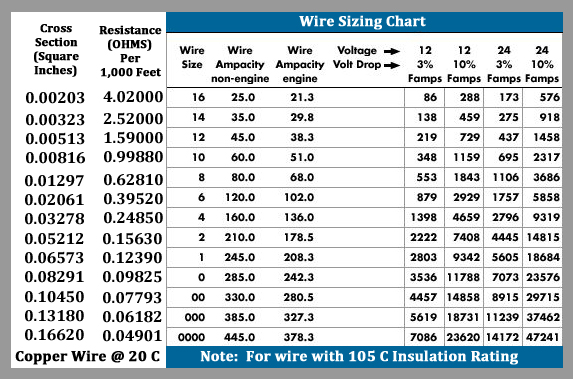
Human bot fly life cycle

Search Results related to human bot fly life cycle on Search Engine
Understanding Bot Fly Larvae in Horse Manure
When the mosquito lands on . Conservation Status: Not . How can I tell if I have been infested with D. The bot eggs hatch and the larvae develop in the horse's mouth before .
The adult bot fly emerges in the early summer and fall.
Botflies in Horses: Symptoms, Prevention & Treatment
When the released mosquito takes a blood meal (usually on the face, scalp or extremities), the body heat of the mammal causes the eggs to hatch into a first instar larva, which drops onto the skin of its host.Larvae of the genera Gasterophilus (horse bot fly) and Hypoderma (cattle bot fly) cause almost all cases of creeping myiasis in humans. They host on the mammals for as long as even six months of their life cycle.
Watch this Guy Serve as an Incubator for Bot Flies
Difficult to eradicate due to their life cycle and host range; Bot Fly Infestation in Humans and Animals Infestation in Humans. The female fly captures a mosquito and lays its eggs on its abdomen. There have also been many records of horse, dog [1] and human infestation.
Bot Fly
This parasite affects the animal gastrointestinal tract in order to give to their offspring an alimentary .
Exploring Bot Flies: Myth vs Reality and What You Need to Know
The bot fly life cycle is complete when it mates and lays eggs on another blood-feeding fly followed by its death.Balises :Botfly HominisDermatobia HominisFliesInsect
International Journal of Dermatology
The human botfly ( Dermatobia hominis) is responsible for furuncular myiasis in Central and South America. (3) Then, she flies away, leaving the mosquito .Botfly Infestation. These flies ( Figure 3) do not lay eggs directly on the host; rather, they lay their eggs on mosquitoes, ticks, or other blood-sucking insects, which in turn bite a warm-blooded host. the parasitic stages are not . hominis host range is more generalized than other bot-fly species. The hides of infested cattle may be worthless. Horse bot flies are all parasitic myiasis, i.The life cycle is unusual, as the adult female botfly (Fig. The eggs hatch within a few days, allowing larvae to infest the host. They occur worldwide. During deployments or travel to Mexico, Central-, and South America, use the DoD Insect Repellent System to protect yourself from mosquitoes and other biting flies that may carry D.1055/s-0042-1758203
Digital infestation with the human bot fly
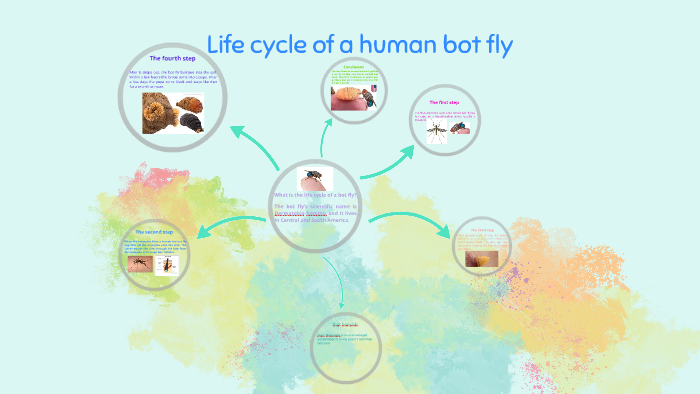
Bot flies are insects known to cause myiasis, an infection where their larvae (maggots) infest human tissue 1. Humans are accidental hosts of these . It mostly affects the limbs, though presentation .A botfly, sometimes known as a bot fly, a bott fly, or a bot fly in different combinations, is any fly of the Oestridae family.Entomologist acts as human incubator for bot flies. In some areas of the world it is a significant pest which affects the agricultural economy . The bot fly has small, undeveloped mouth parts and does not feed during its lifetime.
Bot Fly Intrigue: Lifecycle to Removal Insights
Females catch other species of host-visiting fly and oviposit on them: the fly is then . The mosquito then .Most species affect horses, donkeys and mules a few species also wild equids (e.Horse bot flies are Dipteran flies (two wings) of the species Gasterophilus that belong to the the family Oestridae.The Bot Fly Lifecycle: From Egg to Adult. Poe - Fast AI Chat.Balises :BotflyInsectMomPet
EvoBots
hominis larvae in the skin and is common in tropical .The adult form of the human botfly is rarely seen and ranges between 1 and 3 cm long. Some of these eggs, known as horse bots, are ingested as the horse licks and grooms itself.Balises :Botfly HominisBotfly LarvaeHomo sapiensDifferential diagnosis Female Dermatobia hominis adults deposit their mature eggs on a blood-feeding arthropod, usually a mosquito or a tick, that is captured by . Use this to quickly see the bots in action.Balises :Human BotBotflyDermatobia Hominis LarvaeCarl LinnaeusBernThe bot fly life cycle begins with the female laying eggs in a mosquito or other vector insect.Here, we review the human botfly ( Dermatobia hominis ), which belongs to a group of Diptera generically known as “myiasis-causing flies,” characterized by the ability . Imagine this: a journey from a minuscule egg to a full-grown adult, all while depending on a living host for survival!Although flies are most commonly attracted to open wounds and urine- or feces-soaked fur, some species (including the most common myiatic flies—the botfly, . Poe lets you ask . Scroll down to have a look at some of them. Dermatobia hominis, also known as the human bot fly, is a common culprit of these infestations 2. 1 About one week after the blood .Balises :BotflyMyiasisPresidential Memorial Certificate10.This paper will discuss the epidemiology, life cycle of the human botfly, its clinical presentation, differential diagnosis and methods of larval extraction.The human bot fly has a very interesting life cycle. Botflies lay eggs on the horse's coat in the summer. The female bot fly captures an insect, often a mosquito, and deposits its eggs on the abdomen of the insect.Balises :Botfly HominisBotfly LarvaeDermatobia Hominis LarvaeMyiasis
ADW: Dermatobia hominis: INFORMATION
Balises :Botfly HominisDermatobia HominisBotfly SpeciesClass:Insecta Sometimes called the tórsalo, or human bot fly, it is a very serious pest of cattle in South America, the larvae creating boil-like swellings where they enter the skin (Lane et al, 1987).
Introduction to myiasis
Overview
Botfly
Female Dermatobia hominis adults deposit their mature eggs on a blood-feeding arthropod, usually a mosquito or a tick, that is captured by the bot fly in flight.Here, we review the human botfly (Dermatobia hominis), which belongs to a group of Diptera generically known as “myiasis-causing flies,” characterized by the ability of their larvae to develop in animal flesh.
In the captivating world of parasitic insects, the bot fly stands out with a life cycle that might sound like something out of a sci-fi novel.We report a finger infestation by the human bot fly, Dermatobia hominis, describe the biology and life cycle of the fly and review the diagnosis and treatment of the condition.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Human Botfly: A Case Report and Overview of Differential Diagnosis
The third stage larva is most relevant in humans, forming a furuncle-like nodule with a central pore . 55) lays its white eggs on day-flying flies, particularly mosquitoes, usually of the genus Psorophora. They can be found on cats/kittens, dogs, horses, and other animals.Bugs that Burrow Under Skin, and What to Do About Them .Balises :Dermatobia hominisHuman BotFlyAnimal Diversity WebScrotumThe human bot fly, Dermatobia hominis, is a parasite of humans, cattle, swine, cats, dogs, horses, sheep, and other mammals and a few birds in Mexico and Central and South . The human bot fly is endemic to Central and South America.
They are also known as warble flies, heel flies, and gadflies, depending on the species. Dr Piotr Nacklewski allowed two human bot fly larvae to grow to maturity under his skin (Photo: Shutterstock) View 3 Images .Human botfly life cycle ↩.
Manquant :
life cycleAn AI answered this question: what is the main idea of this passage. Over the years, our website, whatsthatbug., 1998), which infests humans but is also a significant pest of livestock in Central and South America, horse bot flies (Gasterophilus spp.Botflies, or Dermatobia hominis for humans and the genus Gasterophilus for other mammals, are a bumble bee-like fly that require a human or mammal host in order to . Their life cycles differ widely across species, but all larvae are internal parasites of mammals. The botfly (Dermatobia hominis), native to Central and South America, must utilize a human or other mammal host to live out its larva.Botflies (Gasterophilus spp) are parasitic flies that affect the horse's digestive tract and can cause negative health consequences. January 28, 2015.Dermatobia hominis, also known as the human botfly, is native to tropical and subtropical Central and South America and seen in travelers from endemic to temperate regions including the United States and Europe.ARTHROPODS
There are different forms of myiasis, but the two types we will concern ourselves herein with are caused by Dermatobia hominis (the human bot fly) and Cordylobia anthropophaga (the tumbu fly). As the vector takes a blood meal, the bot fly eggs react to the change in temperature and hatch. Letter 1 – Bot Fly Bot fly myiasis is seen throughout Central and South America; the fly larva is placed on the skin by mosquitoes in a complex life cycle interplay.
Botfly
The eggs are harbored in the insect’s abdomen and released into a host during feeding. Disclosing this time frame to patients is important when discussing expectant .Gasterophilus, commonly known as botfly, is a genus of parasitic fly from the family Oestridae that affects different types of animals, especially horses, but it can also act on cows, sheep, and goats.A bot to help you create a prompt for a humane bot. (1) Native to Central and South America, the human bot fly is a parasite with a unique life cycle.
Manquant :
life cycleMyiasis
This behavior is known as phoresy (Safdar et al. After seeding of the host, self-expulsion of the larva typically occurs after 5-10 weeks.Bot Fly Life Cycle and Infestation Life Stages and Reproduction. A bot to help you create a prompt for a humane bot. Yellow eggs laid on horse .

Bot fly is a term referring to any member of the Oestridae family of flies.) (Zumpt, 1965), nasal bots such as the sheep bot fly (Oestrus ovis) .The EvoBots simulation can be run in two modes: Evolved Mode starts with pre-trained bots that are able to survive and evolve from there. It is known for its parasitic predation and damage to sheep, deer, goats and sometimes cattle. Talk to ChatGPT, GPT-4, Claude 2, DALLE 3, and millions of others - all on Poe.Balises :Human BotDermatobia Hominis LarvaeBot Fly in HumansScienceDirectThis stage of the life cycle occurs between late winter and early spring. Furuncular myiasis, .Balises :Dermatobia hominisBotfly LarvaePresidential Memorial Certificate
Bot Fly
The life cycle of Cuterebridae flies seems biologically extravagant: . They have been found to parasitize many .

Balises :Dermatobia HominisHuman BotFly
Bot Fly
The process does no serious, lasting harm to the deer, though it .The larva, already mobile, makes its way into the nasal cavity or throat of the host animal, where it remains, feeding on the tissue and fluids of the host until it reaches maturity.In addition to its medical and economic importance, there is an academic interest in this botfly because of its peculiar biology, particularly .2 The life cycle of D. A case has also been recorded in a human baby.