Importance of urea cycle

The urea cycle is a set of biochemical reactions that produces urea from ammonium ions in order to prevent a toxic level of ammonium in the body.
The Importance of Recycling: How to Recycle Right
Urea cycle
It is an important metabolic pathway for balancing nitrogen in the bodies of animals and it takes place primarily in the liver and kidney. In these reactions, an amine . Recycled metals create six times more jobs than sending the metals to a landfill. Ammonia is produced in our bodies by amino acid catabolism, deaminations and .Recent genome analysis has suggested that an ornithine-urea cycle similar to that found in metazoans is present in diatoms, unicellular algae important in marine ecosystems. Consistently, hepatic metabolomics profiling showed reduced . Protein catabolism produces ammonia, which is highly toxic to the body organs.
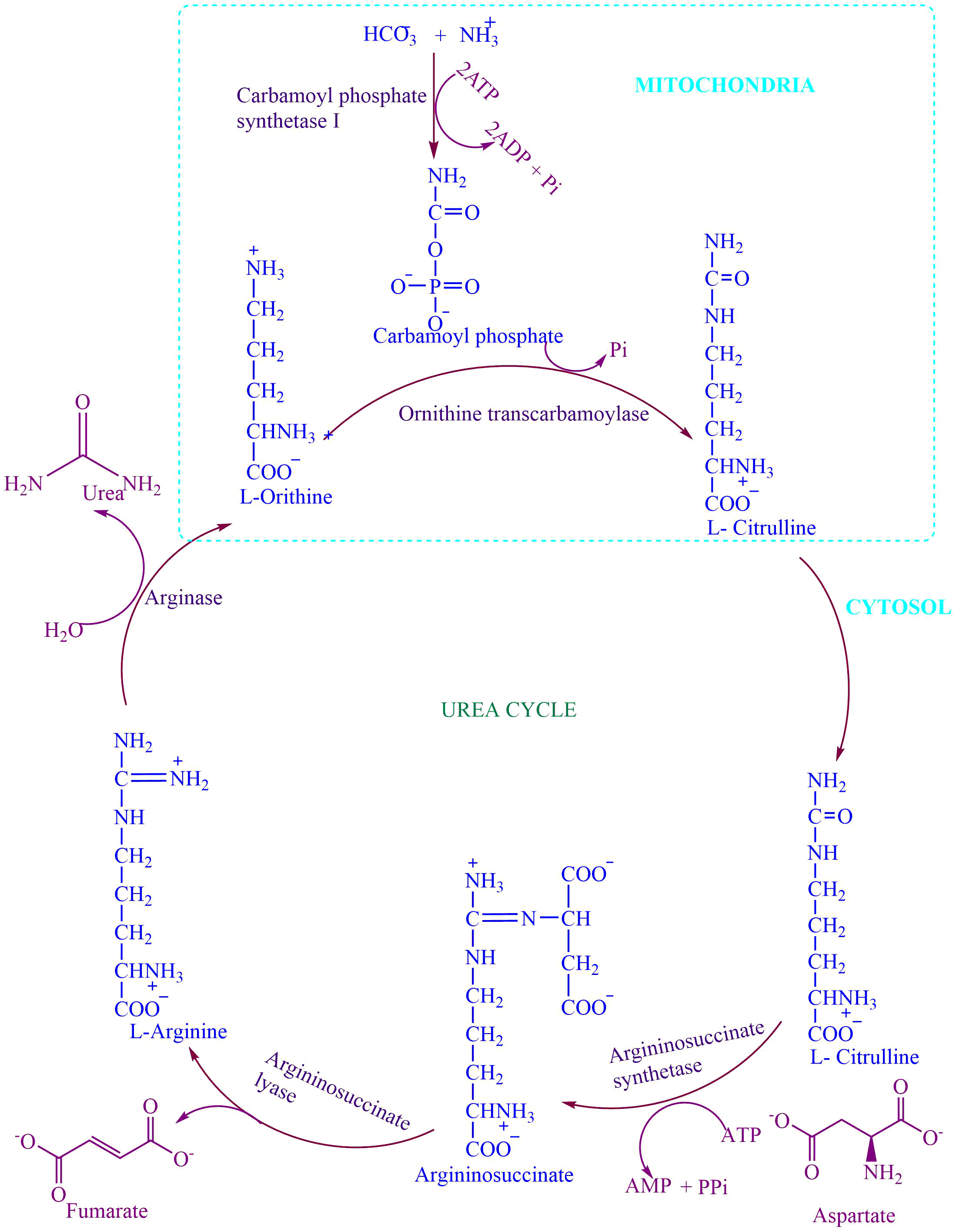
The key metabolic system known as the urea cycle is essential for the body’s process of excreting extra nitrogen. A failure of ureagenesis occurs because of acquired disease, such as cirrhosis secondary to .When considering any biochemical pathway it is always important to balance the system, and while the urea cycle is usually described in textbooks as a pathway of nitrogen metabolism such . The absence of a fully functional urea cycle may result in hyperammonemic encephalopathy and irreversible brain injury in severe cases. It was discovered in 1932 by Hans Krebs and Henseleit.Recycling will reduce the amount of waste of landfills which is potentially hazardous for the environment.The study found that in a single year, recycling and reuse activities in the United States accounted for: 681,000 jobs, $37. One important aspect of the nitrogen cycle is the urea cycle, which involves biochemical reactions that produce urea from ammonia.Introduction Urea is the major disposal form of amino groups derived from amino acids pool and 90% of nitrogen containing component of urine Urea cycle is a cyclic process Urea formation takes place in the liver Some reaction occur in mitochondria (1,2) and some In cytosol (3,4,5) Synthesis of 1 molecule of urea need • 3 Molecule of ATP • 1 . Living organisms must have some mechanisms of removing this ammonia from the cell environment because even low concentrations of .The fate of the amino group: the urea cycle.The urea cycle is a metabolic pathway for the disposal of excess nitrogen, which arises primarily as ammonia. One turn of the cycle: consumes 2 molecules of ammonia. Ammonia, of course, is generated by metabolism of amines and is toxic, so managing . The urea cycle takes place primarily in the liver, and to a lesser extent in the kidney. However, in some animals including . creates 1 molecule of urea ( (NH 2) 2 CO. Prior to the urea cycle, ammonium ions are produced from the breakdown of amino acids. First, the enzyme CPS takes ammonia and bicarbonate and forms carbamoyl phosphate .We believe that it is very important to study organisms that have a high potential for efficiently metabolizing urea in order to apply this knowledge to improve .42 in tax revenue for every ton of materials recycled.Since the TCA cycle is a cycle, an equivalent of one oxaloacetate must return to the cycle. consumes 1 molecule of carbon dioxide. Detoxification of Ammonia: The primary function of the urea cycle is to convert highly toxic ammonia into urea, a relatively non-toxic compound. Toxic ammonia is . To evaluate whether the urea cycle is associated with the progression of gliomas, . Although our bodies cannot tolerate high concentrations of urea, it is much less poisonous than ammonia.
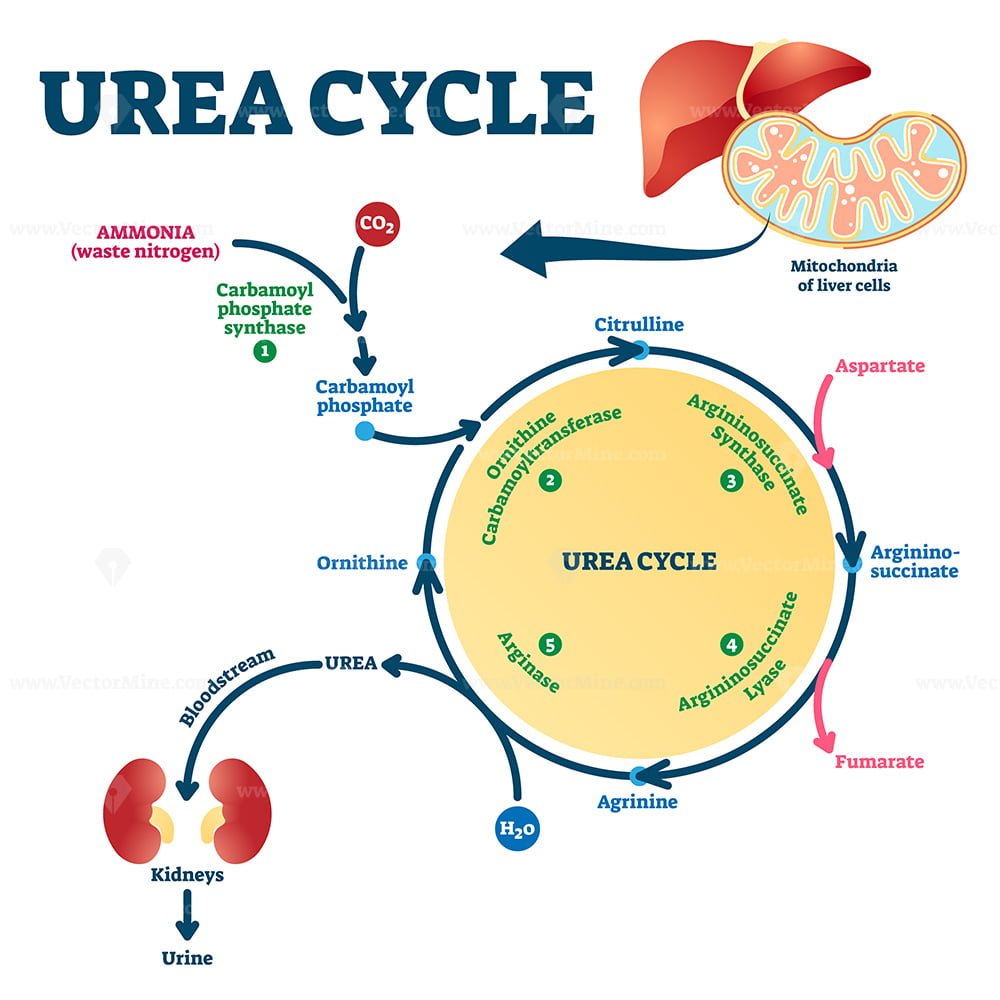
Urea cycle or ornithine cycle helps to excrete two harmful gases ammonia and carbon dioxide out of the body.
Urea Cycle
This equates to 1. Most organisms eliminate ammonia directly to the external environment. regenerates a molecule of ornithine for another turn. One of its primary benefits lies in its ability to reduce waste. By recycling, we can divert materials from . This occurs by deamination.Improves Wetlands.Urea, a nitrogenous waste material, is the end product excreted in urine when ammonia is metabolized by animals, such as mammals. The urea cycle, also known as the “Ammonia Detox Cycle”, is the process by which ammonia is removed from the body. Recycled materials might be cheaper than the virgin materials for manufacturers and this can help to reduce the price of those products. The urea or ornithine cycle is a series of biochemical reactions found primarily in the liver and, to some extent, in ureotelic animals such as amphibians . Steps of this cycle take place in the mitochondria and cytoplasm. Deamination of amino acids results in the production of ammonium ( NH 4 + ). Les déficits du cycle de l’urée ( urea cycle disorders, UCD) sont des maladies héréditaires du métabolisme dont les signes cliniques sont en majeure .The urea cycle is a series of reactions that result in the production of urea from ammonia.Reactions of the Urea Cycle.The importance of recycling cannot be overstated. CPS1, a first key enzyme in the urea cycle that transforms ammonia and bicarbonate into carbamoyl phosphate, is elevated in glioblastoma (Wu et al.The first two steps of the urea cycle occur in the mitochondria of the cell.Whilst recycled materials are valuable commodities in the worldwide market and are financially important; recycling is good for the environment too.
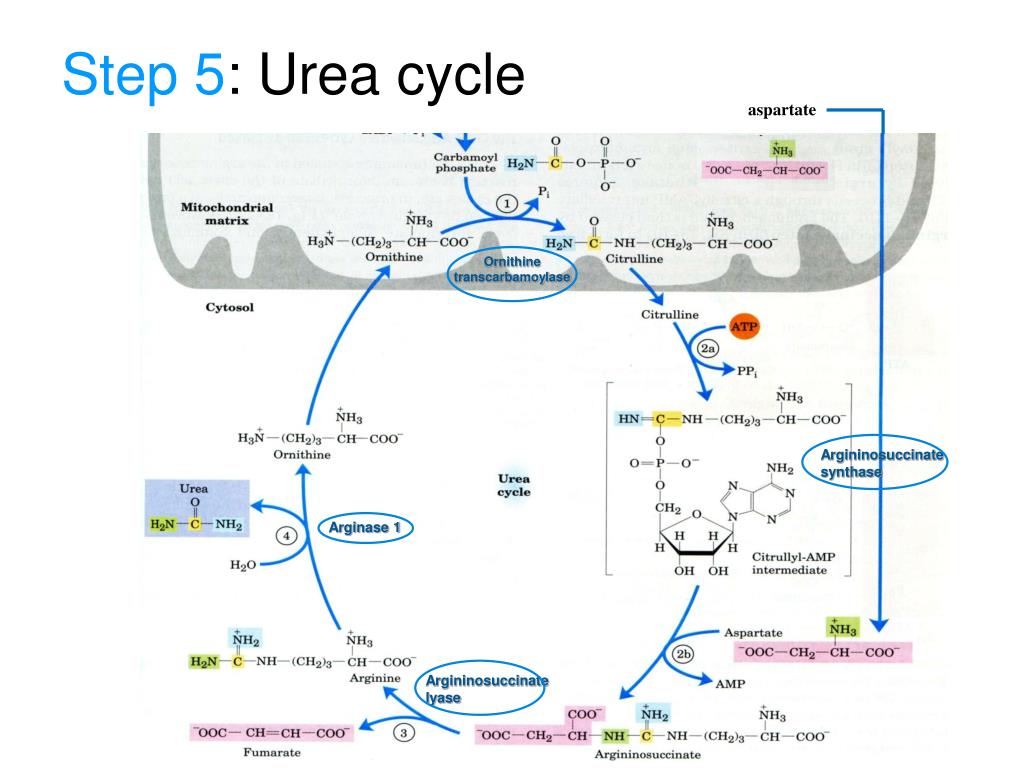
Liver is the main organ synthesising urea along with the kidney to a lesser . The first two steps of the urea cycle occur in the mitochondria of the cell. Allen, Christopher L. The animals that excrete in the form of urea are called ureotelic.2 The Urea cycle. First, the enzyme CPS takes ammonia and bicarbonate and forms carbamoyl phosphate with the use .5 billion in tax revenues. Dupont, Miroslav Oborník, Aleš Horák, Adriano .

Temps de Lecture Estimé: 4 min Thus, the kidney releases ARG which is required by other tissues.
Recycling Basics and Benefits
There, it gets converted to malate, which can get transported into the mitochondria by a transport protein, mitochondrial 2 .It is an important pathway in amphibians and mammals as they help in disposing highly toxic ammonia by converting it into urea. Most of our nitrogenous waste comes from the breakdown of amino acids.
What is the Urea Cycle?
Importance of Urea Cycle. Using recycled metal, known as scrap metal, instead of new metal reduces mining waste by 97% and saves more than 90% on energy, depending on the material.Metal is also very important as it saves energy, reduces emissions, and creates jobs. About 10 to 20 g of ammonia is removed from the body of a healthy adult every . Ammonium is an extremely toxic base and its . The absence of a fully functional urea cycle may result in hyperammonemic encephalopathy . In 2008-09 over . Two nitrogen atoms enter the urea cycle as NH 4+ and aspartate. • The urea cycle is the first metabolic pathway to be elucidated • The cycle is known as Krebs–Henseleit or Ornithine cycle • Urea is synthesized in liver & transported to kidneys for excretion in urea • The two nitrogen atoms of urea are derived from two different sources, one from ammonia & the other directly from the a- amino group of . Ammonia is highly toxic to the central nervous system . Now we are in a position to see what happens to excess NH 3 /NH 4+ that accumulates in the liver mitochondria. 44-6) mediates the removal of ammonia as urea in the amount of 10 to 20 g per day in the healthy adult. The urea cycle was discovered by Hans Krebs and Kurt Henseleit in 1932.
10: Nitrogen metabolism and the urea cycle
The urea cycle takes place primarily in the . Hence, decrease in ARG availability for the liver slows down ureagenesis.The below mentioned article provides notes on Urea Cycle.

Carbamoyl phosphate reacts with ornithine, a compound both required as input to, and regenerated by the cycle, to .
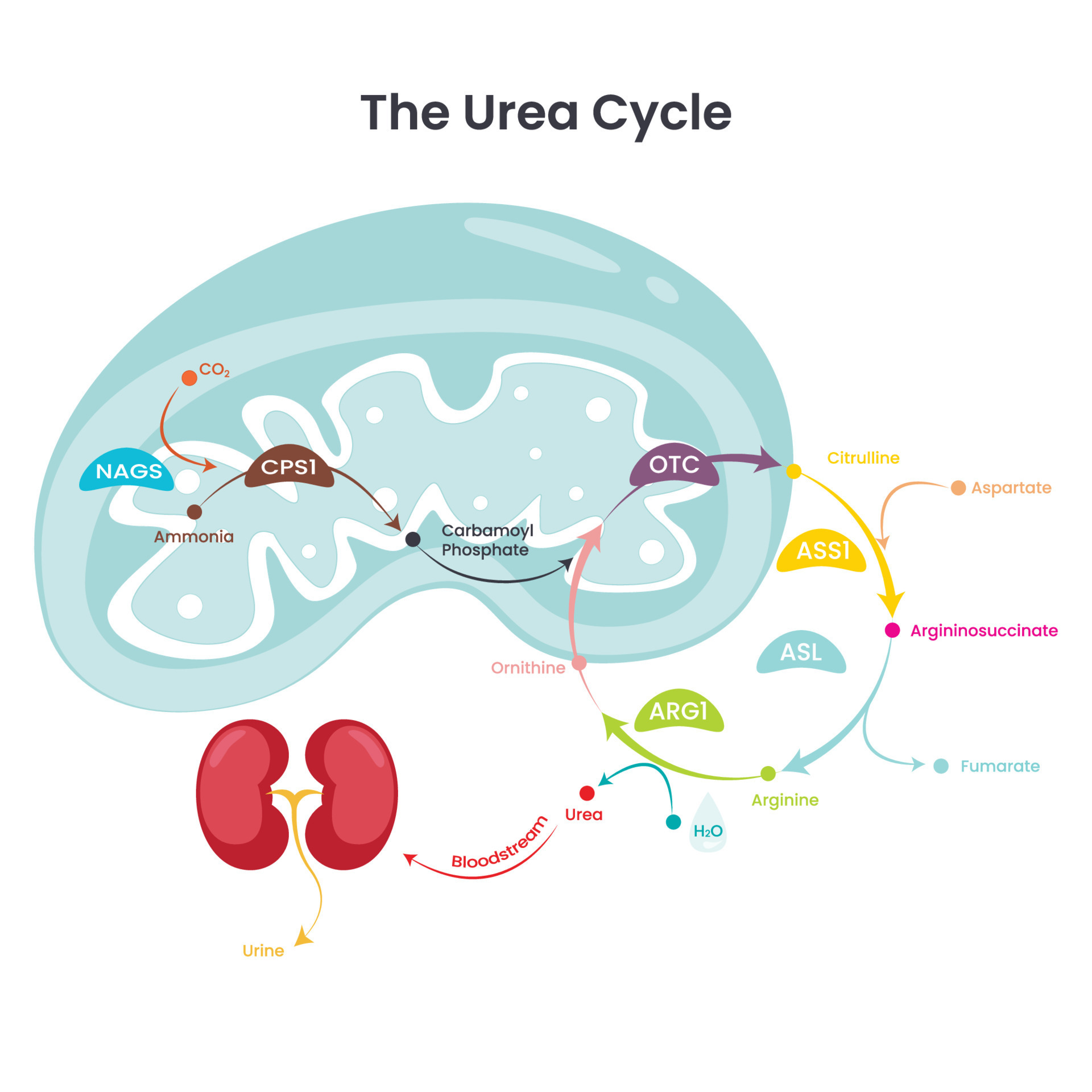
Yet another cyclic pathway important in cells is the urea cycle (Figure 7. Ammonia is highly toxic to the central nervous system and needs to be eliminated from the body.The ornithine–urea cycle (urea cycle) makes a significant contribution to the metabolic responses of lower photosynthetic eukaryotes to episodes of high .
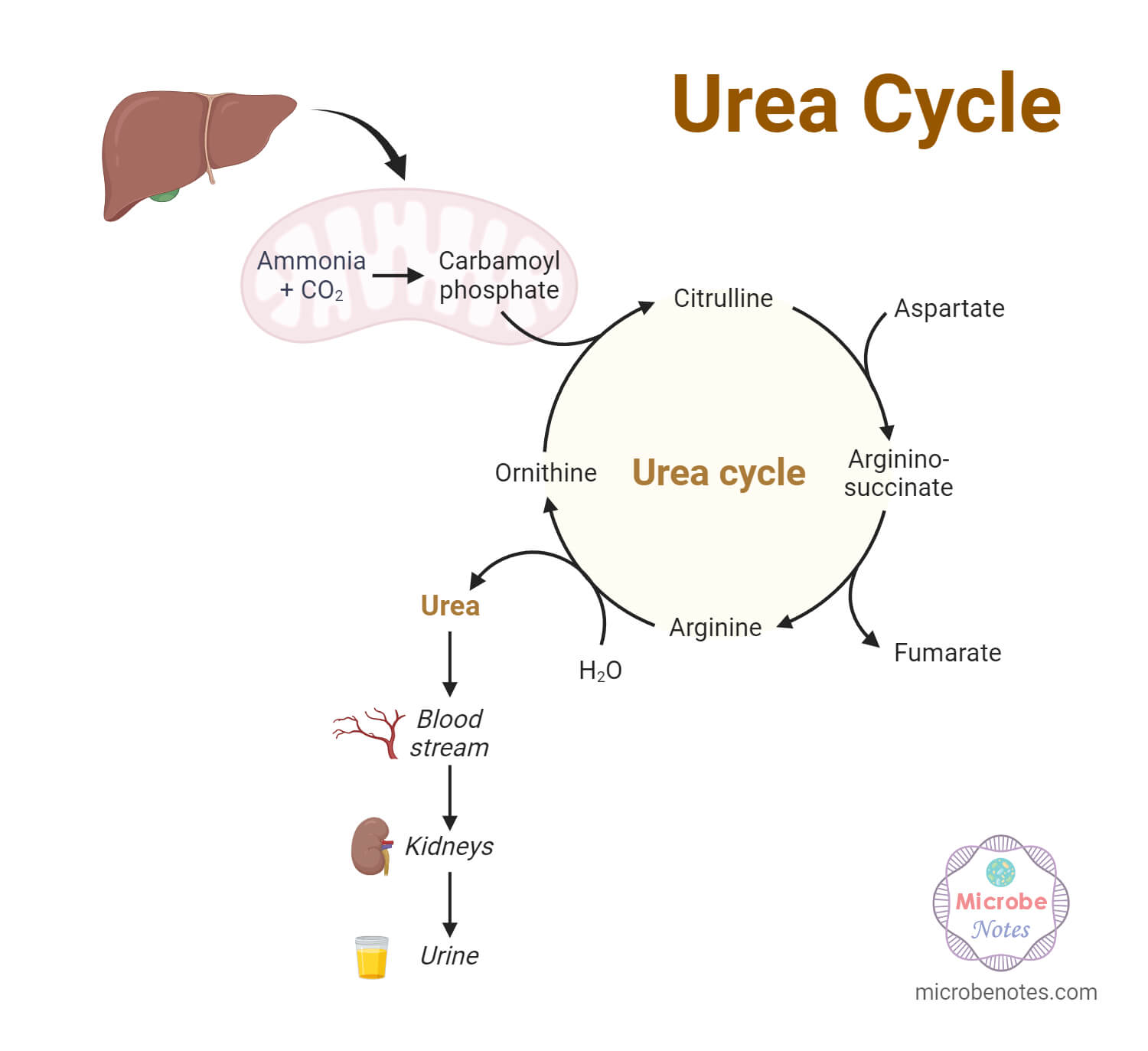
The main purpose of the urea cycle is to eliminate toxic ammonia from the body.Of major importance CIT is not taken up by the liver.Thus, controlling more than half of the steps of the urea cycle may confer p53 strong surveillance on ammonia metabolism to enable tumour suppression, underscoring the importance of the urea cycle .
Why is recycling important?
Urea cycle disorders (UCDs) are inborn errors of metabolism (IEMs) resulting from defects in any 1 of the six enzymes or 2 transporters involved in the hepatic removal of ammonia from the .
The Biological Roles of Urea: A Review of Preclinical Studies
Our planet is faced with an ever-increasing amount of waste generated by human activities.
The Biological Roles of Urea: A Review of Preclinical Studies
Ammonia is a byproduct of amino acid metabolism, and its accumulation in the body can be harmful.The urea cycle ( Fig.The urea cycle holds the distinction of being the first metabolic cycle discovered - in 1932, five years before the citric acid cycle.The urea cycle plays an important role in the proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma cells in vitro. Urea cycle or ornithine cycle helps to excrete two harmful gases ammonia and carbon dioxide out of the body.Evolution and metabolic significance of the urea cycle in photosynthetic diatoms. Learning Objectives. The nitrogen cycle is the process by which nitrogen is converted between its various chemical forms. This was a surprise .17 jobs per 1,000 tons of materials recycled and $65. Many times, recycled water can be added to the dried wetlands, helping them to once again thrive into a lush habitat. Landfills are reaching capacity, and the disposal of waste presents significant environmental risks.Urea is the chief nitrogenous waste of mammals.
23 in wages and $9.
Urea cycle disorders—update
It occurs primarily in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the kidney. With reactions spanning the cytoplasm and the mitochondria, the urea cycle occurs mostly in the liver and kidney.These results confirmed a regulatory role of SIRT5 in urea cycle at the metabolite level, and support the functional importance of succinylation of urea cycle .The product of this pathway, urea, is made of two nitrogenous groups with the first coming from the free ammonia released by glutaminase. While not all recycled cotton fabric will become the hottest new clothing styles, it still has value for . It makes best use of our limited natural resources. Composting is another way to recycle which improves soil and keeps organic wastes like the garden .







