History of atomic force microscopy
The precursor to the AFM was developed by Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer in the early 1980 at IBM .
Kamal Youcef-Toumi. While scanning probe microscopy allows accessing atomic-scale structures in real space, elemental discrimination and defect characterization usually rely on indirect assumptions and . Haynes, Philip J.Auteur : Kavit H. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is an amazing technique that allies a versatile methodology (it allows the imaging of samples in liquid, vacuum or air) to imaging with unprecedented resolution. Their original AFM consisted of a diamond shard attached to a strip of gold foil. Habibullah
History and Background of Atomic Force Microscopy
Analytical Sciences Digital Library. 121 likes • 72,709 views.Müller DJ, Dumitru AC, Lo Giudice C et al (2020) Atomic force microscopy-based force spectroscopy and multiparametric imaging of biomolecular and cellular systems.This article reviews the progress of atomic force microscopy in ultrahigh vacuum, starting with its invention and covering most of the recent developments.Atomic Force Microscopy: An Introduction.Auteur : Yves F. AFM is a term that refers to a collection of non-destructive surface analysis techniques employed at . This Review addresses experimental considerations, including operating modes and .Atomic Force Microscopy in the Life Sciences.AFM - Scanning Probe Microscopy. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) was developed in 1986 by the researchers Gerd Binnig, Christoph Gerber, and Calvin Quate ( .
Atomic Force Microscopy: An Introduction
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) has become a powerful tool to investigate 2D materials and the related 2D materials (e. The conductive atomic force microscope (CAFM) records the currents flowing at the tip/sample nanojunction simultaneously to the topography.
Introduction to Atomic Force Microscopy
It begins with a broad discussion on a list of tools available for imaging at micro-/nanoscale.
Atomic force microscopy: from theory to application in food science
In fact, one of the earliest applications of AFM outside of . Based on contributions from the first international conference of AFM in biological sciences and medicine (AFM . Today, dynamic force microscopy allows us to image surfaces of conductors and insulators in vacuum with atomic resolution.Since its invention, atomic force microscopy (AFM) has established a significant role in a wide range of scientific and technical study domains as a potent instrument for . Nat Rev Phys 3 (2):76–91.
Introduction to Atomic Force Microscopy
16), of which atomic force microscopy (AFM) is perhaps the best known example [51].Before answering the question, let us look at the history of atomic force microscopy quickly.

These large forces can have drastic effects on the contrast mechanism of repulsive contact imaging.With the improvement of the AFM many new measurement modes evolved: Especially tailored tips for Magnetic Force Microscopy (MFM, 1995), hardend tips (Diamond, 1999), conductive AFM (conductive Diamond tips, 1999), high resolution measurements (SuperSharp Silicon, 1997), measurements of sub-micron features in .Atomic force microscopy.Atomic force microscopy (AFM) meets these demands in an all-in-one instrument. Here, we review key technological improvements that have established AFM .The atomic force microscope (AFM), built in the mid-1980s, uses a sharp probe to enlarge surface features.

In its more than 25-year history, AFM has had its scope rapidly expanded to various scientific fields.
Atomic-force microscopy
This article reviews the progress of atomic force microscopy in ultrahigh vacuum, starting with its invention and covering most of the recent . The forces in the contact region can become so large that the . Chapter © 2019. Atomic-force microscopy enables subnanometer imaging resolution, to extract geometric parameters of reference structures that advance measurement science, and to quantify the accuracy of device .Atomic force microscopy (AFM) enables the imaging and manipulation of individual molecules at atomic resolution.
The realization of scanning tunneling microscopy 1 and atomic force microscopy (AFM) 2 has enabled the real-space imaging of surface morphology . Atomic force microscopy utilizes a microscale probe to produce three dimensional image of surfaces at sub nanometer scales.
Imaging modes of atomic force microscopy for application in
Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. Imaging of nano-sized particles and sample features is crucial in a variety of research fields, for instance, in biological sciences, where it is paramount to investigate .

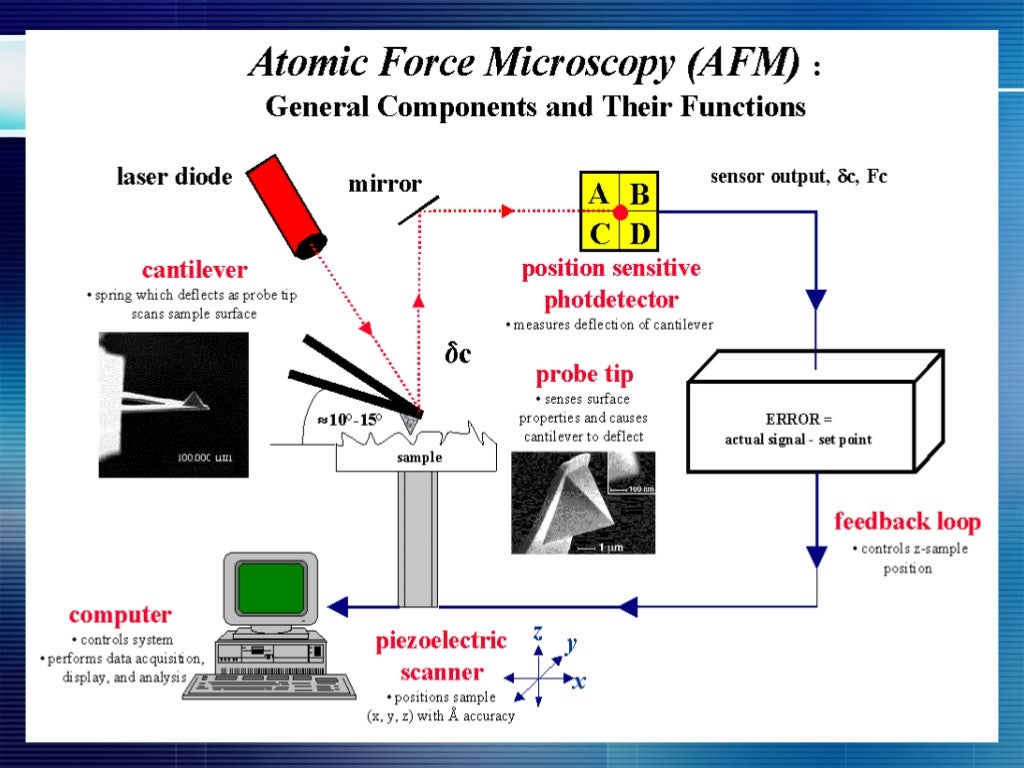
In this commentary, I will describe AFM image . The first MFM images were obtained by Martin and Wickramasinghe [52] in 1987. HOW DOES THE AFM WORK? AFM .The invention of atomic force microscopy (AFM) in 1986 1 is a milestone in the history of nanotechnology 2 and created new opportunities in physics, chemistry, ., 21 and within 18 months, the technique was used to accomplish atomic-scale imaging of crystalline surfaces. First Online: 13 October 2023. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Page ID. Chem Rev 121 (19):11701–11725.Magnetic force microscopy (MFM) is one of the scanning probe microscopy (SPM) techniques (see Fig. The most widely used technique for atomic-resolution . A mechanical probe is used to gather information by touch with the aid of piezoelectric elements that enable very small but precise movements through electronic . Here, data on the field profile of a thin-film magnetic recording head were . Cite this protocol.First demonstrated in 1987, 1,2 magnetic force microscopy (MFM) is a well-established and widely used technique. (Right) Method of two-axis surface scanning. Over the last three decades, the method has been extensively used in a vast number of applications, where the knowledge of the local distribution of the magnetic properties of thin film materials and their nanostructures is of . The AFM opened the door to imaging other materials, such as polymers and biological . Several techniques derived from this microscopy have appeared in recent years, .During the last three decades, a series of key technological improvements turned atomic force microscopy (AFM) into a nanoscopic laboratory to directly observe and chemically characterize molecular and cell biological systems under physiological conditions. Here, I first provide a brief history of HS-AFM, then ., graphene) for . Dufrêne, Toshio Ando, Ricardo García García, David Alsteens, David Martinez-Martin, Andreas . To introduce this special issue of the Journal of Molecular Recognition dedicated to the applications of atomic force microscopy (AFM) in life sciences, this paper presents a short summary of the history of AFM in biology.
Atomic force microscopy
Over the past three decades, atomic force microscopy (AFM) has emerged as a key platform enabling the simultaneous morphological and mechanical . 22 AFM is a force .My lecture at the Joint IUPAB/NanoLSI Workshop on Computational and Theoretical Methods Applied to Atomic Force Microscopy gave an opportunity to speak about the history of image files and image analysis methods and describe the recently developed Localization AFM method. Subsequently, the book’s scope, objectives, and chapter topics are outlined.Brief History and Comparison In 1986, the Atomic Force Microscope was invented by Gerd Binning to overcome a limitation of the AFM’s predecessor, the Scanning Tunneling Microscope. The diamond tip contacted the surface .Abstract: Over the past three decades, atomic force microscopy (AFM) has undergone a series of design changes to attain a flat XY scan and stable non-contact mode in ambient atmosphere. Ideally the interaction occurs at an atomically .Brief History of AFM .Atomic Force Microscopy 27 For a typical tip radius of R = 100nm and -y = 70mN/m a force of 90nN is calculated which is large compared to typical van der Waals forces of 1-10nN. The fundamental principle of atomic force microscopy (AFM) is to obtain images of a surface by measuring deflections on a nanoscale probe.This page titled 3: Atomic Force Microscopy is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 2. The CAFM can be used to monitor the properties of materials, as well as to modify them with atomic resolution.This insightful book covers the theory, practice and applications of atomic force microscopes and will serve as an introduction to AFM for scientists and engineers .History and Background of Atomic Force Microscopy Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM) is the result of a long evolutionary process that has its roots in the . Mar 20, 2015 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) was developed when people tried to extend STM technique to investigate the electrically non-conductive materials, like . Bullen & Robert A. Article 18 December 2017. It begins with a broad .Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a technique in the diverse scanning probe microscopy (SPM) family. References Atomic force Microscopy by Peter Eaton and Paul West. The atomic force microscope obtains images by measurement of the attractive and repulsive forces acting on a microscale probe interacting with the surface of a sample.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Dissemination of IT for the Promotion of Materials Science (DoITPoMS) via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request. The AFM makes it possible to image the surface topography of an object with very high .History of atomic force microscopy. The CAFM became a very popular tool in the field of characterization . After the inception of atomic force microscopy [] (AFM) in 1986 as a method to image surface topography unaffected by the optical resolution limit, it sparked a wide variety of methods allowing probing of electrical [], chemical [], magnetic [] and mechanical [] properties.The Atomic Force Microscope was invented in 1982, by scientists working in IBM, just after the invention of the Scanning tunneling Microscope in 1980 by Gerd .AFM was first proposed by Binnig et al.Critical-dimension atomic-force microscopy: (Left) Geometric parameters of flared tip. AFM was first proposed by Binnig et al.









