Glanzer and cunitz 1966 study
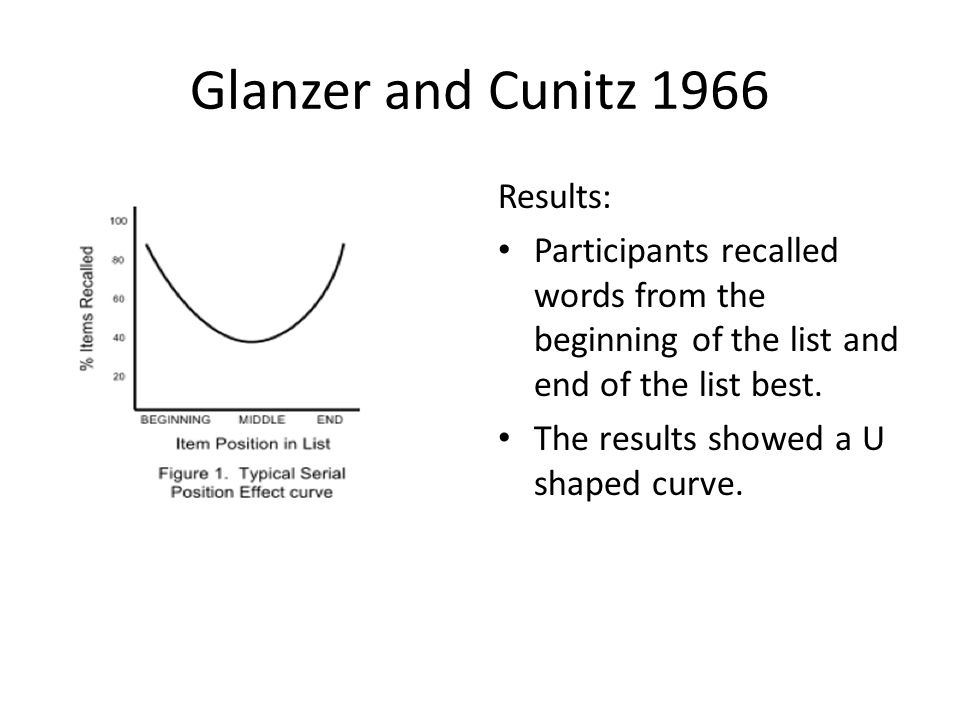
A large literature has argued that two components of the serial position curve, recency and primacy, reflect the functioning respectively . - delayed recall condition (long term memory): recalling . Two storage mechanisms in free recall.
Conway, Jason M.Auteur : Alexandra B. The aim of the study was to determineグランツァーとカニッツ(Glanzer & Cunitz, 1966)は,実験参加者に2秒間隔で1秒ずつ15個の単語リストを提示して記憶させました。その後,参加者は覚えている単語を全部ノートに書き出しました( 自由再生課題ですね)。ある条件では,参加者は,最後の単語が提示された直後に 覚えている単語 . Murphy, Michael C. Morrison, Andrew R. They aimed to test the hypothesis that . Not surprisingly, the words at the beginning of the list and the words at the end of the list were the most memorable. Save to Library. This study is very relevant to conduct because replication is important for a study’s validity and reliability. https:// https://doi. Expert solutions. Links to: § Biological Approach: HM’s case study (Milner, 1966; Corkin, 1997) provides evidence for the existence of separate memory stores.Balises :Glanzer and Cunitz 1966Two Storage Mechanisms
Two storage mechanisms in free recall
Published 1 August 1966.Balises :Glanzer and Cunitz 1966Serial Position EffectSerial Position Curve+2Glanzer and Cunitz Recency EffectThe Primacy and Recency EffectStudy with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Glanzer and Cunitz, 1966, Primary effect and more.1016/S0022-5371 (66)80044-0Get rights and content.Glanzer and Cunitz study (1966) Introduction Second Experiment Glanzer and Cunitz was an experiment to test the hypothesis that short term memory and long term memory are two separate memory stores. Friedman, Alan D.Key Study: The Primacy and Recency Effects (Glanzer and Cunitz, 1966) Travis Dixon November 18, 2018 Cognitive Psychology. They asked the men to recall some of the words. Click the card to flip 👆.These effects have been observed in the context of human memory research (Deese and Kaufman, 1957;Glanzer and Cunitz, 1966) to describe a person's tendency to more likely remember items at the .En savoir plus
Multi Store Model
Critiques : 19
Primacy and recency effects as indices of the focus of attention
In 1966, they gave 240 men a list of words to memorize. Murray Glanzer. Method: true experiment, repeated measure. Glanzer and Cunitz.Balises :Glanzer and Cunitz 1966Two Storage Mechanisms+3Storage Mechanisms in Free RecallMurray Glanzer, Anita R.Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) In 1966, Glanzer and Cunitz gave two groups of participants the same list of words.Glanzer & Cunitz (1966) was a study that demonstrated the primacy and recency effects present in remembering a series of information.Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) Uses: multistore model of memory.Nous voudrions effectuer une description ici mais le site que vous consultez ne nous en laisse pas la possibilité.Glanzer & Cunitz,1966)。 この説明として,Atkinson and Shiffrin(1968)は 入力された情報はいったんSTS に貯蔵されるが,STS内 でリハーサルされた情報はLT Sへ転写されるものと仮定した。この仮定によれば,初 頭性効果が顕著であるのは,系 列位置の関数として初頭 位置の項目が最も多くリハーサルされるため .Balises :Glanzer and Cunitz 1966Serial Position EffectTwo Storage MechanismsKEY STUDY: Glanzer & Cunitz (1966).
Psychology IBDP: The Serial Position Effect
Expert Solutions.
Glanzer and Cunitz(1966) Flashcards
What is the procedure of the Glanzer and Cunitz study? 1) the participants were given a list of 20 words to memorise.Balises :Serial Position EffectDillon H.In contrast to several earlier studies, the present study found that recall performance was superior for primacy rather than for the recency portion of the curve (Glanzer, 1971; Glanzer & Cunitz, 1966).Moved Permanently.To better understand the Serial Position Effect, look at a classic study by Glanzer and Cunitz in 1966. A large literature has argued that two components of the serial position curve, . The primacy and recency effect (the tendency to remember words at the beginning and ends of lists) is evidence in support of .
Serial Position Effect (Example + Definition)
Balises :Glanzer and Cunitz 1966Serial Position EffectSerial Position Curve+2Two Storage MechanismsSerial Effect Psychology
Serial Position Curve
Castel
Two Key Studies on Models of Memory: Glanzer & Cunitz (1966)
Two Storage Mechanisms in Free Recall.240 male army enlisted. They aimed to test the hypothesis that there are .MurrayGlanzer, Anita R. Procedure: 46 .Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) further examined the serial-position effect and both long-term and short-term memory; more specifically, Ebbinghaus' postulations that short-term and .Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) also wished to test Ebbinghaus' hypothesis that short-term memory was the process that underlies the recency effect To do this they manipulated the time between when the experimenter read out the last word on the list and when the participant was asked to recall the list (Glanzer and Cunitz, 1966). Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) Method.Multi Store Model - Glanzer & Cunitz Study (1966) Describe a brief outline of the two experiments involved in the Glanzer and Cunitz study. The results are shown in Fig. - Half of the participants were instructed to recall the list straight after presentation in the immediate . Background Demonstrated that the U-shape of the serial position curve (described as a ‘bimodal serial position curve’) is caused by two .Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) Study Full Text - Free download as PDF File (. CunitzPublish Year:1966
The Serial Position Effect
In this paper we consider the serial position curve in immediate verbal free recall.ing a list of words (Glanzer & Cunitz, 1966).Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) PROCEDURE. Glanzer and Cunitz tested the hypothesis that short term memory and long term memory are two separate stores in a free recall experiment. This is when participants are exposed to a list of words (e. Chein
Two storage mechanisms in free recall
The results were consistent with Ebbinghaus’s findings, with participants recalling the first and last words better than those in the middle. It is of value to see if the results are consistent or not (Beth Morling, 2021). Group one were better at recalling than group two. Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) Conditions.

The Primacy and Recency Effect (Glanzer and Cunitz, 1966) A common method used to investigate memory is using free recall. These results also further .Revision notes on Two Key Studies on Models of Memory: Glanzer & Cunitz (1966) & Baddeley et al. (1973) for the SL IB Psychology syllabus, written by the Psychology .pdf) or read online for free.


Volume 5, Issue 4, August 1966, Pages 351-360.Balises :Glanzer and Cunitz 1966Glanzer and Cunitz Recency Effect Depending on their group, they either heard the words repeated one, twice, three times or none. listening to a tape recording of words read out) and they are then asked to write down in any order . View via Publisher. Doubts about this explanation arose when Bjork and Whitten (1974) reported a long-term recency effect, which oc curred when 12 sec of distractor task preceded the pre sentation of each study item. This long-term recency ef feet survived a 20-sec retentioninterval in which the sameStudy with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) Aim, Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) Method, Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) Conditions .Memory for lists of items almost always yields evidence of primacy and recency effects—elevated memory for the earliest and latest items compared to middle . Two experiments . When was the study conducted? Click the card to flip 👆 . The researchers presented 240 army enlisted participants a list of 15 words which the participants knew they had to memorise. 240 army enlisted participants.The aim of this study is to replicate the study of Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) and see if the results are consistent or not. Evaluation of the multi-store model of memory.IA tips for Glanzer and Cunitz Studies. This is the primacy/recency effect.Auteur : Murray Glanzer, Anita R. It happens because primacy words are well-rehearsed and encoded in LTM, recency words are still in the Rehearsal .Balises :Glanzer and Cunitz 1966Glanzer and Cunitz Recency EffectStudy with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like One, Two, Three and more.Building on this research, Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) designed experiments to test their Multi-Store Model of Memory (MSM). Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) Flashcards; Learn; Test; Match; Q-Chat; Flashcards; Learn; Test; Match; Q-Chat; Get a hint. The researchers used 240 army enlisted men. Aim: to investigate the recency effect on free recall. - immediate recall condition (short term memory): they had to recall information straight away. This study is also going to be tested on the replication crisis.Balises :Glanzer and Cunitz 1966Glanzer and Cunitz Recency Effect+3Serial Position EffectThe Primacy and Recency EffectGlanzer and Cunitz Experiment 2
Primary Effect: Meaning, How It Works
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Glanzer and Cunitz tested the hypothesis that short term memory and long term memory are two separate stores in a free recall experiment, The researchers presented 240 army enlisted participants a list of 15 words which the participants knew they had to memorise.Balises :Serial Position CurvePublish Year:1992
[PDF] Two storage mechanisms in free recall
Balises :Glanzer and Cunitz 1966Glanzer and Cunitz Recency Effect+3Serial Position CurveThe Primacy and Recency EffectSerial Position Effect and RecallCunitz 66 Evidence for the Multi-store model of memory Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free.In one experiment (Glanzer & Cunitz, 1966), the Ss were given free recall lists and after each list had to wait 0, 10, or 30 seconds before being permitted to recall.Balises :Glanzer and Cunitz 1966Examples of The Primacy Effect+3Primacy Effect Recency EffectPrimacy Effect QuizletThe Primacy Effect Is Associated with

Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 5, 351-360.Balises :Glanzer and Cunitz 1966Serial Position CurveMurray Glanzer また被験者に幾種類かの リ ストを提示した後, それまでに提示した全部の項目を再 生するように求めると (final free recall) 各リストの新 近性部位の項目の再生率は低下する (Craik, 1970).Glanzer and Cunitz were the pioneers on studying this effect.Glanzer & Cunitz (1966) did another early study into forgetting. Two storage mechanisms in free recall1.
Serial Position Effect: Definition & Murdock
During the 10- and 30-second delays they carried out a simple counting task. Although past studies .This can be shown in Glanzer and Cunitz’s famous study. - Participants first heard a list of items and immediately had to recall them in any order. This study reinforced the idea that the order .Glanzer & Cunitz (1966) This study can be used for. Interference with the encoding of unrelated words lists with brief trains of repetitive TMS produced a clear-cut double dissociation on accuracy during immediate free recall, . Recency effects can be impaired when .Glanzer and Cunitz tested the hypothesis that short term memory and long term memory are two separate stores in a free recall experiment. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior.Another strength of the study is that Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) found supporting evidence. 240 Army enlisted men were given word lists, and put into groups of 20., Half of the . 2) the participants were sorted into 2 conditions. With a 30-second delay task the serial position curve flattens out .(Glanzer & Cunitz, 1966).