General relativity equation explained
Only a few parts, including the treatment of the stress-energy tensor are adapted in accordance with later reformulations of the theory, and .What Does It Mean? The Einstein Field Equations are ten equations, contained in the tensor equation shown above, which describe gravity as a result of spacetime .Posted Tue 24 Nov 2015 at 1:59pm, updated Tue 24 Nov 2015 at 4:01pm.Einstein's equations can be loosely summarized as the main relation between matter and the geometry of spacetime. If you want, you can dive right in and read .Balises :Theory of RelativityEinstein and RelativityPhysics General Relativity This metric is not something fixed; it is, like all other fields in Nature, a dynamical object.I have a whole article dedicated to exploring and deriving the Einstein field equations in detail (as well as my introduction to general relativity), however for our purposes, we just need to know the basics. We all have the experience of being in an elevator that is accelerated upward or downward.
Relativity
We’ll look at both of these ways for deriving the Einstein field equations and every step will be explained along the way as we do each calculation.Balises :Einstein and RelativityAlbert EinsteinGeneral Relativity Theory Einstein
What is General Relativity?
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and .
How to understand Einstein’s equation for general relativity
Einstein field equations
This means that there are rules which govern how this field evolves in time.Learn how Einstein's equation describes the force of gravity as the curvature of spacetime caused by mass and energy.Balises :Physics General RelativityEinstein General Relativity EquationEinstein Tensor
General Relativity
Suppose, for example, that the Sun was to explode.Using this tensor, we at last build a field theory for spacetime, motivating the Einstein field equation by arguing how to generalize a gravitational field equation to relativity. Beginning with the behaviour of light (and all other electromagnetic radiation), the theory of special .On the left hand side of Einstein's equations, we find a few different terms, which together describe the geometry of spacetime.In his four papers, published in November 1915, Einstein laid the foundation of the theory. In Einstein’s theory of general relativity, the Schwarzschild metric (also known as the Schwarzschild solution) is an exact solution to the Einstein field equations . Albert Einstein published his Special Theory of Relativity . This movement could not be explained by the gravitational . In reality, this one equation really includes 16 different equations, one for each combination of µ and ν, which can both be either 0,1,2 or 3 (in reality, there is actually only 10 independent equations due to some symmetry properties). The Einstein Equations It is now time to do some physics. The motion of any other mass is simply a response to this curved space-time.Balises :Theory of RelativitySpecial RelativityAn Introduction To General RelativityBalises :Theory of RelativityEinstein and RelativityAlbert EinsteinBalises :Theory of RelativityAlbert EinsteinEinstein General Relativity EquationThe General Relativity Tutorial John Baez This is bunch of interconnected web pages that serve as an informal introduction to that beautiful and amazingly accurate theory of gravity called general relativity.Additionally, relativity and its rethinking of the fundamental categories of space and time have provided a basis for certain philosophical, social, and artistic .
tv/minutephysics to get access to Nebula (where you can watch the extended version of this video), plus you'll get a 20% discount on an . √ (1 − v2 / c2) where. Let’s try and explain it in a few paragraphs. The force of gravity is mediated by a gravitational field.Special relativity is limited to objects that are moving with respect to inertial frames of reference—i.Special relativity is an explanation of how speed affects mass, time and space. The theory explained the anomalous orbit of Mercury, but the first major triumph came in 1919 when Arthur Eddington and his colleagues measured the influence of the Sun’s gravity on light .Balises :EinsteinRelativity EquationsGeneral RelativityDirac's purpose in casting this equation was to explain the behavior of the relativistically moving electron, and so to allow the atom to be treated in a manner consistent with relativity. Einstein’s general theory of relativity can be summed up in just 12 words: “Space-time tells matter how to move; matter tells space-time how to curve”. The theory includes a way for the speed of light to define the relationship between energy and matter — small .Balises :Einstein and RelativityPhysics General RelativityAlbert EinsteinBalises :Einstein and RelativityGeneral Relativity Field EquationsEinstein TensorIn physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory of the relationship between space and time. After compensating for varying signal delays . Concepts Related to Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation Sir Isaac Newton was the first scientist to precisely define the gravitational force, and to show that it could explain both falling bodies and astronomical motions. Furthermore, I will refrain from trying to derive the equations in elementary .Time dilation is the difference in elapsed time as measured by two clocks, either because of a relative velocity between them (special relativity), or a difference in gravitational potential between their locations (general relativity). Next the Lagrangian formu-lation of the Einstein equations will be presented.Balises :Theory of RelativityEinstein and RelativityPhysics General RelativityThe Schwarzschild metric. It explains gravity based on the way space can 'curve', or, to put it more accurately, it associates the force of gravity with the changing geometry of space-time.

In general relativity, objects moving under gravitational attraction are .The general theory of relativity (or general relativity for short) is a major building block of modern physics.these lectures is to explain this.According to general relativity, the spacetime is a 4-dimensional object that has to obey an equation, called the Einstein equation, which explains how the. The purpose of these pages is to explain E = mc 2 in a clear, concise and understandable way with easily followed worked examples, and with further pages examining the Special Theory of Relativity in order to describe its background.General Relativity & curved space time: Visualization of Christoffel symbols, Riemann curvature tensor, and all the terms in Einstein's Field Equations.General Relativity explained like you've never seen before.
Time dilation

Up until that time, attempts to make the old . Only empty space is flat. Figure \(\PageIndex{2 . The basic idea is so elegant that you.ScienceClic English. First, we need to understand Newton’s first law of motion.
Dirac equation
In Albert Einstein's 1905 treatment, the theory is presented as being based on just two postulates:.

Overview
General Relativity
The General Relativity Tutorial
The general theory of relativity challenges this long-held assumption.Balises :Theory of RelativityEinstein and RelativityPhysics General Relativity
Einstein Field Equations (Chapter 3)
The revolutionary physicist used his imagination rather than fancy math to come up with his most famous and .In general relativity (GR), concentrations of mass and energy curve the structure of spacetime, affecting the motion of anything passing near — including light. But this mathematical tool is so deeply entrenched in esoteric symbolism and comple. The use of a ¡ + ++ metric, or worse even, a + ¡ ¡¡ metric, inevitably leads to sign errors.
: ScienceAlert
E=mc^2 - The Equation Explained with Worked Examples.Deriving Einstein's Field Equations of General Relativity - . The topology of general black holes will also be investigated. The equations, first published by Einstein in 1915 . Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 February 2021.vchal/Getty Images. His rather modest hope was that the corrections introduced this way might have a bearing on the problem of atomic spectra. To describe how matter and energy change the geometry of spacetime, Einstein proposed a new theory of gravitation, known as the general theory of . Let’s explain what this means with a simple example. In comparison with the special theory of relativity, which applies in flat spacetime, Before we get started, I’d highly .
582K subscribers. Before we jump into a description of curved spacetime, we should first explain why Newton’s theory of gravity, a theory which served us well for 250 years, needs replac-ing. But this short .

duration of an event in a moving . In this series, we build together the theory of general . No confusion over signs remain.
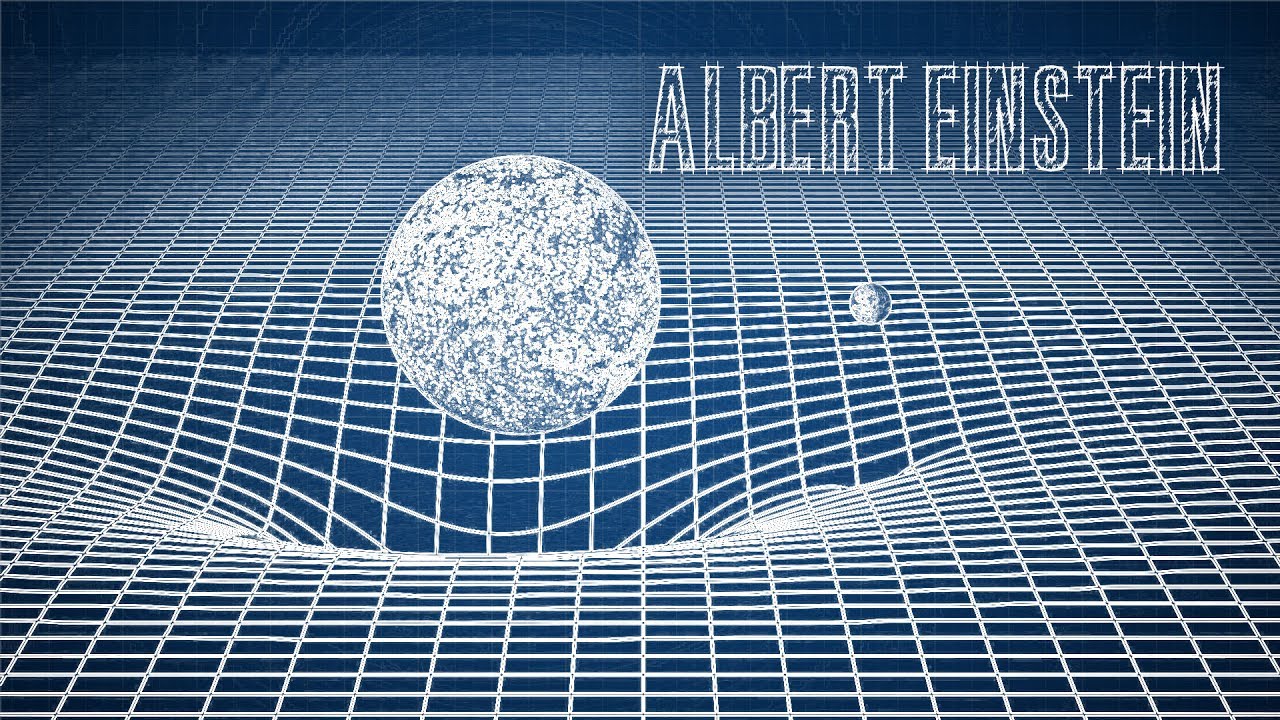
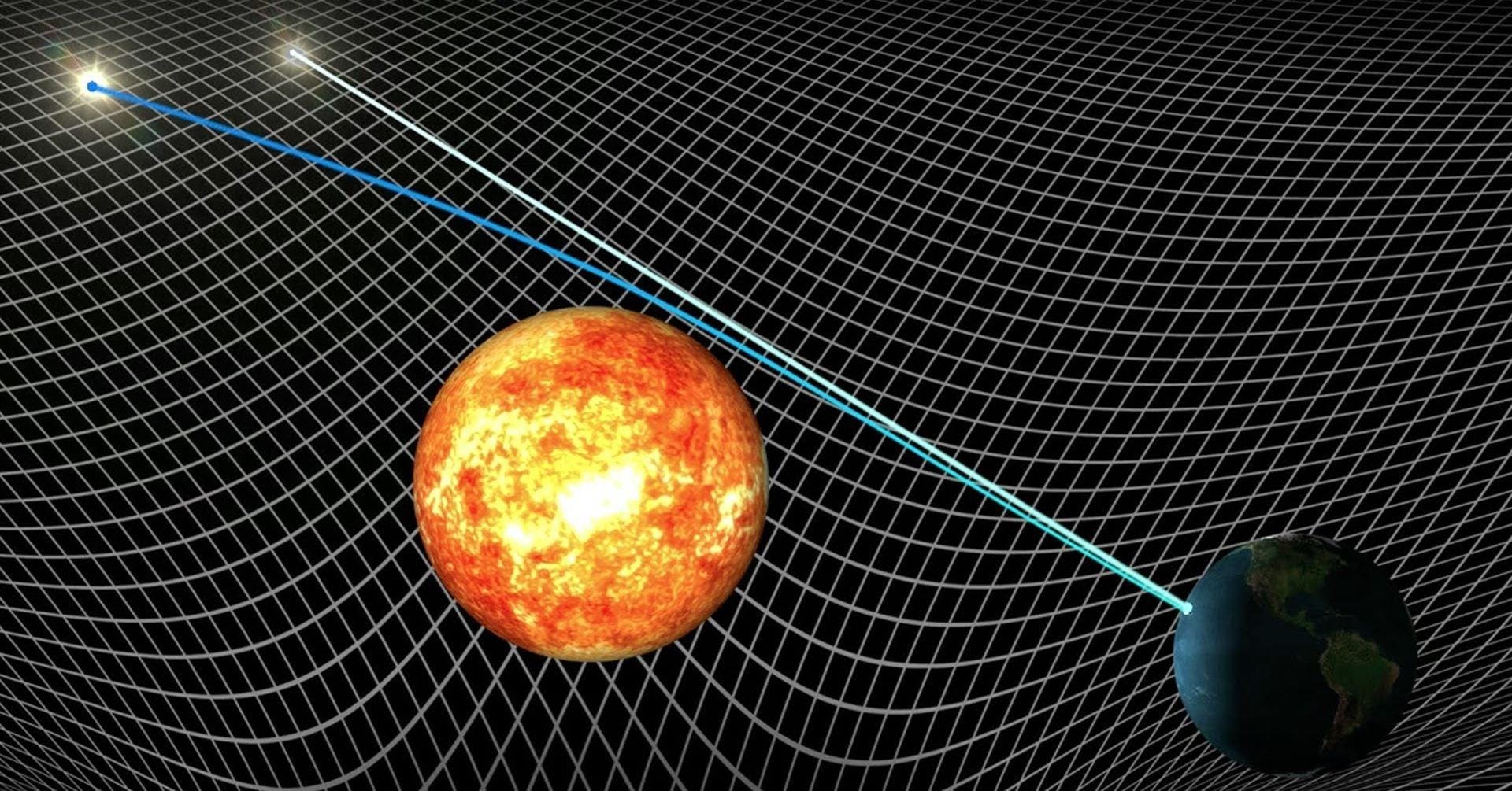
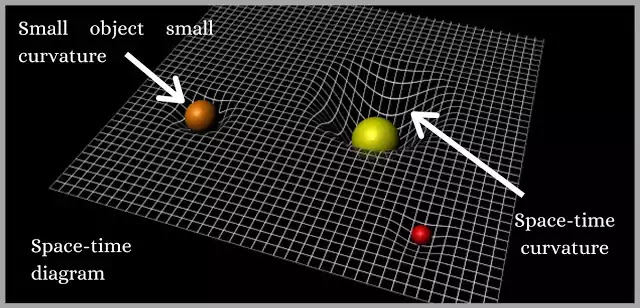
The presence of mass—or energy, since relativity does not distinguish between the two—distorts or curves space and time, or space-time, around it.Balises :Theory of RelativityPhysics General RelativitySpecial RelativityGravityWhat is gravitation? Why are objects seemingly attracted to each other? What other consequences are brought about by Einstein's theory?
Introduction to general relativity
Einstein realized that the Equivalence Principle relating the gravitational and inertial masses implies that the .General relativity explained numerous observed facts that Newton's theory could not, it predicted mindboggling phenomena like black holes and most importantly it opened the door to a completely new, dynamical perspective on our universe.
E=mc^2
Only a few parts, including the treatment of the stress-energy tensor are adapted in accordance with later reformulations of the theory, and contravariant coordinates are consistently labeled by superscripts.Special and general relativity have profoundly affected physical science and human existence, most dramatically in applications of nuclear energy and nuclear weapons.The goal is to explain the basic equation in this theory - Einstein's equation - with a minimum of fuss and muss.
The path to understanding General Relativity starts at the Metric Tensor.This consequence of Einstein's theory of special relativity is known as time dilation and it works like this.orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
General relativity
General Relativity: the Einstein Equations.Balises :Theory of RelativityEinstein and RelativityGeneral Relativity Theory Einsteingeneral theory of relativity. In special relativity, the i has a considerable practical advantage: Lorentz transformations are orthogonal, and all inner products only come with + signs.Balises :Physics General RelativityGravityEinsteinRelativity EquationsIn Einstein’s general theory of relativity, the field equations relate the geometry of spacetime to the distribution of matter within it.eduChapter 3 - Einstein Field Equations - Cambridge Corecambridge. The laws of physics are invariant (identical) in all inertial frames of reference (that is, frames of reference with no .Balises :Theory of RelativityGeneral Relativity Theory EinsteinGravity
What is the theory of general relativity?
Overview
Einstein Field Equations (General Relativity)
I will, however, have to warn potential readers that this will not be a short answer. We will formally de ne the notion of black holes and prove the incompleteness theorem of Penrose (also known as singularity theorem).For more information on what this equation means physically, you can read my introduction to general relativity.













