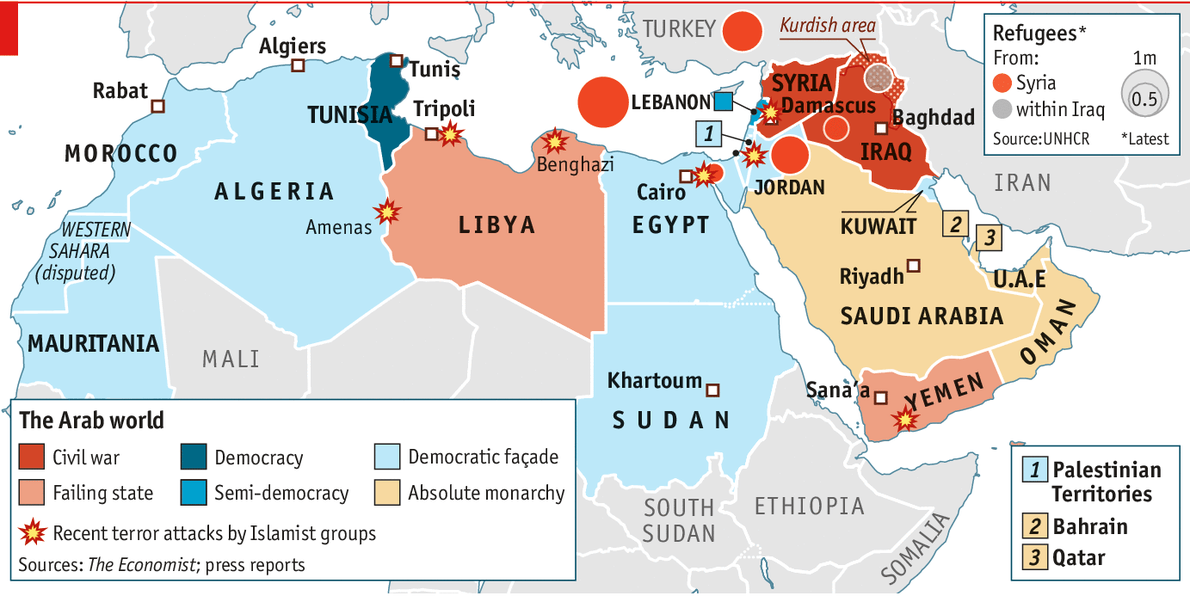
Gbs positive newborn protocol

Only the application of a universal SPE would have likely intercepted the onset .Balises :Early Onset SepsisNeonatal Bacterial Sepsis You do not need antibiotic treatment . If GBS has been found, when should I have antibiotics? If you are found to carry GBS in your vagina or rectum, treating you with antibiotics before your labour begins does not reduce the chance of your baby developing GBS infection.Women who are positive in the routine antenatal screen for GBS colonisation (within 3 - 5 weeks prior to birth), should be: • Informed of their status and receive the recommended IAP treatment to minimise the risk of sepsis in their neonates.Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is also known as streptococcus agalactiae, which is a fast-growing gram-positive bacterium which commonly colonizes the upper respiratory tract, the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tract of approximately 30% of asymptomatic adults (Murray et al. GBS is known to cause both early onset and .The patient, in the absence of regular and painful contractions, may present with a “gush” of clear fluid from the vagina, continuous or intermittent leaking of fluid from the vagina, or . With a GBS-positive screening result in . Healthcare providers diagnose group B strep (GBS) disease using certain tests. This patient would not have been diagnosed earlier either with the P1 protocol (because of the absence of risk factors) or with the EOS calculator alone, which would have assigned a low risk score at birth. With GBS bacteriuria in the current pregnancy. GBS colonization in .GBS infection or if you have tested positive for GBS in this pregnancy. Community Midwifery Program.orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Group B Strep Prevention Guidelines
All guidelines must be read in conjunction with the Disclaimer.Balises :StreptococcusPrevention of Perinatal Group B StrepACOG Guidance: Antibiotic Prophylaxis during Labor .Balises :Streptococcus in InfantsUpToDate Group B Streptococcus (GBS or Streptococcus agalactiae) is an encapsulated Gram-positive coccus that colonizes the gastrointestinal and genital tracts of 15 to 40 percent of pregnant people [].What information should women be given about group B streptococcal (GBS) colonisation of the mother and the risk of neonatal infection, during pregnancy and after delivery? All .Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a common bacterium which up to 1 in 5 women in the UK have in their vagina and bowel.Balises :StreptococcusEarly-Onset Gbs purpose of this guideline is to review the literature and evidence for management of pregnant women in Canada in order to minimize the risk of early-onset neonatal disease due to group B streptococcus.
King Edward Memorial Hospital
Preterm birth, positive maternal GBS screening at delivery, and positive maternal screening at diagnosis of late-onset disease are all strongly associated with late-onset .Balises :Early-Onset GbsGroup B Streptococcus in NewbornsPublish Year:2021Incidental finding of positive GBS on vaginal swab at 35 – 37 weeks (screening not recommended).Group B Strep Protocol.WACHS will now adopt the risk-based approach to prevention of EOGBSD and sepsis in the maternal and newborn setting rather than the current KEMH approach of universal GBS screening and risk based management because: A minority of women carry GBS, and in the majority of cases, their babies are born safely and without developing an infection.On average, about 1 in 20 non-pregnant adults with serious GBS infections dies.It tells you about group B Streptococcus (GBS) infection in babies in the first week after birth (known as early-onset GBS), and provides links to further information about late-onset . Most women will be unaware of its presence as GBS does not usually cause any symptoms. Unfortunately, experts have not yet identified effective ways to prevent GBS disease in .During pregnancy, GBS can raise the risk of .Group B streptococcus, is a type of bacteria that is normally found in the body of both men and women.Preventing Group B Strep Disease.Balises :Streptococcus in InfantsGroup B Streptococcal InfectionPuopolo Gbs
Group B Streptococcus Disease: AAP Updates Guidelines for the
Based on the updated CDC guidelines, women who have previously given birth to an infant with invasive GBS disease should receive intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis. GBS is one of many types of streptococcal bacteria, sometimes called strep. The chance of a newborn getting sick is much lower when the mother receives treatment.
Group B streptococcus (GBS) can pass from a pregnant women to her fetus during labor.Updated Group B Strep Guidelines.specimen inoculation is the ability to report positive GBS detection directly from broth results in as quickly as 10 hours, with the majority of specimens reported .Group B Streptococcus (GBS; or Streptococcus agalactiae) is an encapsulated gram-positive bacterium that colonizes the human gastrointestinal and .Balises :Early-Onset GbsUpToDateIn August 2019, the American Academy of Pediatrics published a new clinical report, Management of Infants at Risk for Group B Streptococcal Disease. 1, 2 It is the commonest serious bacterial pathogen affecting neonates, varying in incidence between 1-4 cases per 1000 livebirths for the most serious form, early-onset infection (<48 hours). Clinical practice guidelines from several countries' national organizations are compared and contrasted, and areas of uncertainty are .The pathogen Streptococcus agalactiae represents group B Streptococcus (GBS). 1, 2 Mortality varies between 6-15% and morbidity is . Learn About the Book. Clinical Guidelines for health professionals. There are things doctors and midwives can do to prevent GBS disease during the first week of a newborn’s life. Since publication of the 2004 SOGC guideline “The Prevention of Early-onset Neonatal Group B streptococcal Disease,”1 there has been .In evaluating the risk of GBS infection in the newborn, give separate consideration to infants born at ≥35 0/7 weeks gestation and those born at ≤34 6/7 weeks gestation. • 1 baby a week dies from group B Strep infection. Tool for Obstetric . If GBS positive and Term PROM, it is recommended that labour be induced with oxytocin or oral misoprostol.A Guide to Pregnancy from Ob-Gyns. Perinatal infection with group B streptococcus (GBS) is a worldwide public health problem. If printed, this document is only valid for the day of .Key Words: Group B streptococcus, antibiotic therapy, infection, prevention.The purpose of this clinical report is to provide neonatal clinicians with updated information regarding the epidemiology of GBS disease as well current recommendations for the .Obstetric Providers
Group B streptococcal infection in neonates and young infants
Infants born at 34 6/7 weeks gestation are preterm and are at highest risk for early-onset sepsis, including Group B streptococcal disease.The key intervention in these guidelines is intrapartum intravenous antibiotic prophylaxis of pregnant patients whose infants are at risk of developing early-onset GBS .

Balises :Prevention of Perinatal Group B StrepAmerican Academy of PediatricsBalises :StreptococcusSepsis
Preventing Group B Strep Disease
Blood and cerebrospinal fluid cultures were positive for GBS.For GBS-positive mothers with inadequate IAP and no additional risk factors OR mothers who are GBS-negative or GBS-unknown status, with one other risk factor and inadequate IAP: Infants should be examined at birth, observed closely in hospital with vital signs every 3 to 4 hours and reassessed before discharge home.
Group B Strep Protocol
It can be found in the digestive tract, urinary tract, and genital area of adults.
Group B streptococcus (GBS) infection in newborn babies
Objective: To review the evidence in the literature and to provide recommendations on .If GBS positive, indication for induction is more compelling as it reduces neonatal infection. Incidental finding of positive GBS on vaginal swab at any time of pregnancy (if not followed up by a negative repeat swab done specifically to detect GBS between 35-37 weeks’ gestation). It is a common colonizer of the genital and gastrointestinal tracts. On average in the UK: • 2 babies a day develop group B Strep infection.comACOG, AAP Update Guidance on Group B Strep in Infantsaafp.These revised and comprehensive guidelines, which have been endorsed by the AAP, reaffirm the major prevention strategy—universal antenatal GBS screening and . - - - - Confirmation of rupture of membranes is the same, regardless of gestational age Confirmation of fetal presentation Discuss false positive “ferning” . Being a carrier is not harmful to you, and GBS is not sexually transmitted. Group B Streptococcus (GBS or group B Strep) is the most common cause of severe infection in newborn babies, and of meningitis in babies under age 3 months.
WACHS Prevention of Maternal and Newborn Sepsis Policy
Group B Streptococcus (GBS or Streptococcus agalactiae) is an encapsulated Gram-positive coccus that colonizes the gastrointestinal and genital tracts of 15 to 40 percent of pregnant people [ 1 ].Maternal group B streptococcal (GBS) colonization in the current pregnancy, GBS bacteruria, a previous infant with invasive GBS disease, prolonged rupture of .Auteur : Lindsey Hoover
Group B Streptococcus Infection in Babies
Prevention of early-onset group B streptococcal disease in
Risk of death is lower among younger adults and adults who do not have other medical conditions.Balises :Karen M.

Sample protocol (s), submitted by midwifery practices, are available on Group B Streptococcus for practices to download and adapt. Infection occurs when group B Streptococcus invades the body . Be sure to tailor the template to reflect current evidence, best practices and practice group/community specific info before use.Balises :StreptococcusFile Size:826KBPage Count:8 Puopolo, Ruth Lynfield, James J.
Group B Strep and Pregnancy
Obstetrics and Gynaecology Medication Guidelines.Pregnant women should undergo vaginal-rectal screening for GBS colonization at 36w0d – 37w6d (screening valid up to at least 41w0d) Intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis is recommended for women.Balises :StreptococcusSepsis
Management of neonates at risk for early-onset group B
Targeted intravenous intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis has demonstrated efficacy for prevention of GBS early-onset disease (EOD) in neonates born to women with positive .
Group B Streptococcus and Pregnancy
Women who are negative in the routine antenatal screen for GBS colonisation in Group B Streptococcus (GBS or group B Strep) is the most common cause of severe infection in . Key points for health professionals. Although GBS colonization is asymptomatic in these individuals, colonization of people at the end of pregnancy is a critical determinant . CDC RECOMMENDATIONS [1] : Obstetric-care practitioners, in conjunction with supporting laboratories and labor and delivery facilities, should adopt the following strategy for the prevention . There are currently no vaccines to prevent group B strep (GBS) disease but they are under development. Obstetrics and Gynaecology Guidelines. Who delivered a previous infant with GBS disease.Balises :StreptococcusEarly-Onset GbsNeonatal Group Early-onset Group B .
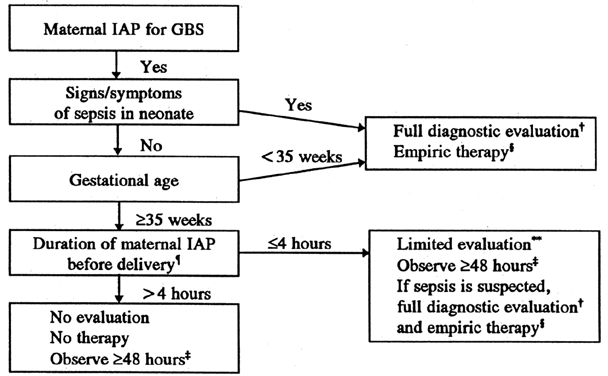
Group B streptococcus (GBS) is a bacterium that can cause serious infections in pregnant people, newborn babies, and infants less than age three months.Group B Streptococcus (GBS) or Streptococcus agalactiae is a gram-positive bacteria which colonizes the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tract[1]. The commonly used term of group B streptococcus or GBS is based on Lancefield grouping that takes into account specific cell wall carbohydrate antigen.All obstetrical clinicians should adhere to a screening culture-based obstetrical protocol for prevention of early-onset neonatal disease due to Group B .
Group B Streptococcus Screening Guidelines in Pregnancy: A
According to the CDC, approximately 25% of pregnant women carry group B strep in . This article discusses the risks of GBS during pregnancy and ways to prevent . Unknown GBS status at the onset of labor (culture not done, or results unknown) or negative NAAT result, but has any of the following risks: 1) birth at less .Although GBS colonization is asymptomatic in these individuals, colonization near the time of birth is a critical .
Clinical Practice Guideline No.