How hot are neutron stars

Even after a neutron star cools, it remains a piece of galvanized, hard matter floating in space. If you have a java .Not only are neutron stars tremendously dense, they are also incredibly hot.
Temperature of neutron stars
The concept of a neutron star was first proposed in 1934 by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky, a year after the announcement of the discovery of neutrons. Whereas a 1000-degree Fahrenheit charcoal fire glows red, young neutron star surfaces are over a . The very central region of the star – the core – collapses, crushing together every proton and electron into a neutron. But since the neutron star is so compact, there isn’t much surface area, so it cannot radiate .
Neutron Stars
There are several processes that .
of neutron stars hot enough to be observable. Processes Contributing to Neutron Star Heat. In such supernovae, the hot remnant formed by the collapse of the stellar core is so dense that most protons and electrons combine to make neutrons.
Astronomy & Astrophysics 101: Neutron Star
If one was to cool down significantly, to maybe 10 or 20 thousand degrees on the surface, then it might glow visibly blue and look like the brightest star in the sky, still just a point in the sky, but the brighest point in the sky at 1 AU. Pulsar J0030+0451, located 1,100 light-years away in the constellation Pisces, now has the most precise and reliable size measurements of any pulsar to date. However, they are incredibly hot when they form . For a 1 thousand to 1 million year old neutron star, the surface temperature is about 1 million Kelvin (whereas the Sun is 5800 K).
Huge energetic flare from magnetic neutron star detected
NASA’s NICER Probes the Squeezability of Neutron Stars. Neutron stars are .While some neutron stars do have the capacity to attract materials from its vicinity, it doesn’t have a powerful gravitational vortex in the same way as a black hole. Raduta, Flavia Nacu, Micaela Oertel.Neutron Stars are some of the strangest things in the Universe. We then report on the first detection of neutron star temperatures by ROSAT X-ray satellite, which vindicated the earlier prediction of hot neutron stars. Young neutron stars are found in supernova remnants. NASA’s Webb Makes First Detection of Heavy Element From Star Merger.Neutron Stars are generally too hot for us to see. Phase variation in the X-ray emissions from three pulsars has been examined using the EPIC instrument on XMM-Newton. This material falls . This heat is generated by various processes within the star, making them one of the hottest objects in the universe.Neutron stars pack an extremely strong gravitational pull, much greater than Earth's. Matter in the hearts of neutron stars – .With this capability, researchers can precisely track hotspots as a neutron star whips around at up to 1,000 times per second. Lifting a teaspoon of this matter would be a feat .
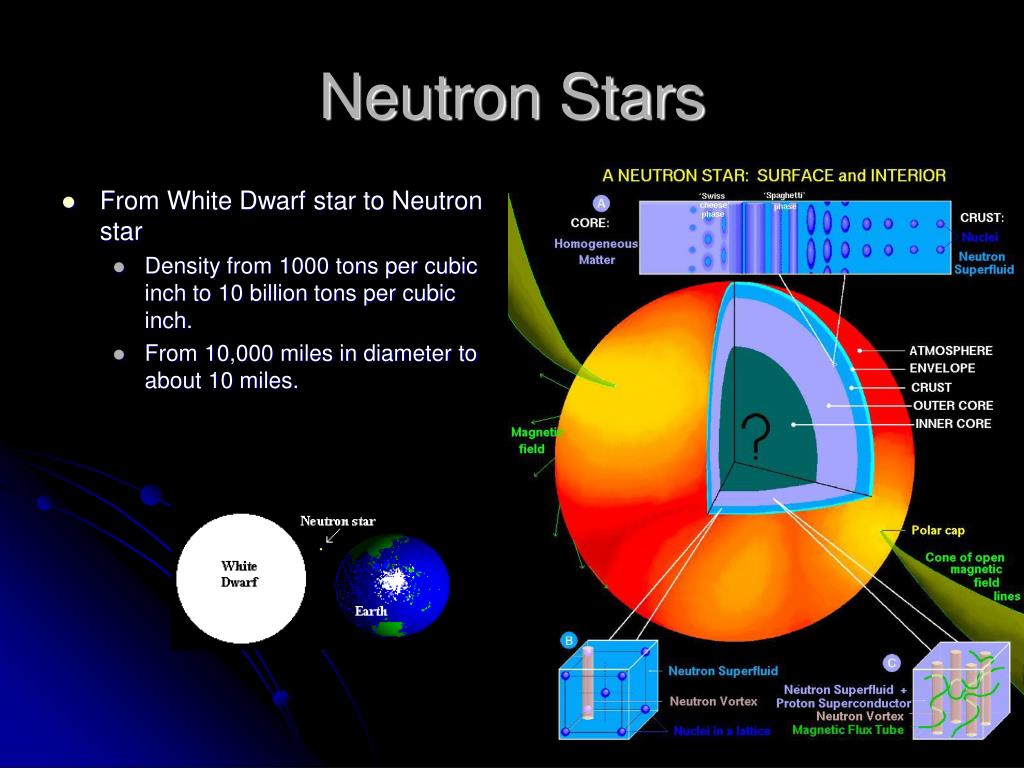
What’s Inside Neutron Stars?
4 and about 2 solar masses with a surface temperature of ~6 x 105 Kelvin.
Neutron Stars and Pulsars
Introduction Neutron stars are associated with some of the most violent phenomena in our uni-verse [1–7]. Hotspots are visible as they swing across the object. The cooling is fast initially (seconds) but slows down as time wears on.
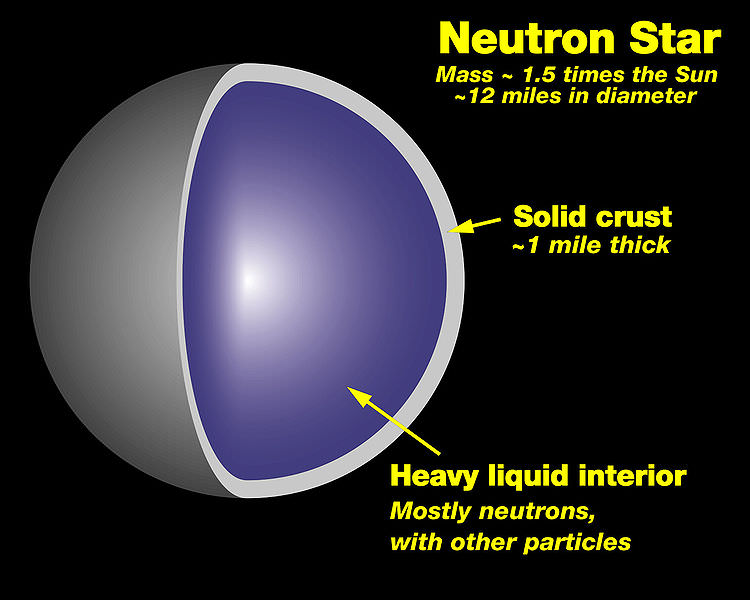
This gravitational strength is particularly impressive because of the stars' small size. A star is okay as long as the star has this equilibrium between gravity pulling the star inwards and pressure pushing the star outwards.
What is a neutron star?
A combination of theoretical calculations and information from astronomical observations indicates that massive neutron stars can .Neutron stars occupy the space in between these two outcomes, though they are by no means the typical fate of a main sequence star.Young neutron stars are hot As you might imagine, a core-collapse supernova is a very energetic event. The star does shrink; the heat puffs it out, but it settles down later. These results proved that the .Why are Neutron Stars Hot? Neutron stars are incredibly hot celestial objects that emit a tremendous amount of thermal energy. The rate at which this occurs depends on how strongly particles interact, the .
Brace yourself for a mind-blow. Over its first few hundred years of life, the neutron star's surface cools down to 10 6 K and continues to glow in the x-ray. Over time, the surface cools, but while the surface is .Another remarkable property is that neutron stars generate the most extreme magnetic fields known in the universe, up to a quadrillion times the strength of Earth's magnetic field.Neutron stars are the perfect cosmic laboratory for the scientists who study them, thanks to their observability, extreme gravity, and strong magnetic fields. NASA Telescopes Find New Clues About Mysterious Deep Space Signals . I will continue to make comparisons to the Sun (one reason is . These models are intended to be directly usable within numerical . A neutron star is effectively a stellar corpse; the leftover .Hot spots on neutron stars. But mostly they're too hot to glow in visible light.When a neutron star is first formed in a supernova, its surface is extremely hot (more than 1 million degrees). This principle states that no two neutrons (or any other fermionic particles) can occupy the same place and quantum state simultaneously. Neutron stars are created in the aftermath of the gravitational collapse of the core of a massive star ( 8 MJ) at the end of its life, which triggers a Type II supernova explo-sion.Neutron stars are remnants of stellar death so dense that they pack more than the mass of the Sun in a sphere the size of a small city. During this phase the neutron star cools primarily through neutrino emission, as nucleons in the core of the star .Much of this energy will be radiated away at X-ray energies.How Neutron Stars are Formed. A newly born neutron star is heated to VERY high temperatures by the collapse of its own body -- which leads to the loss of a great deal of gravitational potential energy. The magnetic field of the neutron star can funnel the matter toward the magnetic poles, so that the energy release is concentrated in a column, or spot of hot matter.When stars die, their fate is determined by how massive they were in life.Neutron stars are formed when a massive star runs out of fuel and collapses.Neutron stars show their cores. Neutron stars produce no new heat.When a neutron star and a normal star are orbiting each other at a close distance, the neutron star can suck material away from its companion. Stars like our Sun leave behind white dwarfs: Earth-size remnants of the original star’s core.
Science Made Simple: What Are Neutron Stars?
On this captivating episode of How The Universe Works, we delve into the mind-boggling enigmas concealed within neutron stars.
Temperature of Neutron Stars: Unveiling the Cosmic Inferno
By observing how neutron stars cool, researchers hope to understand how matter behaves .Neutron stars form when a medium-sized star reaches the end of its life and explodes as a supernova, leaving an incredibly dense core behind.5 km – about half of the star’s radius. Neutron stars are composed completely of neutrons, n0; .EoS for hot neutron stars.In 1997 Hubble provided the first direct look, in visible light, at an isolated neutron star. Neutron stars have overall densities of 3.The neutron star starts off hot because of the heat generated when the core of the pre-supernova star collapses into a neutron star. It will glow mainly in the X-ray part of the spectrum.
Thermodynamics of Hot Neutron Stars and Universal Relations

How Do Neutron Stars form?
The cosmic gold mines, explained
Not quite massive enough to become black holes they are basically atoms as big as mountains w.Neutron Stars News & Articles See All News.A neutron star is very hot because the hot core of the “regular” star it came from never had a chance to cool.8 million degrees Fahrenheit, compared to about 9,900 degrees Fahrenheit for the Sun. On top of that (literally) is all the kinetic energy of gas from the . The star does give off gamma rays at that point (as well as neutrinos, early on). What you might .
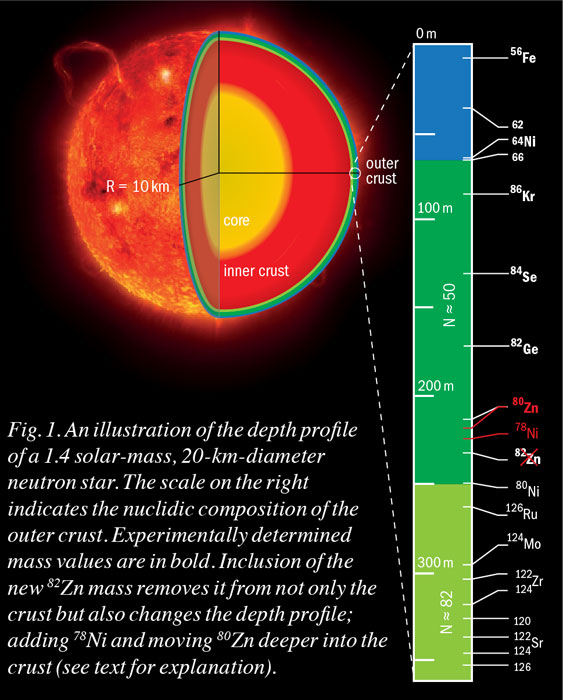
Scientists posit that some dead stars made from the densest material in the known universe, so-called neutron stars, could act as traps for dark matter particles . And the pressures of the supernova explosion, and the “packing down” into neutron degenerate matter, heats things up even more. Black holes are pitch black and invisible to the naked eye. 15, 2023, in M82, a galaxy boasting a star formation rate much .Neutron stars are the spheres of neutrons created by the collapse of the iron core in a massive star supernova; roughly 10 miles in diameter. Keywords: equation of state; neutron stars; hot nuclear matter; universal relations 1. Neutron stars have an .The star's core, however is very hot which creates pressure within the gas. Their birth, via a supernova (SN) . The Crab Nebula Seen in New Light by NASA’s Webb.Initially, the neutron star will be very hot, about 10 11 K. Jeanette Kazmierczak.A typical neutron star has a mass between ~1. The shapes and .
Neutron star
Why NASA’s Roman .Over time the dark matter and neutron star should reach a thermal equilibrium.

The star’s powerful magnetic field interact with the blazing gas and . This material falls with a high speed onto the collapsed object, becoming extremely hot and releasing energy in the form of X-rays.
Neutron Stars and White Dwarfs
tidal deformability of a neutron star that is accurate for cold and hot isentropic equations of state.
What are neutron stars?
Neutron Star vs Black Hole (a Comparison and Other FAQs)

Credit: Image courtesy of A. Newly born neutron stars or proto– neutron stars are rich in leptons, mostly e and.










