Febrile convulsion management

This guideline addresses the emergency management of convulsive status epilepticus (CSE) in children and infants older than 1 month of age.En savoir plus
Convulsions fébriles
Symptoms of simple febrile seizure are: loss of consciousness.Most febrile seizures stop on their own within a couple of minutes. 1, 8 – 11 Measures include clinical history, presence of chronic . Elles apparaissent lors d’un épisode de fièvre et . Children with simple febrile seizures, who rapidly recover and are otherwise well, require no investigations following a febrile seizure. On the basis of risk/benefit analysis, neither long-term nor .Febrile seizures are generalized seizures, typically in children between the ages of 6 months and 5 years, that occur with a fever >100. The aetiology is multi-factorial, although most episodes occur in children with viral infections. Convulsion fébrile.Les convulsions apparaissent généralement entre 6 mois et 6 ans.How to identify a seizure. In most children the seizure will have self . Approximately 1 in 30 children will have a febrile convulsion because of a fever. Seizures with fever in children who have suffered a previous nonfebrile seizure are excluded from this definition. • When a child presents with a seizure . [Google Scholar] 77.Complex febrile convulsion: A febrile convulsion with one of the following features: Longer than 15 minutes, partial/focal onset or focal features, more than one convulsion .This article discusses the aetiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis and management of children with febrile convulsion, and best practice for care in EDs. The International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) defined FS as a seizure in association with a febrile illness in the absence of a central nervous system (CNS) infection or acute electrolyte imbalance in children older than 1 month of age without prior afebrile seizures”[].Les symptômes des convulsions fébriles de l'enfant. “Fever from any viral or bacterial infection can .
Febrile convulsion
1–4 years of age: 5 mg.Le traitement des convulsions durant 5 min est symptomatique. FCs are relatively.A febrile seizure is a seizure (convulsion) which occurs in a febrile child (between the ages of 6 months and 5 years) and is not caused by a central nervous system infection. This occurs most often in children aged 6 months to 5 years.comLes convulsions chez l'enfant - Doctissimodoctissimo.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 6 min
The management of febrile seizures
Febrile convulsions are seizures that occur in children .
making jerking or twitching movements.
Treatment and prognosis of febrile seizures
• A convulsion can occur with a temperature change from the normal 37ºC to as little as 38. They affect kids 6 months to 5 years old and are most common in toddlers 12–18 months old. They can occur in children who have a rapid increase in body temperature and may be the first sign of a child developing a fever. Le développement et les processus mentaux sont généralement normaux, mais pendant ou après la convulsion, le développement et . It is important to exclude hypoglycaemia in an actively seizing child or if there is a prolonged recovery period.Investigations. epilepsy in the later age o f . tout le corps de l'enfant est soudain secoué par des spasmes (contractions) musculaires symétriques ;Febrile seizures are convulsions that happen in some children with fevers. It replaces a previous position statement from 2011, and includes a new treatment algorithm and table of recommended medications based on new evidence and reflecting the evolution of clinical . A febrile seizure is a seizure accompanied by fever (temperature higher than 38°C), without central nervous system infection, in infants and .4 °F (38 °C) not associated with a central nervous system (CNS) infection, a known seizure-provoking etiology (eg, electrolyte imbalance, hypoglycemia, or substance abuse), or history of an afebrile .Febrile convulsions can happen in children with high fever, without warning.

BSUH Clinical Practice Guideline – Febrile convulsion Page 1 of 3 Febrile convulsion Author: Dr Miki Lazner Publication date: December 2015 Review date: December 2017 See also: Fever no focus in under 5s / Paediatric sepsis 6 To skip straight to management flow chart, click here Background Meningitis / encephalitis may cause seizures and fever and . They usually happen on the first day that a child has a fever above 100.

Febrile seizure: Summary. Escalation and advice outside of ED.Febrile convulsions (also called febrile seizures or fits) are caused by a sudden change in a child’s body temperature and are associated with a fever. Fever and suspected or confirmed neutropenia Fever in the recently returned traveller.
Convulsions fébriles
During a febrile convulsion you may witness the child to have .well as attitude towards febrile convulsions (P < 0. thought that it can be developed into.This was a quasi-experimental study (a pre and post-test interventional, one group), aimed at assessing the impact of health education on knowledge and home management of febrile convulsion .6–11 months of age: 2. Febrile convulsions (FC) are characterised by convulsions associated with.frPRISE EN CHARGE DES CONVULSIONS FÉBRILES CHEZ . Signs include: becoming stiff or floppy. A febrile seizure often occurs in the first few hours of a fever, when the temperature is rising.Febrile seizures are described as being simple or complex. Febrile seizures can be alarming and upsetting to . 5–9 years of age: 7. The majority occur between 12–18 months and are more common in those with a family history. The fit can last a few seconds or up to 15 minutes and is followed by drowsiness.In this article: What causes a febrile seizure? A febrile seizure is sometimes called a febrile convulsion. In-person appointments available upon request. Capovilla G, Mastrangelo M, Romeo A, . Febrile seizures are not associated with increased long-term mortality or negative effects .Updated guidelines for the evaluation and management of febrile seizures were published by the American Academy of Pediatrics . febrile convulsion.Febrile seizures are the most common seizure disorder in childhood, affecting 2% to 5% of children between the ages of 6 and 60 months. Traitement d'une crise > 5 minutes par benzodiazépine.

A febrile convulsion is a fit or seizure that occurs in children when they have a high fever.Prise en charge.

Febrile convulsions are also known as febrile fits or fever seizures.
Clinical Practice Guidelines : Febrile seizure
fever in children aged between 6 months and 6 years. Les convulsions d'une durée 5 min sont traitées par le lorazépam IV, le diazépam intrarectal ou le midazolam . EMPs can help others best understand and respond to your needs.
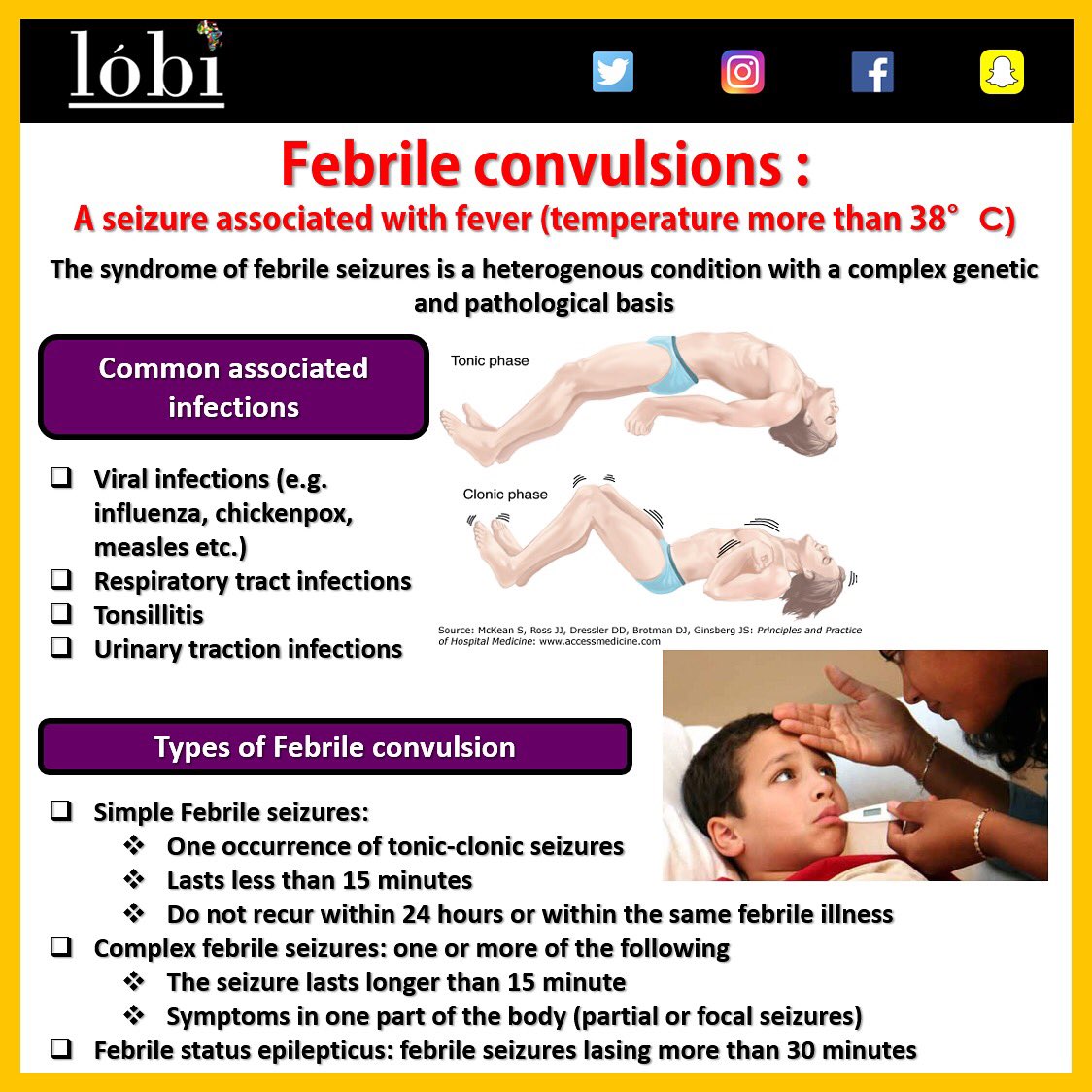
2015; 29 (52):36–43. developing a blue colour around the lips. One in every 20 children will have one or more febrile convulsion. Most febrile seizures are brief, isolated, generalised tonic-clonic seizures that . It also includes a . Febrile seizures (FS) are seizures or convulsions that occur in children between six months and six years of and are triggered by fever [ 1 ]. 1,2 Febrile convulsions are . 1 Febrile seizures are the most common cause of seizures in children, with 1 in 20 children having a febrile seizure at some point. becoming unconscious or staring off into the distance.To guide Emergency Department (ED) staff with the assessment and management of febrile convulsions. If your child has a febrile seizure, stay calm and follow these steps: Place your child on his or .Auteur : Daniela Laino, Elisabetta Mencaroni, Susanna Esposito
Réagir en cas d'urgence : Convulsions fébriles de l'enfant
Diazépam intrarectal : 0,5 mg/kg, à renouveler 1 fois après 5 à 10 .2 Mothers’ beliefs regarding. Recognition and management of febrile convulsion in children. Petechiae and Purpura Sepsis – assessment and management Local antimicrobial guidelines. Background Febrile convulsions are seizures that occur in children aged between 6 months and 5 years that result from a sudden rise in temperature associated with an acute febrile (usually viral) illness. Author: Robert J Baumann, MD; Chief Editor: Amy Kao, MD more. GENERAL ENQUIRIES (03) 8809 0600.

Troubles convulsifs
FS can be extremely frightening for . DONATION LINE 1800 437 453. This can happen in children aged 6 months to 6 years. no arm or leg weakness. In 56% of mothers’, information was based on what their . Avant la première crise myoclonico-atonique, deux tiers des enfants présentent des convulsions fébriles et des crises convulsives d’apparition généralisée. A febrile seizure refers to an event in infancy or childhood, usually occurring between six months and five years of age, associated with fever but without evidence of intracranial infection or defined cause [ 1 ]. Most febrile seizures will .Updated: Nov 09, 2018.comLes convulsions fébriles - Hopital de Montreal pour enfantshopitalpourenfants.
Management of Pediatric Febrile Seizures
Febrile seizures (FS), events associated with a fever in the absence of an intracranial infection, hypoglycaemia, or an acute electrolyte imbalance, occur in children between six months and six years of age.Convulsions fébriles – L’étiologie, la physiopathologie, les symptômes, les signes, les diagnostics et les pronostics à partir des Manuels MSD, version pour professionnels de la santé.frCrises fébriles | Société Française de Pédiatriesfpediatrie.
Febrile seizures: an overview
Management of Febrile Convulsions
Most seizures stop on their own after a few minutes and don't cause any other health problems.
Convulsions fébriles
Most fits last less than 2 to 3 minutes. Management Immediate management of a seizure. Febrile convulsions should stop within a few seconds to a couple of minutes without any . Any illness that causes a high temperature (fever) can .
Clinical features and evaluation of febrile seizures
They can be very concerning and very upsetting for parents and caregivers to witness.00); 66% of mothers agreed to administer rectal diazepam by themselves if trained. Related documents.Key points for management of febrile seizures • Febrile seizures occur in 3% to 5% of children between 3 months and 5 years of age. Les convulsions fébriles de l’enfant se manifestent par des contractions musculaires involontaires saccadées. Simple febrile seizures are the most common type and are characterized by a single generalized . Scenario: Acute management of febrile seizure: Covers the acute management of a child who is currently having a suspected or known febrile seizure. Rectal diazepam may be given as a rectal solution if preferred or if buccal midazolam is . La plupart des convulsions fébriles sont .• A rapid rise in body temperature can cause convulsions.For seizures lasting more than five minutes, a benzodiazepine should be administered. The Epilepsy Foundation recommends the use of Epilepsy Management Plans (EMPs).Nous voudrions effectuer une description ici mais le site que vous consultez ne nous en laisse pas la possibilité. common and affect 3–4% of children . Simple febrile seizures are .