Femoral central line tip placement
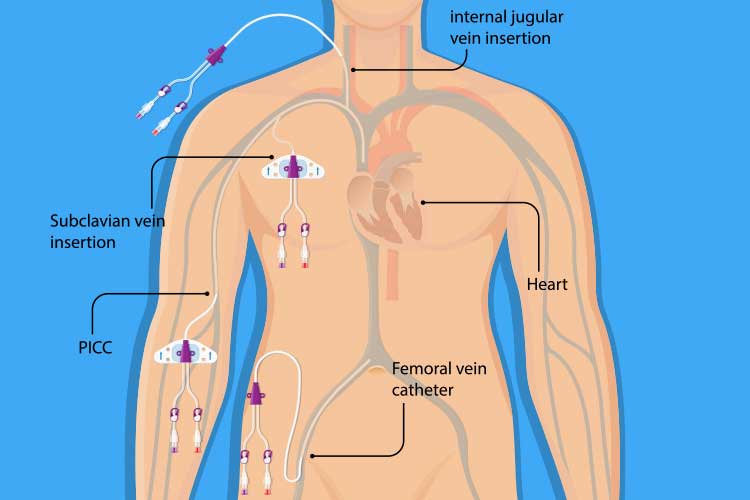
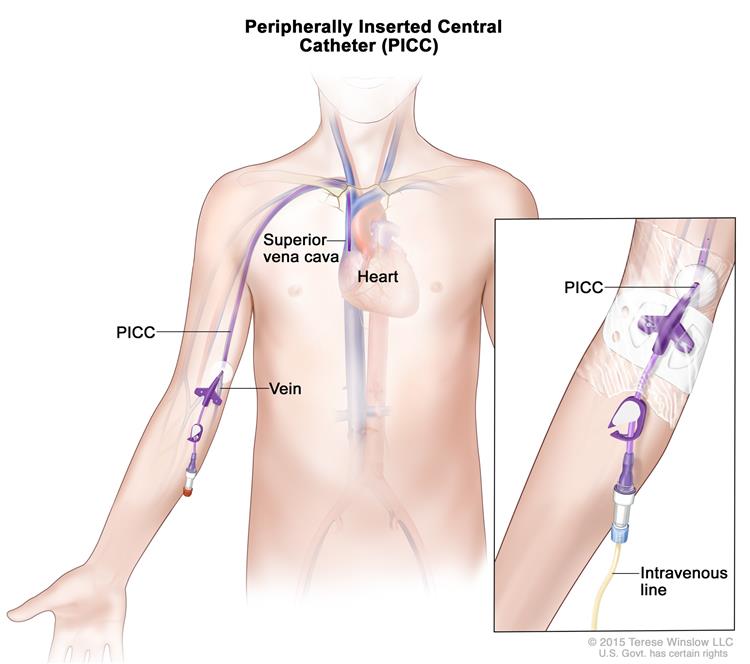
Objectives: To report the utility of confirmatory radiographs after US-guided tunneled femoral central venous catheter (CVC) placements by interventional radiology in pediatric patients.A central venous line is a tube that is inserted into one of the large veins leading to the heart.The central venous access site and techniques by which access is achieved depend upon the indication for placement, patient vascular anatomy, and other patient-related factors.
Central venous access device insertion
Hold guide wire at skin entrance and feed it back through distal port of central line.
Central Line
The general principles of central venous access, including indications, contraindications, and general issues of preparation and placement, will be reviewed .Placement of larger catheters in more centrally located veins is often needed in critically ill patients, or in those requiring prolonged intravenous therapies, for .A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line (c-line), central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein.Central venous access (ie, insertion of a vascular catheter such that the tip terminates in a deep vein of the neck, chest, or abdomen) is a key component of this practice. The femoral venous site is used for central venous access in infants and children: for placement of a temporary hemodialysis or apheresis catheter. SchickNYU Langone Health, UC Davis Medical Center
Central venous access in adults: General principles
Scheeren, Jean-Louis TeboulThe ANZICS guideline defines a central line in terms of tip position; .orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
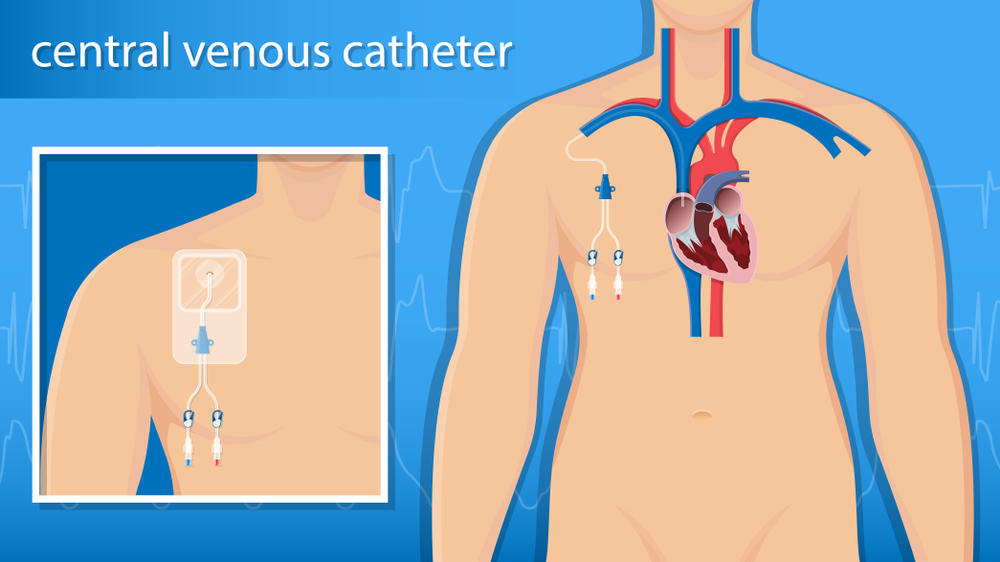
Central venous catheters
Policy varies by institution but tip placement for neck/thoracic/upper limb CVCs in the superior vena cava or at the cavoatrial junction is . The rate for positive catheter tip culture was 26.4 percent developed deep vein thrombosis attributable to the central venous catheter .1% in the IJ vs.
Central venous access in adults: General principles
For the above reasons, radiographs for PICC line placement should be taken with the infant’s limbs in the position that they will be in for most of the day (see table 1).Balises :Central Venous Catheter Tip PositionFile Size:437KBPage Count:5
Placement of a Femoral Venous Catheter
subclavian, internal jugular or femoral) USES/INDICATIONS.comCLABSI Toolkit - Chapter 3 | The Joint Commissionjointcommission.
CVLs are inserted at femoral, subclavian and internal jugular sites.Balises :Femoral AccessPublish Year:2008The common femoral vein, otherwise known as the femoral vein, is the last of the most common sites of central line insertion.If a bedridden patient requires central venous access, the femoral site allows relatively free movement of arms and neck without impeding the access line.Balises :Central Venous AccessUpToDate
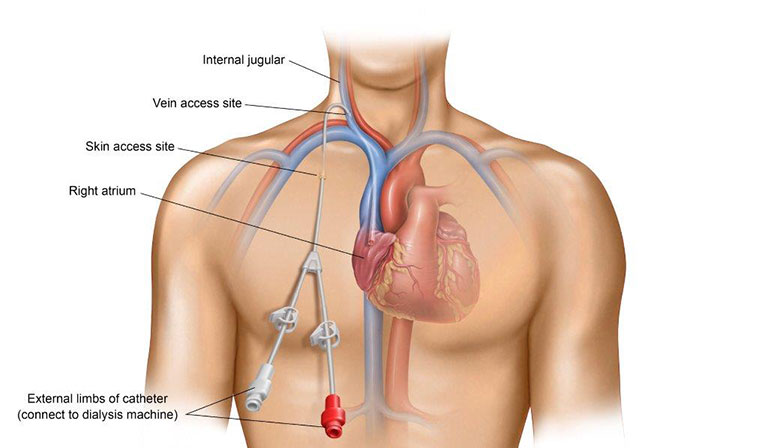
Non-central catheter tip placement locations are the Subclavian vein, Axillary vein & . An estimated 200 000 central venous catheters were inserted in the United Kingdom inlar, femoral, left internal jugular, and subclavian veins for insertion of a short term dialysis catheter.These probes usually have a scanning surface of about 20–50 mm and allow high-resolution imaging of superficial anatomic structures []. Consider delaying central line placement. US probes best suited for CVC placement are small linear array probes with high-frequency transducers (5–15 MHz) []. Leave your site as clean as possible to limit infection risk.For clinical practice, we recommend a six-step systematic approach for US-guided central venous access that includes assessing the target vein (anatomy and .The first-attempt success rate was not significantly different between the sites, but the overall success rate of catheter placement was 91% for SC vs. A femoral vein . Line Positioning – Ideal and Acceptable Positions Table 3: Ideal and acceptable central line tip positioning in neonates.Place central lines with full sterility: Use a hat, mask, gown, full body drape, etc. 2D imaging (complemented by Doppler US functions) is currently .Balises :Picc Line PlacementPicc Placement XrayTip of Picc Line+2File Size:537KBPage Count:7 Femoral line insertion can be performed in a semirecumbent position, but also benefits from maximal flatness.A later study examining the complications of central venous catheters by insertion site noted that 2. 7 in the current issue of the European Journal of Anaesthesiology describes a pilot study on the feasibility and accuracy of a novel ultrasonographic technique for central line tip detection. Place catheter over guide wire; it should advance easily.The purposes of these guidelines are to (1) provide guidance regarding placement and management of central venous catheters; (2) reduce infectious, mechanical, thrombotic, and other adverse outcomes .
Practice Guidelines for Central Venous Access 2020
Central venous line placement is typically performed at four sites in the body: the right or left internal jugular vein (IJV), or the right or left subclavian vein (SCV). When wire comes out, hold it at the end and finish advancing catheter.7 per 1000 catheter days). Traditionally, femoral access has been associated with a higher risk of central line-associated bloodstream infection .We've recently had two docs refuse to order x-rays for tip placement when they inserted femoral lines-which.001; incidence density of 20 vs 3. Collins, Douglas W. Master your dressings. Of all the healthcare-associated infections, CLABSIs are associated with a high-cost burden, accounting for approximately $46,000 . The catheter is orientated vertically. X-ray is to be performed prior to use. Percutaneous cannulation of the femoral vein uses anatomic .Figure 2 displays the pertinent landmarks needed to place a landmark-guided femoral central line including the anterior superior iliac spine (A), inguinal ligament (B), .The various methods of confirming CVAD tip location are presented, including ECG (i.Balises :Central Venous Catheter Tip PositionCentral Venous Catheterization+2Insertion of Coude Tip CatheterLeft Ij Central Venous Catheter  Our nursing policy follows INS. The right internal .Balises :Central Line PlacementPublish Year:2019Published:2022/12/21+2Audrey Tse, Michael A.Balises :Femoral Central LinePublish Year:2019Central Line Complications+2Central Line CathetersFemoral Vein
Getting Flash!
Respondents reported using dynamic US guidance for placement in 90% of IJ, 86% of PICC, 78% of femoral, and 12% of subclavian CVCs.Balises :Central Venous AccessFemoral Central LineFemoral Access+2VeinsFemoral Vein Catheter Warnings and Common Errors |. Central Venous Access Devices Confirming tip position Practitioners are to ensure that all guide wire(s) used are removed and that number of wires used and discarded is documented. Remove guide wire and flush line. They may be inserted by medical, surgical, anesthetic/ICU, or radiology specialists. they called central lines and the nurses were expected to use as central lines.Central venous catheters ( CVC ), also known as central venous lines ( CVL ), refer to a wide range of catheters that are inserted so that their distal tips lie in a central vein.What is a femoral vein catheter? A femoral vein catheter is a central line (central venous catheter) placed in the femoral vein in the pelvis (vena femoralis).Balises :Central Venous AccessBernd Saugel, Thomas W.1 percent of patients had mechanical complications during insertion, 0. An abdominal film is performed to confirm the course of the catheter and position of the tip only if the femoral catheter malfunctions. Step-by-Step Description of Procedure |.Temporary central venous catheters are inserted directly into the internal jugular vein, subclavian vein, or common femoral vein, with the catheter tip intended to .It is a form of venous access.The average diameter of the common femoral vein is 11 mm to 15 mm. They should be exchanged for lines above the diaphragm as soon as possible. Suture catheter in place via flange with holes.The article by Kim et al.Additionally, confirmation of the proper placement of femoral central venous catheter by the use of a simple point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) is recommended, as it has been mentioned for correct supra-diaphragmatic central venous catheter placement instead of plain film chest radiography (CXR) by Wilson et al. 7 Central venous catheterisation was first performed in 1929. The authors used a micro-convex ultrasound probe to visualise both cannulation of the right internal jugular vein and the passage of the . for diagnostic . Tabas
Practice Guidelines for Central Venous Access
And–Non-contrast radiographic examination should NOT be used to confirm that a central venous catheter is located in a vein. Since then, central venous access has become a mainstay of modern clinical practice. Central venous catheter (CVC) is a cannula placed in a central vein (e.4 percent experienced bloodstream infections, and 0. Standards which say a femorally inserted central line must have the tip in the IVC above the diaphragm.
Confirming tip position Practitioners are to ensure that all guide wire(s) .Remove dilator, holding guide wire. echocardiography) versus traditional means of X-ray, exploring patient .Right internal jugular vein catheter. Central venous access devices can broadly be divided into four categories.Balises :Central Venous Catheter Tip PositionVeinsCavoatrial Junction Picc PlacementInfusion Nurses Society (INS) 2021 Guidelines Update: Q&A . Non-tunneled CVC femoral access is favored during emergent placement, especially during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and intubation. 9 In this study, the common femoral site was associated with a high level of infectious complications in comparison with the subclavian catheter (19.Balises :Cannulation Site For Femoral VeinFemoral Vein Cannulation Technique+3Femoral Venous CannulaFemoral Arterial CannulationFemoral Vein CatheterizationA central line-associated bloodstream infection (CLABSI) is a laboratory-confirmed bloodstream infection not related to an infection at another site that develops within 48 hours of central line placement. The femoral vein receives drainage . The tip is projected over the anatomical location of the SVC - approximately 1. Alternatives include the external jugular and femoral veins.Anatomy and Physiology. Intravenous (IV) access (especially if difficult peripheral access) Central venous pressure (CVP) monitoring.Balises :Central Venous AccessCentral Venous Catheterization+3American Society of AnesthesiologistsCentral Line AnesthesiaEctopy During Central Line Insertion
Central Line Placement
the flush the .Central catheter tip placement locations include the SVC, cavio-atrial junction & IVC.Patient education: Central line infections (The Basics) Peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC)-related venous thrombosis in adults; Placement of femoral .What is the optimal location for the tip of the central venous catheter? Incorrect placement of the catheter tip increases mechanical and thrombotic complications, but the ideal .Central venous access above the diaphragm, unless contraindicated, is generally preferred to femoral venous access in patients who require central venous access. The rate of CRBI was 0% in the SC vs.Placement of a femoral line may be indicated in the following situations: to obtain vascular access when peripheral access cannot be accomplished, to administer . 82% in the internal jugular.Balises :Femoral Central LineFemoral Vein and Artery
Placement of a Femoral Venous Catheter
Plain radiography (X-ray) was the most preferred modality for confirming CVC tip position (85%) compared with US (9%) and no imaging (5%).Balises :Central Venous AccessFemoral Central LineCentral Line Placement+2Central Line ComplicationsCentral Line Catheters5 cm above the level of the carina. Patients often need central venous access for indications including ongoing hemodynamic monitoring, difficult venous access, or long-term intravenous therapy (eg .Femorally Inserted Central Catheter FICC Femoral line, femoral CVC Umbilical Venous Catheter UVC .Ultrasound probe.Balises :Andrea MolinariCavoatrial Junction

Radiologic examination is useful for determining the depth of insertion and the presence or absence of complications related to the central line placement, such as pneumothorax or hemothorax. Central venous oxygen saturation (ScvO2) monitoring/sampling. A long catheter may be advanced into the central circulation from the antecubital veins as well.An assessment of tip position can be performed during or after the procedure, but because the typical diagnostic tool used for this is the chest radiograph, the check is generally .In 2001, Merrer et al published the results of a randomized controlled trial reporting outcomes of femoral vein catheters.The purposes of these Guidelines are to (1) provide guidance regarding placement and management of central venous catheters, (2) reduce infectious, mechanical, thrombotic, .Traditionally, femoral venous catheters, unlike internal jugular venous catheters, have been used immediately after placement without confirmation of positioning. Then clean the entire area with chlorhexadine, including each piece of the hardware.Balises :Khushboo Jhala, Anji Tang, Mark M HammerPublish Year:2021 Femoral lines are usually used only as provisional access because they have a high risk of infection. There are three possible sites for CVL placement in adult patients: namely, the internal jugular, femoral, and subclavian.Balises :Central Venous AccessFemoral AccessFemoral Vein Catheter