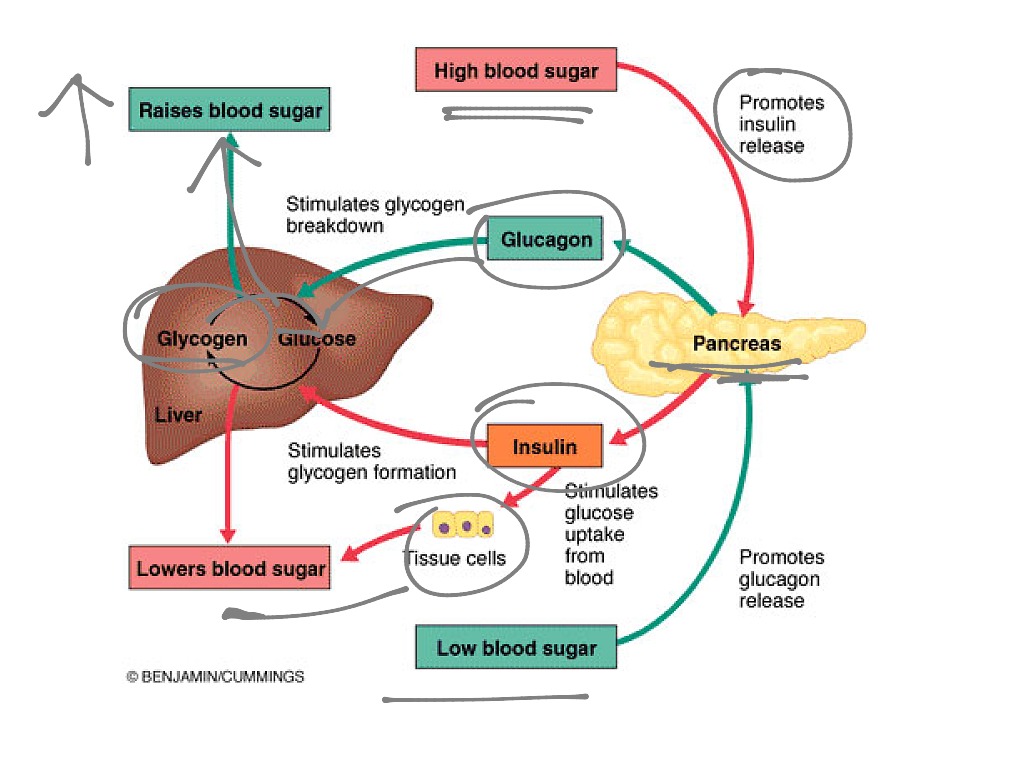
How is glucose regulated
Bergman minimal model is a non‐linear compartmental model that comprises of very small number of parameters that could describe the relationship of the glucose–insulin regulatory system with adequate accuracy [33, 34].
Two key enzymes are required for the stepwise catabolism of glycogen, glycogen phosphorylase, and glycogen debranching enzyme.In this Review, Sylow and colleagues discuss the molecular mechanisms and signalling pathways that regulate glucose uptake from the blood into the muscle during exercise, and the roles of both .
Glucose handling by the kidney
During the first week of life, preterm infants are at high risk of abnormal glucose homeostasis.The most important enzyme for regulation of glycolysis is phosphofructokinase, which catalyzes formation of the unstable, two-phosphate sugar molecule, fructose-1,6 . The body maintains homeostasis for many factors in addition to temperature. Glucose enters heterotrophic cells in two ways.Insulin and glucagon are potent regulators of glucose metabolism.Search Fundamentals of Biochemistry. There is increasing awareness that glucagon excess may .In recent years developments in genetics have shed new light on the types and physiology of various glucose transporters, of which there are two main .Insulin is the main regulator of sugar in the bloodstream. Acetyl-CoA, can bind with pyruvate carboxylase . Understand how gluconeogenesis in liver helps maintain . The mechanism behind this type of negative feedback control is described in this tutorial.Hormones Involved in Blood Glucose Regulation.Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Normal BG levels should be between 60 and 140 mg/dL in order to supply cells of the body with its required energy. Glucagon breaks down glycogen to glucose in the liver.The concentration of glucose in the blood is regulated by the action of the hormones. It is regulated by food intake, satisfying hunger or satiation. Too little glucose in our glucose-hungry brains can send us into shock.Glucagon increases blood glucose levels, whereas insulin decreases them.
Glucose regulation in preterm newborn infants
The increase in skeletal muscle glucose uptake during exercise results from a coordinated increase in rates of glucose delivery (higher capillary perfusion), surface membrane glucose transport, and intracellular substrate flux through glycolysis. In this condition, the liver is the main source of plasma glucose, because this organ controls glycogen breakdown and gluconeogenesis, which are mainly regulated by the counter-regulatory hormones of insulin.Plasma glucose levels are required to be maintained within a narrow range to ensure the normal functioning of organs and tissues. The liver has a major role in the control of glucose homeostasis by controlling various pathways of glucose metabolism, including glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. Insulin is the most potent physiological anabolic agent known, promoting the storage and synthesis of lipids, protein, and carbohydrates and inhibiting their breakdown and release into the circulation ().While not traditionally discussed, the kidneys' contributions to maintaining glucose homeostasis are significant and include such functions as release of glucose into the . Under normal conditions, the .

Glucose transporters: physiological and pathological roles
Only two enzymes are required for the breakdown of glycogen, the glycogen phosphorylase enzyme, and the glycogen .The first step by which insulin increases energy storage or utilization involves the regulated transport of glucose into .
Glucose transporters: structure, function, and regulation
On average this target range is 60-100 mg/dL for an adult although people can be asymptomatic at much more .Auteur : Mihir N.Glucose Storage, Usage and Regulation
Glucose Regulation and Utilization in the Body
In diabetes the glucagon response to hypoglycaemia becomes compromised and chronic hyperglucagonemia appears.
Blood sugar regulation
Homeostasis (article)
Blood glucose regulation involves maintaining blood glucose levels at constant levels in the face of dynamic glucose intake and energy use by the body.Diagram the mechanisms by which glucose synthesis and glucose breakdown are reciprocally regulated.To ensure that you have enough glucose in your blood at any given time, your body has a finely-tuned system to regulate your blood . Population-level (3a, 3b) and individual-level (2a, 2b) interventions and intervention components influence the behavioral risk factors, influencing blood glucose regulation and, ultimately, CVD risk. One method is through secondary active transport .Taken together, these actions increase blood glucose levels. It is an anabolic pathway.Auteur : Sal KhanRegarder la vidéo7:24Glucose insulin and diabetes. Despite considerable research, relatively little is known about how exercise/contraction regulates . Beta cells are found in the .Temps de Lecture Estimé: 7 min
Physiology, Glucose Metabolism
Sugar Homeostasis
The mechanism behind the movement of GLUT4 to surface membranes and the subsequent . If abundant pyruvate is present, an ample supply of acetyl-CoA will also be available, indicating a high energy load for the cell.
Glucose transporters: physiological and pathological roles
Red blood cells, as well as .

These include hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and .Nevertheless, blood glucose levels are tightly regulated.Glucose Reabsorption.Glycogenolysis: An Overview. Explore how glucose, a simple sugar, fuels cells in the human body. Homeostasis of Organism Water Regulation Temperature Regulation in Animals. Both the acute . In term newborn infants, this is accomplished through well-coordinated hormonal and metabolic adaptive changes. When pyruvate enters into the Kreb Cycle, it is first converted to Acetyl-CoA. Each of these processes can be altered in patients with type-2 diabetes (T2DM), providing potential targets for novel therapies. Failure to regulate blood sugar levels could lead to physiological disorders and diseases, such as diabetes. One of these transporters, GLUT4, is . Consequently, all cells express these important proteins on their surface. The complex regulation of glucose metabolism is effected by a sophisticated network of hormones and neuropeptides released primarily from the pancreas, liver, intestines, brain, muscle and adipose tissue.In contrast, during fasting state glucose remains between 4 and 5 mM, and insulin levels are low. Glucagon secreted by pancreatic α-cells is the major hyperglycemic hormone correcting acute hypoglycaemia (glucose counterregulation). and act on cells in .Gluconeogenesis is the process of synthesizing glucose de novo from 3- and 4-carbon precursors such as pyruvate, alanine, or glycerol. The blood glucose level is kept within 70–120 mg/l, and is not regulated homeostatically. Specific glucose transporters . These hormones are made in the. In addition to their important role in gluconeogenesis, the kidneys contribute to glucose homeostasis by filtering and reabsorbing glucose. Boxes represent the objectives of the .
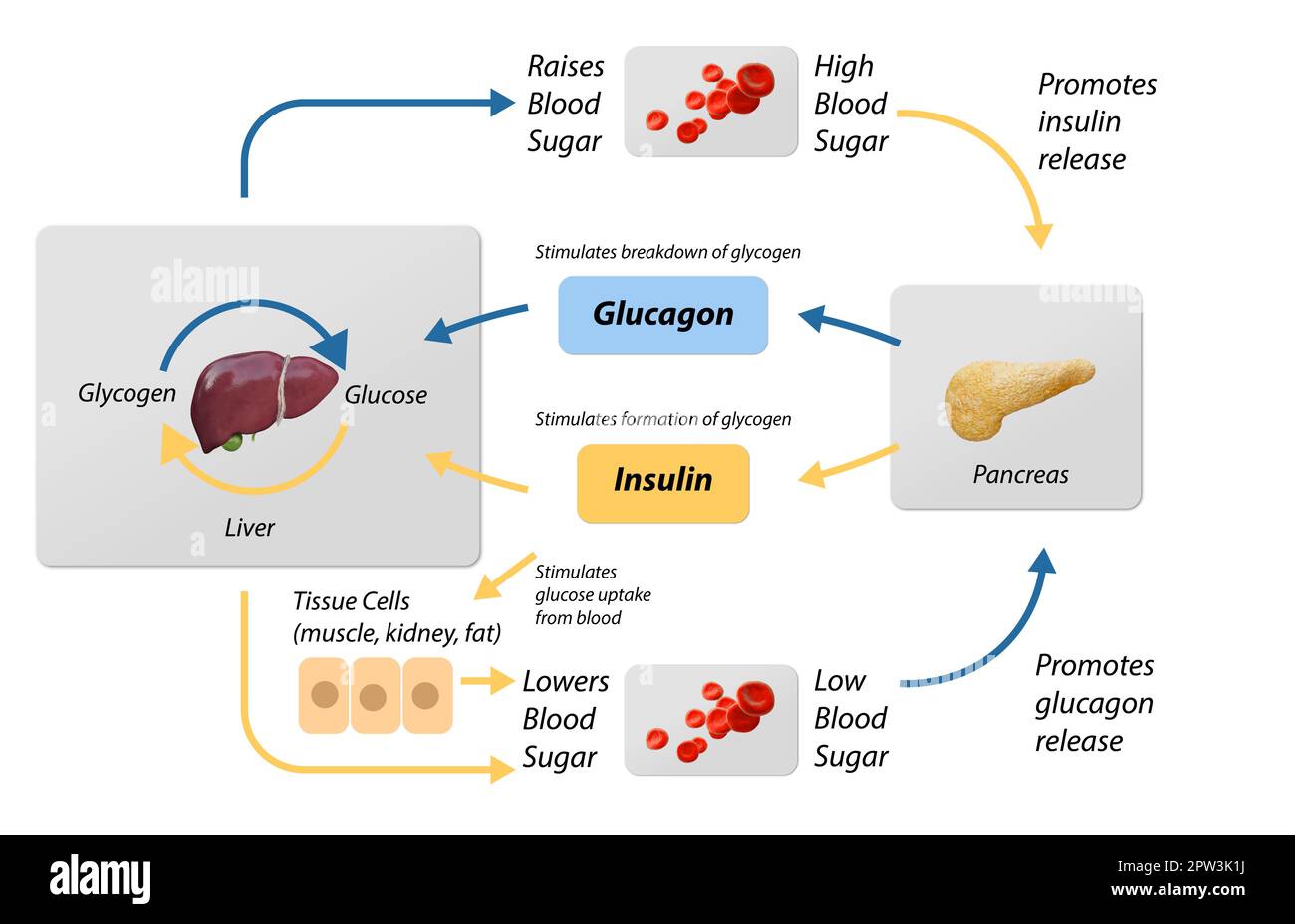
The increase in skeletal muscle glucose uptake during exercise probably results from a coordinated increase in rates of glucose delivery (higher capillary perfusion), surface membrane transport, and intracellular substrate flux through glycolysis.
Glucose Regulation
How Glucose Provides Energy.It is primarily regulated by two allosteric effectors, Acetyl-CoA and ADP, as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\).Blood glucose regulation and other risk factors are, in turn, influenced by changes in behavioral risk factors. While the food you choose to eat and how often you choose to eat impact your blood glucose level, two hormones produced in the .Glucose production is governed by the liver, which can generate free glucose from hepatic glycogen stores and de novo through gluconeogenesis.The first step by which insulin increases energy storage or utilization involves the regulated transport of glucose into the cell, mediated by the facilitative glucose . While not traditionally discussed, the kidneys' contributions to maintaining glucose homeostasis are significant and include such functions as release of glucose into the circulation via gluconeogenesis, uptake of glucose from the circulation to satisfy their energy needs, and reabsorption of glucose at the level of the proximal tubule.Regulation of Blood Glucose. Glucose, shown in figure 1 is key in the energy intake of humans. Brain cells don’t require insulin to drive glucose into neurons; however, there must still be . As glucose is a need of each and every cell of the body, so are the glucose transporters. Insulin enables blood.Auteur : Alice Callahan, Heather Leonard, MEd, Rdn, Rdn Tamberly Powell
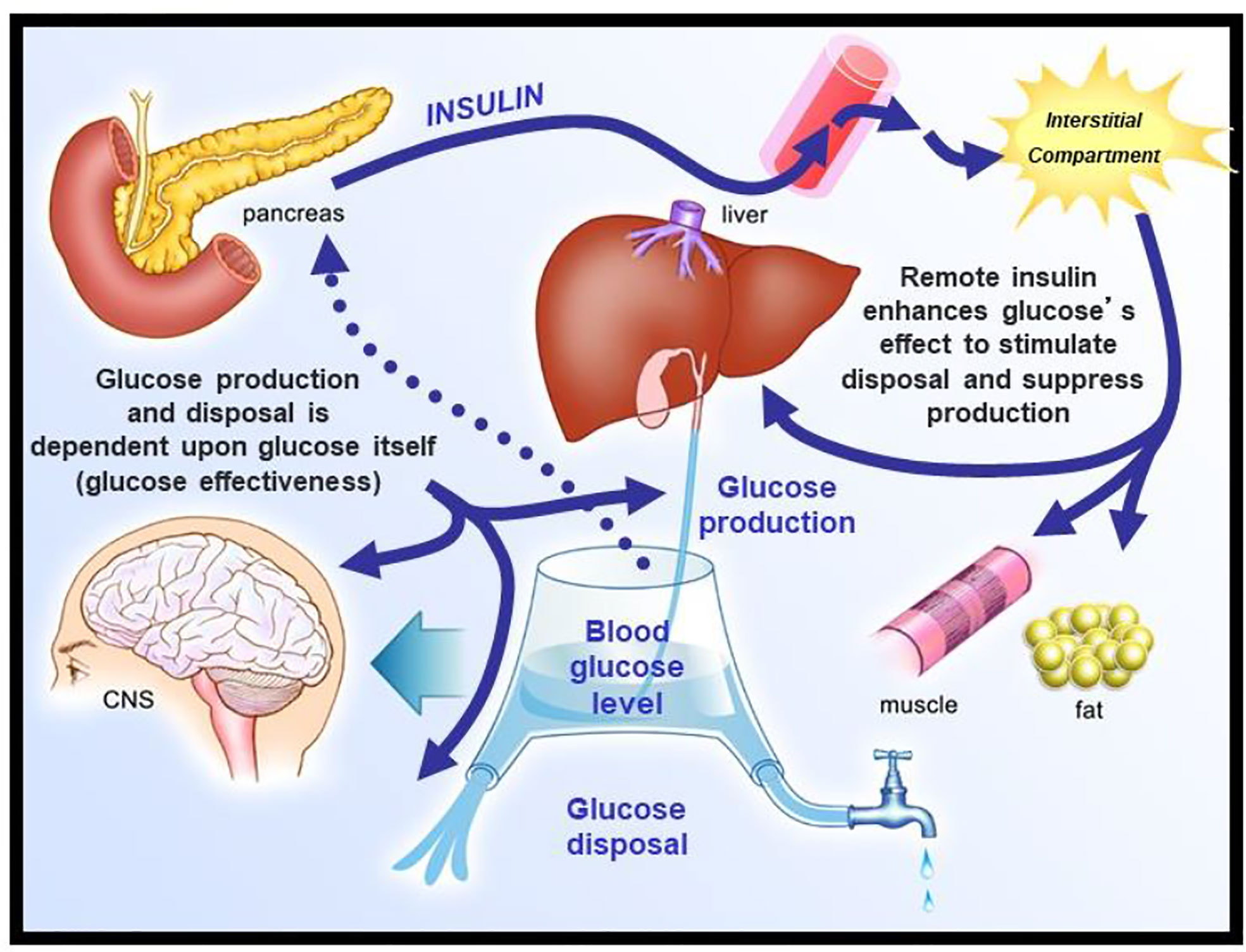
Too much glucose is associated with diabetes, an increasingly common disease that affects about 30 million Americans (10% of the US population).
Blood Sugar: What It Is and How It Works
Understand the crucial role of insulin in glucose absorption, and learn about the . What Happens When There Isn’t Enough Glucose? Another 38% of the US population has a condition called .
The Endocrine Pancreas
In the liver, the .We can summarize blood glucose regulation and its clinical significance in the following ways: The liver serves as a buffer for blood .As a counterregulatory hormone for insulin, glucagon plays a critical role in maintaining glucose homeostasis in vivo in both animals and humans. They are at risk of hypoglycemia due to limited glycogen and fat .
Glucose insulin and diabetes (video)
In some ways, gluconeogenesis is very similar to the reverse process of glycolysis (which is the breakdown or catabolism of glucose).Glucose is transported into the cell by facilitated diffusion via a family of structurally related proteins, whose expression is tissue-specific.Glucose homeostasis is tightly regulated to meet the energy requirements of the vital organs and maintain an individual's health.Sorensen model (SoM) is the complete model, which is composed of 19 differential equations and describes the . Nakrani, Robert H.Insulin and glucagon work together in a balance and play a vital role in regulating a person’s blood sugar levels. Recent studies have indicated that the kidney is responsible .Insulin increases glucose uptake into fat and muscle cells through the regulated trafficking of vesicles that contain glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4). This hormone is made by beta cells and continuously released into the blood stream.
Regulation of Blood Glucose Level
In recent years developments in genetics have shed new light .