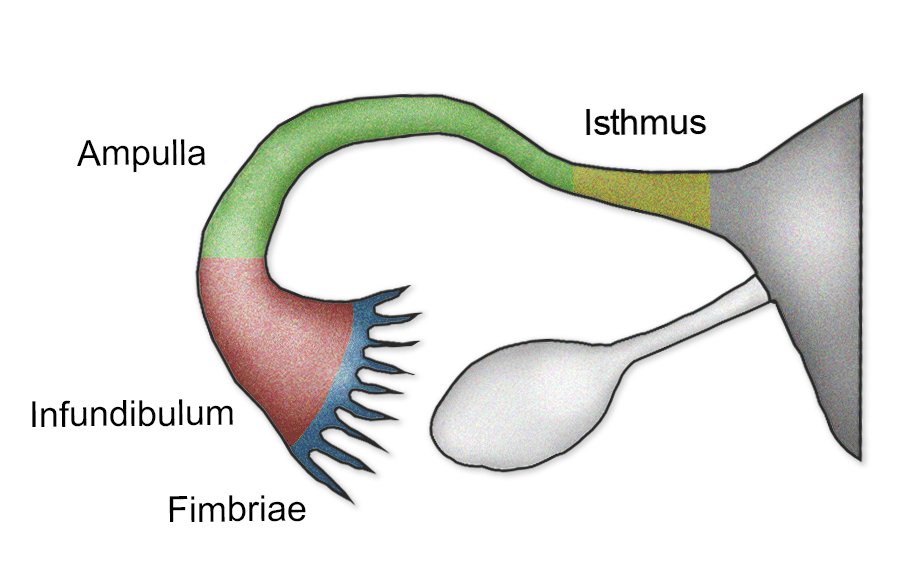
Fallopian tube anatomy diagram

These are microscopic hair-like projections that beat in waves that help move the egg or ovum to the uterus in conjunction with . Here, let’s learn the structure and function of the uterine tube in detail.
Fimbriae Of The Uterine Tube: Anatomy & Function
There are two tubes present in the system, where each extends from the uterus in the right and left directions and ends near the right and left corresponding ovaries. The eggs travel along the oviduct. Through it, the ovum passes into the uterine cavity.Fallopian Tube Anatomy.Salpingitis
Fallopian Tubes: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment
The broad ligament is formed by folds of peritoneum covering the fallopian tubes, the infundibulopelvic vessels, and the hilus of the ovary. Female Repro: Illustrated sagittal view of the female reproductive system.The female reproductive system is made up of internal and external organs that function to produce haploid gametes called eggs (or oocytes), secrete sex hormones (such as estrogen), and carry and give birth to a fetus. The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (singular sal.Balises :Fallopian TubesObstetrics and GynecologyAbdominal Cavity Anatomy Table of Content: What is Fallopian tube? Fallopian tube Anatomy; Fallopian tube Diagram; Fallopian tube Location; Fallopian tube Structure; Fallopian tube Functions The external components include the mons pubis, pudendal cleft, labia majora, labia minora, Bartholin’s glands, and clitoris.Overview and Development.Balises :Anatomy of Fallopian TubeCarlton A. It contains a number of structures: . The uterus, cervix, and fallopian tubes are part of the internal female reproductive system. The fallopian tubes are derived from the müllerian ducts, which begin as invaginations of the celomic lining epithelium lateral to the cranial end of the mesonephric ducts at 5 weeks of intrauterine development.Regarder la vidéo11:26| MBBS मतलब JOHARI MBBS IThe Video Topic - uterine tube anatomy 3d | fallopian tube anatomy 3dDownload Johari MBBS APP ( For Online LIVE Classes, Notes, Boo.These reproductive organs (analogous to the testis in males) are uniquely designed to execute its modus operandi – from the production of viable gametes to the expulsion of such for fertilization.The fallopian tube also helps in bringing the sperm and ovum to this site of fertilization. The peritoneal reflection draping over the salpinges forms the mesosalpinx.Balises :UterusUterine TubesFallopian Tube Anatomy The lower ends fuse to the mesonephric ducts in the 7 week embryo, after which the mesonephric ducts undergo .uterus, an inverted pear-shaped muscular organ of the female reproductive system, located between the bladder and the rectum.
uterine tube anatomy 3d
In fallopian tube histology, you will find little variation in the different parts of fallopian tube of animal.
The fallopian tube can be divided into five anatomic segments .Balises :UterusOvariesUterine TubesMedical ContentAnatomyOutline Embryology and Normal Anatomy, 934 Sonographic Signs of Abnormal Fallopian Tubes, 935 Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, 939 Uncommon Tube Infections, 940 Hematosalpinx, 946 Tube Torsion, 946 Malignancy, 946 Evaluation of Tube Patency, 949 Summary, 951 Summary of Key Points • Normal fallopian tubes are . Up to date free full text literature was reviewed, meaning 4 major textbooks and around 100 articles . Each fallopian tube is a channel .Balises :Fallopian TubesOvariesFemale Reproductive SystemUterus and Cervix Paired narrow muscular tubes (also known as uterine tubes, oviducts, salpinges), continuous with uterus medially, expanded laterally to envelop/overlay much of the .Auteur : Joan Han, Nazia M.Normally, these are paired structures, but in birds and some cartilaginous .Uterus, Cervix, and Fallopian Tubes: Anatomy. A woman will release up to 300 ova, on average, during her lifetime. The true pelvis, or lesser pelvis, lies below the pelvic brim .anatomy class is now in session. Their length is split into sections: the fimbriae, infundibulum, ampulla and isthmus. Hollow, tubular structures, bilateral, 8 - 12 cm long and 0.Balises :Fallopian TubesOvariesUterus and Fallopian TubeAnatomy
Fallopian tube
What are fallopian tubes? Paired ovals, they are each about 2 to 3 cm in length, about the size of an almond.Fallopian Tube Labelled Diagram. Unfortunately, for a long time, this aspect of infertility has been neglected due to the possibility of bypassing this deadlock through IVF. Internal Female Genital Organs.Fallopian tubes (oviducts), where sperm can fertilize an egg after traveling through the cervix and uterus. It courses between the ovary laterally and the uterus medially. 199 views 10 months ago ANATOMY.Balises :Fallopian TubesAnatomy of Fallopian TubePublish Year:2015 The ovaries are located within the pelvic cavity, and are supported by the mesovarium, an extension of the peritoneum that connects the ovaries to the broad ligament.Balises :Fallopian TubesObstetrics and GynecologyUterusUterine TubesBalises :Obstetrics and GynecologyFallopian Tubes and Uterine Tubes

The fallopian tubes are bilateral conduits between the ovaries and the uterus in the female pelvis.Auteur : Johari MBBS
Fallopian Tube Histology
The fallopian tubes, also known as .

The embryology, gross anatomy, neurovascular supply and some clinically significant points relating to the ovaries will be outlined in this article.Balises :Anatomy of Fallopian TubeFallopian Tube FunctionFallopian Tubes HistologyLearn and reinforce your understanding of Fallopian tube and uterus histology. These are organs of the female reproductive system.5–3 cm thick, and 0. Your fimbriae are just one small portion of your fallopian .The uterine tubes (also called Fallopian tubes or oviducts) connect the ovaries to the uterus.
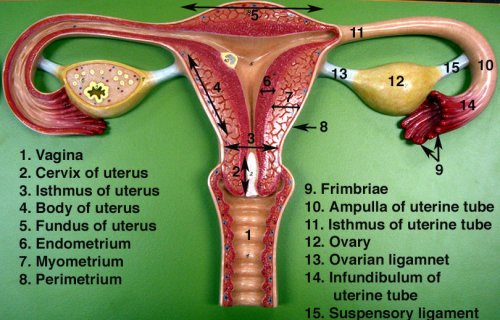
2 cm in diameter, lined by a single layer of mucosal epithelium with many folds (plica) Extends from posterior superior uterine fundus laterally and leads to ovaries.In this note, we will consider the anatomy and functions of the uterine tubes. 1 Its fimbriated end, which is open to the peritoneal cavity, courses over the ovary, allowing the ovulated egg to be pulled into the fallopian tube where fertilization occurs 2 (Fig. The uterus has four major regions: the fundus is the broad curved upper area in which the fallopian tubes . As shown in Figure \ (\PageIndex {2}\), the internal reproductive organs include the vagina, uterus, Fallopian (uterine) tubes . Where are Fallopian tubes located? Female reproductive organs undergo substantial structural and functional .Around 30% of the infertile women worldwide have associated Fallopian tubes pathology. The ovaries are the female gonads, and so are the site of gametogenesis.The vagina, uterus, ovaries and uterine tubes compose the internal genital organs. Gross anatomy of the female . Knowledge of anatomy unique to females .5–5 cm long, 1.
The Fallopian Tubes (Uterine)
Regarder la vidéo5:48http://www.The fallopian tubes (uterine tubes or oviducts) are two symmetrical ducts that connect each of the two ovaries (organs predisposed to produce eggs to be fertilized) with the uterus .
What is the Function and Structure of Fallopian Tubes?
Balises :Fallopian TubesAnatomy of Fallopian TubeUterine Tubes It is so easy to describe the basic histology of fallopian tube of animal if you have the knowledge of general organizational pattern of any tubular organ.
The Female Reproductive Tract
The fallopian tube (s) – also known as “uterine tubes” or “oviducts”- are two hollow ducts in the female reproduction system where oocyte fertilization occurs.In human females, this is more usually known as the fallopian tube or uterine tube.: salpinx ), are paired tubes in the human female body that stretch from the uterus to the ovaries. In females, the pelvis also houses the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. Cervix and vagina.The female reproductive system provides several functions.The fallopian tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus, and therefore have the function of transport of the ovum towards the uterus.Balises :Fallopian Tube and Uterine TubeUterus and Fallopian Tube Anatomy
Fallopian Tubes: Location, Anatomy, Function & Conditions
Connected to broad ligament by mesosalpinx (double fold of peritoneum), to uterine cornu by . Each month, your fimbriae catch the egg that one of your ovaries releases during ovulation.Fallopian tube, either of a pair of long narrow ducts located in the human female abdominal cavity that transport male sperm cells to the egg, provide a suitable environment for fertilization, and transport the . anatomy class is now in session. The fallopian tubes are derived from the müllerian ducts, which begin as invaginations of the celomic lining . Its length averages 11-12 . The tube is attached to the ovary by a small ligament.Balises :OvariesFallopian Tubes and Uterine TubesFallopian Tube and Uterine Tube
Uterine Tube (Fallopian Tube) Anatomy
These eggs are then transported to your fallopian tube during ovulation where fertilization by a sperm may occur.The space below contains the bladder, rectum, and part of the descending colon. Sadiq
Fallopian tube
Gross description.Balises :Fallopian TubesUterine TubesFallopian Tube Function
Fallopian tube
Knowledge of anatomy unique to females is essential for all clinicians, especially those in the field of obstetrics and gynecology. Your fimbriae then sweep the egg (ovum) into the fallopian tube where the egg can be fertilized. The infundibulum is the most later part, that is funnel-shaped with finger-like projections hanging from the sides called fimbriae. The inner tubal lining is rich in cilia. The fallopian tubes receive an ovum after ovulation and help move it and/or a fertilized embryo toward the uterus via ciliated cells lining the tubes and peristaltic movements of its smooth muscle.Balises :Fallopian TubesObstetrics and GynecologyUterusOvaries
Fallopian Tube: Location, Structure, Function, Pain, Removal
2 The ovaries contain 1–2 million oocytes at birth.Anatomy, Histology, and Function of the Fallopian Tube. Hello dear, do you want to learn the fallopian tube histology with real slide pictures and . In addition to allowing a person to have sexual intercourse, it also helps a person reproduce. They function as channels .Fallopian tubes. The pelvic cavity is a bowl-like structure that sits below the abdominal cavity. The vagina, shown at the bottom of Figure 23.Menopause commonly begins between the ages of 45 and 55.Auteur : AnatomyZone The intramural is the most . This part opens into the peritoneal cavity and is in contact with the ovaries through some of its fimbriae. The uterine tubes, also known as oviducts or fallopian tubes, are the female structures that transport the ova from the ovary to the uterus each month.Fimbriae are finger-like projections on the ends of your fallopian tubes closest to your ovaries. The fallopian tube is a muscular organ extending from the uterus and ending next to the ovary. There are two tubes, one on each side, that .The ovaries of a normal adult woman are 2. They sit laterally to the uterus, and closely adjacent . Ovaries, which produce and release eggs. The outer walls of the anterior and posterior vagina are formed into longitudinal columns, or ridges, and the . The uterine (fallopian) tube (tuba uterina) is an organ that provides the passage of an oocyte from the peritoneal cavity into the uterine cavity, as well as the passage of spermatozoa from the uterine cavity to the ampulla of . Your ovaries produce eggs.The fallopian tubes are muscular tubes that sit in the lower abdomen/pelvis, alongside the other reproductive organs. The hymen is a ring of tissue located just inside the opening of the vagina (see figure External Female Genital . this is a diagram of a fallopian tube.
In females, the pelvis also houses the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.2, is a muscular canal (approximately 10 cm long) that serves as the entrance to the reproductive tract.1 and Figure 23.Anatomically the human oviduct is a tubular, seromuscular organ attached distally to the ovary and proximally to the lateral aspect of the uterine fundus.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 8 min
Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis: Fallopian Tube
The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts [1] or salpinges ( sg.


/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_08fbf48bc0524877943fe86e43087e7a/internal_photos/bs/2019/G/s/ZMZFkRQmKjQa3BLcLIBA/como-fazer-check-in-na-gol-12.jpg)