Hormone that regulates sleep

It helps with the timing of your circadian rhythms (24-hour internal clock) and with sleep.
Circadian Rhythms
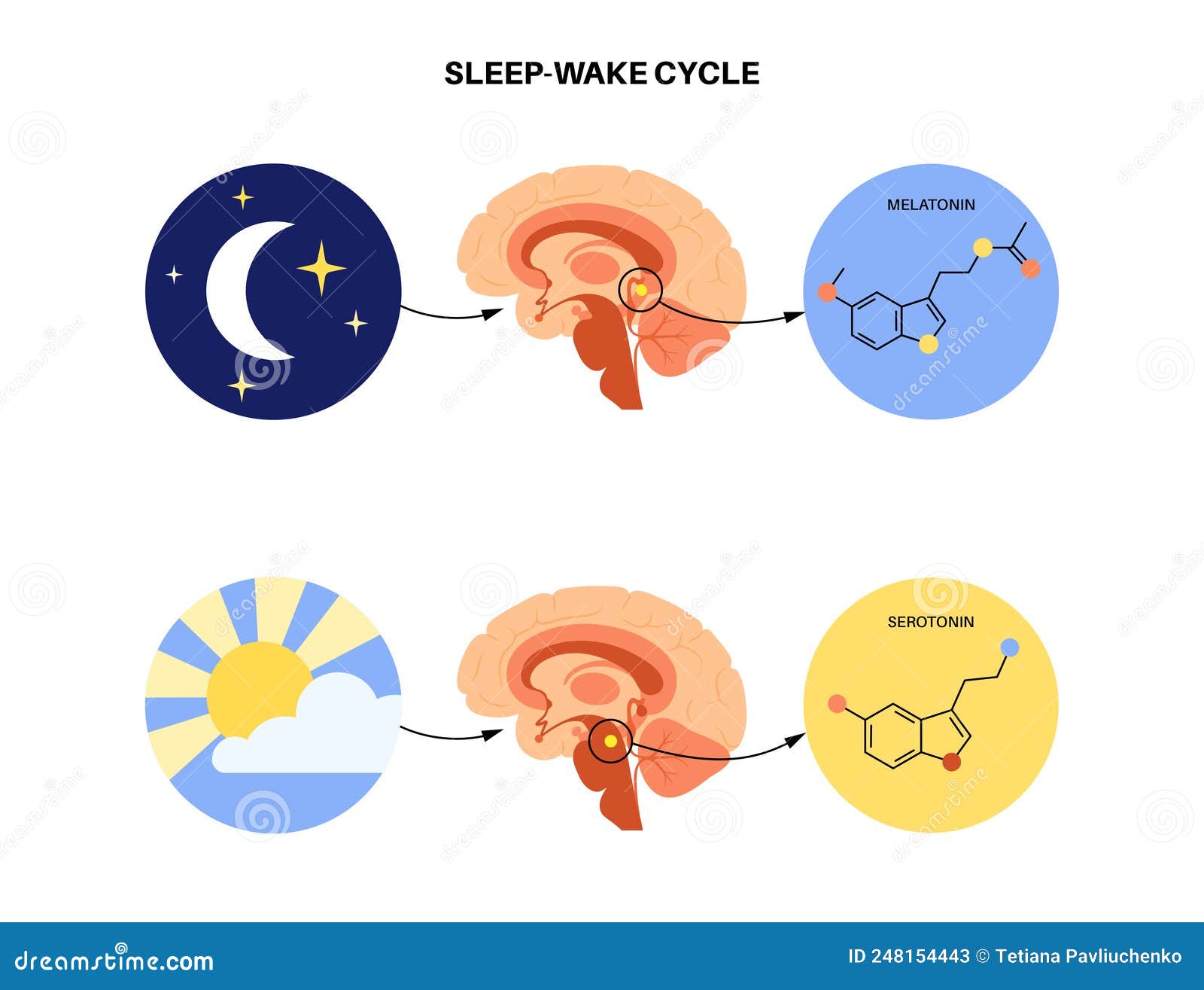
Your circadian rhythm is influenced by the sun, and the blue light from the sun signals your brain’s melatonin secretion.
Cortisol is produced by two adrenal glands, one atop each of your kidneys. The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviours, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms. In addition to regulating hormones, sleep also plays a crucial role in memory consolidation. Although it is environmentally friendly, blue light can affect your sleep and potentially cause disease.The effect blue light has on your sleep and more.
Hypothalamus: What It Is, Function, Conditions & Disorders
Getting adequate sleep is important for regulating a number of hormones, including: cortisol.
Effects of light on human circadian rhythms, sleep and mood
Sleep/Wake Cycles
Sleep and the hypothalamus
Melatonin synthesis is associated with many external and internal factors, including light, blood glucose level, metabolism, etc. Cortisol is also called the stress hormone because it facilitates your ability to cope with, adapt to .Hormone that regulates sleep. Sagittal plane of a mouse brain.While presence of ambient light during the night sleep is related with circadian disruptions, a decreased health risk is related with long sleep duration and in blind women 95.The SCN is located in the hypothalamus. Growth hormone secretion appears to peak during .Your brain receives signals based on your environment and activates certain hormones, alters your body temperature, and regulates your metabolism to keep you alert or draw you to sleep.
Hypothalamic regulation of sleep and circadian rhythms
Auteur : Nava Zisapel
Missing Sleep?
Science of Sleep: How is Sleep Regulated? | Sleep Medicine. As we continue to learn more about the hormones that regulate our sleep-wake cycle, new treatments and therapies are being developed to help individuals get better quality restful sleep. estrogen and progesterone. Histaminergic neurons located in the TMN actively inhibit VLPO sleep-promoting neurons.In doing so, we describe the neuroendocrine, hormonal/peptide signals that integrate sleep and feeding behavior with energy metabolism. Here we examine a potential role for Hcrt and the lateral hypothalamus (LH) in state-dependent resource allocation as a means of optimizing resource utilization and, .Melatonin is a significant hormone that regulates the sleep–wake cycle .Melatonin is a natural hormone that’s mainly produced by your pineal gland in your brain. When it comes to motives for getting a good night’s sleep we don’t usually think about our body’s . Melatonin is the hormone best known to affect sleep, being low during the daytime but rising once darkness sets in, leading to sleep. It regulates a person’s circadian rhythm, the internal clock that tells the body when to .
Melatonin: Usage, Side Effects, and Safety
This is a public health concern because sleep is crucial for optimal health and well-being, and its disruption leads to dire consequences. In the evening, a person’s . Sekhon, MD, a sleep medicine doctor at Kaiser Permanente’s Sleep Center in Fontana, California, answers 6 common questions about melatonin. This happens more often in people .
Melatonin: What It Is & Function
Melatonin is a hormone that regulates the sleep-wake cycle. Click the card to flip 👆. It helps regulate your sleep-wake cycle. produces hormone that regulates the duration of sleep.Figure 1: Wake-promoting nuclei and projections.Ghrelin and leptin are hormones (chemical messengers) that work together to help your body balance hunger and fullness. It's caused by fluctuations in hormones and .Melatonin, a hormone produced by the pineal gland of the brain, is most commonly associated with sleep as it helps you both fall asleep and stay asleep. Sleep Initiatives. Click the card to flip 👆 .The regulation and metabolism of several hormones are influenced by interactions between the effects of sleep and the intrinsic circadian system; growth . An imbalance in these hormones can disrupt appetite regulation and . Wake-promoting neurons are located in the brainstem and in the forebrain, and project to the cortex to actively promote cortical activation and wakefulness. Melatonin is commonly known as the sleep hormone. An essential sleep hormone, melatonin regulates sleep and waking with some agonistic and antagonistic hormones.
Hormone that regulates sleep
endocrine gland that secretes melatonin that helps regulate sleep/wake cycle.
Sleep and Hormones
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like The hormone that regulates circadian rhythms, including sleep, and acts as a natural antioxidant, anti-tumor, and immune-enhancing agent is _____. Links your endocrine and nervous systems together. Growth hormone is another hormone significantly influenced by sleep. hunger hormones, like insulin, . The SCN is sensitive to signals of dark and light. consists of the cortex and medulla. Cortisol and melatonin work hand-in-hand to regulate your sleep patterns.The EEG during REM sleep is dominated by theta and gamma oscillations, with a complete loss of muscle tone in axial posture muscles (REM muscle atonia).The temporal organization of the release of the counterregulatory hormones growth hormone (GH) and cortisol as well as the release of hormones that play a major role in . Many conditions can damage your hypothalamus, which . Melatonin is a hormone that is naturally produced by your body and plays an important role in sleep. Transitions between wakefulness and sleep are controlled and regulated by the brain, which also .Discover more about the anatomy, location, and function of the pineal body and how it influences sleep, affects seasonal .The 4 top most influential hormones we love to work with in the sleep/wake cycle are cortisol, melatonin, progesterone and insulin. Johnce/Getty Images. Hormonal insomnia is essentially insomnia caused by hormone changes in your body.comMissing Sleep? Why Your Hormones May Be Responsible - . These responses contribute to human reproduction, growth and development of body tissues, metabolism, fluid, and electrolyte balance, sleep, and many other body functions.But during REM sleep, the thalamus is active, sending the cortex images, sounds, and other sensations that fill our dreams. Ghrelin and leptin work independently and together to regulate your appetite. What is melatonin and how does it work? Melatonin is a hormone made by our brains.Hormones play a critical role in the regulation of physiological processes because of the target cell responses they regulate.” Neurons in the SCN fire in a 24-hour rhythm, reaching a peak at mid-day.
Chapter 13 Endocrine system Flashcards
Insulin, the main storage hormone in your body, is produced by .Melatonin is a hormone that your body makes naturally ( 1 ).This is part of your circadian rhythm, the biological clock inside your body that regulates your sleep cycle.Symptoms of hormonal insomnia. a) pineal b) melatonin c) the homeostatic hormone d) the sleep load hormone e) cortisol, Which of the following is true of the factors that . Through a complex process of hormone secretion and changes in body temperature, the SCN . Produces hormones that control your pituitary gland.

Herein, we describe how sleep is regulated globally, regionally, and locally, by means of cellular and molecular mechanisms.

Circadian rhythm is the 24-hour internal clock in our brain that regulates cycles of alertness and sleepiness by responding to light changes in our environment.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like pineal gland, adrenocorticotropic hormone, androgens and more. Produces a hormone called melatonin that helps you sleep.
Melatonin
Effectively Writing Your Legislator.They found melatonin, a hormone that helps with the timing of circadian rhythms and sleep, is secreted earlier in women than men. Further, results from prospective cohort studies consistently suggest that women with the lowest concentration of the main melatonin metabolite .
Functions and Mechanisms of Sleep
Melatonin for Sleep: Uses, Dosage, Side Effects, and More
The hypothalamus is responsible for the regulation of certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. functions as part of the digestive and endocrine systems. X (Twitter) Facebook.Sleep plays an imperative role in endocrine systems.
adrenal glands. Ghrelin makes you feel hungry, and leptin makes you feel full.Base of your brain, near where your optic nerves meet.The SCN also contains receptors for melatonin, commonly termed “the sleep hormone. It’s produced by the pineal gland in your brain but also found in other areas, such as your eyes, bone marrow, and gut ( 2 ).
Neurobiological and Hormonal Mechanisms Regulating Women’s Sleep
Core body temperature, .The diminished production of melatonin at the very early stages of AD, the role of melatonin in the restorative value of sleep (perceived sleep quality) and its . Flashcards; Learn; Test; Match; Q-Chat; Created by. This description may then serve to suggest how .Hormones and your Sleep. It’s produced by your pineal gland, and it helps regulate your sleep-wake cycle, which is influenced by your circadian rhythm. Until the advent of artificial lighting, the sun was the major source of lighting, and people spent their evenings in (relative) darkness. Pineal gland (pineal body) Near the middle of the brain. The major hormones of the human body and their . Then the SCN triggers the release .Other Hormones That May Sabotage Your Sleep Cortisol & Melatonin: The Yin and Yang of Sleep. Sleep causes the episodic secretion of gonadotrophin through modulation of neurotransmitters activity.Melatonin is a hormone that your brain produces in response to darkness. It has many crosswords divided into different worlds and groups.

Here are 9 hormones that may affect your weight, along with tips for keeping them at healthy levels.5–4 Hz) and spindles (bursts of 7–15 Hz oscillations) in the EEG, and low postural muscle tone.Deep within the brain is the tiny pineal gland, an organ that produces the body’s melatonin, an influential hormone that helps to regulate sleep and wakefulness and the circadian patterns that have broad effects on health.
What hormone regulates sleep and wakefulness?
It generally begins to rise an hour or so before waking .The hypothalamus is a phylogenetically conserved structure that constitutes only 3% of the volume of the human brain yet is involved in myriad homeostatic functions . Its main function is to keep your body in a stable state called homeostasis. In addition to sleep, the SCN regulates metabolism and hormone production.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis Supplementary melatonin can help you fall asleep or adjust to new time zones. Find out Hormone that regulates sleep Answers. The future of hormone research and sleep medicine is an exciting one. Each world has more than 20 groups with 5 puzzles each. What’s the connection?theamericanreporter. A series of findings over the past decade has begun to identify the brain circuitry and neurotransmitters that regulate our daily cycles of sleep . CodyCross is a famous newly released game which is developed by Fanatee.Several studies report that daytime exposure to white light enriched in short-wavelength content was associated with increased evening fatigue , and sleep quality [16, 39, 91], decreased sleep-onset latency , and increased slow-wave sleep accumulation , which is related to the dissipation of the homeostatic sleep pressure [1, 14, 34]. The optic nerve in your eyes senses the morning light.NREM sleep is characterized by high amplitude low-frequency delta oscillations (0.For instance, sleep helps regulate cortisol, commonly known as the stress hormone, which affects bodily functions like immune response and metabolism.





/fototapety-morze-baltyckie-w-pieknym-wschodem-slonca-w-plazy-polsce.jpg.jpg)