How to find cohen's d

NEW YORK (AP) — It was the kind of tawdry tale that Donald Trump might have .Effect size calculator - Cohen's d, Cohen's h, Phi(φ), R .Cohen's d in between-subjects designs.Cohen’s d from a Stude...
NEW YORK (AP) — It was the kind of tawdry tale that Donald Trump might have .Effect size calculator - Cohen's d, Cohen's h, Phi(φ), R .Cohen's d in between-subjects designs.Cohen’s d from a Student’s t-test¶.
Cohen’s D
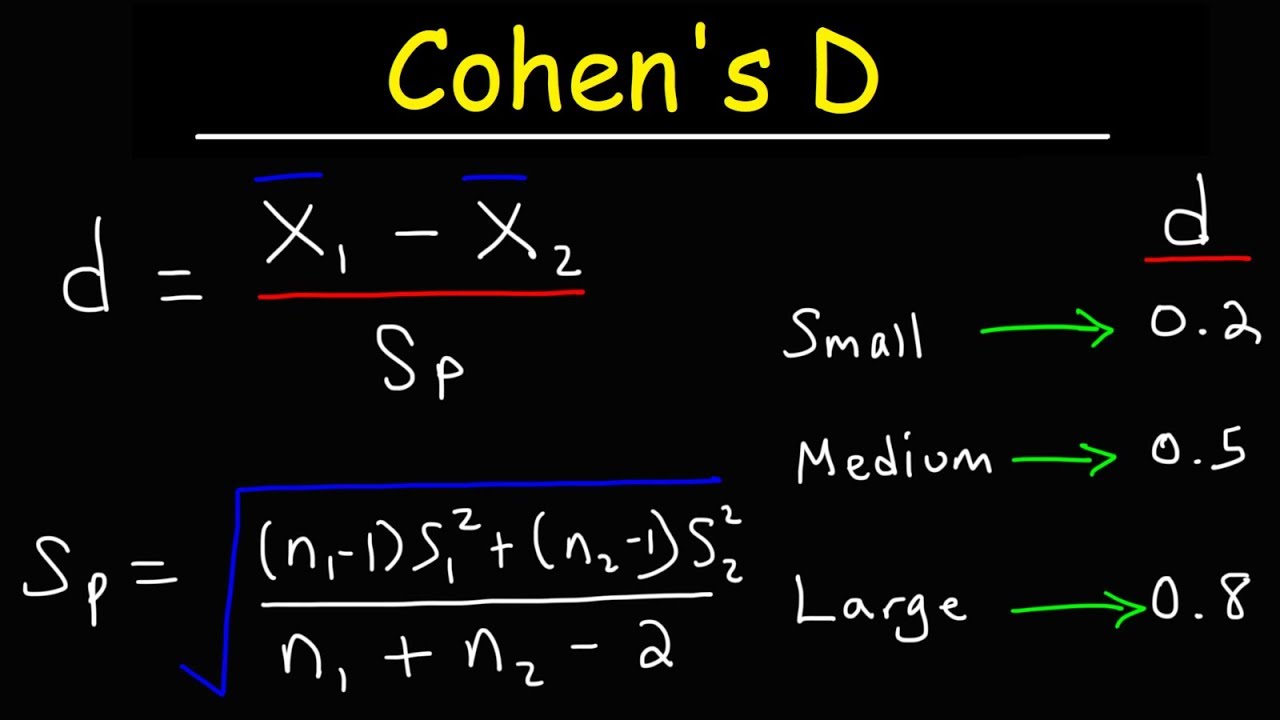
For older versions you will . This measure reports the size of the mean difference by comparing it to the data’s .by will find Cohen's d for groups for each subset of the data defined by group2.It can be computed from Cohen’s D with $$R_{pb} = \frac{D}{\sqrt{D^2 + 4}}$$ For our 3 benchmark values, Cohen’s d = 0. A d of 1 indicates that the . Companion website at https://PeterStat. Trump’s lawyers . The summary of the output produces a simplified listing of the d values for each variable for each group. It can be interpreted as a measure of the amount of overlap between the two . I am supposed to be calculating effect size (d) from a collection of research papers, but I am struggling to find the proper numbers to . Why is this not part of t-test or GLM? PROC GLM has an effectsize option, but it doesn't report Cohen's d.The formula for Cohen’s d can be seen below. Cohen’s d from a Welch test. Cohen's d = (M 1 – M 2) / SD pooled.
cohens d
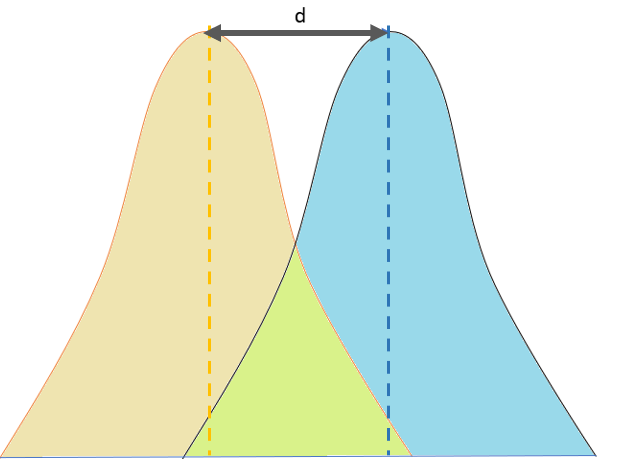
orgCohen’s d: How to interpret it? | Scientifically Soundscientificallysound. Engrais n°2 : x2 : 14. The larger the effect size, the stronger the relationship between two variables. s12, s22: variance of sample 1 and sample 2 .
Comment interpréter le d de Cohen (avec exemples)
The most commonly used measure of effect size for a t-test . Cohen's d = (M 2 - M 1) ⁄ SD pooled. Cohen's d measures the DIFFERENCE between two variables' means divided by the Standard Deviation.
Cohens D: Definition, Using & Examples
The majority of discussions of Cohen’s d focus on a situation that is analogous to Student’s independent samples t-test, and it’s in this context that the story becomes messier, since there are several different versions of d that you might want to use in this situation.How a hush money scandal tied to a porn star led to Trump’s first criminal trial. SDpooled = √((SD12 + SD22) ⁄ 2) I have a dataset with two independent groups. Voici comment nous calculerions le d de Cohen pour quantifier la différence entre les moyennes des deux . 42K views 3 years ago Statistics by Peter.Cohen’s D = ( x1 – x2 ) / √ ( s12 + s22 ) / 2.Cohen's d is calculated as the difference between means or mean minus mu divided by the estimated standardized deviation. Note this is a new . a measure of effect size based on the standardized difference between two means: It . To understand why there are multiple versions of d, it . Updated on 04/19/2018.The easiest way to calculate Cohen’s d in SPSS is to use Analyze > Compare Means and Proportions > Independent-Samples T Test.Cohen’s d is a measure of effect size, which is used to compare the magnitude of the difference between two means. Table \(\PageIndex{5}\): Cohen's Standard Effect Sizes; . where δ is the population parameter of Cohen’s d. Cohen’s d is an appropriate effect size for the comparison between two means.I am working on a compiling the results of each paper in a table, but I am unsure of how to list the results with numbers.Cohen's d effect sizes should only be regarded as a guideline; effect sizes should be examined within the research context and information from similar studies/interventions may facilitate this evaluation.There are two methods we can use to quickly calculate Cohen’s d in R: Method 1: Use lsr Package.Cohen's d is an effect size used to indicate the standardised difference between two means. a paired samples design), then that's a paired-samples t-test model, and you should use the cohen's d estimated in the paired samples t-test.Cohen’s \(d\), named for United States statistician Jacob Cohen, measures the relative strength of the differences between the means of two populations based on sample data.5 indicates that the two group means differ by 0. Step 2: Calculate the difference in means.orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Comment trouver le d de Cohen ?
The thread uses Proc Mixed and I simply do not understand it.How to run an independent samples t-test in SPSS 22 and calculate and interpret effect size using Cohen's d. The calculated value of effect size is then compared to Cohen’s standards of small, medium, and large effect sizes. May be called directly from cohen. the cohen's d we report, is always appropriate for the model you are fitting.Cohen’s d is calculated by subtracting one mean from another and dividing the result by the pooled standard deviation. if you want to calculate a cohen's d for the mean of the difference between two measurements (i. library(lsr) #define plant growth values for each group. Read real-time updates, .
How To Interpret Cohen’s D (With Examples)
How to determine Cohen's d (pooled variance, and difference version), Hedges g, and the Hedges correction (approximation) for a paired samples t-test, using . It can be used, for example, to accompany reporting of t-test and ANOVA results.Reporting effect size is becoming increasingly popular yet I cannot find a solution to this question anywhere.d = (mean 1) − (mean 2) std dev. où: En utilisant cette formule, voici comment nous interprétons le d de Cohen : Un d de 0,5 indique que les moyennes des deux groupes diffèrent de 0,5 écart-type.Example: Calculating Cohen’s d To calculate Cohen’s d for the weight loss study, you take the means of both groups and the standard deviation of the control . Evan Matthews explaining how to calculate a Cohen's d effect size that would accompany a t-test comparison. I can write increased, but I don't know how to find out the actual numbers to list.Effect Size measures the relationship between two variables (how large an effect is). Example: How to .Though the district attorney, Alvin L. A positive d indicates that the first mean is .5 standard deviations. Over the next six weeks, Mr. Cohen (1977) defined U 3 as a measure of non-overlap, where “we take . It is calculated by dividing the difference in means between two groups by the standard deviation of the pooled data from both groups. It can be used, for example, to accompany the reporting of t-test and ANOVA results.Where it is assumed that σ 1 = σ 2 = σ, i.For the independent samples T-test, Cohen's d is determined by calculating the mean difference between your two groups, and then dividing the result by the pooled standard . Bragg, has assembled a mountain of evidence, a conviction is hardly assured.D de Cohen = ( x 1 – x 2 ) / √ (s 1 2 + s 2 2 ) / 2. δ = σ μ 2 − μ 1 ,.
Effect Size
Sorted by: Cohen's d is the mean difference divided by the (pooled) standard deviation of the data within the groups.

Hoe Cohen's d te interpreteren (met voorbeelden)
n1, n2 = len(d1), len(d2)
Interpreting Cohen's d
, homogeneous population variances. The basic formula to calculate Cohen’s d is: d = [effect size / relevant standard deviation] The denominator is sometimes referred to as the standardiser, and it is important to select the most appropriate one for a given dataset.socscistatistics. Cohen's d is an appropriate effect size for the comparison between two means.5 implies \(R_{pb}\) ± 0.In statistics, an effect size tells us how large the difference is between the mean of two groups. Cohen's d is used to describe the standardized mean difference of an effect. B = [ 8, 9, 12, 15, 7] B = [8, 9, 12, 15, 7] B = [8,9,12,15,7].
SPSS and Excel
Cohen’s d from a paired-samples test. In this video this is done w.Using this formula, here is how we interpret Cohen’s d: A d of 0. It is also widely used in meta-analysis.
What Does Effect Size Tell You?
Effect Size Calculator (Cohen's D) for T-Test
How to Interpret Cohen's d (With Examples) - Statologystatology.100; Cohen’s d = 0. Cohen's d rm (which assumes the correlation between measures is known) and can be calculated as: Cohen's drm = ( M diff /sqrt (SD 12 +SD 22 -2*r*SD 1 *SD 2 ))*sqrt (2 (1-r)) Where Mdiff is the . def cohend(d1: Series, d2: Series) -> float: # calculate the size of samples.7 that takes a Pandas Series and returns Cohen's d: from numpy import var, mean, sqrt. Where: M 1 and M 2 are the means for the 1 st and 2 nd groups, SD pooled is the pooled standard . If two groups have similar standard deviations and have the same group size, . One of the most common measurements of effect size is Cohen’s .Quick Reference. Instructional video on how to determine Cohen's d for an independent samples t-test, using SPSS.And μ i is the mean of the respective population. One of the most common measurements of effect size is Cohen’s d, which is calculated as: Cohen’s d = (x1 – x2) / √(s12 + s22) / 2. In this regard, the pooled SD is used since the population SD is usually unknown.Regarder la vidéo3:27Instructional video showing how to determine Cohen's d for a one-sample t-test (as an effect size measure) using SPSS. The pooled SD is calculated based on the sample . Een d van 1 geeft aan dat de groepsgemiddelden 1 standaarddeviatie verschillen.

2 implies \(R_{pb}\) ± 0.Calculate Cohen’s d by taking the difference between two means and dividing by the data’s standard deviation.
Learning How

Un d de 1 indique que les moyennes du groupe diffèrent de 1 écart type.
How to Calculate Cohen's d in R (With Example)
To calculate the standardized mean difference between two groups, subtract the mean of one group from the other (M1 – M2) .
Effect size — Learning statistics with jamovi
243; Cohen’s d = 0.
How to Interpret Cohen's d (With Examples)
APA style strongly recommends use of Eta .
If the t-test did not make a homogeneity of variance assumption, (the Welch test), the variance term will mirror the Welch test, otherwise a pooled .Instructional video on determining Cohen's d for a paired samples t-test using SPSS.
What is Effect Size and Why Does It Matter?
A measure of effect size, the most familiar form being the difference between two means ( M1 and M2) expressed in units of standard deviations: .comEffect Size Calculator (Cohen's D) for T-Test - Social .Engrais n°1 : x1 : 15,2.

Cohen’s d from a Student t test.
T-test Effect Size using Cohen's d Measure
where: x1 , x2: mean of sample 1 and sample 2, respectively. First, we will enter the values for the mean, standard deviation, and sample size (n) for two groups. This statistics video tutorial explains how to calculate Cohen's d to determine if the size of the effect is small, medium, or large based on the. Ce processus quantifie la . These quantities are relative effect sizes: roughly speaking, Cohen’s d and f values correspond to the ratios of effect size to outcome standard deviation for T-test and ANOVA test, respectively. This value can be used to compare effects across studies, even when the dependent variables are measured in different ways, for example when one study uses 7-point scales to measure dependent variables, while the .Step 1: Enter the data.Here is how we would calculate Cohen’s d to quantify the difference between the two group means: Cohen’s d = (x 1 – x 2) / √ (s 1 2 + s 2 2) / 2; Cohen’s d = (15.Auteur : stikpet