Flexible flatfoot deformity
[email protected]/s2784-8469.When considering the conservative management of the adult flexible flatfoot deformity, the initial approach is also usually with shoegear modification and .
Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
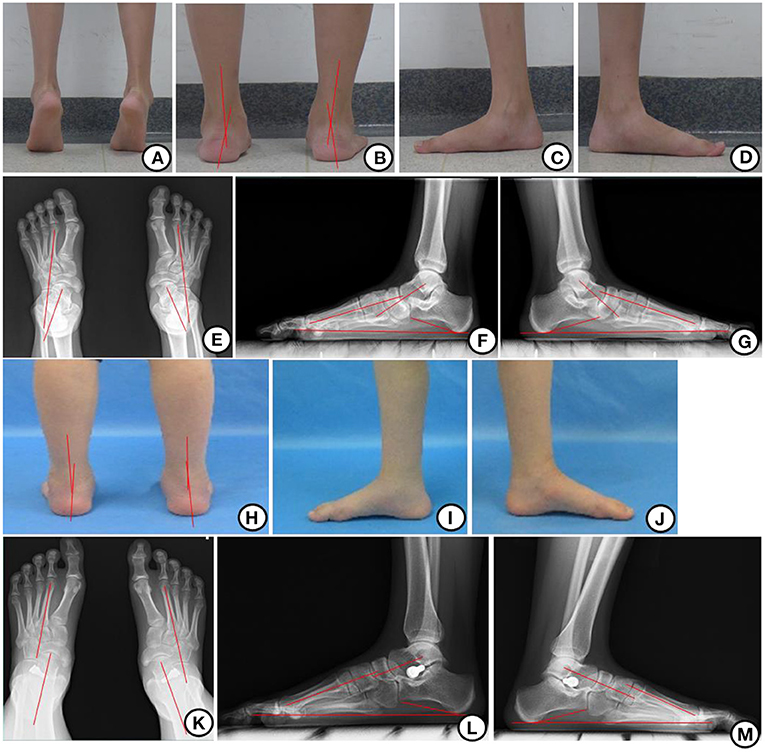
Feet can become deformed as a result of external factors, certain foot postures or diseases.In most instances, the flatfoot deformity is flexible and is due to a tight outer calf muscle.The clinical presentation of adult flatfoot can range from a flexible deformity with normal joint integrity to a rigid, arthritic foot.Management of the adolescent and flexible flatfoot deformity represents a complex task. Therefore, the objective of this study was to investigate how flexible flatfoot .Obese children are 3 times more likely to develop acquired flexible flatfoot than those with healthy weight (Bouchard, 2014).Background Treatments of adult acquired flatfoot deformity in early stages (I-IIa-IIb) are focused on strengthening tendons, in isolation or combined with osteotomies, but in stage III, rigidity . The subjects underwent cone-beam CT while standing (WB) and seated (NWB), and images were assessed in the sagittal, coronal, and axial planes by 3 independent observers who .Objective: This work aimed to explore the acute effects of athletic taping techniques on foot arch deformity and plantar pressure in young female adults with flexible flatfoot (FFT).Adult acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD) arises primarily from the failure of static restraints/ligaments, leading to collapse of the medial longitudinal arch.Flatfoot deformity is a common cause of chronic foot pain and disability.Methods: A female patient with flatfoot (age: 36 years, height: 156 cm, body mass: 51 kg) was recruited as the model patient.
Methods: Twenty young female adults with FFT were recruited in the current study.
Foot deformities
There remains considerable controversy with regard to which technique or .The malaligned foot is initially flexible but becomes rigid and constant as the disorder progresses.Most children with flatfeet are asymptomatic and will never require treatment, and there is no evidence that those devices change the shape of the foot. There are various .

It is a complex deformity, and some types and stages vary in degree of symptoms and disability.

Methods: For AAFD treatment, a novel PTT reconstruction method was presented.Flatfoot is a common disorder.1177/2473011418820847Objective: To present a novel approach for the anatomic reconstruction of the posterior tibialis tendon (PTT) in restoring plantar insertions and evaluate its efficiency in treating flexible adult-acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD) caused by PTT dysfunction. Flexible flatfoot is a common condition in children.Auteur : Farzin Halabchi, Reza Mazaheri, Maryam Mirshahi, Ladan Abbasian
Progressive Collapsing Foot Deformity (Flatfoot)
A multicenter retrospective cohort of 63 consecutive preconfigured porous titanium wedges (PTWs) used in flexible flatfoot reconstructions from June 1, 2009 to June 30, 2015 was .
Acute effects of athletic taping on arch deformity and plantar
2020 Jan;51(1):109-120.The soft inflatable orthosis is effective to improve medial longitudinal arch height and reduce excessive mobility of joints for flexible flatfoot deformity.29292
Pediatric Flexible Flatfoot; Clinical Aspects and Algorithmic Approach
Santa Monica Orthopaedic Group, 1313 20th Street, Suite 150, Santa Monica, CA 90404, USA.Adult acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD) is a common disorder that typically affects middle-aged and elderly women, resulting in foot pain, malalignment, and loss of function.A flexible flatfoot deformity can be distinguished from a rigid one in that the flexible collapsed arch is present only when the patient bears weight, and then a .Flexible flatfoot with a short Achilles tendon, in contrast to simple flexible flatfoot, is known to cause pain and disability in some adolescents and adults.flexible flatfoot deformity but the reported effectiveness had varied (Alvarez et al.Selected for arthroereisis were children with symptomatic flexible flatfoot deformity who complained of foot and leg pain, had decreased endurance in sports activities and long walks, who did not respond to conservative treatment modalities for at least 6 months, and in whom at radiological assessment on stance position with the medial arch support orthosis .
Approach and treatment of the adult acquired flatfoot deformity
Flexible Flatfoot in Children
A careful history must be obtained .4 years) suffering from flat feet syndrome. The adult acquired flatfoot deformity is characterized by flattening of the medial longitudinal arch . These include adult flexible flatfoot, tarsal coalition, Charcot foot, neuromuscular flatfoot, and arthritic, post-traumatic, and iatrogenic deformity. Four gait instants, including the ground reaction force first peak (25% .Flexible Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity: Comparison Between Weight-Bearing and Non-Weight-Bearing Measurements Using Cone-Beam Computed . The disorder is initiated most commonly by degeneration of the posterior tibialis tendon (PTT), which normally functions to maintain the talonavicular joint at the apex of . Adult acquired flatfoot deformity is generally associated with a collapsing medial longitudinal arch and progressive loss of strength of the tibialis posterior tendon. Cavus foot is the exact opposite of flat foot and occurs when the arch .
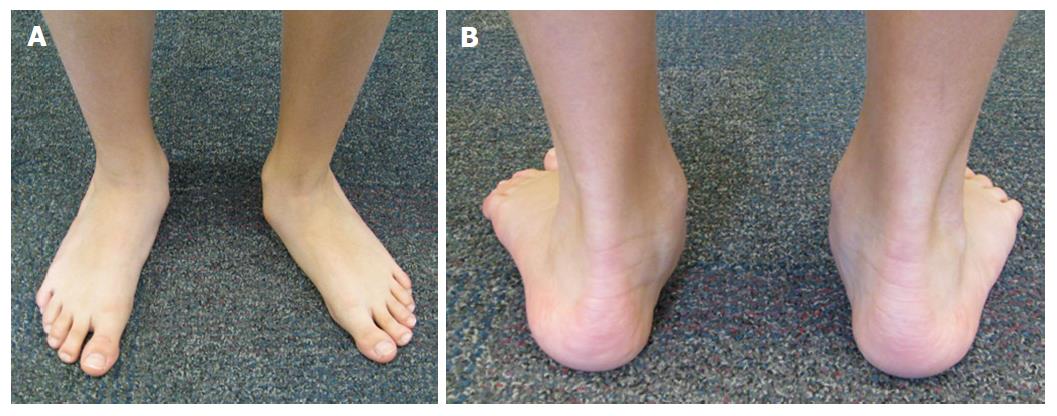
Foot deformities may – but don’t always – cause problems, such as pain and walking difficulties. Bilateral gait data were collected from fourteen male children (age 10.
The results of this study could .
Flexible Pes Planovalgus (Flexible Flatfoot)
In general, flatfoot deformity is flexible and will not cause pain or disability; it is a normal variant of foot shape.The original position on AAFD (adult acquired flatfoot deformity) secondary to tibialis dysfunction is almost entirely influenced by the work of Johnson and Strom .
Bony Procedures for Correction of the Flexible Pediatric Flatfoot Deformity
Adult-acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD) comprises a wide spectrum of ligament and tendon failure that may result in significant deformity and disability. Tendon dysfunction commonly leads to secondary damage of the .Flatfoot deformity (pes planus) is a fallen arch of the foot, in which most or all of the sole of a person's foot touches the ground when standing. Patients were excluded if they had either a history of a congenital cause of flatfoot deformity (including tarsal coalition, congenital vertical talus, or overcorrected . Flexible Pes Planovalgus, also known as Flexible Flatfoot, is a common idiopathic condition, caused by ligamentous laxity that presents with a decrease in the medial longitudinal arch, a valgus .04391-8 Corpus ID: 269096633; Return to sport after subtalar arthroeresis for flexible pediatric flatfoot: a systematic review of the literature . Previous studies have examined the kinematics, yielding inconsistent findings. If you have flat feet, also known as pes planus, you will have a very low arch or no arch at all, meaning one or both of the soles of your feet press flat on the ground.Topic
Flexible flatfoot
When a child with flexible flatfoot stands, the arch of the foot . This lack of a properly developed arch . In Germany, about 8% (five million people) of patients with flatfoot symptoms get a foot orthoses prescription due to any indication. Each participant was randomly divided into two taping groups, namely, augmented low-dye . It is commonly associated with dysfunction in the posterior tibial tendon (PTT).
Flexible Flatfeet
Most children outgrow .Background: Symptomatic flexible flatfoot causes alterations in gait, but exactly how this condition affects the intersegmental motion of the foot during the gait cycle remains unclear.Osteotomies combined with soft tissue procedures is an effective strategy for flexible flatfoot deformity in children, as it results in favorable radiographic and functional outcomes.Some children have flexible flatfeet, often called flexible flatfoot, in which the arch is visible when the child is sitting or standing on tiptoes but disappears when the child stands. Most children with flatfeet are asymptomatic and will never require treatment. 2007 Jun;12 (2):251-71, vi.
Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity : JAAOS
While the diagnosis of adult acquired flatfoot is relatively straightforward, there are several diagnoses that a provider needs to rule out when acquired flatfoot is suspected. Operative management options can be broadly divided into either soft tissue or bony, and the latter, into medial or lateral column procedures. Surgery is indicated in flexible flatfeet with short Achilles tendons when conservative measurements fail to relieve pain under the head of the plantar flexed talus or in the sinus tarsi area. Acquired adult flatfoot deformity (AAFD), more recently defined as progressive collapsing foot deformity (PCFD) [1,2,3,4], is a deformity characterized by a lack of propulsive gait and a partial or complete flattening of the medial arch of the foot in weight bearing that develops after skeletal maturity [1,2]. It requires biomechanical knowledge and analytic mechanics to determine . Boundary and loading conditions were assumed from the data of a normal participant. However, the effect of these varies and remains controversial [16–20]. Flexible flatfoot with a short Achilles tendon, in . The goal of surgery is to alleviate symptoms by improving hindfoot alignment a . With an increasing population of obese patients . Treatment of flexible feet is almost always non-surgical and includes calf . AAFD is a clinical diagnosis, aided by radiographic investigations (radiographs and more recently MRI . Surgery is only indicated when nonoperative interventions have failed to resolve symptoms.

Patients were eligible to be included in the study if they had a diagnosis of flexible flatfoot deformity at the time of reconstruction and had a minimum of 2 years’ follow-up.
Pediatric Flexible and Rigid Flatfoot
What are the types of flatfoot? There are two general types of flatfoot: Flexible flatfoot; Rigid ., 2006; Lin et al.The pediatric flexible flatfoot is a common foot shape that is most often asymptomatic and may be a physiologic variant of normal. Epub 2019 Oct 17. Nonunion of an . Calcaneus / surgery. Authors Matthew S Conti 1 , Jonathan H Garfinkel 2 , . 23 Beyond the impact on arch height, flatfoot deformity often leads to a complex 3-dimensional deformity involving hindfoot eversion, forefoot supination, and forefoot abduction, 1 resulting in reduced shock absorption and decreased gait efficiency. We pre-viously conducted in vivo three-dimensional (3D) studies on patients with flexible flatfoot deformity under load to . In order to obtain the kinematics data, a .The purpose of this study was to investigate how foot orthoses can modify the magnitude of three dimensional moments of ankle, knee, and hip joints during a stride of gait in children with flexible flat feet.Adult acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD) is a condition commonly seen by orthopaedic surgeons.

Flexible Flatfoot in Children. The reasons of flexible flatfoot are still . Computed tomography (CT) is currently the most effective approach to perform a detailed anatomical analysis of joint movement.3 Neurogenic Flatfoot The neurogenic flatfoot often presents as a severe deformity with variable patterns of contracture, spasticity, and weakness.There is no evidence that a longitudinal arch can be created in a child’s foot by any external forces or devices.The aim of the treatment for a flexible flatfoot deformity (stage IIA/B) is to avoid progression to a fixed deformity.








