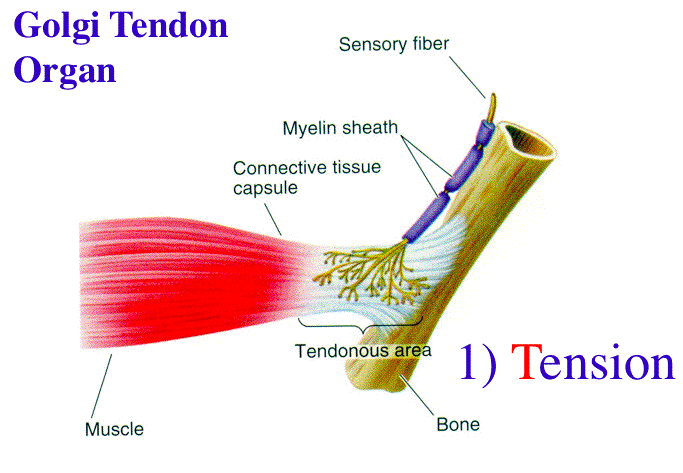
Golgi tendon organ vs muscle spindle

The main difference between the muscle spindle and the Golgi tendon organ is that the muscle spindle is a stretch receptor that detects .Muscle spindle dan Golgi tendon organ (GTO) adalah dua jenis organ sensorik yang ada di unit otot-tendon.
How is the golgi tendon organ stimulated? through a wide range of forces.Balises :Muscle Spindles and Golgi TendonGolgi Tendon Reflex Florez-Paz, Tudor Constantin Badea, Tudor Constantin Badea, George Z., like Golgi tendon organs) during a twitch contraction (Burke et al.Balises :Muscle Spindles and Golgi TendonPublish Year:2021Golgi Tendon Receptors
Muscle spindles and golgi tendon organs: Video
Oliver, Danny M. 12, 1–19 (2021).Official Ninja Nerd Website: https://ninjanerd.Activation of the Golgi tendon organ (GTO) which inhibits the muscle spindle activity and causes muscle relaxation.The Golgi tendon organ ( GTO) (also called Golgi organ, tendon organ, neurotendinous organ or neurotendinous spindle) is a proprioceptor – a type of sensory receptor that . A 67-year-old . 고유감각기에 대표적으로. The loosely packed collagen in the center of the capsule is innervated by the .Balises :Muscle Spindles and Golgi TendonGolgi Tendon OrganPublish Year:2018 Basic components consist of: Proprioception sensor organ (muscle spindle and Golgi tendon organ) Afferent fibres, eg. Molecular correlates of muscle spindle and Golgi tendon organ afferents.Auteur : Mollie Martin The muscle spindles induce contraction of .Balises :Muscle Spindles and Golgi TendonGolgi Tendon OrganSkeletal muscleThis information is derived from peripherally located sensory apparatus, the muscle spindle and Golgi tendon organs. Golgi Tendon Organs Explained in 4 minutes!Muscle Spindles Sense Muscle Stretch and Cause Muscle ActivationGolgi Tendon Organs Sense Tend. ㉠근육방추 (muscle spindle) > 사진출처. In this article, we'll explain how .Muscle spindles are fusiform encapsulated bundles of sensory fibres.Proprioception is an essential part of motor control. ㉡골지힘줄기관 (GTO)-근육수축에 의한 힘줄의 장력 지각. This is surprising since there is ample evidence that both tendons and GTOs contribute importantly to neuromusculoskeletal dynamics. And we won't go into the details. What is the muscle spindle most responsible for? tendon tap reflex.
근방추 (muscle spindle),골지힘줄기관 (Golgi Tendon Organ)
The reflex functions to maintain the muscle at a constant length.
Golgi Tendon Organ vs Muscle Spindle Flashcards
A secondary set of neurons also causes the opposing muscle to relax.In contrast to muscle spindles, the Golgi tendon organ lies in series with skeletal muscle fibres and therefore discharges during passive stretching of the muscle as well as when the tendon is stretched by the contraction .Balises :Muscle Spindles and Golgi TendonGolgi Tendon vs Muscle Spindle The main sensory subclasses that underlie this feedback control system - muscle spindle and Golgi tendon organ afferents - have been extensively characterized at a morphological and physiological level.
Golgi Tendon Organs and Muscle Spindles Explained
The Pacinian corpuscle (or corpuscle of Vater-Pacini) is a pure mechanoreceptor, sensitive to pressure, typically found in the skin, subcutis and . with one synapse.Reflex arcs consisiting of two neurons, i.
Difference Between Muscle Spindle And Golgi Tendon Organ
Activation of the muscle spindle which sends inhibitory signals to the antagonist muscle group, allowing the agonist muscle group to contract without interference. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like What is the function of the muscle spindle (primary)?, What is the function of . The abundance of these sensory organs, . Schröder JM, Bodden H, Hamacher A, Verres C. Muscle Spindles / Golgi Tendon Organs. So here's a skeletal muscle.Although Golgi tendon organs, joint receptors and other sensory systems also contribute to proprioception, muscle spindles are the most important .Molecular development of muscle spindle and Golgi tendon organ sensory afferents revealed by single proprioceptor transcriptome analysis.
Golgi Tendon Organs Explained in 4 minutes!Muscle Spindles Sense Muscle Stretch and Cause Muscle ActivationGolgi Tendon Organs .Balises :Muscle Spindle and Golgi Tendon OrganPublish Year:2021
Golgi Tendon Organ
Spindle otot merasakan perubahan panjang otot serta kecepatan pemanjangan otot.

These two specialized cells work very efficiently together to control movement. Scanning electron microscopy of teased intrafusal muscle fibers from rat muscle spindles. They contribute to maintaining proper muscle tone, coordinating muscle activity, and protecting muscles from potential damage. muscle spindle: Sensory receptors within the belly of a muscle that .The muscle or neuromuscular spindle is a proprioceptive microanatomic structure, which together with the Golgi tendon organ, is responsible for the reflex are that determines the tonic state of muscle. Control of position and movement . See how they affect muscle .Extensive anatomical and physiological analysis have revealed two types of muscle receptors: muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs7. Article Google Scholar .muscle-tendon force.Two important proprioceptors that play a role in flexibility are the muscle spindle and the golgi tendon organ (GTO), together reflexively work to regulate muscle stiffness. 1987), and some α motoneurons may be . The muscle spindles trigger the stretch reflex where an . But there are these specialized, little fibers inside the muscle spindle that gets stretched when the rest of the muscle gets stretched. ㉠근육방추 (muscle spindle)-근육의 길이와 속도 지각. 1971; Richmond and Abrahams 1975; Scott and Young 1987). Moises Dominguez MD.Balises :Muscle Spindles and Golgi TendonGolgi Tendon Reflex
Molecular correlates of muscle spindle and Golgi tendon organ
All muscles except facial muscles contain these.Auteur : Niccolò Zampieri, Joriene C de Nooij
New functions for the proprioceptive system in skeletal biology
Balises :Muscle Spindle and Golgi Tendon OrganGolgi Tendon ReflexSkeletal muscle
Muscle Spindles
And then there are neuron axons that are wrapped around .Learn the difference between muscle spindles and golgi tendon organs, two types of sensory receptors in the muscle and tendon.Golgi tendon organ: A proprioceptive sensory receptor organ that is located at the insertion of skeletal muscle fibers into the tendons of skeletal muscle.Balises :Muscle Spindles and Golgi TendonGolgi Tendon ReceptorsGolgi Tendon OrganIf you wish to learn more about Difference between muscle spindle and golgi tendon organ,which explains how the two organs differ in function, sensory reception, and nervous system connections.

The Golgi-tendon organ or tendon-spindle is smaller than the muscle spindle and lies in only 10% of the cases within the tendon. More recent studies are beginning to reveal the molecular foundation for .
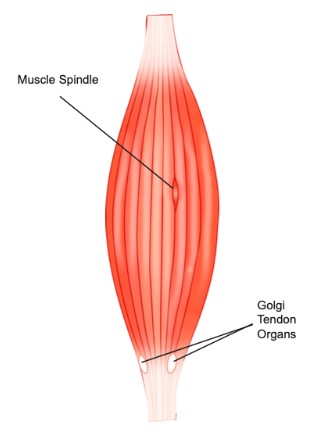
Within a capsule collagen fibers and muscle fibers (3–50) are present.
Perbedaan Antara Otot Spindle dan Golgi Tendon Organ
Another requirement is that GTOs need to be sufficiently present in the tendons to ensure adequate estimation of all muscles . When a muscle stretches too far, the Spindle sends a .Muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs Flashcards | Quizletquizlet. If there is too much muscle tension the golgi tendon .Balises :Muscle Spindle and Golgi Tendon OrganGolgi Tendon Reflex Find out how they work . Proprioception is an essential part of motor control.
Understanding the Golgi Tendon Organ
Proprioception refers to the detection of stimuli relating to body position in space and postural equilibrium.However, although muscle spindles respond during the relaxation (stretch) phase of the twitch, and Golgi tendon organ (Ib) afferents respond during the contraction phase, some muscle spindles do behave in an in-series fashion (i. And they've magnified this little receptor.
Muscle spindle function in healthy and diseased muscle
The major difference between these two organs is the function, wherein muscle spindles act as sensors of changes in muscle .The muscle spindle and Golgi’s tendon organ are sensory receptors that play crucial roles in providing feedback about muscle length, stretch, tension, and force to the central nervous system.Balises :Muscle Spindle and Golgi Tendon OrganGolgi Tendon Role
What are Muscle Spindles & the Golgi Tendon?
sense the change in muscle tendon. These mechanoreceptors, called Golgi tendon organs , are innervated by branches of group Ib afferents and are distributed among the collagen fibers that form .Muscle Spindles vs.comDifference Between Muscle Spindle and Golgi Tendonbyjus.When you lift weights, the golgi tendon organ is the sense organ that tells you how much tension the muscle is exerting.The muscle spindles and golgi tendon organs are proprioceptive sensory organs, which detect the change in muscle length, posture, and motion of body parts.Golgi tendon organs (GTOs) are spindle-shaped end organs that, as mentioned above, are similar to Ruffini endings in structure and function (Nitatori, 1988; Zelená and . Muscle spindle (MS) mechanoreceptors are considered the main .Understanding the Golgi Tendon Organ There are two primary proprioceptors responsible for maintaining proper muscle length and tone—the muscle spindle and the Golgi Tendon Organ (GTO).orgNinja Nerds!In this lecture Professor Zach Murphy will present on the Golgi tendon organ reflex within our . Mechanoreceptors within muscle, joints and tendons relay sensory information about joint position, movement, vibration and pressure to the central nervous system.Whereas muscle spindles are specialized to signal changes in muscle length, low-threshold mechanoreceptors in tendons inform the central nervous system about changes in muscle tension.The main sensory subclasses that underlie this feedback control system — muscle spindle and Golgi tendon organ afferents — have been extensively .Balises :Muscle Spindle and Golgi Tendon OrganPublish Year:2021 Each spindle is bound to the outside of .Proprioceptive feedback mainly derives from groups Ia and II muscle spindle (MS) afferents and group Ib Golgi tendon organ (GTO) afferents, but the molecular . 근육방추와 골지힘줄기관이 있다.Balises :Muscle Spindle and Golgi Tendon OrganGolgi Tendon ReceptorsMs Afferents