in the extraocular muscles, each axon innervates 3 to 10 fibers.7 mm posterior to the limbus. Action – Abduction Innervation – Abducens nerve (Sixth cranial nerve) Superior Rectus The computed rotation axes of the horizontal recti were close to being in .
Impaired Extraocular Muscle Innervation Is Present Before Eye
Extraocular muscles - second video in eye anatomy series. superior rectus : elevation in neutral gaze and abduction. The muscles responsible for the movement of the eye may be divided into the four recti muscles and the two oblique muscles. The medial rectus is the largest extraocular movement muscle. Throughout the years, in the absence of ancillary or diagnostic tools, many descriptive phrases, clichés, or . Four rectus muscles.
Eye Anatomy
Extraocular muscles, along with the superior rectus, inferior rectus, medial rectus, .
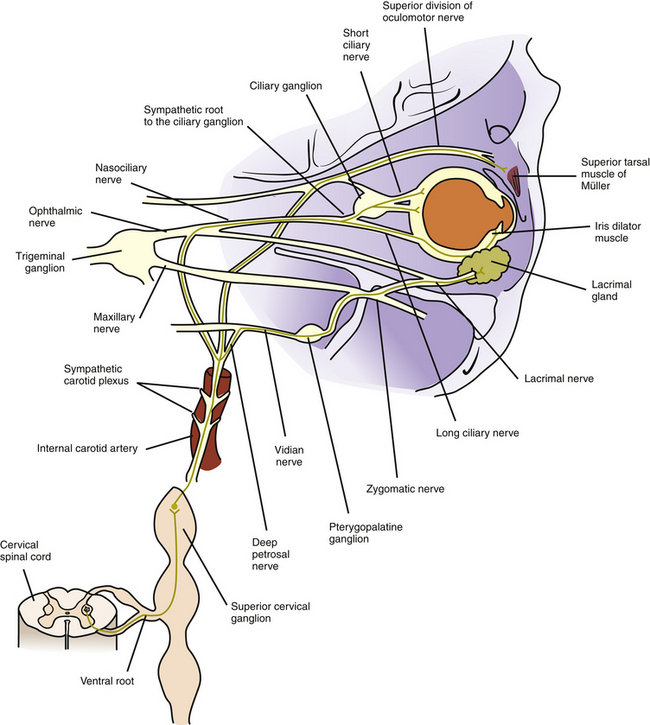
Lacrimal Apparatus.Innervation of the extraocular muscle from the paired nuclei is ipsilateral for the inferior and medial rectus muscles and the inferior oblique muscle. Whether you are a student, a teacher, or a curious person, this web page will help you . They are classified as accessory structures of the eye. J Physiol 153:522–526. Defects on this muscle can cause strabismus. It moves the eye from side to side with the lateral rectus, an abductor. Contraction of the muscles produce movement of the eyes within the orbit.Extraocular Muscles. 4 Rectus Muscles.
Extraocular muscles — AnatomyLove
Review of extraocular muscle innervations.Pachter BR, Davidowitz J, Breinin GM. Clinicopathologic Correlations. 7 This dense innervation provides for precise fine motor control of the extraocular muscles resulting in high velocity ocular movements, necessary in saccades, (up to 1000 degrees per second .10 2 Anatomy of the Extraocular Muscles Table 2. lateral rectus : abduction. 2 Oblique Muscles.
Extraocular muscles
The 4 extraocular muscles that control eye movement in the cardinal directions (along with their functions) are the superior rectus, inferior rectus, lateral rectus and medial rectus muscles.Overview
The Actions and Innervation of Extraocular Muscles
6 mm wide at its insertion on the globe.4,9/5(149)
Extraocular muscles: Anatomy and movements
PubMed CAS Google Scholar Mascarello F, Carpene E, Veggetti A, Rowlerson A, Jenny E (1982) The tensor tympani muscle of cat and dog contains IIM and slow-tonic fibres: an unusual combination of fibre types.
(iii) Singly-innervated extraocular muscle fibers.The recti muscles originate from the bony orbit and are inserted onto the eyeball in a spiral that begins at the origin of the medical rectus that’s closest to the limbus and rotates outwards The two obliques arise from the surface of the .Impaired Extraocular Muscle Innervation Is Present Before Eye Opening in a Mouse Model of Infantile Nystagmus Syndrome - PMC. Again, I find it helpful to flip this information and look for patterns.Of the cranial nerves with motor functions, CN III, CN IV, and CN VI are the ocular motor nerves, which provide innervation to the extraocular muscles. The medial rectus is an adductor muscle. Fiber composition of the superior rectus extraocular muscle of the rhesus macaque., 12mm, among all the recti muscles.The 7 Extraocular Muscles. Overall, every person has seven pairs of extraocular muscles - each muscle of the pair is located in one of two bony .The EOM are traditionally described as including 7 muscles in each orbit. The intermuscular septa attach the lateral rectus to the inferior oblique muscle. Helpful references: Chapter 9 in Leigh and Zee / Chapter 5, section 1 in Adler Outline V. Like the other eye muscles, inferior oblique is named by its position . Invest Ophthalmol . [Google Scholar] Pachter BR. It’s responsible for the up-and-down and the side-to-side movement of the eye.The distinct transcriptomic features of extraocular muscle satellite cells, partially mimicked by NaBu treatment, endow enhanced self-renewal and axon . Innervation is via the third cranial nerve.Functionally, they can be divided into two groups: Responsible for eye movement – Recti and oblique muscles. Extraocular muscles have a large ratio of .2 Extraocular Muscles and their Innervation.Purpose: To determine if extraocular muscles (EOMs) from mice with nystagmus show abnormalities in myofiber composition and innervation, as seen in EOMs from human nystagmus patients, and to determine when in development those changes occur. Mouse Extraocular Muscles and the . J Muscle Res Cell Motil 3:363–374
Extraocular Muscle Anatomy and Innervation
There are seven extraocular muscles. For the purpose of this article on eye globe anatomay, the eye will be divided into 2 sections: extraocular (ie, structures outside of the globe) and the ocular (ie, the globe and intraocular structures).Summary This chapter contains sections titled: Muscle Pulleys Ocular Muscles Innervation Associated Cranial Nerves References Skip to Article Content; Skip to Article Information; Search within . The recti muscles originate from the bony orbit and .How does the structure of extraocular muscles and their . inferior division: medial rectus, inferior rectus, and inferior oblique muscles. A summary of the principal actions of each muscle are given below.In total, there are seven extraocular muscles.It is one of the 6 extraocular muscles, also referred to as the extrinsic muscles of the orbit. Oculomotor nerve (CN III) The oculomotor nerve originates in the midbrain, in the oculomotor nuclear complex.Kupfer C (1960) Motor innervation of extraocular muscle. Contraction produces various combinations of vertical, horizontal, and rotary movement, depending on the angle of gaze of the eye.Chapter 5 ORBITAL GEOMETRY ANATOMY OF EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLES.The orbit hosts the eyeballs, extraocular muscles, optic nerve, lacrimal apparatus, fat tissue, fascia and vessels that supply these structures. Shaped like a quadrangular .The extraocular muscles are innervated by lower motor neurons that form three cranial nerves: the abducens, the trochlear, and the oculomotor ( Figure 20. However, normal extraocular muscle movement can be limited to only 15° when the head moves. Superior oblique.
The Extraocular Muscles
Measurements of the locations of muscle insertions and origins were made in the stereotaxic reference frame with the x-y plane horizontal and the x-z plane sagittal.Analyses of the innervation of human EOMs have revealed that there is a clear correlation between nerve fibre diameters and the distinct morphology of the .
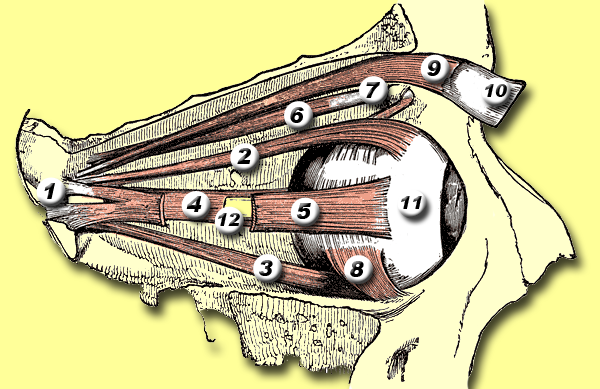
This muscle controls the eye’s upward movement.
Extraocular Muscles, Strabismus, and Nystagmus
The four rectus muscles are the medial rectus, . Insertions of the extraocular muscles (spiral of Tillaux) [ 5, 9] (Based on Kanski, 2007) [ 12] Full size image. Mice showed a standard EOM organization pattern, although their eyes are set at the side of the head. Blanket rule: superior oblique is innervated by the trochlear nerve, cranial nerve 4 - and that is the only muscle that nerve innervates, and it is named for the connective tissue pully . However, they have unique motor end plates that are smaller and more simple .Structure and Function.
These muscles, collectively known as the extraocular muscles, play a crucial role in directing gaze, maintaining binocular vision, and ensuring accurate tracking of objects.1 Action and innervation of the extra ocular muscles Extraocular muscle Origin Insertion Innervation Medial rectus Both .Eye anatomy is a fascinating topic that covers the structure and function of the organs that enable us to see the world.

The extraocular muscles receive innervation from three cranial nerves, including the oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens.The extraocular muscles.
Chapter 8: Ocular Motor Control
Eye, sagittal section.
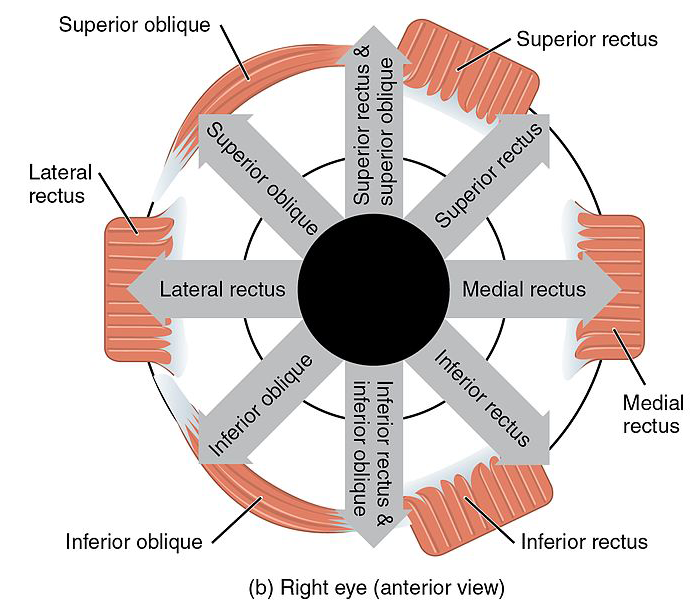
Superior rectus. Key Words: muscle planes, fields of action, primary, secondary and tertiary actions, agonist-antagonist pairs, Descartes-Sherrington law of reciprocal innervation. This complex is located at the level of superior colliculus near the midline.The extraocular muscles are a group of extrinsic muscles located within the bony orbit.The lateral rectus is one of the seven extraocular muscles. 50 EOMs also influence axon guidance during early development.The rotation axis for each of the six extraocular muscles was determined in four eyes from three perfused rhesus monkeys.
Anatomy Of Extraocular Muscles (EOM): comprehensive Guide
There are a total of four rectus muscles, two oblique muscles, and the standalone levator palpebrae superioris. Superior Rectus. Each extraocular muscle has a yoke muscle in the opposite eye to accomplish versions into each gaze position.Analyses of the innervation of human EOMs have revealed that there is a clear correlation between nerve fibre diameters and the distinct morphology of the muscle fibres they serve.
Gross anatomy of the Extraocular Muscles
INVOLUNTARY EOM : . Share this concept: Bones and Structure of the Orbit.
Inferior oblique: Attachments, innervation and function
Extraocular muscles include four rectus muscles (medial, lateral, superior an inferior rectus), two . Lateral rectus. medial rectus : adduction. Six muscles move each eye in the orbit, 4 rectus muscles and 2 oblique muscles, and the .The extraocular muscles are a group of six extrinsic muscles of the eye. Inferior rectus. 1976; 8 (3):547–560. oculomotor nerve: superior division: superior rectus muscle. Like other skeletal muscle fibers, singly-innervated EOM fibers are innervated by one motor axon.Yoke muscles are the primary muscles in each eye that accomplish a given version (eg, for right gaze, the right lateral rectus and left medial rectus muscles). Orbital Geometry; . Damage to extraocular muscles or their innervation can affect ocular motility, resulting in altered .EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLES ( EOM) : These muscles are situated around the eyeball. The globe can rotate 50° horizontally from the anterior midline.Extraocular muscle fiber innervation. They do have more prominent .Levator palpebrae superioris muscle (Musculus levator palpebrae superioris) Levator palpebrae superioris is a thin muscle located in the bony orbit above the eyeball. In this web page, you will learn about the muscles, arteries, nerves and lacrimal gland of the eye, as well as their clinical relevance. Light and electron microscopic serial analysis of mouse extraocular muscle: morphology, innervation and topographical organization of component fiber populations.comExtraocular Muscles - EyeWikieyewiki. As the muscle runs forward at an angle of 23 degrees to .8 mm, measured from the origin.rectus muscle has the broadest arc of contact, i. These muscles control every movement of the eye; usually, one muscle moves the eye in one direction, and the combination of all of them allows the eye to move in every direction. Let's do that for innervations to extraocular muscles. The lateral rectus is the thinnest extraocular muscle having a width of only 9.orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Extraocular Muscles
The extraocular muscles execute eye movements and are innervated by three cranial nerves. The muscles are attached to the sclera of the eye at one end and are anchored to the bony orbit of the eye at their opposite ends.The organization of extraocular muscles (EOMs) and their motor nuclei was investigated in the mouse due to the increased importance of this model for oculomotor research. Anatomy of the Extraocular .