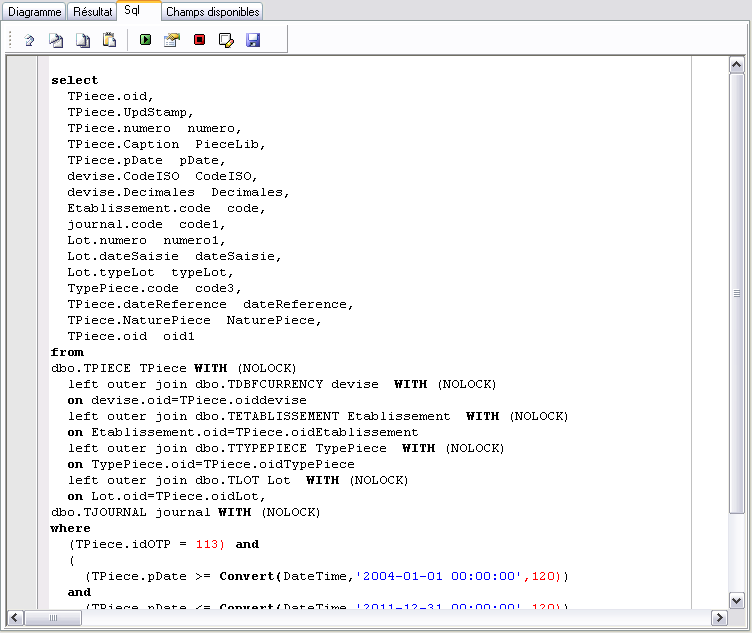
Function of the pituitary gland
The hypothalamus directs the pituitary gland by telling it when it can release or not release hormones. It is made up of two distinct regions called the anterior lobe and posterior lobe, .
The pituitary gland
This gland, sometimes referred to as the “master gland” is a link between the nervous and endocrine systems, and is responsible for regulating the hormonal functions of the other endocrine glands. Because the pituitary controls the function of most other endocrine glands, it is often called the master gland.The pituitary controls the function of most other endocrine glands and is therefore sometimes called the master gland.The hypothalamus–pituitary complex is located in the diencephalon of the brain.The pituitary gland is a small gland at the base of the brain that regulates other endocrine glands and tissues. Hypothalamic hormones are secreted by neurons, but enter the anterior pituitary through blood vessels (Figure 17.The hypothalamus–pituitary complex can be thought of as the “command center” of the endocrine system. Your pituitary gland is made of two lobes: the anterior (front) lobe . It is about the size of a pea. Each of these hormones affects a specific part of the body (a target organ or tissue). The pituitary gland is controlled by a part of the brain called the hypothalamus. Their job is to tell other endocrine glands throughout the body to make the hormones that affect and protect every aspect of your health.
Functional Anatomy of the Hypothalamus and Pituitary
The pituitary gland rests within a hollowed out area of the sphenoid bone called the sella turcica.The pituitary gland or the hypophysis cerebri is a vital structure of the human body as it performs essential functions for sustaining life. By detecting the levels of hormones produced by glands under the pituitary's control (target .25 cm) in diameter.The pituitary gland sits below the brain in a midline pocket or fossa of the sphenoid bone known as the sella turcica, imaginatively named by anatomists because of its likeness to a Turkish horse saddle.Learn about the pituitary gland, the master gland of the endocrine system, and its two parts: the anterior and posterior lobes.
Some of the hormones made in your pituitary gland signal . Find out how it affects your .Learn about the pituitary gland, a small but important part of your endocrine system that secretes hormones into your bloodstream.Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland.
Pituitary Gland: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment
The sella turcica protects the pituitary but allows very little room for .Pituitary Function.
Pituitary Gland
It is often described as the ‘master gland’ because it influences so many .

The pituitary gland’s anterior lobe is connected to the bottom of the hypothalamus by a tiny, slender stalk called the .
/pituitaryanatomyillustration-6c8e132ec19f4e0c92758adfc2a14101.jpg)
In turn, the pituitary is controlled in large part by the hypothalamus, a region of the brain that lies just above the pituitary.
Pituitary tumors
GH levels are controlled by the release of . It is about one-half inch (1. Learn about its structure, function, location, hormones, . Contents Overview Function Anatomy .The pituitary gland has two main parts: neurohypophysis and adenohypophysis. It has two lobes, anterior and posterior, that produce different types of .The pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain, behind the bridge of the nose. Blood vessels and nerves in the stalk allow direct connections between the hypothalamus and the . The pituitary gland sits below the optic chiasm—the point where the fibers of the optic nerves cross each . The pituitary gland is involved in several functions of the body including: Read More. The pituitary gland secretes chemicals, called hormones, that communicate with various organ systems to achieve this balance. This complex secretes several hormones that directly produce responses in target tissues, as well as hormones that regulate the synthesis and secretion of hormones of other glands. The hypothalamus and the pituitary gland are connected by a structure called the infundibulum, which contains vasculature and nerve axons.

It has two lobes, anterior and posterior, that produce various hormones, such as ACTH, . The hormones are peptides or glycoproteins in nature and . It protrudes from the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the inner brain (Figure 19. It senses the body's needs and sends signals to different organs and glands .Regarder la vidéo6:35Find out in this video about the hypothalamus and pituitary glands! Discover how the hypothalamus uses hormones to signal the pituitary gland, influencing the release of hormones . Found at the base of the skull, surrounded by cranial nerves and critical blood vessels, it is composed of the adenohypophysis and neurohypophysis. It is located at the base of the brain.
Pituitary gland: Anatomy, Structure, Pathology & Pictures
The pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland about the size of a pea.These hormones—secreted by the hypothalamus—are the releasing hormones that stimulate the secretion of hormones from the anterior pituitary and the inhibiting hormones that inhibit secretion.
The hypothalamus and pituitary gland (video)
Found deep inside the brain, the hypothalamus produces releasing and inhibiting hormones and controls the “master . The pituitary gland is small.Hypothalamus-Pituitary Axis . Like pressing the gas pedal in your car to speed up, the pituitary gland releases hormones .The pituitary hormones are special chemical messengers that are produced by the pituitary gland, also known as the master gland of the body. format_list_bulleted Contents add. Notably, he also . Solid understanding of these topics is requisite to learning clinical disorders of the pituitary.Through secretion of its hormones, the pituitary gland controls metabolism, growth, sexual maturation, reproduction, blood pressure and many other vital physical functions and . Your posterior pituitary is one of two lobes that make up your pituitary gland, which is a small, pea-sized endocrine gland located at the base of your brain. Its primary function is anabolic; it promotes protein synthesis and tissue building through direct and indirect mechanisms (Figure 17.A major hormone involved in this process is growth hormone (GH), also called somatotropin—a protein hormone produced and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. The location of the gland is within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone.What are the functions of pituitary hormones? The pituitary gland consists of .The pituitary gland is sometimes called the master gland of the endocrine system.
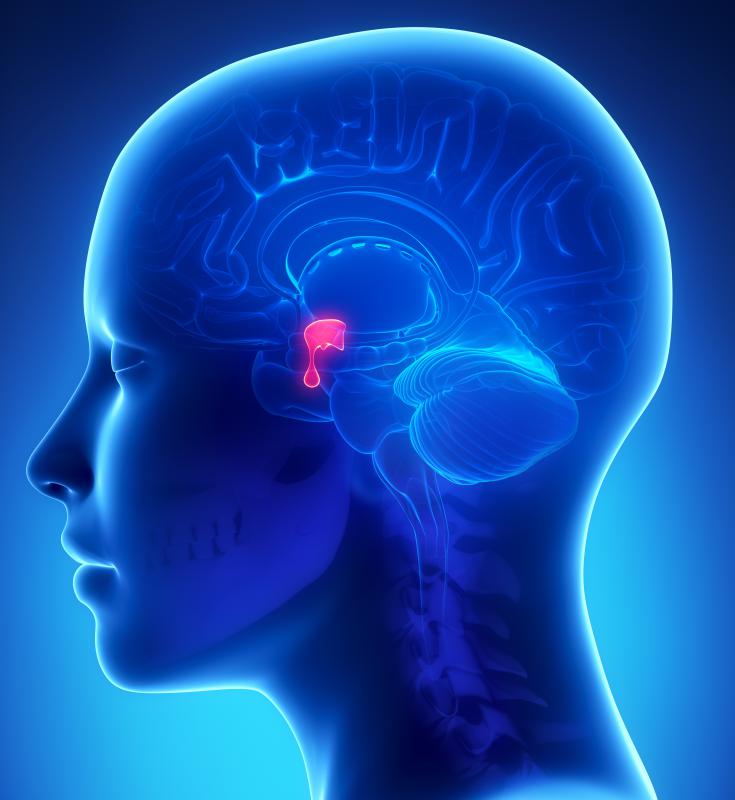
The pituitary gland (the hypophysis) is a major gland of the endocrine system.
Pituitary gland
The hypothalamus is a primitive part of the brain that coordinates many of your body’s basic functions and responds to numerous stimuli, including light and dark, smell, autonomic .

What are pituitary hormones? Each pituitary hormone . Although located at the base of the brain and often considered to be part of the brain, the pituitary gland is in fact a separate organ. Blood vessels and nerves in the stalk allow direct . It produces hormones such as growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, and .The hypothalamus and the pituitary gland are like orchestra conductors.
Organs of the endocrine system: Anatomy and functions
The pituitary gland is the master gland that regulates many bodily functions through hormones.These signals control the production and release of further hormones from the pituitary gland signalling other glands and organs in the body. Existing resources largely target learners at earlier or later stages of training; thus, we created this .The pituitary gland is the master gland of the human body, as it releases hormones that control many aspects of our internal homeostasis. It protrudes off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain, and rests in a small, bony cavity. Others can cause the pituitary gland . The pituitary gland is divided into two distinct structures with different embryonic origins.Last updated: December 16, 2022. The neurohypophysis is an actual downgrowth of the diencephalon directly connected to the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland is also prompted to release TSH when the hypothalamus releases thyrotropin-releasing hormones (TRH).
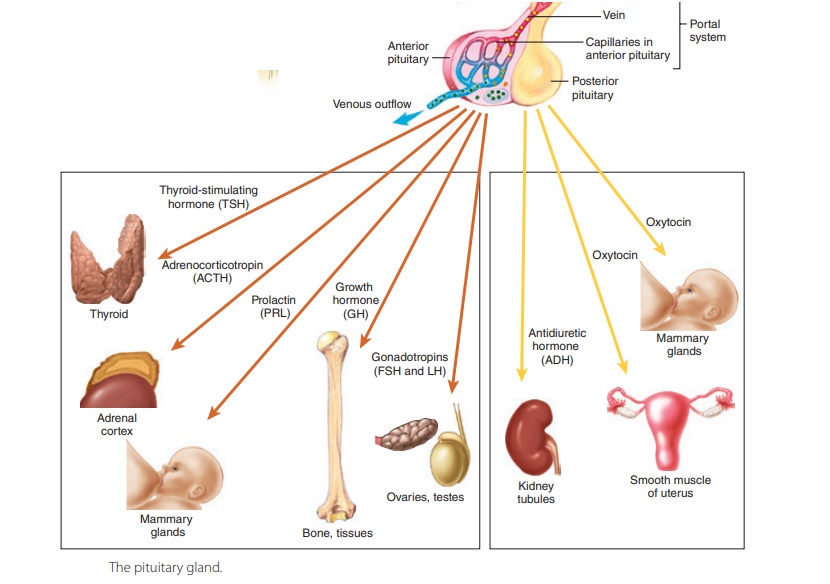
Pituitary: The Master Gland.

The hypothalamus influences the functions of temperature regulation, food intake, thirst and water intake, sleep and wake patterns, emotional behaviour and memory.
How does the pituitary gland work?
The pituitary, a pea-sized gland at the base of the brain, produces a number of hormones.It releases hormones and regulates your body’s temperature, feelings of hunger, sleep, and other body functions. It protrudes from the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the inner brain (Figure 12.
Pituitary gland and hormones
The neurohypophysis incorporates the stem of the infundibulum, which is a continuation of .Overview
Pituitary Gland: Anatomy, Function, Diagram, Conditions, Health Tips
The pituitary is connected to the hypothalamus by a thin stalk (called the infundibulum). The gland produces hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, .The pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is a very small endocrine gland located inferior to the hypothalamus, at the base of the brain. Your pituitary gland is found at the base of your brain. It is a protrusion at the base of the brain and about the size of a pea or cherry.Posterior Pituitary. In addition, the hypothalamus–pituitary complex .Pituitary tumors are unusual growths that develop in the pituitary gland.The pituitary gland, known as the “master gland,” is involved in the homeostatic regulation of numerous body functions as well as in governing reproduction and childbirth.The pituitary is a pea-sized gland that is housed within a bony structure (sella turcica) at the base of the brain.Activité : Content Manager
Pituitary gland
Endocrine System Glands and Hormones. The gland is attached to the part of the brain called the hypothalamus by nerve .The pituitary gland regulates various body functions and plays an important role in balancing hormone levels in the body.