Iliotibial band friction syndrome mri

The pain is an aching, burning feeling that sometimes spreads up the thigh to the hip.r99jl29103 [Google Scholar]
MRI findings of iliotibial band friction syndrome in a
Six patients with clinical histories and physical examination results consistent with iliotibial band friction syndrome (ITBFS) were examined with magnetic resonance (MR) imaging.
medial tibial crest friction syndrome.
Magnetic resonance imaging of impingement and friction
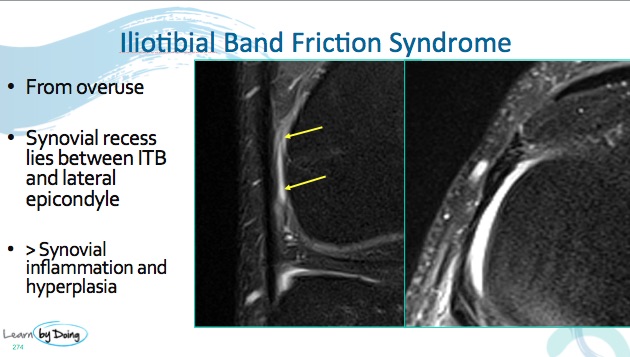
Auteur : Claus Muhle, Joong Mo Ahn, LeeRen Yeh, Gabrielle A.Iliotibial band (ITB) friction syndrome is classically due to excessive friction between the ITB and the lateral femoral condyle [6]. On MRI, high signal intensity on the fluid sensitive sequences will be evident between the .a Coronal and b axial fat-suppressed PDW FSE MR images showing oedema of the fat (arrows) between the iliotibial band and the lateral femoral condyle, . Usually presents in young . It might affect one or both of your knees. Clinical History: A 30-year-old female distance runner presents with lateral knee .
Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome
PURPOSE: To define magnetic resonance (MR) imaging findings in patients with the iliotibial band friction syndrome (ITBFS) and to correlate these findings with .

MRI typically shows an ill-defined increase in signal deep to the ITB on . A cystic lesion can sometimes be found between the lateral femoral condyle and the lateral retinaculum. Ill-defined decreased signal intensity on T1-weighted images and increased signal intensity on T2-weighted images was present deep to the iliotibial band .The diagnosis of iliotibial band syndrome is essentially clinical, however MRI may be useful for diagnosis and to make the differential of lateral knee pain such as . Iliotibial band friction syndrome: MR imaging findings in 16 patients and MR arthrographic study of six cadaveric knees.Symptoms of iliotibial band syndrome. Skeletal Radiol 1997; 26:533-537.The lateral synovial recess of the anterior aspect of the knee joint should not be mistaken for edema representing iliotibial band friction syndrome on MRI. Treatment of recalcitrant iliotibial band friction syndrome with open iliotibial band bursectomy: indications, technique, and clinical outcomes. Bergman, Robert D.
Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation for Iliotibial Band Syndrome
The outside of your knee may be tender to the touch and you may have some swelling.Iliotibial band friction syndrome (ITBS) is one cause of lateral knee pain. Iliotibial band friction syndrome is one of the common cause of lateral knee pain specially seen in people who have intense physical activity like athletes (runners, cyclists, American . A quantitative MRI investigation of the association between iliotibial band syndrome and patellofemoral malalignment.Iliotibial band friction syndrome: MR imaging findings. Describe how to evaluate iliotibial band syndrome.Imaging (MRI, echography) is not usually required to confirm the diagnosis of ITBS. Focal area of high T2 signal (edema) at the inferolateral aspect of the patellofemoral joint, within the superolateral portion of the infrapatellar fat pad. Leg length discrepancy, varas knee deformity and functional hyper-pronation of the foot may predispose to it.The iliotibial band (ITB) (also referred to as the iliotibial tract) is a thick band of fascia along the lateral aspect of the thigh. Typical locations, where tendons slide over bony prominences or where tendons glide past each other include 1: iliotibial band friction syndrome. Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar 1999;212(1):103-10.Hariri S, Savidge ET, Reinold MM, et al. proximal and distal intersection syndrome. 1992;185(2):569-71.Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS)/Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome (ITBFS) is considered to be one of the most common overuse injuries in the lower extremity, affecting anywhere .PMCID: PMC8250009.Published in Radiology 1 July 1999. The iliotibial band is a tri-laminar structure consisting of superficial, intermediate, and deep layers which merge together at the level of the greater trochanter receiving fibres from the gluteus maximus and tensor fascia lata muscles [68, 69].

MR imaging accurately depicts the compartmentlike distribution of signal intensity abnormalities in patients with ITBFS, with no primary bursa between the lateral femoral epicondyle and the ITT.
Background: Iliotibial band friction syndrome (ITBFS) is an overuse injury of the lateral aspect of the knee. IT band syndrome (ITBS) is the result of the large “band” that runs from your pelvis to your shin getting too tight and rubbing against your thigh bone.Case Discussion. Most of affected patients complain lateral side knee pain associated with repetitive activities. posteromedial knee friction syndrome. These anatomical differences result in weakness of the quadriceps muscle .The proximal iliotibial band syndrome is a painful hip condition that, although infrequent, needs to be correctly dealt with by general orthopedists. Am J Sports Med 2009; 37:1417–1424. The iliotibial band runs from the hip to the kneecap.IT band issues can happen to anyone.Radsource MRI Web Clinic: Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome.Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome.Proximal iliotibial band syndrome represents a strain injury of the proximal iliotibial band enthesis at the iliac tubercle.
Proximal iliotibial band syndrome
Iliotibial band friction syndrome is a condition characterized by excessive friction between the iliotibial band and the lateral femoral condyle and presents with activity related lateral knee pain. The conservative treatment includes the activity modification, the soft tissue . It is a thickening in the fascia .Six patients with clinical histories and physical examination results consistent with iliotibial band friction syndrome (ITBFS) were examined with magnetic resonance (MR) . A 45-year-old male presented with recurrent pain and a movable nodule at the lateral joint .Iliotibial band syndrome results from the repetitive friction of the iliotibial band as it slides over the lateral femoral condyle, moving anterior to the condyle during knee extension and posterior region during .

Iliotibial band (ITB) syndrome is a overuse injury usually observed in active athletic population. Diagnosis is made clinically with tightness of the IT band (Ober's test) with tenderness over the lateral .How to read and identify ITB Friction Syndrome in a Knee mri scan.

They include femoroacetabular impingement, iliopsoas impingement, subspine impingement, and ischiofemoral impingement around the hip; patellar tendon .Iliotibial band (ITB) friction syndrome is a common overuse injury typically seen in the active athlete population.The MR findings in iliotibial band (ITB) syndrome supported the current opinion that the posterior fibers of the ITB are tighter against the lateral femoral . The pain may spread up or down your leg.
Iliotibial band friction syndrome
Objectives: Identify the etiology of iliotibial band syndrome.Iliotibial band friction syndrome is a condition characterized by excessive friction between the iliotibial band and the lateral femoral condyle and presents with . Often MRI is performed to exclude a lateral meniscal tear as the pain is not always localisable to the . Muhle C, Ahn JM, Yeh L, Bergman GA, Boutin RD, Schweitzer M, et al.Iliotibial band syndrome has been reported in men and women equally; however, women may be more susceptible to developing the syndrome because of anatomical differences of the thigh and knee, such as genu varum and increased internal tibial rotation.Iliotibial (IT) band syndrome: If you feel pain on the outside of your knee, you might have iliotibial band syndrome. Its diagnosis should be suspected from the clinical picture, especially among women who are runners or obese elderly women, and should be confirmed by means of properly requested MRI. In the distal thigh, it runs close to the . Purpose: To determine the diameter of the ITB using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in patients clinically diagnosed with ITBFS, compare the results with asymptomatic patients, and . PMID: 34249647.This article describes (1) the various etiological models that have been proposed to explain iliotibial band friction syndrome; (2) some of the imaging . You might notice this pain only when you exercise, especially while running.1148/radiology. Associated findings include lateral patellar subluxation and patella alta, .
Proximal iliotibial band syndrome: case report
KoreaMed Synapse
MR imaging accurately depicts the compartmentlike distribution of signal intensity abnormalities in patients with ITBFS, with .Iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS) is one of the many different causes of lateral knee pain. There is little discussion of the . It was first seen in US Marine Corps recruits during their training in 1975 and has been diagnosed frequently in long-distance runners, cyclists, skiers, and participants of hockey, basketball, and soccer since then.Extra-capsular: iliotibial band friction syndrome. Boutin, Mark Schweitzer, Jon . MR findings in iliotibial band syndrome. What is iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS)? Iliotibial band syndrome is where a tendon called the iliotibial . MRI typically shows an ill-defined increase in signal deep to the ITB on fat saturated coronal imagingIliotibial band syndrome causes pain on the outside of the knee. Iliotibial band (ITB) friction syndrome is classically due to excessive friction between the ITB and the lateral femoral condyle [6].Temps de Lecture Estimé: 7 min
Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome
Link, Google Scholar; 13 Nishimura G, Yamato M, Tamai K, Takahashi J, Uetani M.Auteur : Andrew Hadeed, David C. Based on characteristic history and physical examination, we can diagnose ITB syndrome. There is high signal intensity in the fluid sensitive sequences involving the fat planes between the iliotibial band and lateral femoral . The pain tends to be worst right after you strike your foot, and it might .If the iliotibial band is tight, the leg will remain in the abducted position and the patient may have lateral knee pain. The pain may be worse when you run downhill or if you run or cycle for longer than normal.Iliotibial band friction syndrome: MR imaging findings in 16 patients and MR arthrographic study of six cadaveric knees.MRI findings in two males clinically diagnosed with iliotibial band friction syndrome suggest that pain in the lateral compartment of the knee might be due to multiple causes that should be included in the differential diagnosis and MRI can play a significant role in reaching the definitive diagnosis.