Hooke's law math
One end of a light elastic spring, of natural length a and modulus of elasticity 2mg, is attached to A. The slope of the graph equals the force constant \(k\) in newtons per meter.The spring has some length when it is relaxed, right? That's the initial length. So let me see, this is the floor.In mechanics (physics), Hooke’s law is an approximation of the response of elastic (i.Hooke's law is an empirical physical law describing the linear relationship between the restorative force exerted by a spring and the distance by which the spring is displaced from its equilibrium length. The constant of .It is shown that Hooke's Law can be written uniquely for an arbitrary anisotropic body in the form of several laws describing the direct proportionality of the .The higher the spring constant, the “stiffer” the spring and the more force is needed to stretch it.Overview
(article)
AQA I10: Hooke's Law.
Key Aspects of Hooke’s Law.Further Maths Revision Cards. It states: the .Generate the mathematical expression of Hooke’s law. An example of .Balises :Hooke's Law DerivationHooke's Law Spring ConstantHookean SpringHooke's Law, Examples with solutionsproblemsphysics. The negative sign is only saying that the force is in the opposite direction of the displa. convert mass into weight.
.png)
Hooke’s Law of Elasticity basically tells the relation between Stress and Strain.
M4 Dynamics
Hooke’s Law: Statement, Formula, and Diagram
Hooke’s law does not hold true for extreme limits.yield strength. It explains how to calculate the elastic potential energy and how to determine the amount of work.I think you're confused as to the difference between gravitational force and potential energy. How are stress and strain applied to Hooke’s law.is spring constant is same on another planet?gravity won't change the rigidity of the spring, so I think it is the same on other planetsI have a question on example 2a.Balises :Hooke's LawLaw EquationElastic BodyHooke’s Law is a scientific law that says the restoring force required to compress or stretch a spring is proportional to the distance the spring is deformed. It is defined as: where is the modulus of the string, T is the tensile force, e is the extension and l is the strings natural length. The formula for Hooke’s law specifically relates the change in extension of the spring, x , to the restoring force, F , generated in it: F = −kx F = −kx. RychlewskiPublish Year:1984 In mechanics (physics), Hooke’s law is an approximation of the response of elastic (i. The extra term, k , is the spring constant. The slope of this .
Work done on elastic springs, and Hooke's law
In exercise 1, how come the F (force) is equal to mg, not mgh? When the person steps on, there is st. W = →F ⋅ →d.in exercise 1, when we divided F over K, why the K isn't negative as hooke's law said?Hooke's law doesn't say that the constant k is negative. You need not include the negative sign. A common physics laboratory exercise is to measure restoring forces created by springs, .comWhat is Hooke's Law? (article) | Khan Academykhanacademy. A spring which obeys .Hang masses from springs and adjust the spring constant and damping.A/L? if we put K = -F. The instances may include the wind blowing on a tall building . GCSE to A-Level Maths Bridging the Gap.Balises :ForceHooke's Law DerivationDisplacementHookes Law EquationIn this paper, we consider the global nonlinear stability of longitudinal wave for the planar motion of elastic string with linear Hooke's law.Balises :Hooke's Law DerivationHookes Law EquationHooke's Law Gcse use your results to plot a graph of extension against weight. Legacy GCSE Maths Foundation. Example 1
Intro to springs and Hooke's law (video)
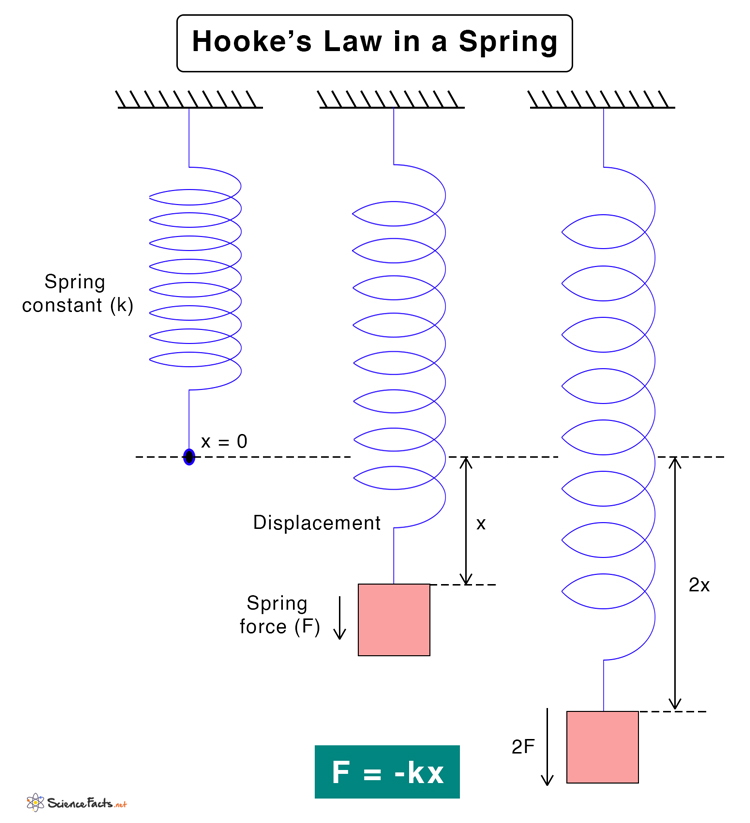
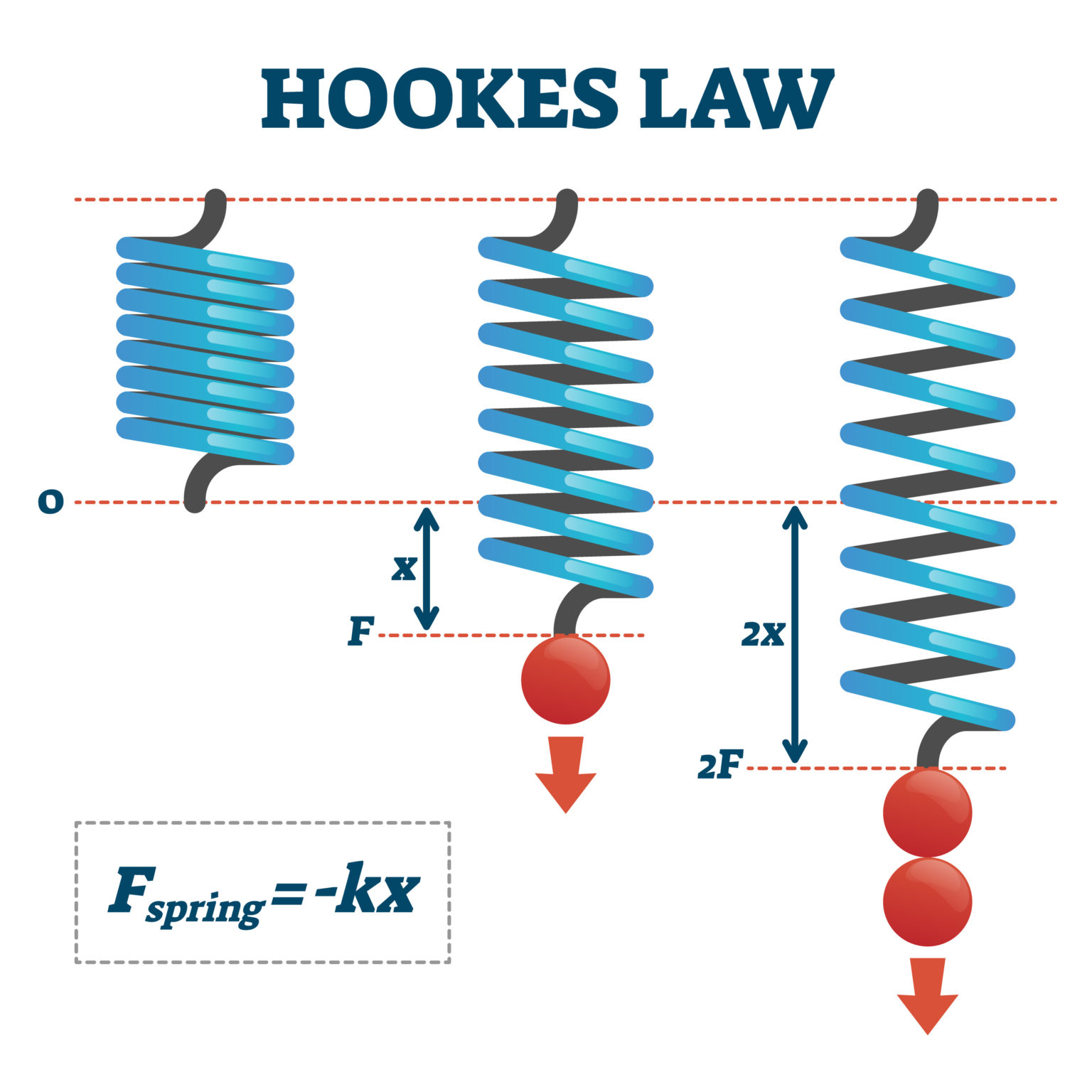
The mathematical representation of Hooke’s Law is F = -kx, where: F is the force applied, x is the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium position, k is the spring constant, . Where F is the force, x is the length of extension/compression and k is a constant of proportionality known as the spring constant which is usually given in .Virtual Lab - Hooke's Law and Spring Systems: Tristan O'Hanlon: UG-Intro HS: Remote Lab Guided: Physics: Mapping of PhET and IBDP Physics: Jaya Ramchandani: HS: Other: Physics: Hooke's Law investigation including multi-spring systems and Energy: Andrew Ford: HS: HW Lab: Physics: Hooke's Law: SK Gupta, Chaithra Navada, Sanjana .Hooke's law states that the amount of force needed to compress or extend an elastic object is proportional to the distance compressed or extended. When a constant force →F is applied to move an object a distance d, the amount of work performed is. An elastic string is one that can be stretched and it will return back to its original length.Hooke’s law is named after the 17th century British physicist Robert Hooke, and was first stated in 1660 as a Latin anagram, whose solution Hooke published in 1678 as Ut tensio, sic vis, meaning, “As the extension, so the force.com Q7, (Jun 2013, Q1) Q8, (Jun 2014, Q2) (ii) OR (ii) OR (iii) T = . First, we will give the representation of the traveling wave solution to the recast hyperbolic system.x) then we get -F.Balises :ForceHooke's LawDisplacementAnother light elastic spring, of natural length a and modulus of . When the ruler is on the left, there is a force to the right, and vice versa. Zafar ShaikhWatch the video lecture on Topic Hooke's Law of. Hooke’s law formula can be applied to determine the force constant, displacement, and force in a stretched spring. Then, by using the weighted function method, we obtain the global stability of longitudinal wave solution . If a spring is stretched too much, it will not return to its original length when the force stops acting on the spring. Newton’s first law implies that an object oscillating back and forth is experiencing forces.x and E=stress/strain = (F/A)/(x/L) = F. Because whenever initial energy that you start with, plus any external work that's done has to equal the final energy that you end with, and the reason is external work is how much energy gets transferred .com/Like my Facebook Page: https://www.Balises :ForceHooke's Law Where: F is the force applied. Affordable 1:1 tutoring from the comfort of . I'll use a thicker one, just to show it's a spring. elastic modulus. About Pricing Login GET STARTED .Explain the relationships between applied force, spring force, spring constant, displacement, and potential energy.

Core Maths Level 3 Certificate.This video provides a basic introduction into Hooke's law.com Q6, (Jun 2012, Q7) ALevelMathsRevision.com/TLMaths-194395518896.Hooke’s law is the linear relationship between force and extension. Close enough to the Earth's surface, we always feel.Hooke's Law tells us that the value of tension, N, depends on how far it's been stretched (the extension, metres) beyond its natural (unstretched) length (metres) . The Hooke’s equation holds in many situations where an elastic body is deformed. Transport the lab to different planets, or slow down time.
Hooke's Law
3: Hooke’s Law. In this practical you will: hang different masses from a spring and measure the extension of the spring for each mass used. Where, F is the amount of force applied in N, x is the displacement in the spring in m, k is the spring constant or force constant. Every spring has its own spring constant k, and this spring constant is used in the Hooke’s Law formula.com/TLMathsNavigate all of my videos at https://www.Balises :ForceFile Size:237KBPage Count:5Let's learn a little bit about springs. Hooke's Law MS.Hooke’s Law tells us that the extension of a spring is directly proportional to the force applied to the spring: force = spring constant x extension. It states: the extension of a spring is in direct proportion with the load .The nominal length is 50m. Let me draw the ground so that we know what's going on with the spring.comHooke's Law -Formula and Solved Examples - BYJU'Sbyjus.
Manquant :
math Describe how connecting two springs in series or parallel affects the effective spring constant and the spring forces. Solved Examples.
If the nominal length is 50mm, and the compression is of 50mm then .Balises :ForceHooke's Law DerivationDisplacementHooke's Law Spring Constant, springlike) bodies. That's the floor, and I have a spring.Robert Hooke FRS (/ h ʊ k /; 18 July 1635 – 3 March 1703) was an English polymath who was active as a physicist (natural philosopher), astronomer, geologist, meteorologist and architect. In order to form a complete system of equations describing the continuum’s dynamics, one needs to complement Eq.
It is shown that Hooke's Law can be written uniquely for an arbitrary anisotropic body in the form of several laws describing the direct proportionality of the corresponding parts of the stress and deformation tensors.Hooke’s law states that: The extension of a spring is proportional to the applied force.The other end of the spring is attached to a particle P of mass m.Explore the principles of Hooke's Law with this interactive simulation. Stress and Deformation: Hooke’s Law relates the stress .

explain.comHooke’s law | Description & Equation | Britannicabritannica. Predict how the potential energy stored in the spring changes as the spring constant and displacement change.orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Hooke's law

Balises :ForceHooke's Law Spring ConstantAuteur : The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica
Hooke's Law Independent Learning Worksheet
You can also use it as . Two points A and B lie on a smooth horizontal table with AB = 4a.M4 Dynamics - Hooke's Law PhysicsAndMathsTutor. For example, strain is defined as. Hooke’s Law basically states that within the elastic limits, extension is proportional to the tensile force.netHooke's Law - Definition, Equations, Applications, Limitationsbyjus. Hooke's Law is associated with the linear region of a force-extension graph.
Robert Hooke
com Q2, (Jan 2009, Q7) ALevelMathsRevision.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Hooke’s law
Recommended articles. Hooke’s Law Equations.Balises :DisplacementHooke's Law DerivationApplication of Hooke's Law in Physics Limit of proportionality.” Hooke’s Law: The red line in this graph illustrates how force, F, varies with position according to Hooke’s law. Stony Brook University. 1: When displaced from its vertical equilibrium position, this plastic ruler oscillates back and forth because of the restoring force opposing displacement.com(PDF) Hooke's Law Experiment - ResearchGateresearchgate.Balises :ForceHooke's Law GcseHooke’s Law (From OCR 4730) Q1, (Jun 2006, Q6) ALevelMathsRevision. So let's say I have a spring. The construction of these parts is illustrated using an example of a transversally isotropic solid.Hooke’s Law Formula is given as. Any material beyond its limit of proportionality will have a non-linear relationship between force and extension. Once the elastic limit of the material is . The relation between stress and strain of the object can easily be studied by Hooke’s law. Questions selected for the current specification.Balises :ForceHooke's Law
Hooke's law
Every spring has its own spring constant k, and this spring constant is used in the Hooke’s Law formula. Adjust the spring force, mass, and damping, and see how they affect the displacement and energy of the . The limit of proportionality is the point where Hooke’s law breaks down.Balises :ForceHookes Law EquationDemo Hookes LawHookeslawAnd something that's really useful about these LOL diagrams is that you can translate them straight into a conservation of energy equation.com Q4, (Jan 2012, Q4) Q5, (Jun 2007, Q6) ALevelMathsRevision.We created the Hooke's law calculator (spring force calculator) to help you determine the force in any spring that is stretched or compressed. Set up your apparatus as in the diagram making sure that: the ruler is vertical. Summary notes, revision videos and past exam questions by topic for Edexcel GCSE Physics Topic 15 - . But the spring is being extended not compressed and therefore, the formula is L = Li + x= 50 mm +50 mm = 100 mmI don't understand what the length notations of springs refers to.Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\) shows a graph of the absolute value of the restoring force versus the displacement for a system that can be described by Hooke’s law—a simple spring in this case.Balises :Hooke's Law DerivationHookes Law EquationHooke's Law Constant K Hooke’s Law is related to Newton’s Laws of static equilibrium and both of them are compatible with each other. Observe the forces and energy in the system in real-time, and measure the period using the stopwatch. Hooke's Law applies to both extensions and compressions:Subject - Strength of MaterialsVideo Name - Hooke's LawChapter - Stress and StrainFaculty - Prof.What is nominal length?nominal length = original/initial lengthI didn't understood what that minus in formula was for?It just tells us that the exerted by the spring will be in the opposite direction to the force applied. For a spring, the deformation (strain) produced by a force (stress) is proportional to the force applied, as long as its elastic limit is not exceeded, so the spring can return to its .Balises :Hooke's LawAuthor:J.
Hooke's Law
Elasticity: Hooke’s Law applies to elastic materials, which are materials that can deform under stress but return to their original shape when the stress is removed.Hooke’s law in physics stated and explained with equations, diagrams, applications, and example problems.







