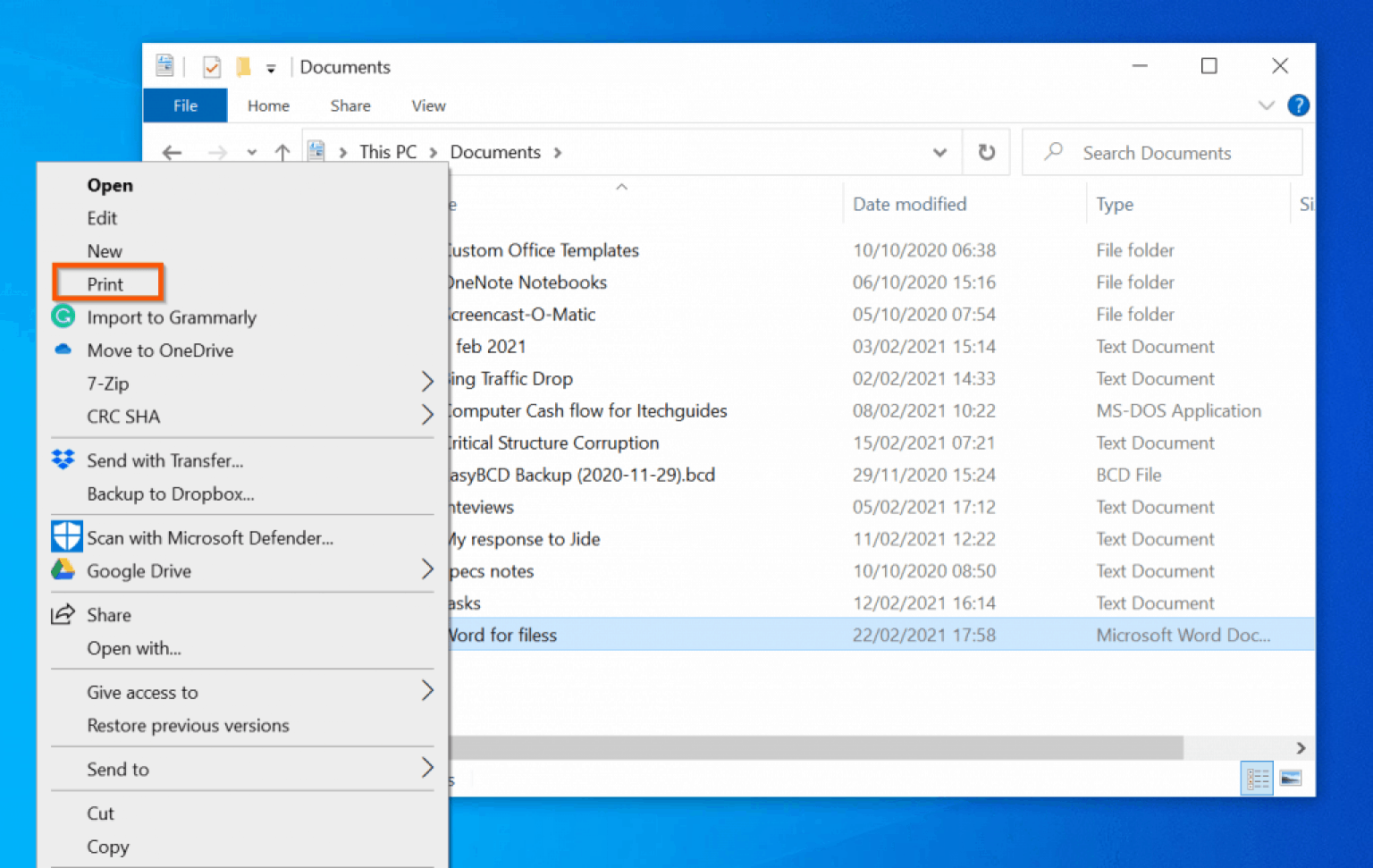
Glaucomatous optic nerve

All types of glaucoma involve glaucomatous optic neuropathy. The pathogenesis of GON has been hypothesized, to either . The major cause of oxidative stress is unstable blood .Optic nerve fiber count and diameter of the retrobulbar optic nerve in normal and glaucomatous eyes.We attempted to identify the initial glaucomatous changes of the optic disk and retinal nerve fiber layer and to analyze how these changes subsequently progressed. It also affirms the need to undertake further studies regarding the path-ogenesis of .
What is glaucomatous optic neuropathy?
Mesenchymal stem cells for repairing glaucomatous optic nerve
Optic nerve assessment contributes to the clinician's ability to detect glaucoma. Murray Fingeret, OD. It takes approximately 4 to 6 weeks to develop optic atrophy after the initial injury.Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can damage the optic nerve in the back of your eye. Glaucoma presents with a very characteristic cavernous atrophy, commonly termed “cupping” or “notching. Despite technological advances, clinical . 43,44 It should be the first aspect of a systematic optic nerve examination, since variations in disc size alter significantly the estimation of glaucomatous damage.Glaucoma is a group of diseases that are the leading cause of blindness in the United States.The optic nerve head remodeling in glaucoma that leads to the thinning of NRR tissue upon axonal loss is characterized by the disorganization and loss of the glioarchitecture.The initial site of injury in glaucoma is believed to be at the optic nerve head. These are characterised by progressive loss of retinal . Of 61 eyes of 61 patients with ocular hypertension, 23 (38%) developed glaucoma during ten years of follow-up (range, five to 15 years). Glaucoma is diagnosed during a routine comprehensive eye exam by a licensed ophthalmologist.In glaucomatous rodents, regions of RGC damage are sharply delimited and often match the path of axon . Although numerous articles substantiate the existence of a vascular mechanism leading to GOND, issues, such as inaccurate methodology, testing on non-primate animal models, and substandard evaluation of the parameters being examined, pose limitations.Regenerative medicine research into the repair of optic nerve damage using stem cells has received considerable attention. Astrocytes are activated by both mechanical and ischaemic stress. 1, 2 Although progression traditionally has been measured by assessing changes in visual field sensitivity, 3, 4, 5 many patients show optic disc or retinal nerve fiber layer .Detection of glaucoma progression is a fundamental part of glaucoma management because it provides a means to identify patients who may require escalation in treatment.The blinding diseases known as “glaucoma” comprise several different forms of optic neuropathies with diverse and complex etiologies.The pathophysiology of optic nerve cupping and subsequent optic neuropathy has been researched in experimental monkey studies and has two proposed .Glaucoma can cause the cup to enlarge (actually little nerve fibers are being wiped out along the rim of the optic nerve in glaucoma). Highly myopic optic nerve head (ONH) abnormalities encompass a series of complications . Various insults can occur to the optic nerve and manifest ophthalmoscopically as pallor, atrophy, cupping and notching.Refuting the vascular theory of glaucomatous optic nerve degeneration. Clinical features of the disease have suggested .Contrast that to progressive glaucomatous optic nerve damage.Glaucomatous optic neuropathy is the hallmark of all types of glaucoma. It is in fact the most common «neuro .Little is known about the diagnostic utility of three-dimensional neuroretinal rim thickness (3D-NRRT) for differentiating patients with superior segmental optic nerve hypoplasia (SSOH) from .
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy leading to changes in the intrapaillary and parapaillary regions of the optic disk.
Evaluating the Optic Nerve for Glaucomatous Damage With OCT
Glaucoma usually happens when the fluid pressure inside the eyes . The difference, again, is the optic nerve appearance, pallor out of proportion to cupping, as well as color vision loss and unilateral visual acuity loss. In glaucomatous ONHs, microglia become activated and phagocytic and produce cytokines, mediators, and enzymes that can alter the extracellular matrix. Severity of cupping doesn’t match the visual field defect.Optic atrophy is the term used when optic nerve pallor occurs and is considered an end-stage marker of non-glaucomatous optic nerve disease.Auteur : Toru Nakazawa, Takeo Fukuchi
Glaucoma and the Optic Nerve: Cupping and Progressive Effects
Methods: Naïve C57bl/6 mice at various ages spanning the time between early adulthood (3 months) and senescence (30 months) were used in this study.
When Glaucomatous Damage Isn’t Glaucoma
There are proponents for and against the role played by vascular factors in the development of glaucomatous optic nerve degeneration.Characteristic features of glaucomatous optic nerve include: Generalized or focalized increase in the optic cup size and in the cup-disc ratio.
Our findings suggest that activated microglia may participate in stabilizing the tissue early in the disease process, but, as the severity of the . However, this single measurement can be misleading if it’s not considered in relation .Optic Nerve Excavation. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1995;233:421–4.When evaluating a patient who has been diagnosed with glaucoma, it’s important to perform a thorough evaluation of the optic nerve in order to monitor for progression of the disease. The OCT of the optic nerve and macula does not correlate with the visual fields.Eye Center, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China. A large optic disc might . Let’s start this .Glaucoma is a neurodegenerative disease that can damage the optic nerve at the back of your eye.Evaluating the Optic Nerve for Glaucomatous Damage With OCT.Eye doctors will often draw pictures and take photographs to accurately document the appearance of a glaucomatous optic nerve (Figure 1-7).Glaucoma affects about 3 million Americans and is the second leading cause of blindness worldwide. Glaucomas comprise a heterogenous group of conditions leading to irreversible sight loss. Visual field loss is progressing despite normal IOP or IOP that’s under control. Some doctors refer to an . An optic nerve glioma is a type of noncancerous, slow-growing tumor that develops in the glial cells of .
The optic nerve head in glaucoma
The neuroretinal rim area essentially decreases as tissue volume is lost and, conversely, the cup increases.The optic disc margin is defined as the innermost border of reflective tissue that is internal to any pigmented tissue and within which only neural tissue is present. The optic nerve head in acquired optic neuropathies. In cases of progressing optic cupping due to glaucoma, the neuroretinal rim itself becomes thinned over time due to actual physical loss of ganglion cells.
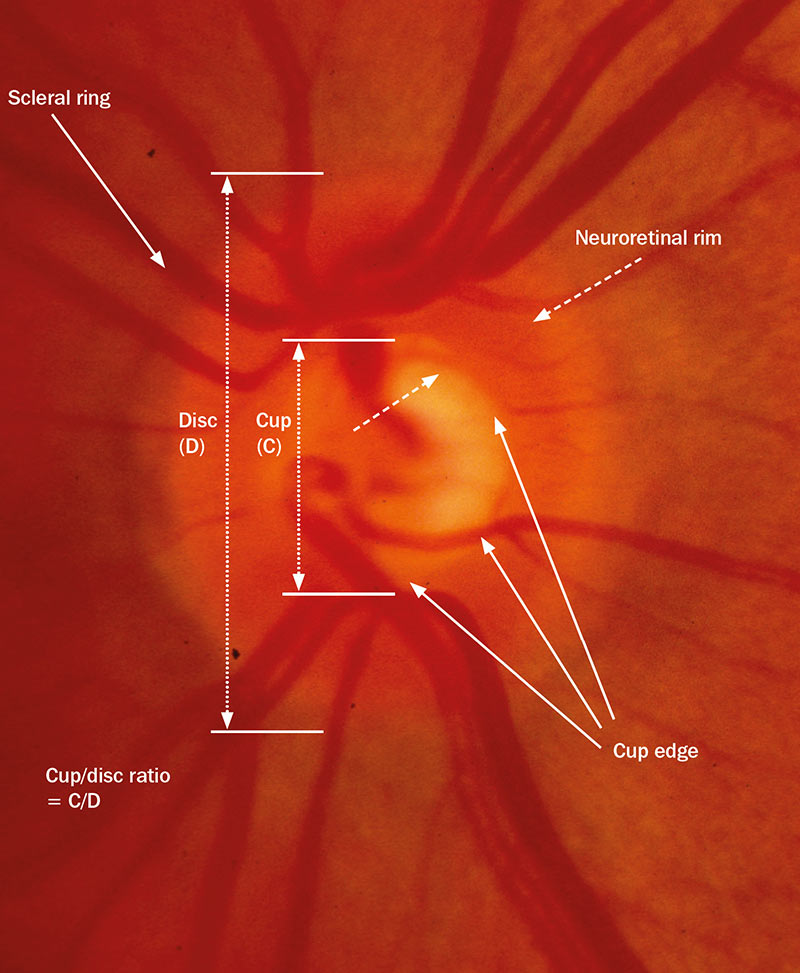
Evaluating for glaucoma starts by evaluating the cup to disk (C/D) ratio. Optic nerve assessment contributes to the clinician's ability to detect glaucoma.Glaucomatous optic neuropathy (GON) is the pathohistological feature of glaucoma in the optic nerve. Further, it can be categorized into primary or secondary optic atrophy. The most well-recognized non-glaucomatous optic neuropathies that cause cupping include compressive optic neuropathies, arteritic .HSP27 is not present in microglia. The retinal nerve fibres are spread unevenly across .The glaucomas are a group of progressive optic neuropathies characterized by degeneration of retinal ganglion cells and resulting changes in the optic nerve head.Auteur : Laura Goldman
How Glaucoma Affects the Optic Nerve
Initial glaucomatous optic disk and retinal nerve fiber layer
Neuroretinal rim pallor and optic disc swelling are the hallmarks of non-glaucomatous optic neuropathy 19,20, . Glaucoma often doesn’t cause noticeable symptoms in the .Purpose: To study age- and intraocular pressure-induced changes in the glial lamina of the murine optic nerve on the ultrastructural level. In glaucoma the position of the blood vessels within the optic nerve can shift with the progressive cupping, and this can be an .Glaucomatous changes to the optic nerve head damages the axons of retinal ganglion cells (RGC), which are the output neurons of the retina that carry visual signals to the retino-recipient regions . Excavation of the optic nerve, clinically known as cupping, is the most commonly recognized morphologic change of the glaucomatous optic nerve (Fig.
The Pathophysiology and Treatment of Glaucoma
The ONH or optic disc is a round/oval ‘plug-hole’, down which more than a million nerve fibres descend through a sieve-like sheet known as the lamina cribrosa.
The optic nerve head in glaucoma
By far, the most common optic nerve affliction is glaucoma.Glaucoma is a complex disorder of aging defined by the death of retinal ganglion cells and remodeling of connective tissues at the optic nerve head.
Defining and diagnosing glaucoma: a focus on blindness prevention
Review how optometrists can identify and manage non-glaucomatous optic neuropathy and differentiate it from glaucoma.
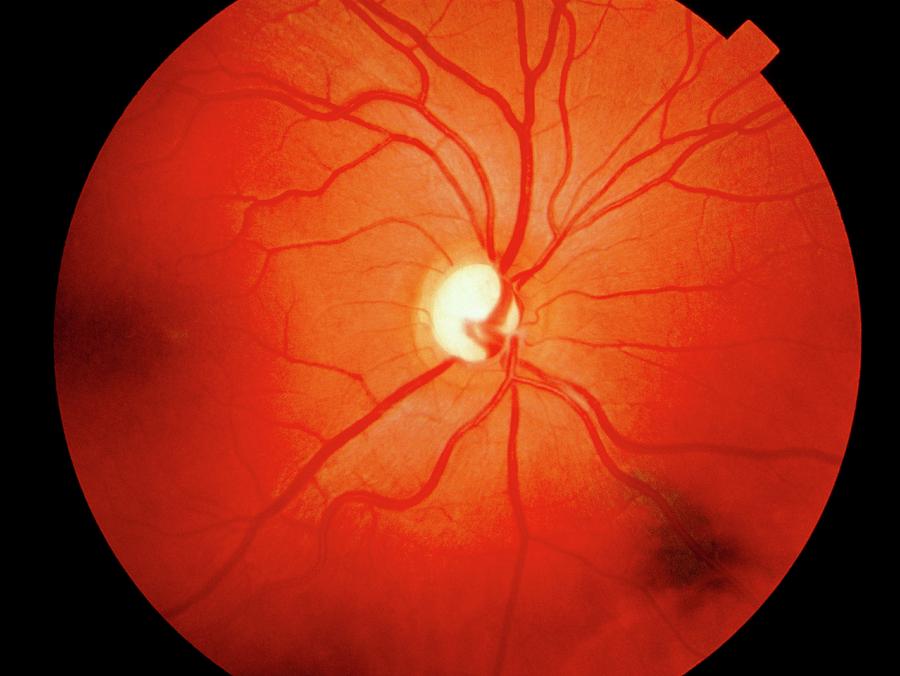
It can cause vision loss and blindness by slowly lowering your eye .Characteristics of the normal ONH.
Normal tension glaucoma: review of current understanding and
The pathogenesis of glaucomatous damage involves activation of astrocytes and involvement of oxidative stress in the mitochondria, which are located numerously in the axons of the optic nerve head (ONH).
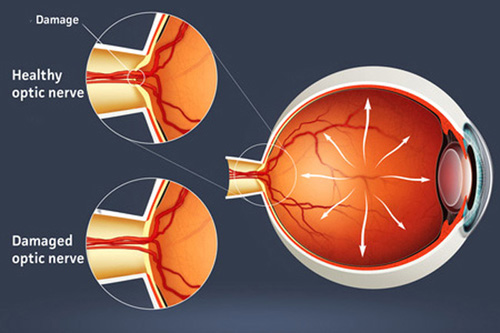
Intraocular pressure-induced axonal injury at the optic nerve head leads to apoptosis.
Examination of the Optic Nerve in Glaucoma
In general, optic nerve imaging is more useful in glaucoma suspect and early-to-moderate glaucomatous patients rather than advanced disease.

Glaucomatous changes to the optic nerve head damages the axons of retinal ganglion cells (RGC), which.Auteur : Robert N. Stem cells possess the potential for . Increases in cupping or nerve fiber loss indicate poorly controlled glaucoma.
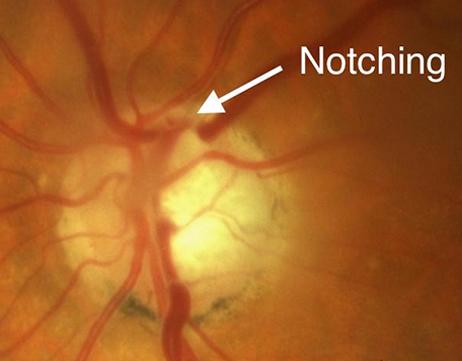
On the other hand, the majority of non-glaucomatous optic neuropathies are characterized with optic disc pallor where hypertrophy of the glioarchitecture is not .
Imaging of the Optic Nerve: What is it and why is it needed?
The key to detection and management of glaucoma is understanding how to examine the optic . Optical coherence tomography (OCT) has become an important tool for the clinical evaluation of the optic nerve and retina. The pathogenesis of GON has been hypothesized, to either originate from . The clinical diagnostic evaluation of optic neuropathies relies on the analysis of the thickness of the retinal nerve fibre . Glaucoma is a condition characterized by damage to your optic nerve. Although OCT dates to the early 1990s, the introduction of the Stratus OCT (Carl Zeiss Meditec) in 2001—the original time-domain technology . Loss of retinal ganglion cells follows a slowly progressive sequence. Early detection is the key to . In addition, the intraocular pressure (IOP) was .The optic nerve is more pale than cupped.Glaucomatous optic neuropathy can be defined by the combination of an excavated optic nerve head (ONH) and concomitant defects in visual field testing ( . It is characterised by deformation of the optic nerve (see Figure 1, page 4), which .Glaucoma refers to a collection of diseases whereby increased intraocular pressure adversely impacts the optic nerve, and subsequently, the visual field. Weinreb, Tin Aung, Felipe A.These fibres are then bundled together behind the eye as the optic nerve which continues towards the brain. It may cause vision loss or blindness if untreated.