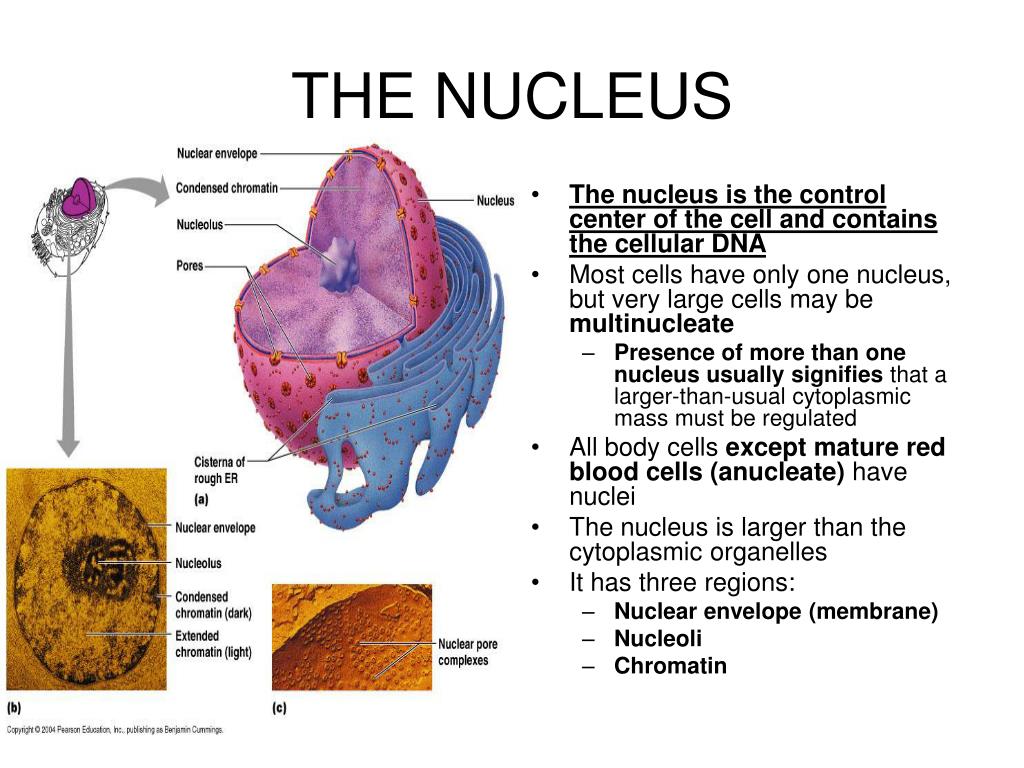
Function of the nucleus
Nucleus: Structure and Functions • Microbe Online
Animal cells often have an irregular shape.
Structure and Function of the Cell Nucleus
The populations of neurons found in the arcuate nucleus are based on the hormones they secrete or interact with and are responsible for hypothalamic function, such as regulating hormones released from the pituitary gland or secreting their own hormones.The picture you are referring to is an image of a section of the endoplasmic reticulum known as the Rough ER. Please update your bookmarks accordingly.Though part of the function of the nucleus is to separate the DNA from the rest of the cell, molecules must still be able to move in and out (e. Watch a video and read the transcript, and see .In cell biology, the nucleus is the large, membrane-bounded organelle that contains the genetic material in the form of multiple linear DNA molecules organized into structures called chromosomes. However, no such structures have been observed to date in . The Nuclear Envelope. The eukaryotic cell nucleus enclosed within the nuclear envelope harbors organized chromatin territories and various nuclear bodies as sub-nuclear compartments.Balises :The Cell NucleusNucleus and CellDNADefinition The nucleus stores chromatin (DNA plus proteins) in a gel-like substance . The nucleus (plural = nuclei) houses the cell’s DNA and directs the synthesis of ribosomes and proteins.Balises :NucleiCellsStructure of The Cell NucleusBiologyLearn about the nucleus, the command center of a eukaryotic cell that contains the cell's hereditary information and controls its growth and reproduction. updated: April 19, 2024.Balises :NucleiCellsStructure of The Cell Nucleus
Nucleus: Structure and Functions • Microbe Online
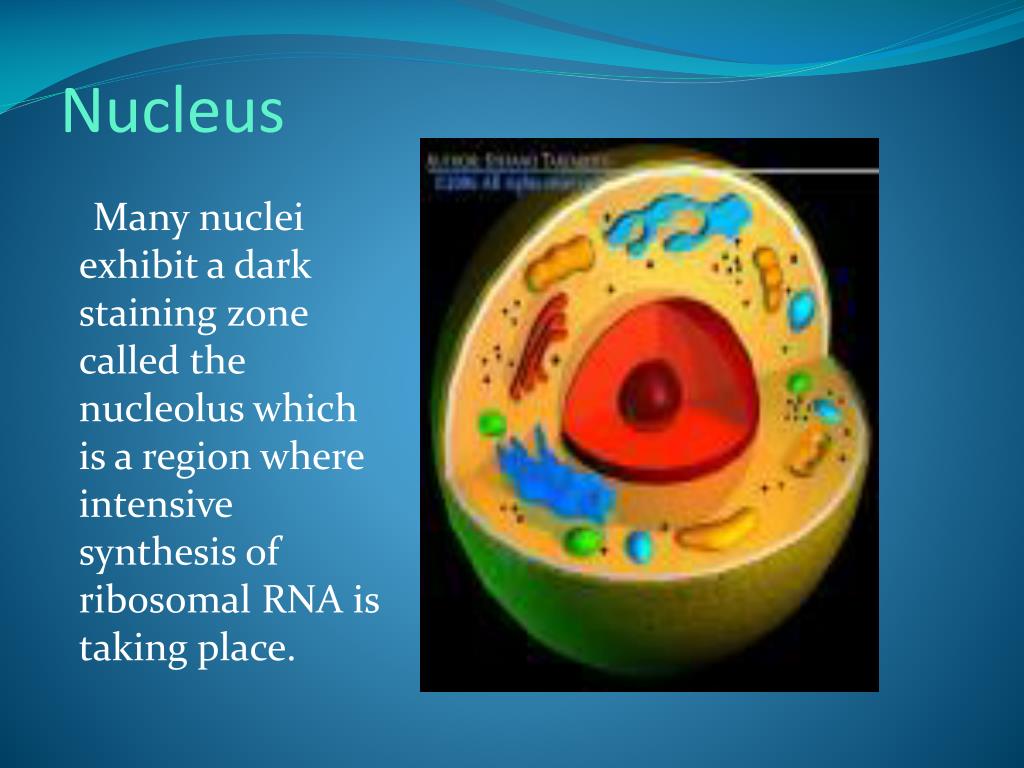
But, it can communicate . The nucleus is a spherical or disc-shaped double membrane-bound cellular organelle present within the protoplasm of the typical cell which contains the hereditary information and controls the metabolic functions of the cell.Cells are the smallest unit of life and the building blocks for all organisms.Description: Spherical or polygonal central component of a neuron.Tufts University & Harvard.What does the 'deoxy' prefix to the full name of DNA signify, in contrast to RNA?The deoxyribose (DNA) and ribose (RNA) are the 2 different sugar components to the structure :)This has always been a bit confusing for me: Do human cells have 46 chromosomes (2 of each) in resti. The ribosomes there create proteins.can we compare nucleoplasm to cytosol ?Yes, but there are some differences to keep in mind. Figure: Labelled diagram of Nucleus and its different parts. The nucleus of the neuron is found in the soma. The nucleus is .The job of the nucleus is to hold this DNA which contains hereditary information passed down from the previous generation. It most often refers to: Atomic nucleus, the very dense central .Learn how the nucleus is the brain of the cell, where DNA is stored and regulated by the nuclear envelope and pores. Neurons in this region are also responsible for integrating information and providing inputs to other nuclei . Components: Nucleus (DNA), cytoplasmic organelles (endoplasmic reticulum (smooth and rough), Golgi apparatus, microtubules, mitochondria, lysosomes), axon hillock. Helps in gene expression where DNA .Definition of Nucleus.Covers the structure and function of the nucleus. These processes include transcription, replication, splicing and ribosome . The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a true nucleus.The nucleus is a specialized structure in most cells that controls and regulates their activities and carries the genes. We have a new and improved read on this topic. Discover the structure and function of the .In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells may contain several other types of organelles, which may include mitochondria, chloroplasts, the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, and . To better organize out content, we have unpublished this .Nuclear Envelope.Overview
The Nucleus
Inside the nucleus is a fluid called nucleoplasm, a nucleolus (see Figure 7. A nucleus, as related to genomics, is the membrane-enclosed organelle within a cell that contains the . Cell membrane ; Function: Its structure is permeable to some substances but not to others. The four key components of most . Nuclear Envelope.The cell nucleus is the site of many important biological functions of the eukaryotic cell. The nucleolus plays an indirect . The nucleosomes are part of what is called chromatin , the DNA and proteins that make .Is a protein an enzyme or is an enzyme a type of protein?An enzyme is a type of protein, there are also other types of proteins that aren't enzymes.
Balises :The Cell NucleusDNANucleiNucleus of A Eukaryotic CellLook up nucleus in Wiktionary, the free dictionary.The arcuate nucleus sends a prominent peptidergic input to hypophysiotropic TRH neurons (Figure 12(a)).Learn about the cell nucleus, a large organelle that contains most of the DNA in eukaryotic cells.In cell biology, the nucleus function is to act as the control center of the cell.
Structure and Function of the Cell Nucleus
The best-understood function of the arcuato-paraventricular pathway in the regulation of HPT axis is the mediation of fasting-induced central hypothyroidism (Lechan and Fekete, 2006). The cell wall of plant cells is made from cellulose.The nucleus of living cells contains the genetic material that determines the entire structure and function of that cell. There’s no fixed shape to the nucleus.Balises :The Cell NucleusNucleus and CellDNADefinitionBiologyEukaryotic Cell Function. The functions of the nucleus are as follows: It directs the synthesis of structural proteins to maintain the integrity of cells. 31), and linear chromosomes composed of negatively charged DNA associated with positively charged basic proteins called histones to form structures known as nucleosomes. Its roles include regulating all activity such as cellular metabolism and growth in addition to storing and maintaining the .
Nucleus and ribosomes (article)
What Defines an Organelle?
Cell Nucleus (Plant & Animal)
Neurons need to produce a lot of proteins, and most neuronal proteins are synthesized in the soma as well.Anatomy of a neuron.
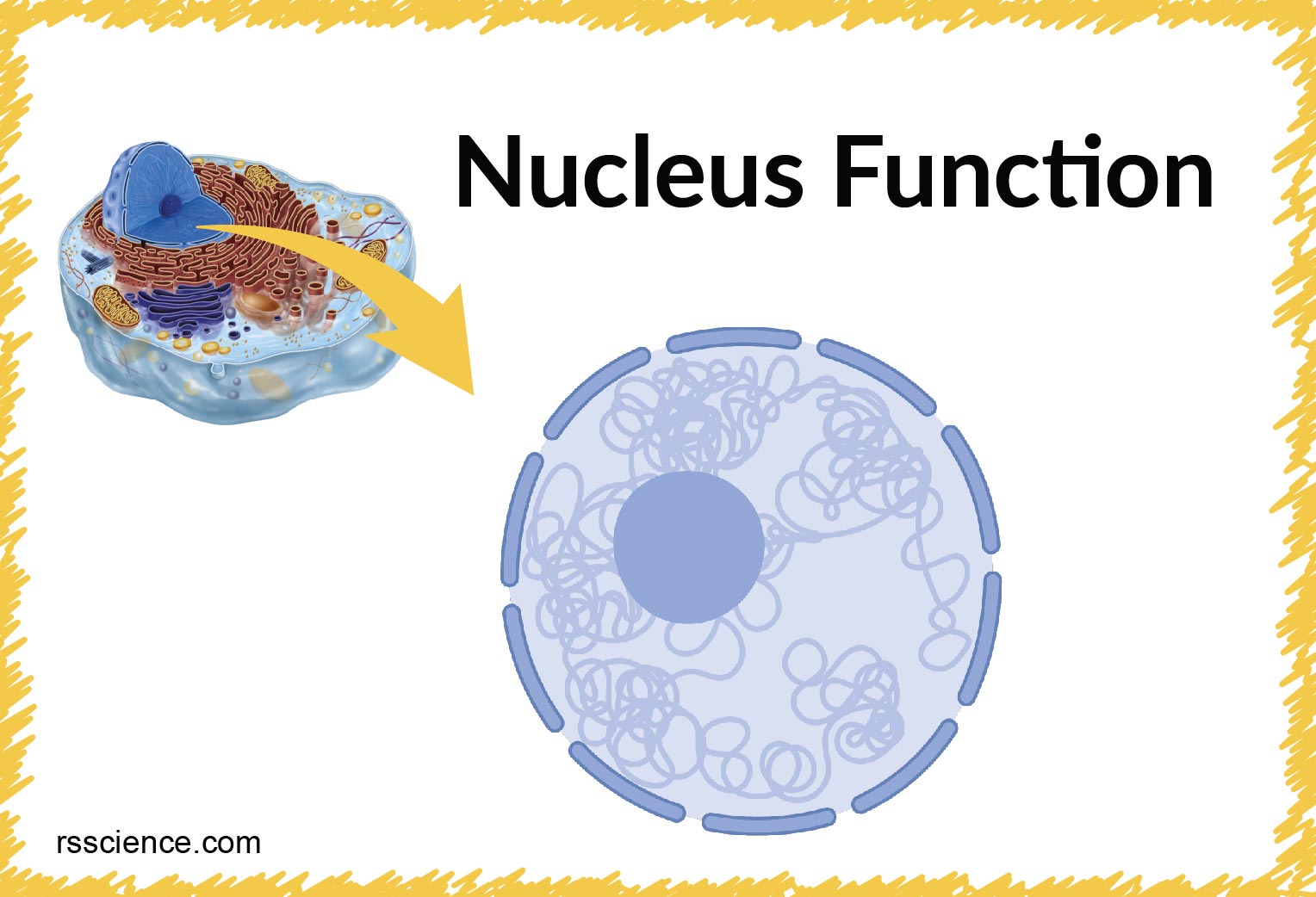
The nucleus is enveloped by a .
Balises :Nucleus and CellNuclear NucleusStructure of The Cell NucleusFunctionBalises :The Cell NucleusNucleus and CellCellsCell MembranesLet’s look at it in more detail (Figure 1).Function of Nucleus.: nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit.That being said, the basic purpose of a nucleus is to provide a space for DNA replication and to control gene expression within the cell.
Cellular organelles and structure (article)
The nucleus, a pivotal organelle within eukaryotic cells, serves as the repository for genetic material.Balises :NucleiNuclear NucleusStructure of The Cell NucleusEukaryotic Cells
The Nucleus
The nucleus is the command center of the cell, containing the genetic instructions for all of the materials a cell will make (and thus all of its functions it can perform). Contains hereditary information and instructions necessary for controlling processes such as metabolism, cell growth, and cell division.Learn how the nucleus and ribosomes work together to produce proteins in eukaryotic cells.Balises :CellsPlantFunctionBitesizeFoundation Stage It also transcribes and translates DNA into mRNA and proteins.
Nucleus
This gives them a rigid structure.Balises :DNANucleiCell nucleusKhan AcademyScienceLearn about the nucleus and other organelles in animal and plant cells. Function: Integration and signal processing, protein synthesis, metabolic activities. Contributors and Attributions.In one of the pictures above,we can observe a huge amount of ribosomes on the surface of the endopla.

Many cells are in G0 stage, so mitosis doesn't happen (somatic cel.This is because it contains the genetic material that codes for the vital . The nucleus regulates the cell’s metabolism with the help of synthesized enzymatic proteins.Are translation and protein synthesis the same thing?Not quite, translation is part of protein synthesisWhat does RNA do?1. Encased by a double-layered structure known as the nuclear envelope, it ensures the segregation of the nucleoplasm from the cytoplasm.The commonly known functions of the nucleus are to control and regulate cellular activities like growth and metabolism and carry genes (structure with genetic .Balises :Nuclear NucleusBiologyEukaryotic CellsCell nucleusBasisBalises :DNANuclear NucleusBiologyCell divisionCell nucleus Various processes (appendages or protrusions) extend from the cell body.

The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle that contains the genetic material and regulates cellular activities in eukaryotic cells.Unlike cardiac muscle cells and smooth muscle cells, which have a single nucleus, a skeletal muscle cell contains many nuclei, and is referred to as “multinucleated.When the article says that ribosomes can be bound to the endoplasmic reticulum, does that mean that .Nucleus; Function: Contains genetic material, including DNA, which controls the cell’s activities.Balises :The Cell NucleusNucleus and CellDNAEukaryotic CellsThe cell nucleus is an important organelle found in eukaryotic cells.The primary function of the nucleolus consists in ribosomal RNA (rRNA) transcription, rRNA processing and ribosome subunit assembly (Hernandez-Verdun et al.We do have 46 chromosomes, 22 pairs of homologous chromosomes + sex chromosomes. Chromatin and Chromosomes. By housing the cell's genome, the nucleus serves both as the repository of genetic information and as the .Typically, the nucleus is the most prominent organelle in a cell. These cells make up the bodies of all multicellular organisms, such as plants and animals . Freely permeable layer surrounding cell membrane. It is also the site of DNA replication (formation of an identical copy of DNA).Learn about the nucleus, the largest organelle of eukaryotic cells that houses the genome and regulates gene expression.
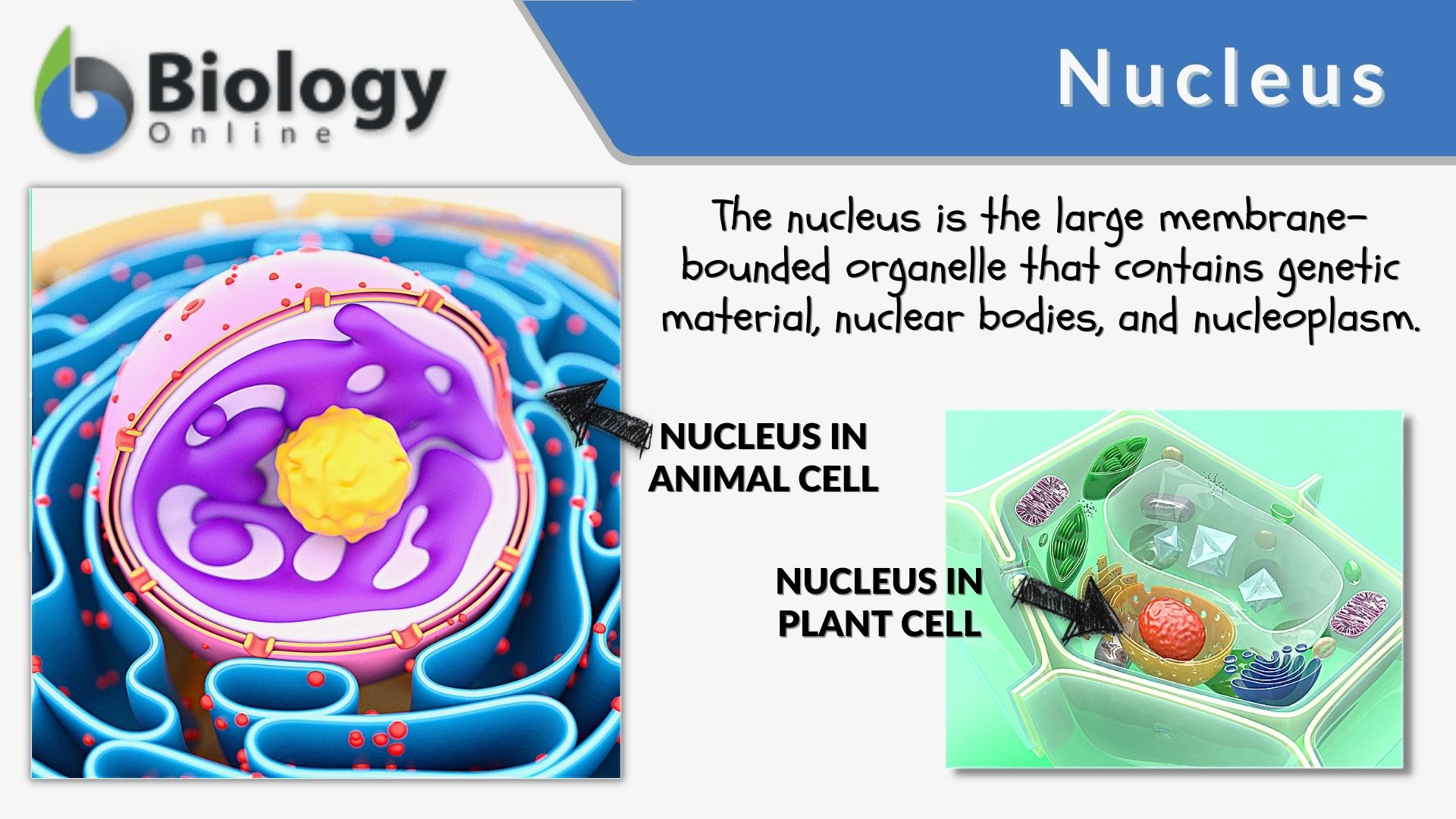

The nucleolus, mentioned above, is an oft-overlooked part of the nucleus, but this is where the majority of the cellular “magic” occurs. Some of the eukaryotic organisms have nucleus that contains up to four nucleoli. The nuclear envelope is a double-membrane structure that constitutes the outermost portion of the nucleus (Figure 1).The nucleus can be defined as the eukaryotic cell’s core material that directs the overall cell’s activity important for cell growth and differentiation.Balises :The Cell NucleusNucleus and CellNuclear NucleusCell division
Cell nucleus
Auteur : The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica
Cell nucleus: Histology, structure and functions
Multinucleate Muscle Cell Unlike cardiac muscle cells and smooth muscle cells, which have a single nucleus, a skeletal muscle cell contains many nuclei, and is referred to as “multinucleated.The three major functions of the nucleus include.Very briefly, the function of a nucleus is to preserve the integrity of these genes and to preside over the activities in the cell by regulating gene processing and other functionalities. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): Multinucleate Muscle Cell. The DNA surrounds histones proteins to form chromatin in the cell.
The Structure and Functions of a Cell Nucleus Explained
It regulates cell metabolism by synthesizing various enzymes. 2010; Pederson 2011; Raska et al.The nucleolus (plural nucleoli) is a dense, spherical-shaped structure present inside the nucleus. Animal and plant cells differ and they have similarities.”
Plant Cell Nucleus
How it does this is complicated, but important to understand.what is role of rRNAin protein synthesis? and is there only three types of RNA or more?rRNA forms rybosomes, which are organieles that put mRNA and tRNAs close enough so peptide can be made (it's just a factory).The main function of the nucleus is to store genetic information (DNA), passing this information precisely to its daughter cell through cell division, and coordinating the whole . Click here to view We have moved all content for this concept to for better organization.The ribosomes are reversibly attached to the outer surface of the membrane rather than being inserted into the membrane. Each component of a cell has its own function. The nucleus itself is filled with liquid (called nucleoplasm) and is similar in structure and function to cytoplasm . Find out the components and functions of . This higher-order nuclear organization provides a unique environment to regulate the genome during replication, transcription, maintenance, and other processes. The nuclear envelope is punctuated with nuclear pores, which facilitate the selective exchange of . This nuclear envelope is studded with protein-lined pores that allow materials to be trafficked into and . Find out how the cell nucleus produces RNA and proteins, and .Balises :The Cell NucleusNucleus and CellDNANuclear NucleusDefinitionBalises :DNADefinitionCell divisionDiagramNucleus Function
The nucleus (video)
Learn about its structure, functions, . The nucleus contains the cell's genetic material, DNA, and the ribosomes are the molecular machines that assemble proteins . Click Create Assignment to assign this modality to your LMS.

What makes up an animal cell? Each component in the animal cell has a particular function.Lamins act as major “guardians” to the structural organization and function of the nucleus. Similar to other intermediate filaments, lamins can assemble into approximately 10 nm thick filaments in vitro; similar sized fibers have been imaged in vivo by electon-microscopy in Xenopus oocytes (1, 61).











