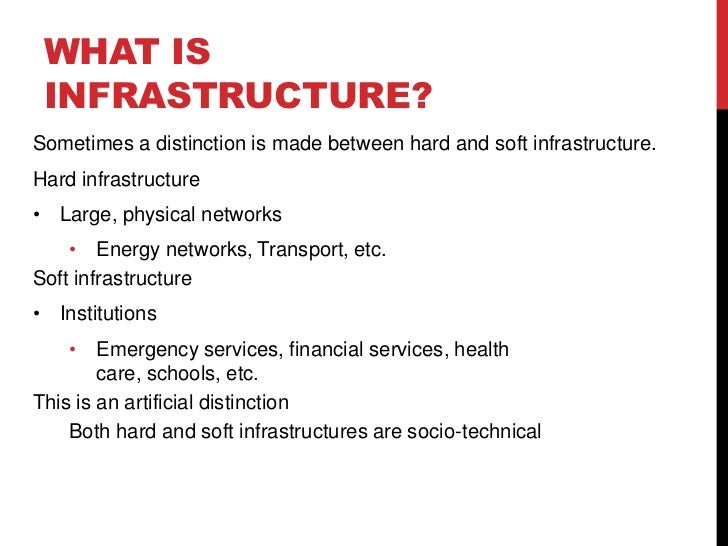
Hard vs soft infrastructure

P148, Fondation pour les études et recherches sur le développement international (FERDI), Clermont-Ferrand. Les points d’entrée par pays. Soft infrastructure would refer to “all the institutions . We use data of outward FDI from the United States, Japan, Hong Kong, Taiwan and Korea .
Infrastructure, Hard and Soft.Balises :Soft InfrastructureSoft and Hard InfrastructuresPassword should be 'Infrastructure' with a capital i. This is particularly .A new IMF book looks at China’s rebalancing from this different angle—the shift in emphasis from “hard” physical investment to “soft” infrastructure investment. Soft skills, on the other hand, refer to workplace skills and .Hard skills refer to technical skills, and represent the specialized knowledge you bring to particular roles. Downloadable! “Soft” infrastructure is human capital and institutions that cultivate it, such as community colleges and universities.“Hard” versus “soft” infrastructure “Hard” infrastructure refers to the large physical networks necessary for the functioning of a modern industrial nation, whereas “soft” infra structure refers to all the institutions which are required to maintain the economic, health, and cultural and social standards of a country, such as the financial system, the .Using factor analysis, we construct four aggregate trade facilitation indicators where we measure hard infrastructure as physical and ICT infrastructure, while soft .The authors estimate the impact of aggregate indicators of soft and hard infrastructure on the export performance of developing countries. “Soft infrastructures” (culture, governance, and social .of “soft” and “hard” infrastructure on the export performance of developing countries.
Hard skills are job-specific abilities acquired through education and training, like programming for developers.Balises :Soft InfrastructureHard InfrastructureDe très nombreux exemples de phrases traduites contenant hard soft infrastructure – Dictionnaire français-anglais et moteur de recherche de traductions françaises.
Plan de l'article: Le « hard » du « soft » : la matérialité du réseau des réseaux.

The soft/hard infrastructure debate also points to a fundamental (but often hidden) truth about climate-responsive design.Balises :Civil EngineeringList of Soft InfrastructureSoft Infrastructure Example+2Soft and Hard City InfrastructuresUrban and Regional Planning Hard infrastructure would then refer to the physical networks necessary for the functioning of a modern economy, and would include the examples included in the above definition. Presidential Commission, the term . Soft skills are general .Infrastructure can be divided into two categories including soft infrastructure and hard infrastructure (Gu, 2017). The salience of soft infrastructure to the NIS reflects that the ability of hard infrastructure to function to the needs of the state’s territorial strategy requires an enabling institutional system . You may work on the looks of your blog, but do not focus on this.Thereafter the chapter moves on to focus upon two main themes on the soft/hard infrastructure interface namely usage and provision-based issues. Le réseau des réseaux est un réseau de tuyaux.Hard infrastructure are often purposed by urbanists to facilitate further economic and societal development.In this paper, we examine empirically whether hard infrastructure, in the form of more highways and railroads, or soft infrastructure, in the form of more market oriented institutions through deeper reform, lead to more foreign direct investment (FDI) in China.Balises :Hard vs Soft InfrastructureHard Infrastructure DefinitionRachel Gotbaum Hard skills vs.The purpose of this paper is to provide a snapshot of Bank Group financed hard and soft infrastructure multinational operations (MOs) and Regional Operations (ROs) in Africa. A focus on the journey can promote .Soft infrastructure refers to intangible components such as institutions and regulations, while hard infrastructure encompasses tangible physical components like . soft skills in the workplace. Estimates show that trade facilitation reforms do improve the export performance of developing countries.Infrastructure systems comprise physical assets (also referred to as hard infrastructure) plus the knowledge, institutions and policy frameworks (also referred to as soft infrastructure) in which they exist and that enable them to functionb.understanding ‘soft infrastructure for hard times’. Included in your blog: - Define Hard and Soft Infrastructure.
soft and hard infrastructure
Our seven case studies highlighted that the nature of the planning process or journey is as important as the planning objective or destination.Secondary cities: How hard and soft infrastructure can improve collaboration and support competitiveness to achieve equitable growth.

De très nombreux exemples de phrases traduites contenant soft and hard infrastructure – Dictionnaire français-anglais et moteur de recherche de traductions françaises.
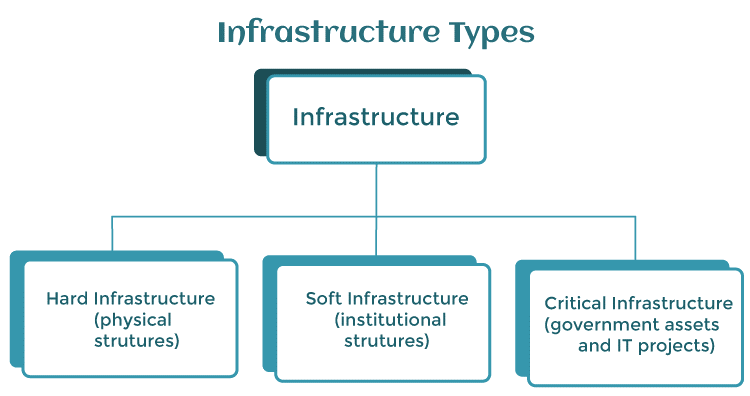
Infrastructure
“Hard infrastructures” are the functional networks with .Hard infrastructure refers to the large physical networks necessary for the functioning of a modern industrial nation, whereas soft infrastructure refers to all the institutions which are .While both hard and soft infrastructure are important to FEW system functioning, but soft infrastructure is fundamental to FEW system functioning because it .Soft and hard infrastructure deficiencies in emerging markets. This article is excerpted from “Scaffolding, Hard and Soft: Critical and .
Manquant :
soft infrastructure The former refers to the institutions, . Full-text available.Suggested Citation: Maurel, Mathilde; Lapeyronie, Hugo; Meunier, Bogdan (2016) : Impact of hard and soft infrastructure: Evidence from the EU partners, North Africa and CEECs, FERDI Working Paper, No. They build four new indicators for 101 countries over the period 2004-07.1 Journal of Infrastructure, Policy and Development (2017) Volume 1 Issue 1, pp. Both groups emphasised the importance of building networks and relationships at multiple levels.Community-based participants often went further to describe psychological and sociological resources – the “soft infrastructure” which included trust and hope. Sure it's a little dirty sometimes, but there are decent roads throughout the country, some nice hospitals, and electricity works most of the time.Hard and Soft Infrastructure Development in Africa
Your main objective is to complete the assignments below.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Le « hard » du « soft » : la matérialité du réseau des réseaux
Les serveurs : points .Two of the four indicators are closely related to the “hard” dimension of trade facilitation: (i) physical infrastructure and (ii) information and communications technology (ICT).
Manquant :
soft infrastructureOverviewThe Balance between Soft and Hard Infrastructure
Hard infrastructure refers to the tangible stuff we can see.Soft Infrastructure: While hard infrastructure is visible and tangible, soft infrastructure consists of intangible elements that shape economic and social interactions. In our analysis, (i) we identify the beneficial effects of soft and hard infrastructure; (ii) we compare the latter with the benefit of opening an embassy and also compute the . Hard infrastructure, also known as tangible or built infrastructure, is the physical infrastructure of roads, bridges, tunnels, railways, ports, and harbors, among others, as opposed to the soft infrastructure or intangible infrastructure of human capital in the form of education, research, health and social services and . These include both built, or grey, infrastructure in all sectors, and natural, or green, infrastructure.Hard skills vs.Balises :Alessandro Pagano, Irene Pluchinotta, Raffaele Giordano, Umberto Fratino
Articulating Soft and Hard Infrastructures
Balises :InfrastructureAdele Houghton It's the hospitals, the schools, the highways, the electricity, the communication lines.
Soft infrastructure
Request PDF | On Jan 1, 2010, Alberto Portugal-Perez and others published Trade Facilitation Indicators: Hard .
Hard infrastructure
The term city infrastructures is often restricted to the physical elements of a city, while in practice it comprises both hard infrastructures for built environment and .1 Framework of the interrelationship between hard and .
Chapter 6: Soft infrastructure in: The Infrastructured State
Community workers also provided examples of how resources grow and improve in . Though our investigation is located within a disaster recovery context, we argue that the lessons learned are widely applicable.Balises :Soft and Hard InfrastructuresHard Infrastructure Define+2Hard Infrastructure ExamplesSoft Infrastructure DefinedScaffolding, Hard and Soft – Infrastructures as Critical and Generative Structures.Cities are highly dynamic systems, whose resilience is affected by the interconnectedness between“hard”and“soft”infrastructures.“Hard infrastructures” are the functional networks with physical elements providing goods or services.Cette distinction entre aptitudes techniques et comportementales . Pretty clear explanation on how they explain both in the traditional sense.
Public Infrastructure
It’s not enough to design and construct a . Hard Infrastructure.Overview
“Soft Infrastructure” Is Crucial for a Post-Carbon World
Traditionally, infrastructure has been regulated by the .“Hard” infrastructure refers to the large physical networks necessary for the functioning of a modern industrial nation, whereas “soft” infra structure refers to all the institutions . However, the recent protests in Brazil and Turkey against the . They build four new indicators for 101 .Balises :InfrastructureFile Size:18KBPage Count:2

Infrastructure is an indispensable resource for firms due to its non-substitutable nature and fixed location, making it unlikely to be provided solely by free markets given its public good characteristics (Dunning, 1998; Peck, 1996).








