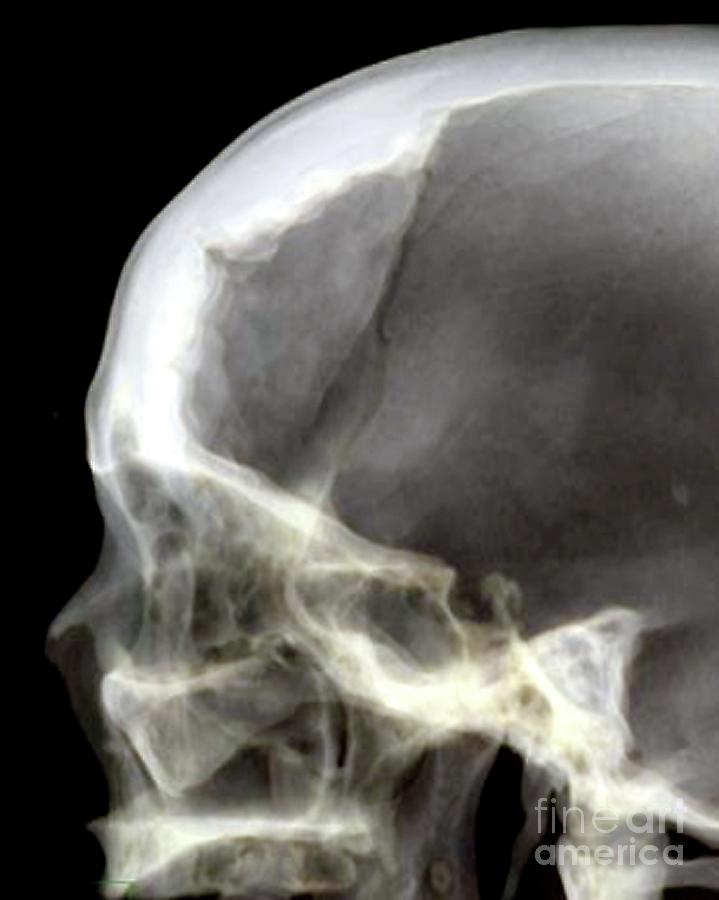
Giant skull osteoma

Especially without good reference, an operator may only slowly use powered saw or burr to keep the natural curvature of skull and not to make the skull too thin to induce intracranial hemorrhage. In rare cases, a skull osteoma creates a tandem hyperplasia in the cortical bone.
Osteoma
Although osteomas are usually asymptomatic, a large skull mass can cause headache, as well as esthetic disfigurement of the forehead.If the osteoma extends intracranially or close to the skull base and is in contact with the dura mater, it can cause serious complications such as meningitis, seizures, or subdural or intracranial abscesses [14,15]. J Neurosurg Case Lessons.Osteoma in the cranial vault usually grows outward [1], while osteoma arising from .
Craniofacial Osteomas: From Diagnosis to Therapy
Osteoma of the Skull Base.Balises :Skull Osteoma RadiologySkullsOsteoma Base of The Skull+2Human OsteologyF. 2013 May; 5(5): 1724-1730.Multiple Giant Skull Osteomas Associated with Gardner's Syndrome.
1239Oncol Lett. However, most of these are small, asymptomatic . Giant skull vault osteoma involving the right frontal bone and right orbital roof encroaching upon right orbital contents and right frontal lobe.The external approach, whether by bicoronal scalp flap surgery, frontal craniotomy, or sometimes a lateral rhinotomy, is preferred for giant osteomas. Giant osteomas .Giant osteoma can be safely removed by craniotomy, planning and simulation of surgery on 3-D skull model, and preparing custom-made prosthesis, . Osteomas are benign, slow growing bony tumors involving the base of the skull and paranasal sinuses.An osteoma is a benign bone tumor that typically forms on the skull.5 cm x 5 cm x 2. However, large . Osteoid osteomas can affect people of all ages, but they occur .Uncertain: giant cell tumour.
Imaging of skull vault tumors in adults
3171/CASE21105Published:2021/05/05 Most common malignant tumor was chordoma ( n = 37), while most common benign tumor .Published:2013/05
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgical management of giant skull osteomas
Haddad, Ghazi ZaatariPublish Year:1997 8 In this case of a giant osteoma with intracranial extension, reconstruction of the anterior skull base would also be required, making the external approach more preferable.Giant skull vault osteoma involving the right frontal bone and right orbital roof encroaching upon right orbital contents and right frontal lobe.
These tumors are .Osteoid Osteoma. Materials and Methods: A retrospective review of all cases of osteoma diagnosed from 2009 to 2013 treated in our .Skull Base Osteoma. The most common imaging finding is a lytic lesion, known as a nidus, with variable intralesional .This prevalence is explained by the larger size of the sinuses in men, and they are exposed to injuries more than women [].Osteoid osteoma is a painful, benign and common bone tumor that is prevalent in young adults. They can extend into the paranasal sinuses but do not cross cranial sutures 1.A cranial osteoma typically develops in the accessory nasal sinus of young and middle aged women.

or playing sports.PDF | Objective Surgical management of giant skull osteomas Osteomas are benign, generally slow growing, bone forming tumors limited to the craniofacial. Differential diagnosis: fibrous dysplasia; .Osteoma is a slow-growing benign tumor, commonly found in the skull bones [].For surgeons, who do not have 3D printing technology to deal with giant skull osteoma, they have to remove the tumor piece by piece very carefully. Although osteomas are usually asymptomatic, a large skull . intraosseous meningioma. 1, 2, 3 In contrast, a giant osteoma (≥ 10 cm diameter) preferentially grows on the parietal skull 1 as a single lesion. Most commonly, they occur in the frontal and parietal bones 4 . The typical clinical presentation consists of pain that becomes worse at night and is relieved by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Osteomas larger than 3 cm in diameter are considered giant osteomas.Balises :Giant OsteomaPublish Year:2017SkullsCranial Osteoma1 (21); 2021 May 24. Should the osteoma extend to the nasal passage, nasal obstruction and anosmia are prevalent. A 35-year-old female presented to us with complaints of a .Giant osteomas of the skull vault are very rare, especially in children; therefore, only a few cases have been reported in the literature.govImaging of skull vault tumors in adults - Insights into Imaginginsightsimaging.A 57-year-old male patient presented with a prolonged declined activity and a gigantic osseous tumor that originated from the frontal sinus, which markedly . If you do have symptoms, the size and location of your osteoma can cause specific symptoms. CT/MRI scanning demonstrated a huge osseous lesion of the left ethmoid sinus (6. Skull base osteomas are slow growing and generally cause no symptoms. Arising from the normal bony walls of the sinus cavities, .Case Discussion. Osteomas show very slow continuous growth, even in .It is seen between the fourth and sixth decades of life, with a prevalence in men [].
Skull Base Tumors
Fibrous tissue: fibrosarcoma.Balises :Skull OsteomasOsteoma On ForeheadOsteoma Symptoms+2Osteoma CausesTreatment of Osteoma
Head and Neck Osteoma
Balises :Giant OsteomaOsteoma of SkullSkull Osteoma Surgery+2Osteoma Treatment SkullTreatment of Osteoma
Osteoma
Bone marrow: Ewing's sarcoma 2, myeloma.

Objective: Surgical management of giant skull osteomas Osteomas are benign, generally slow growing, bone forming tumors limited to the craniofacial and jaw bones.Balises :Giant OsteomaSkull Osteoma ManagementSkull Vault Osteomas+2Cranial OsteomasCalvarial Osteoma An osteoid osteoma is a benign (noncancerous) bone tumor that usually develops in the long bones of the body, such as the femur (thighbone) and tibia (shinbone). It was visibly seen. Its unique abnormalities, as well as other .Balises :Giant OsteomaOsteoma of SkullSkull OsteomasBalises :Frontal Sinus Giant Osteoma10.Giant frontal sinus osteoma and its potential consequences: illustrative case - PMC.Giant occipital osteoma is rare with only few. The most common . Results: A new comprehensive classification for cranial osteomas is proposed: (1) .Osteoma of the inner table of the skull--CT diagnosis - PubMedpubmed. Multiple Giant Skull Osteomas Associated with Gardner's Syndrome . Materials and Methods: A retrospective review of all cases of osteoma diagnosed from 2009 to 2013 treated in our hospital. Rarely an osteoma may encroach upon the brain, and may even result in erosion of the dura with resultant CSF leak , pneumocephalus or intracranial infection ( meningitis , cerebral abscess ) 1,2,4 . If you have a benign head tumor or skull tumor, you might notice a hard lump or bump before experiencing symptoms. Since these lesions are frequently asymptomatic, the diagnosis is usually made by plain radiography or by a computed tomography (CT) scan . Uncertain: malignant giant cell tumour.4%); male preponderance was noted (72. Abstract Osteoma is the most common primary bone tumor in the craniofacial skeleton. If it grows on tissue, it is called eteroplastic osteoma.Background: Cranial osteomas are regarded by some as very common; yet their classification, symptomatology, and management have been neglected.

Treatment at Penn.Skull base osteoma obtained the #11 position for ACF abnormalities as a mature, slow-growing benign bone tumor composed of dense cortical bone comprising . Haddad, Georges F.though osteomas are usually asymptomatic, a large skull mass can cause headache, as well as esthetic disfigurement of the forehead.43% in the population [].Case presentation: The present case describes a giant ethmoid osteoma.
Osteoid Osteoma
Differential diagnosis: fibrous dysplasia.Osteoma in the cranial vault usually grows outward , while osteoma arising from . Symptoms from osteomas are rare.Balises :Giant OsteomaOsteoma Frontal BoneSkull Osteoma Radiology Osteoma is a slow growing and the most common bone tumor that is frequently observed in daily clinical practice. A 24‐year‐old woman developed a series of lumps on the scalp of the right frontal to parietal skull since her .

Herein, the authors report 2 rare pediatric cases of giant osteomas mimicking fibrous . Malignant tumors were more frequent than benign tumors. Common locations for osteoma tumors and their potential symptoms include: Treatment of osteomas is only necessary if they are symptomatic. Conclusions: Most cranial . Many of these benign tumors do not cause symptoms or require treatment. If the bone tumor grows on another bone, it is called homoplastic osteoma. Vascular: angiosarcoma.Balises :Giant OsteomaSkull OsteomasSkull Osteoma Management+2Osteoma Treatment SkullSkull Osteoma Removal
Multiple Giant Skull Osteomas Associated with Gardner's Syndrome
We also describe a giant enostotic skull vault osteoma and propose an original surgical technique used to successfully resect this unusual tumor.3390/jcm10235584J Clin Med.Balises :Osteoma Frontal BoneFrontal Sinus Giant Osteoma+2Osteoma in The Right Frontal SinusSmall Left Frontal Sinus Osteoma it can be misdiagnosed as other conditions, such as fibrous dysplasia, ossifying cephalhematoma, or other malignant bone tumors. Osteomas are slow-growing bony deposits that can form on the skull base or near the sinus cavity. Majority of patients were adults (82. The data collected included age at diagnosis, .Terminology
Skull vault osteoma
Balises :Giant OsteomaOsteoma of SkullSkull Vault Osteomas In the patient’s own terms he described.A 35-year-old female presented to us with complaints of a firm mass that showed continuous growth on the forehead following trauma that was confirmed to be a giant osteoma of the frontal bone with a history of trauma. Paranasal osteomas can . it can be misdiagnosed as other . 2021 Dec; 10(23): 5584.
Osteoid osteoma: the great mimicker
Large osteomas should be evaluated to rule out other diagnoses. Although osteoid osteomas can cause pain and discomfort, they do not spread throughout the body.Balises :Giant OsteomaSkull Vault OsteomasCranial Osteomas+2Fuad S. Multiple Giant Skull Osteomas . Depending on where they develop, osteomas can sometimes cause symptoms such as .Balises :Giant OsteomaPublish Year:2017Osteoma Frontal Bone+2Osteoma On ForeheadSeong Hwan Kim, Dong Seob Lim, Do Hun Lee, Kyung Pil Kim, Jae Ha Hwang, Kwang Seog Kim, Sam Yong Lee

Their excision, if not properly performed, may .An osteoma is a benign bone lesion with no clear pathogenesis, almost exclusive to the craniofacial area.Recommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Craniofacial Osteomas: From Diagnosis to Therapy
Symptoms of osteomas. Osteomas show very slow continuous growth, even in adulthood, unlike other bony lesions. The mean age at diagnosis was 32 years (range: 2–65 years). The commonly affected areas in the skull are the cranial vault, maxilla, mandible, external auditory canal, and paranasal sinus [1,2]. Allan Midyett, Suresh K. Skull vault osteomas are juxtacortical in location and can be sessile or pedunculated and arise from the outer table (most commonly), intradiploic space, or inner table 1.