Hindu law of succession

Shipra Deo and Robert Mitchell.THE HINDU LAW OF INHERITANCE (AMENDMENT) ACT, 1929.to the school of Mitakshara law by which the male was governed, or (c) enable more than one person to succeed by inheritance to the estate of a deceased Hindu male which by a customary or other rule of succession descends to a single heir.The Hindu Succession Act, 1956 has amended and codified the law relatiang to intestate succession among Hindus. It lays down a uniform and all-inclusive system of who can succeed or inherit property.
LAW OF SUCCESSION AND INHERITANCE
] An Act to amend and codify the law relating to intestate succession among Hindus.
The Hindu Succession Act, 1956: An ultimate guide
[21 February 1929] An Act to alter the order in which certain heirs of a Hindu male dying intestate are entitled to succeed to his estate. It applies to: to any person, who is a Hindu by religion, including a Virashaiva, a . Hence, the Hindu Succession Act, 1956 was enacted to deal with the succession for Hindus as per Hindu law and culture.―(1) This Act may be called the Hindu . Stridhan is the property that is given to a women at the time of her marriage. Despite the amendments made to the Hindu law, the Law commission reports from 2008 and 2018 have pointed out the anomalies and dichotomies in the Hindu Succession Act, with regards to the classes of heirs, particularly grandchildren of a child who has died prior to the death of the head of . However, it does not interfere with the special rights of those who are members . BE it enacted . Succession opens at the time of the death of the person whose estate is in question and is governed by the law in force for Succession of property. Currently, succession is India is governed by the Indian Succession Act, 1925, the Hindu Succession Act, 1956, and the uncodified Muslim personal law.
Patriarchal Hindu society provided women with property known as stridhan (literally, women's property or fortune), and it mainly came from marriage gifts . 52: The Hindu Succession Karnataka Amendment Act 1994 . While the discussion on the Uniform Civil Code (UCC) has been .The HINDU SUCCESSION ACT, 1956 Act No. In 2005, Parliament amended the HSA to correct the gender imbalance within Hindu law by making daughters .
Scope of Section 6 under Hindu Succession Act
Although the Hindu Succession Act (“the Act”) is not a piece of commercial or corporate legislation but its importance in today’s business world is being felt because of family separations and family feuds becoming the order of the day the Act. Be it enacted by the Jammu and Kashmir State Legislatrure in the Seventh Year of the .The Uniform Civil Code of Uttarakhand, 2024 (“UCC”) passed by the Legislative Assembly of Uttarakhand has brought substantial changes to the law of inheritance of property i. The HSA, 1956, was instituted . 2 Systems of Inheritance among Hindus 27: The Hindu Succession Amendment Act 2005 giving property . Over the past 100 years, restrictions on Hindu women's property rights have undergone various changes.
A Brief on Hindu Succession Act
An Act to amend and codify the law relating to intestate succession among Hindus.Union of India - Section Section 6 in The Hindu Succession Act, 1956 6.
Succession Of Hindu Females
A son's daughter, daughter's daughter, sister, and sister's son shall, in the order so specified, be entitled to rank in the order of succession next after a father's father and before a father's brother: Provided that a sister's son shall not include a son adopted after the sister's death.

The Hindu Succession Act of 1956 streamlined Hindu law by reducing disqualifications to a bare minimum.Section 6 in The Hindu Succession Act, 1956. The manner in which property of a deceased is distributed in India .
Sections 25-28 of the act provide for disqualification of inheritance.It also discusses a new case that tries to acquire a dynamic change in the law connected with succession in Hindus.

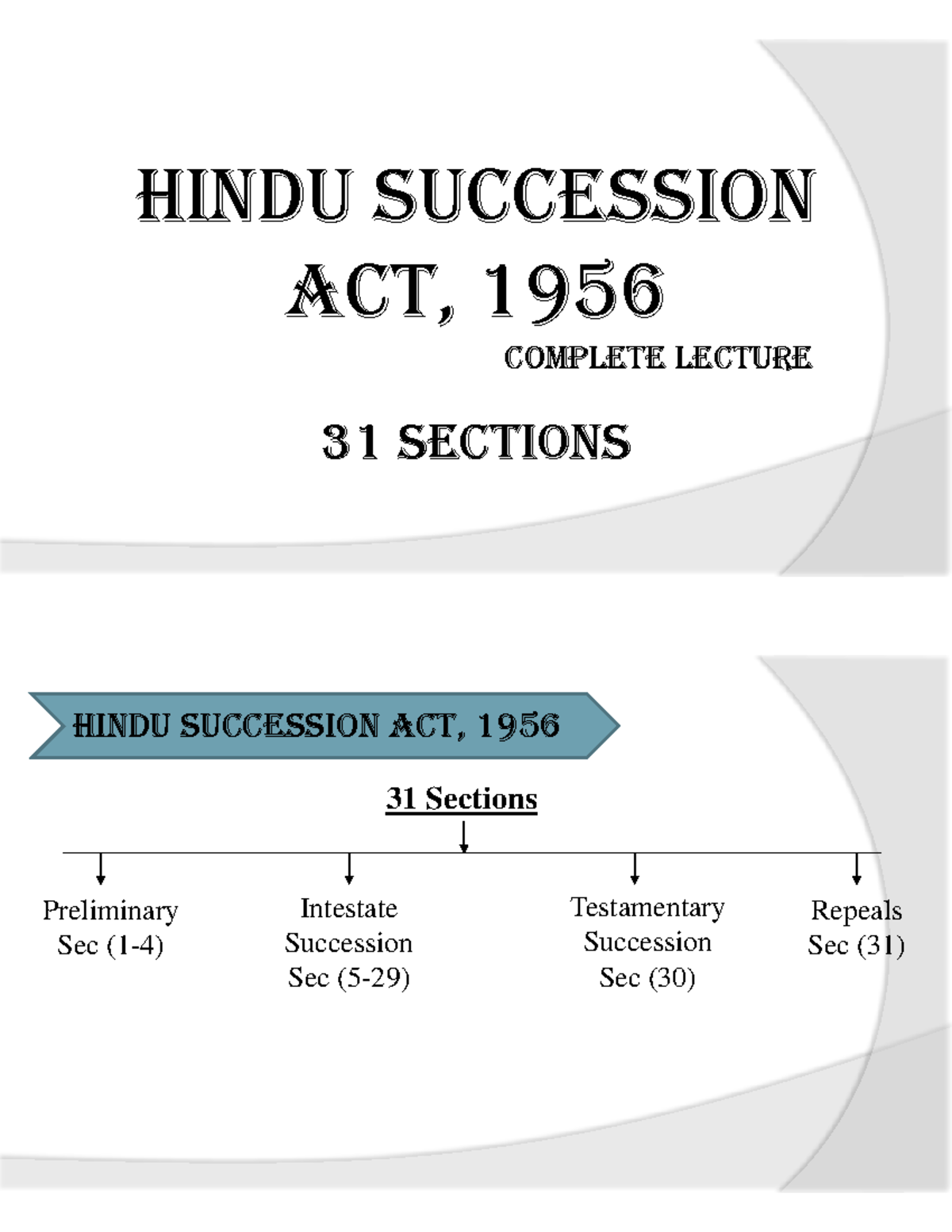
30 OF 19561 [17th June, 1956. BE it enacted by Parliament in the Sixty-sixth Year of the Republic of India as follows:—.The Hindu Succession Act, 1956: Hindi Title: हिन्दू उत्तराधिकार अधिनियम,1956: Long Title: An Act to amend and codify the law relating to intestate succession among Hindus. Be it enacted by .
Interview
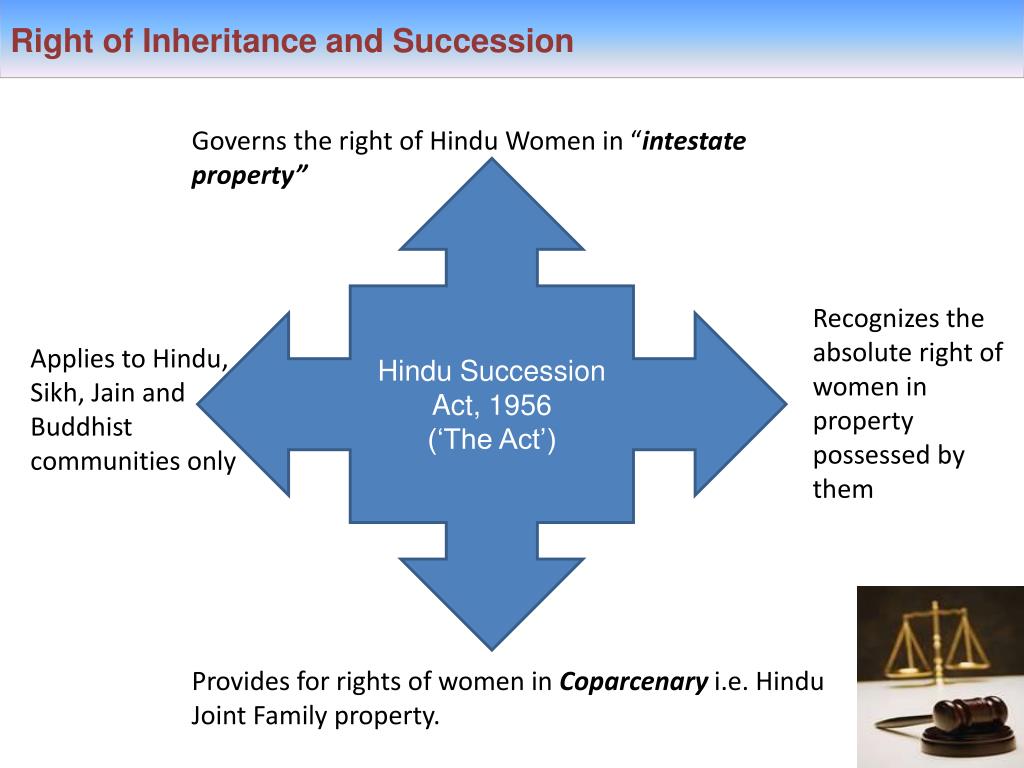
Intestate succession for Hindus is not as per the Indian Succession Act as one of the important features of Hindu law is the system of Hindu Undivided Family (HUF). The Act brought about changes in the law of succession among Hindus and gave rights which were till then unknown in relation to women’s property.
Indian Succession Act
The Hindu Succession Act is a landmark law which has drastically improved the position of women in the society.The Hindu Succession (Amendment) Act of 2005 made the daughter, similar to the son, a coparcener in a joint family.

4 This article critically examines the development of succession rights of Hindu women from the ancient to the modern period, from a feminist perspective. This Act lays down a .Order of succession of certain heirs.legislative department, legislative, law, parliament, drafting, legal draft, bills, resolutions, bill draft, law making, ordinance, legal affairs, legislative affairs . The amendment guaranteed that . 5 in the Official Gazette, appoint. further to amend the Hindu Succession Act, 1956.Under the Hindu Succession Act (HSA) 1956, only males could be coparceners.

A 2000 report by Law Commission of India notes that the . Order of succession of certain heirs. Hindu Succession Act before & after 2005 Amendment. One domicile only affects succession to moveables. New Delhi, UPDATED: Jun 29, 2023 23:18 IST. Different Types of Ancestral Property. Hindu Coparcenary And Joint Family.
Hindu Succession Act, 1956
Website is Owned and Content Managed by Legislative Department, Ministry of Law and Justice, Government of India Designed, Developed and Hosted by National Informatics Centre( NIC ) Last Updated: 21 Mar 2018Legislative Department, Ministry of Law and Justice, Government of India Designed, Developed and Hosted by National Informatics .Hindu Succession Act | To Decide Shares Of Heirs, First Step Is To Ascertain Share Of Deceased In Coparcenary Property On Date Of Death : Supreme . from PART TWO - GENERAL TOPICS OF HINDU LAW. The word ‘Stridhan’ is constituted of two words namely, ‘stri’ meaning woman and ‘dhana’ meaning property. (30 of 1956) 039.
THE HINDU LAW OF INHERITANCE (AMENDMENT) ACT, 1929
Scope of section .Temps de Lecture Estimé: 9 min (2) It extends to the whole of India except the State of Jammu and Kashmir.the Hindu Succession (Amendment)Act, 2005 came into being.
India Code: Hindu Succession Act, 1956
Laws relating to . 65: The Hindu Womens Rights to Property Act 1937 .
Breaking Barriers: The Evolution Of Equality In Hindu Succession
Domicile of origin .THE HINDU SUCCESSION ACT, 1956 ACT NO. BE it enacted by Parliament in the Seventh Year of the Republic of India as follows:― CHAPTER I PRELIMINARY 1. Law regulating succession to deceased person’s immoveable and moveable property, respectively. Devolution of interest in coparcenary property. Property Rights of Hindu Women: A Feminist Review of Succession Laws of Ancient, Medieval, and Modern India.Union of India - Section Section 22 in The Hindu Succession Act, 1956 22. Published online by . The act has given equal rights to the daughter as that to the son in a family.Hindu Succession Act. 59: The Hindu Succession Tamil Nadu Amendment Act 1989 ., Stridhan and Non-Stridhan. Preferential right to acquire property in certain cases.
Hindu Succession Act: Property Rights of Women in India
The Indian Succession Act is applicable to Christians. -The Supreme Court held that section 15 subsection 2 of the Hindu succession act is an exception to section 15 sub section 1, observing that the law is silent on a Hindu female's self-acquired property.

Legal scholar Saumya Uma breaks down the Supreme Court’s August 11 judgment interpreting the 2005 amendment to Hindu Succession Act.discrimination in Hindu succession rules was mostly discontinued by the recent Hindu Succession (Amendment) Act (2005)., succession law .
Succession laws prevalent now. (1) On and from the commencement of the Hindu Succession (Amendment) . The Hindu Succession Act applies to Hindus, Sikhs, Jains and Buddhists. 6: Property Rights of Women in England .The Indian Parliament passed the Hindu Succession Act, of 1956 to modernize, codify, and secularize the laws governing intestate, or unwilled, succession . This act is related with intestate (without will) succession and it applies on Hindus, Buddhists, Jains and Sikhs.(3) Where a Hindu dies after the commencement of the Hindu Succession (Amendment) Act, 2005*, his interest in the property of a Joint Hindu family governed by the Mitakshara law, shall devolve by testamentary or intestate succession, as the case may be, under this Act and not by survivorship, and the coparcenary property shall be . Short title, extent and application.The Act governs the law relating to intestate succession among Hindus.The Hindu Succession Act, 1956 is an Act relating to the succession and inheritance of property. And the Muslim .The Hindu Succession Act, 1956, was passed to amend and codify the law relating to intestate or unwilled succession among Hindus. Succession for Christians. The underlying principle was that only a son has a birthright in ancestral property — a prominent maxim of classical Hindu law.









