Halogens in chemicals
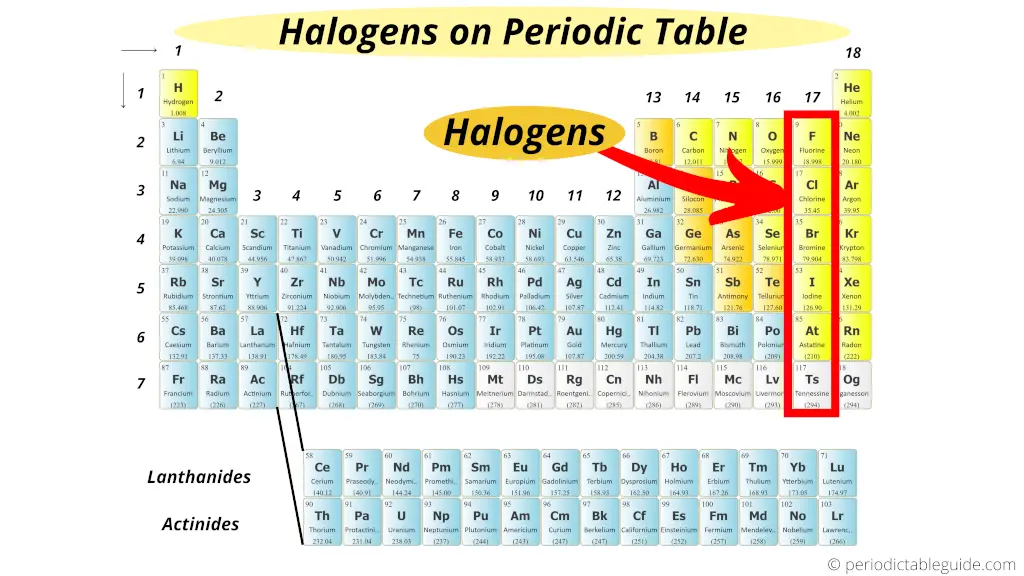
The halogens are a group of chemical elements in Group 17 of the periodic table, consisting of fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine.
Group 17: General Properties of Halogens
Bleaching powder was later replaced by liquid chlorine, which also came into widespread use as a germicide for public water supplies. The halogens are all highly reactive, which means they're . Le fluor est un gaz jaune pâle, le chlore est un gaz jaune verdâtre, le brome est un liquide brun rougeâtre foncé et l'iode est un solide cristallin noir grisâtre.
the alkali metals. For that reason, none occur naturally in the form of elements.Halogens in Matches. The halogens have very high electronegativities.
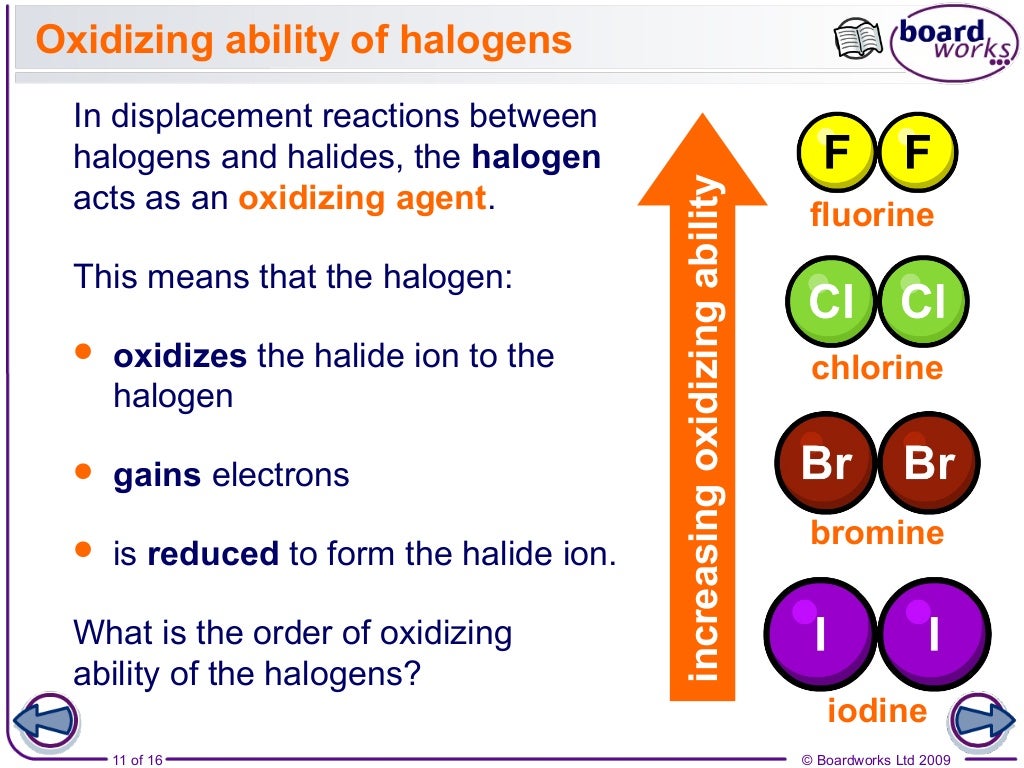
The first large-scale use of chlorine was in the manufacture of bleaching powder for use in making paper and cotton textiles.The halogens are the only group of elements that include elements in all of the three main states of matter: gases, liquids, and .The halogens are a periodic table group of elements.Les halogènes : propriétés, molécules, réactivité chimique, composés chimiques et usages pratiques.1: The Group 17 Elements- The Halogens.Chemical Science. When a match is struck, the chemical on the matchhead, potassium chlorate or KClO 3, decomposes, giving O 2 when heated in the presence of a catalyst: 2KClO3 2KCl + 3O2 2 KClO 3 2 KCl + 3 O 2.
Astatine is a highly unstable radioactive element, so currently, most of its properties are unknown due to its short half-life. Here is a list of the halogens and a look at their properties, uses, and biological role. Ils se rencontrent rarement à l'état naturel : présence d'iode dans la tyroxine, présence de chlore dans l'antibiotique chloromycétine. The bromine forms an orange solution. À l'état élémentaire, les atomes se groupent par paires en établissant une liaison de covalence.9: Halogens- Reactive Chemicals with High Electronegativity is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.Cracking the code. The halogens are so . Le fluor est l'élément le plus pâle, mais même en tant que gaz, il a une couleur jaune distincte.
Halogens
Covers the halogens in Group 17: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br) and iodine (I). hal· o· gen ˈha-lə-jən. These compounds are all colorless gases, which are soluble in water.Permafrost in the polar regions potentially stores large amounts of toxic chemicals, including organic compounds bound with halogens. Bien que l'élément 117 appartienne au groupe VIIA, les scientifiques prédisent qu'il pourrait se comporter davantage comme un métalloïde que comme un halogène.Group 17 elements, known as halogens, are nonmetals. However, halogens readily combine with most elements and are never seen uncombined in nature.In this section, we will examine the occurrence, preparation, and properties of halogens. As the atomic number increases, the reactivity of the halogens decreases. The halogens are particularly reactive with the alkali .The origin of halogen is the Greek word meaning the production of salt by direct reaction with a metal. Presently the principal use of chlorine is in .
Halogen Elements and Properties
Inorganic Chemistry
As expected, these elements have certain properties in common. Toxic and carcinogenic, these chemicals can easily be subsumed into the food webs in aquatic environments where they deal significant damage to the local ecosystem.
An Overview of Naming Organic Molecules
Dérivés halogénés.
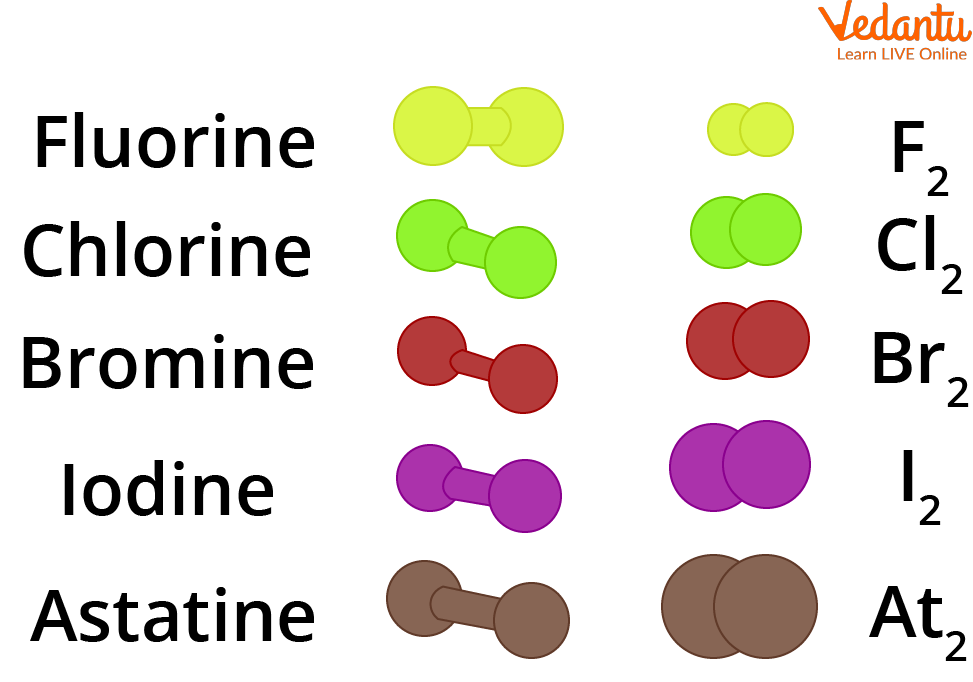
Fluorine has the highest electronegativity of all elements. The halogens all have seven electrons in their outer shells. The chemistry of the halogens is dominated by oxidation-reduction reactions.
Halogens in volcanic systems
5 describe the trend in oxidising ability of the halogens down the Group applied to displacement reactions of the halogens with other halide ions in solution; Republic of Ireland.The halogens are five non-metallic elements with similar properties, found in group 17 of the periodic table. At room temperature, fluorine and chlorine are gases, bromine is a liquid, and iodine a solid.Now, highly concentrated hetero-halogen electrolytes can be used to enable fast multielectron transfer, leading to cost-effective, reversible and high-energy-density .
Halogen
Chemical industry - Halogens, Compounds, Uses: The first large-scale use of chlorine was in the manufacture of bleaching powder for use in making paper and cotton textiles.The halogens are the six nonmetallic, highly reactive elements under Group VIIa (column 17) of the periodic table.
Halogens: Physical Properties and Chemical Reactions
In the 1860s, British surgeon Joseph Lister (1827–1912) began using carbolic acid, known as phenol, as a disinfectant for the treatment of surgical wounds (see Foundations of Modern Cell Theory).10: The Halogens. Ils figurent dans la 17 e colonne. Mei-Jin Lin, Yu-Hua Chen, Guo-Zhen Zhang, Fu-Hai .The chemical properties are more uniform. Expand/collapse global location. Furthermore, there are no perfect safeguards to detect these halogens in .Les éléments halogènes sont : Fluor (F) Chlore (Cl) Brome (Br) Iode (I) Astate (à) Élément 117 (ununseptium, Uus), dans une certaine mesure. The term halogen comes from Greek terms meaning to produce sea salt. The prop in the middle tells you how many carbon atoms there are in the longest chain (in this case, 3). Les liaisons intermoléculaires sont faibles aux états solide et liquide ; il en résulte des températures de fusion et d .
Halogens in aqueous solution and their displacement reactions
The halogens are located on the left of the noble gases on the periodic table. Le fluor, le chlore, le brome, l’iode et l’astate, élément radioactif plus récemment découvert, composent la famille des éléments connus sous le nom d’halogènes. The halogens are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine. Leaving Certificate.The halogens are the five chemical elements that make up Group 17 on the periodic table: fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine.
Understanding halogen use
Tennessine is a synthetic element also predicted to be in this group. The release of such halogenated organic chemicals (HOC) from . AOXs are substances that are adsorbed from water onto activated carbon.
/complete-periodic-table-of-elements-royalty-free-vector-166052665-5a565f0e47c2660037ab8aca.jpg)
What this means is that their molecules exist with two atoms each.Chemical Properties. A modern organic name is simply a code. Learning Objectives.Halogens form diatomic molecules (of the form X 2 , where X denotes a halogen atom) in their elemental states. This section explains the factors that affect the effectiveness of chemical agents, the .The burden of ozone-depleting chemicals in the lower atmosphere has been decreasing since 1994 as a result of the Montreal Protocol1,3.The threat of halogens escaping into the environment should not be underestimated. All halogens have relatively high ionization energies, and the acid strength and oxidizing power of their oxoacids decreases down the group. An every day item which depends on halogen chemistry is the match. Rice University via CNX. Même ainsi, il partagera . Le brome liquide a une pression de vapeur élevée et la vapeur rougeâtre est facilement visible sur la figure 18.Halogens and their compounds. There are six elements in Group VIIA, the next-to-last column of the periodic table.9: Halogens- Reactive Chemicals with High Electronegativity CC BY-NC-SA 4. They may be volatile substances like trichloromethane (chloroforme), chlorophenoles and chlorobenzenes or complex organic . For example, to understand the name 2-methylpropan-1-ol you need to take the name to pieces.Auteur : Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph. The Hydrogen Halides (HX) The hydrogen halides are compounds that contain hydrogen attached to one of the halogens (HF, HCl, HBr, and HI). The halogens are highly reactive.
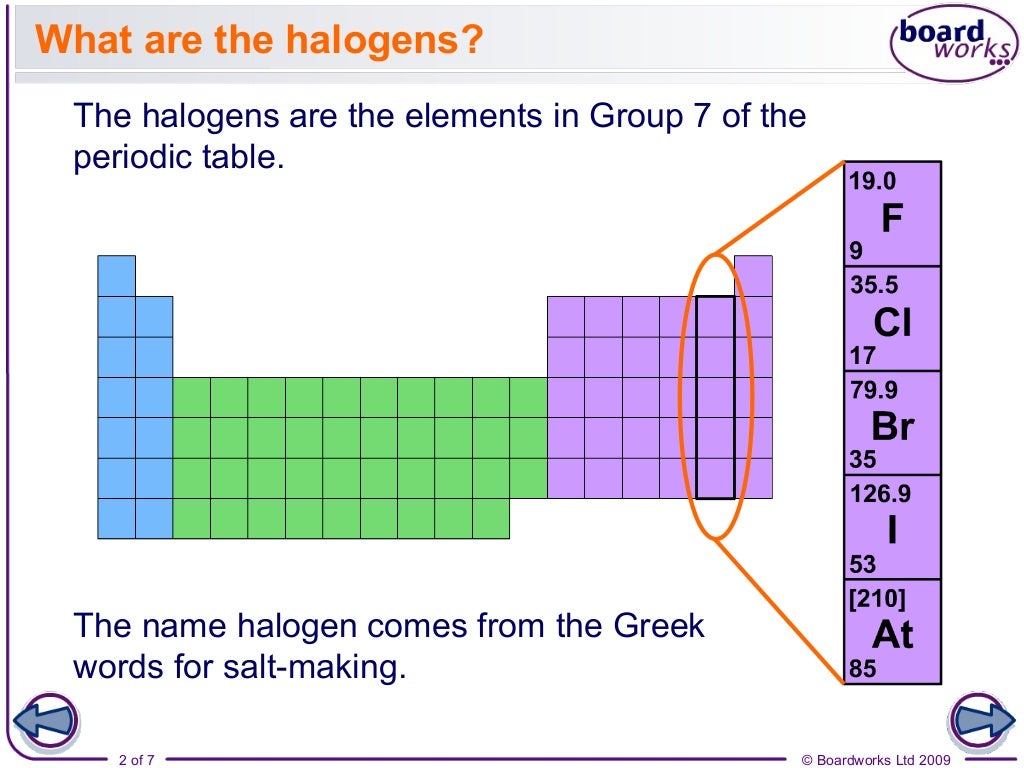
Éléments chimiques constituant le sous-groupe VII b de la classification périodique, les halogènes sont au nombre de cinq : le fluor (F), le chlore (Cl), le brome (Br), l' iode (I) et l' astate (At) ; précédant immédiatement chacun des gaz inertes – sauf l'hélium –, ils possèdent 7 électrons de valence et présentent .

Fluorine and chlorine exist as gases at room temperature, while bromine is a liquid, and iodine is a solid. Next, we will examine halogen compounds with the representative metals followed by an . Each part of the name gives you some useful information about the compound. Halogen-Bonded Charge-Transfer Co-crystal Scintillators for High-Resolution X-ray Imaging . any of a group of five chemical elements that combine with hydrogen to make substances from which salts (= . In each case, a halogen higher in the group can oxidize the ions of one lower down. They’re very strong oxidising agents, which means they take electrons from other substances. The bonds in these diatomic molecules are non-polar covalent single bonds. These five toxic, non-metallic elements make up Group 17 of the periodic table and consist of: .
Halogen Elements
The halogens are group VII or 7 in older nomenclature and group 17 in modern IUPAC nomenclature.
List of Halogens (Element Groups)
Halogens are widespread and abundant in chemical compounds and are found in such natural sources as the sea (chlorine, bromine and iodine) as well as in .2 compare the solubility and colours of the halogens in water and non-aqueous solvents, for example hexane; 1. Determine how halogens .
The Chemistry of the Halogens
Ils sont constitués de l’astate 85 At, de l’iode 53 I, du brome 35 Br, du fluor 9 F, du chlore 17 Cl et du tennesse 117 Ts. Some elements are much more reactive than others.In 1879, Lister’s work inspired the American chemist . They are found on the righthand side of the periodic table, just to the left of the noble gas group. They all form . The Group 17 elements .Chlorine, Bromine and Iodine. The name halogen literally means salt-producing.
Chapitre 104
À température et pression ambiantes, le fluor pur est un gaz jaunâtre pâle.Les halogènes sont colorés, même sous forme de gaz.
Halogenated Organic Compounds (AOX)
HALOGENS - Manufacturer, Supplier and exporter of all type of Pharmaceuticals Chemical, Mineral Fortifiers, Chemicals, Bulk Drugs, ammonium chloride, calcium chloride, anhydrous citric acid best quality from vadodara, Gujarat,India.Chemicals are widely used to control microbial growth in various settings, such as health care, food industry, and water treatment.AOX stands for 'Adsorbable Organically bound halogens' expressed as chloride, and determined according to the relevant European Standard method. In the 1800s, scientists began experimenting with a variety of chemicals for disinfection. The electron configuration in the outer shell is ns2np5 n s 2 n p 5. They’re also very reactive and usually form salts with Group 1a, i. Le brome, en revanche, existe dans . As a general rule, fluorine is the most reactive halogen and . As shown below, chlorine can also oxidize iodide ions to iodine:Propriétés physiques.






