How enzymes work videos

Most enzymes in the human body work best at around 98. Since enzymes are selective for their substrates and speed up only a few reactions from among many possibilities, the set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. PDB-101 training .Auteur : Sal Khan
Introduction to enzymes and catalysis (video)
The enormous catalytic activity of enzymes can perhaps best be expressed by a constant, k cat, that is variously referred to as the turnover rate, turnover frequency or turnover number.Flash Video - McGraw-Hill - How Enzymes Work Photosynthesis.
Investigation: How Do Enzymes Work?
The active sites morph too, making the enzymes useless. They are vital for life and .3M views 6 years ago Learn about Structural Biology from the RCSB PDB. Nature = Futur ! S’inspirer de la photosynthèse de bactéries pour créer un nouveau catalyseur capable de produire de . An enzyme does not add energy to a reaction; . Learn how the proteins called enzymes work to maintain the . For full treatment, see protein: Enzymes. We have a new and improved read on this topic.
How Enzymes Work (from PDB-101)
Regarder la vidéo1:20How Enzymes Work - YouTube.
Manquant :
videosDes enzymes pleines d’énergie. Induced fit occurs when the enzyme changes shape to better . Share: Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions to create products from substrates, binding them through a lock-and-key mechanism . Neuronal Signaling and Sodium-Potassium Pump.#Enzymes #whatareEnzymesIf you are looking online to purchase essential enzymes for your body , please use my amazon affiliate link: https://www. They contribute to the overall plant health in multiple ways. An enzyme is very selective. RicochetScience.This constant represents the number of substrate molecules that can be converted to product by a single enzyme molecule .Regarder la vidéo4:5223K.31 views, 0 likes, 1 loves, 0 comments, 0 shares, Facebook Watch Videos from Susan Richter RN CNC LLC: Learn how enzymes can help us digest our food in. These reactions .9K subscribers.Enzymes are no exception. How Enzymes Work (from PDB-101) Watch on. 114K subscribers.This animation describes how enzymes workand the formation of an enzyme-substrate complexManquant :
Enzymes perform all of the basic chemical tasks needed to sustain life.Enzymes are biological molecules (typically proteins) that significantly speed up the rate of virtually all of the chemical reactions that take place within cells.Regarder la vidéothrough biology and medicine.Auteur : RicochetScienceEnzymes (video)
Specific enzymes break down specific nutrients.Learn how the proteins called enzymes work to maintain the rate of these reactions at a life-sustaining level in this video hosted by PDB-101.Regarder la vidéoThis animation provides a visual explanation about how enzymes catalyse cellular processes.
Through this video, learn more about how enzymes work and how researchers use them every day in the laboratory.Auteur : RCSBProteinDataBank
PDB-101: Learn: Videos: How Enzymes Work
It's a pilot run exp.6-degrees Fahrenheit (F) (37°C), which is the body’s typical temperature.

Auteur : AtomiRegarder la vidéo8:13Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up reactions. The main digestive enzyme in the stomach is pepsin, which works best at a pH of about 1. At lower temperatures, they may still work but much more slowly. For example blood, grease, fat, oil etc.How Enzymes Work – In the cleaning environment. Learn how the proteins called enzymes work to maintain the rate of these reactions at a life-sustaining level in this video hosted by PDB-101.
How Enzymes Work
Enzymes are an integral component of plant growth.
Enzyme
pdf), Text File (.How Enzymes Work _ CIE IGCSE Biology Revision Notes - Free download as PDF File (. SUPER FAST! 5MinuteSchool. Induced fit The matching between an enzyme's active site and the substrate isn’t just like two puzzle pieces fitting together (though scientists once thought it was, in an old model called the “lock-and-key” model). Its three-dimensional shape allows it to act only on specific molecules, referred to as the . The name of the enzyme is catalase.Enzymes work best within a certain pH range, and, as with temperature, extreme pH values (acidic or basic) can make enzymes denature.Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates sufficient for life. In highly acidic or basic conditions, the structures of enzymes change. Suitable enzymes such as cellulase break down dead root matter and convert them into simple sugars, which thereby feeds beneficial microbes.This animation of how enzymes work is a basic rundown of enzyme functions and illustrates what enzymes do.Auteur : EFSAchannel The reaction is: 2H 2 O 2 → 2H 2 O + O 2. Opioids and Pain Signaling. Most enzymes in the human body work best at 98.

For more information on enzymes, go to Another important role of enzymes is to break down substances that would be toxic to cells.How Do Enzymes Work? | Live Sciencelivescience. Find out more about enzymes and research looking for the unique enzymes found in extremophilic microorganisms: Catalysing chemical reactions with enzymes .Regarder la vidéo4:12Enzymes | Cells | Biology | FuseSchoolEnzymes are really important proteins that speed up the rates of reactions such as in photosynthesis, respiration and p.Your body tells your pancreas what types of enzymes to release based on what kinds of nutrients you ingested.A McGraw-Hill website to accompany Essentials of Anatomy &Physiology, 5th editon by Seeley, Stephens, and Tate. .
PDB-101: Learn: Videos
comHow Enzymes Work (from PDB-101) | Channels for Pearson+pearson. They create the conditions needed for biochemical reactions to happen .Regarder la vidéo6:05Explore the vital role of enzymes in speeding up biochemical reactions in the body, as you learn about the different catalytic strategies enzymes use, including acid/base catalysis, . Part of Biology (Single Science) Living processes.Nov 8, 2021 | 1 min read.Enzymes are used in all reactions that are important in cells.Regarder la vidéo8:12Enzymes as catalysts for reactions in biological systems; discussion of substrates, active sites, induced fit, and activation energy. the cell's chemists. How Enzymes Work. Methods for Determining Atomic Structures Structures . The structural features or functional groups on the enzyme that participate in these interactions are located in a cleft or pocket on the enzyme surface. Click Create Assignment to assign this modality to your LMS. Click here to view We have moved all content for . An enzyme does not add energy to a reaction; instead, it speeds up a reaction by lowering the energy barrier. This short animation shows how . 2) E S → E + P. Past news and events have . Explore the PDB-101 Browser to learn more about enzymes.
Enzymes- a fun introduction
How do they work? And how are they used in the food chain? This video explains.Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions to create products from substrates, binding them through a lock-and-key mechanism where substrates bind to specific active sites.This video explains how enzymes work including the structure of the active site, substrates and how enzymes are affected by different factors. These enzymes would not work optimally at .Subtitles are available in English, French, German, Italian . The biological processes that occur within all living organisms are chemical reactions, and most are .Auteur : FuseSchool - Global Education Researchers around the globe make 3D structures freely available from the Protein Data Bank (PDB) archive.Enzymes are proteins that speed up the rate of reactions, and there is a particular enzyme that can help break down hydrogen peroxide.Enzymes and digestion (CCEA) Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts, meaning they speed up reactions without being used up.Regarder la vidéo8:14This video introduces enzymes (a type of protein we couldn't live without!), explaining their structure and how they work.
Enzymes and digestion (CCEA) Video
Introductions to Protein Structure . 515K views 8 years ago Biology 101: Cellular Energetics.

Digestive enzymes secreted in the acidic environment (low pH) of the stomach help break down proteins into smaller molecules.Enzymes are proteins that play a major role in the biochemical reactions happening every moment inside our bodies - everything from digesting a bowl of ramen noodles to flexing your muscles in front of a mirror. The active site is where substrates bind to the enzyme.Watch the next lesson: h.Auteur : Ross Firestone They release energy from food and store it in other types of molecules, and they build other proteins that provide the structures inside cells.Overall, the lowering of the activation free energy has been found to accelerate the reaction rate by more than a factor of 10 11, whereas the transmission coefficient contributes no more than a factor of 10 3 to the rate.These reactions constitute the essential tasks of life such as metabolism, protein synthesis, cell renewal and growth.Enzymes are potent catalysts.What do our cells have, that a test-tube lacks? The answer is: enzymes! Enzymes are life’s great facilitators.We also have vi. Celebrating 50 Years of the Protein Data Bank Archive. In this activity, you will investigate how enzyme activity is affected by temperature.
Enzyme Animation ( Video )
ES → E + P (19.enzyme, a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered in the process.Enzymes work by binding to reactant molecules and holding them in such a way that the chemical bond-breaking and bond-forming processes take place more readily.
Manquant :
videosHow Enzymes Work Animation
A brief treatment of enzymes follows.
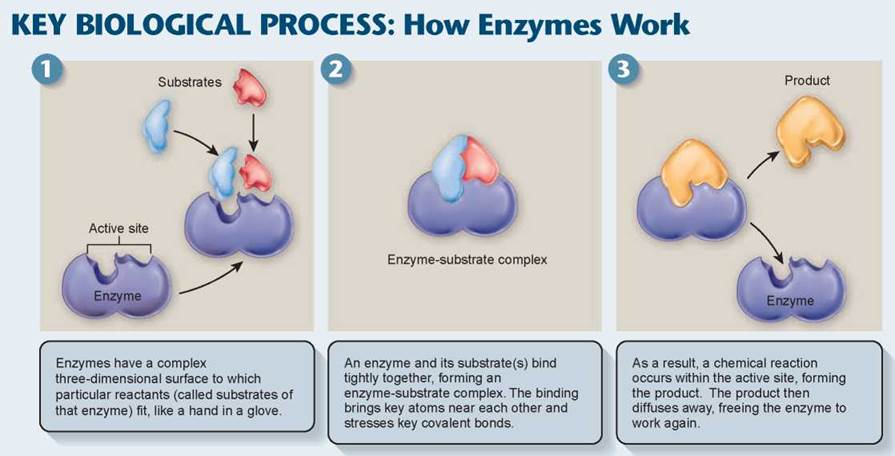
Enzymes act as catalysts that accelerate the speed of natural root zone reactions. The pH of the surroundings matters too.








-montre-comment-se-telecommande-la-grue-au-sous-prefet-d-autun-marc-makhlouf-photo-jsl-estelle-pelletier-1645798324.jpg)






