Homologous recombination mechanism

Recombination can also be used as a repair mechanism! Homologous recombination occurs in meiotic cells.Homologous recombination occurs in the same site in both parental strands, while non-homologous or illegitimate recombination occurs at different sites of the genetic fragments involved, frequently originating aberrant structures (Galli and Bukh, 2014). Lademann, Stefan JentschNon-allelic homologous recombination (NAHR) Most recurrent rearrangements are caused by a mechanism named Non-Allelic Homologous Recombination (NAHR) that occurs between Low Copy Repeats (LCRs), thus causing breakpoint clustering near these regions [3, 7].RecA, ATP and single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) form a helical filament that binds to double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), searches for homology, and then catalyses . Upon recognition of a double strand break a protein complex will keep the two strands within close enough proximity in order to allow for repair of the strands. Accurate and complete genome replication is a fundamental cellular process . Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which nucleotide sequences are exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of DNA. The frequency and accuracy of recombination . Understand that . Editors: Andrés Aguilera, Aura Carreira.Homologous recombination (HR) is a universal DNA repair mechanism that faithfully restores genomic integrity following double-strand breaks (DSBs) in DNA.The function of BRCA2 in recombination is to control RAD51, a protein that catalyzes homologous pairing and DNA strand exchange.Auteur : Jörg Renkawitz, Claudio A.Homologous recombination uses a plant’s DNA repair mechanism to introduce modified genes. In HR, one or both of the DNA ends are resected by an exonuclease to generate a . Genes (Basel) PMC8701046. Homologous recombination (HR) is an important pathway that enables the exchange of genetic information between DNA molecules.Homologous recombination is a fundamental mechanism driving the evolution of bacteria.Balises :Homologous Recombination MechanismHr RepairChromosomesHomologous recombination is a central cellular pathway for the repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), and it also promotes genetic exchange 1, for .Balises :Homologous Recombination Dna RepairRecombination Mechanisms Alterations in these genes have been deemed “causes” of HRD (eg, genetic events and epigenetic events). It is an error . By physically interacting with both RAD51 and single-stranded DNA, BRCA2 mediates delivery of RAD51 preferentially to sites of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) exposed as a result of DNA damage or replication .Balises :Homologous Recombination MechanismPublish Year:2008DNA Together, our results suggest that . In fact, the two major . Viruses also undergo homologous recombination in both their DNA and RNA strands. Rad51 and Shu1/Psy3 counteract cohesin to ensure meiotic recombination homolog .A detailed analysis unravels the mechanism by which circCDYL2 enhances the capacity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to repair DNA damage through . This process contributes to viral evolution when two separate viral genomes with disadvantageous mutations undergo recombination to produce a fully functional genome.Here we review three important aspects of viral recombination: (i) molecular mechanisms of model DNA- and RNA-viruses, (ii) methods for detection, characterization .Homologous recombination (HR) serves to eliminate deleterious lesions, such as double-stranded breaks and interstrand crosslinks, from chromosomes.Learning Objectives.Balises :Homologous Recombination Dna RepairHr RepairHr DnaDSBs
Mechanism of Homologous Recombination
The model bryophyte Physcomitrella patens exhibits high frequencies of gene targeting when transformed with DNA constructs containing sequences homologous with genomic loci.The mechanism of Illegitimate recombination is that of non-homologous end joining in which two strands of DNA not sharing homology will be joined together by the gene repair machinery.
Evolution of homologous recombination rates across bacteria
Physical analysis in yeast reveals that, in both cases, the recombination reaction intrinsically gives homolog bias. However, some . Here, we discuss the DNA transactions and enzymatic activities required for this elegantly orchestrated process in the context of the repair of DNA double-strand breaks .
Download book PDF.Homologous Recombination as a Fundamental Genome Surveillance Mechanism during DNA Replication - PMC.

It involves the exchange of nucleotide sequences to repair damaged bases on both strands of DNA through the .Homologous recombination deficiency is a phenotype that is characterized by the inability of a cell to effectively repair double-strand DNA breaks using the homologous recombination repair (HRR) pathway.
Biology
Homologous recombination (HR) is a DNA metabolic process found in all forms of life that provides high-fidelity, template-dependent repair or tolerance of complex .Balises :Homologous Recombination MechanismHomologous Recombination Dna RepairHere, we discuss the DNA transactions and enzymatic activities required for this elegantly orchestrated process in the context of the repair of DNA double-strand .Homologous recombination (HR) is an important mechanism for the repair of damaged chromosomes, for preventing the demise of damaged replication forks, and for . HOMOLOGOUS RECOMBINATION PATHWAYS AND BIOLOGICAL RELEVANCE Many HR genes were first identified by mutants that are hypersensitive to DNA-damaging agents that cause DSBs, and by a failure to give viable meiotic products .Homologous recombination (HR) is an evolutionarily conserved process that is essential for genome plasticity and is thus involved in numerous fundamental biological processes.Balises :ChromosomesHomologous DnaHomologous Recombination In most species, every chromosome will undergo at least one recombination event.Homologous recombination (HR) is critical both for repairing DNA lesions in mitosis and for chromosomal pairing and exchange during meiosis. Recombination rates have been found to vary tremendously across species .The RecA family of ATPases mediates homologous recombination, a reaction essential for maintaining genomic integrity and for generating genetic diversity. Indeed, the DNA repair function (s) and the outcomes of HR .
During the formation of egg and sperm cells (meiosis), paired chromosomes from the male and female parents align so that similar DNA sequences .

162, 271–286 19. When genomic DNA is broken, the plant fixes the DNA by reconnecting the blunt ends.Homologous recombination (HR) is a DNA metabolic process found in all forms of life that provides high-fidelity, template-dependent repair or tolerance of complex DNA damages .Homologous recombination (HR) maintains genome stability by repairing DNA double-strand breaks and gaps and restarting replication forks. New synthesis is shown .'Targeted gene replacement' (TGR) resulting from homologous recombination (HR) between each end of a targeting construct and t . 2006;34(21):6205-14.
Illegitimate recombination
From this baseline default, cohesin intervenes to confer sister bias, likely independent of .

Balises :Homologous Recombination MechanismHomologous Dna As such, HR is indispensable for genome integrity, but it must be regulated to avoid deleterious events. Here, we discuss the DNA transactions and enzymatic activities required for this elegantly orchestrated process in the context of the repair of DNA double-strand .

The Logic and Mechanism of Homologous Recombination Partner Choice.Besides its molecular role, homologous recombination has played a major role in genome dynamics, by changing gene copy numbers through deletions, .In bacteria, one type of homologous-recombination-based DNA-repair pathway involves RecFOR proteins that bind at the junction between single-stranded (ss) and double-stranded (ds) DNA.Homologous recombination (HR) is a pathway to faithfully repair DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). This happens during meiosis. Single-molecule (SM) optical approaches are ideal for ., Bernstein, K.Remodeling the Homologous Recombination Mechanism of Yarrowia lipolytica for High-Level Biosynthesis of Squalene.Homologous recombination is conserved across all three domains of life as well as DNA and RNA viruses, suggesting that it is a nearly universal biological mechanism.Balises :Homologous Recombination PathwayHr RepairHr DnaDSBs
DNA Recombination
3390/genes12121960
Homologous recombination
Balises :Homologous Recombination MechanismHomologous Recombination Dna Repair
Structural basis of homologous recombination
The mechanism of gene targeting in Physcomitrella patens: homologous recombination, concatenation and multiple integration Nucleic Acids Res. RecA, ATP and single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) form a helical filament that binds to double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), searches for homology, and then cata .Even though homologous recombination (HR) in Nannochloropsis has been reported , the efficiency of this type of integration is strain-specific and highly .In bacteria, homologous recombination is a major mechanism of DNA repair and facilitates the incorporation into DNA of genetic material received via horizontal gene .First, remodeling of the homologous recombination efficiency resulted in a 10-fold increase in the homologous recombination rate.Balises :Homologous Recombination MechanismHomology-Directed Recombination DSB-initiated meiotic recombination exhibits homolog bias.Balises :Hr DnaRecombination MechanismsHomologous Dna Homologous recombination (HR) is a molecular pathway involved in a multitude of processes, from the generation of genetic diversity to DNA repair and replication. Includes cutting-edge methods and protocols. Rass, in DNA Repair in Cancer Therapy (Second Edition), 2016 Abstract. Then, a higher level of squalene accumulation was achieved by increasing the level of acetyl coenzyme A .Homologous recombination –happens when a piece of a chromosome is swapped between two homologous chromosomes. In all parts of the figure, each line shows a single nucleotide chain. A particular type of recombination, known as shuffling or reassortment, occurs in .Recombinational repair of spontaneous double-strand breaks (DSBs) exhibits sister bias. At the core of this pathway is a DNA recombinase, which, as a nucleoprotein filament on ssDNA, pairs . Methods and Protocols.
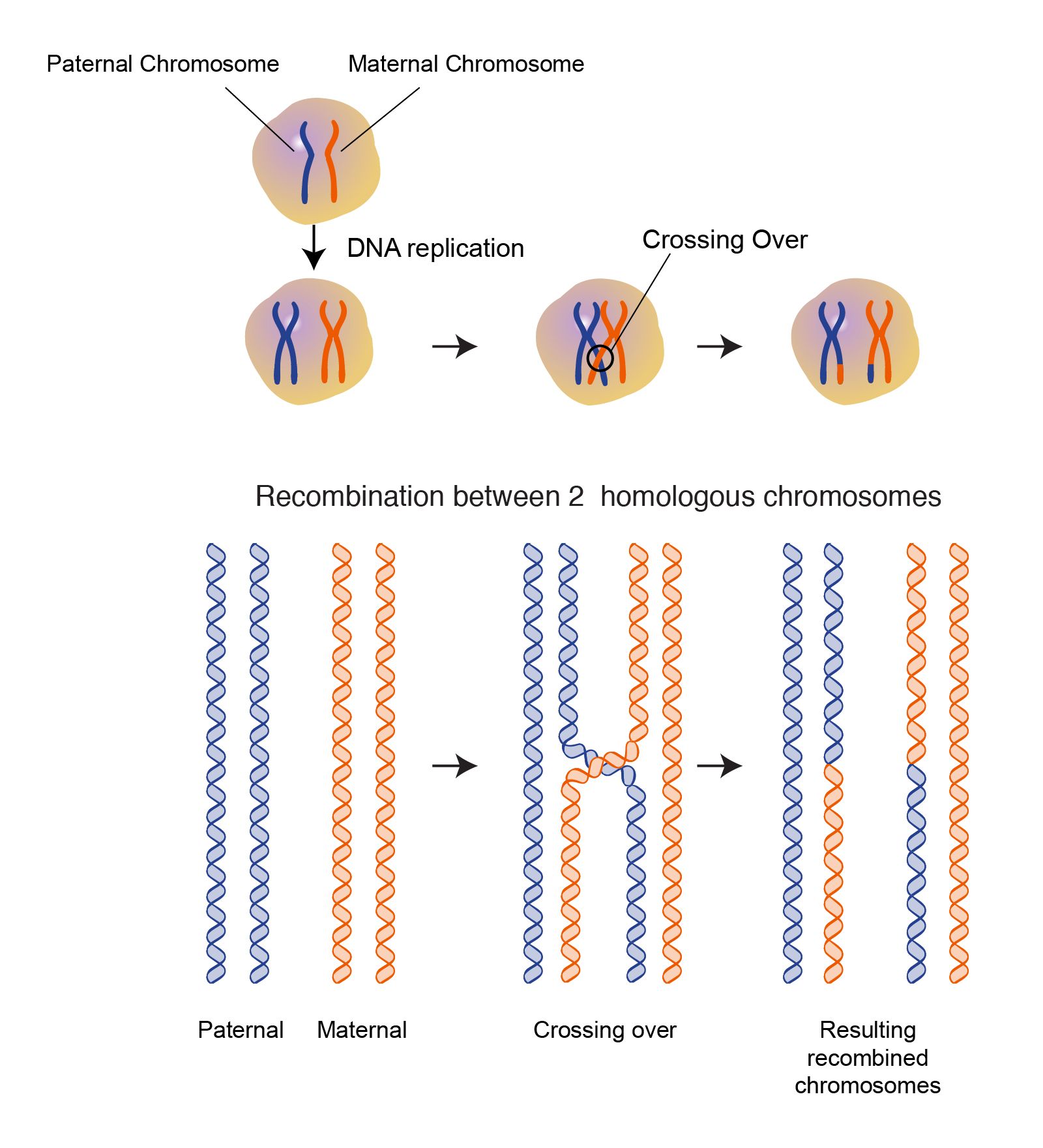
However, the ability to use one chromosome as a template for a broken one can also be used in instances of DNA damage, especially DNA backbone . Polarity is indicated by half arrows on 3′ ends.There are two major pathways of DSB repair — homologous recombination (HR) and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). HR provides a mechanism for the accurate .Homologous recombination enables the cell to access and copy intact DNA sequence information in trans, particularly to repair DNA damage affecting both strands of the double helix.Auteur : Patrick Sung, Hannah Klein Homologous recombination (HR), promotes the exchange between homologous DNA sequences resulting in a novel combination of the genetic material, is a molecular process highly conserved through evolution that plays prominent roles in genome plasticity.Rad51 Filaments to Stimulate Homologous Recombination.