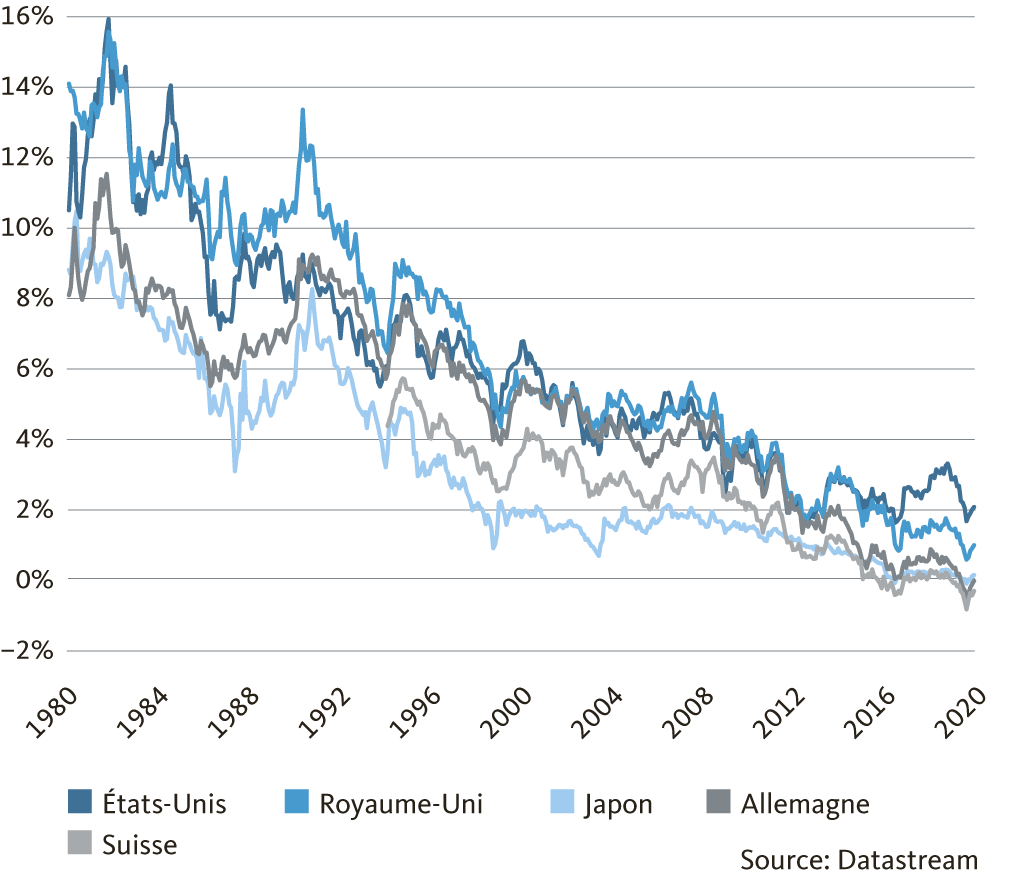
Interpreting interval plots

Contour plots are highly useful for exploring and interpreting spatial data.1 Partial Dependence Plot (PDP).

We don't know if our sample statistic is less than, greater than, or .In a “bad” residual plot, the variance of the residuals increase or decrease in a systematic way. Confidence intervals are often misinterpreted. Additional elements, like box plot .This violin plot shows the relationship of feed type to chick weight.In anticipation of Cyrus Mehta’s webinar next week on new predictive analytics tools for trial forecasting, we thought we might give you a few introductory notes . The output of this function will make it clear either way. However, it doesn't provide specific details like the exact .In a forest plot, the box in the middle of each horizontal line (confidence interval, CI) represents the point estimate of the effect for a single study.
Interpret the key results for Interval Plot
The confidence level refers to the long-term success rate of the method, that is, how often this type of interval will capture the .
R Handbook: Basic Plots
You cannot determine from this graph whether any differences are statistically significant.
Understanding Boxplots: How to Read and Interpret a Boxplot
comExample of Interval Plot - Minitabsupport. Lets look into an existing dataset – Titanic Dataset Usually, the predictor's slope is only significant outside of the range given by the function. A few items fail immediately, and many more items fail later.comInterval Data: Definition, Examples, and Analysisresearchprospect. Funnel plot asymmetry should not be . The x-axis of this plot .Interpreting Line Charts.

I n the last chapters, we learned how we can pool effect sizes in R, and how to assess the heterogeneity in a meta-analysis.

However, if a residual plot is deemed “bad” then it means the results of the .The wider the confidence interval, the wider the range of differences in measurements between the two instruments. The partial dependence plot (short PDP or PD plot) shows the marginal effect one or two features have on the predicted outcome of a machine learning model (J.

Friedman 2001 30). Funnel plots of effect estimates against their standard errors (on a reversed scale) can be created using RevMan. An interval plot shows a 95% confidence interval for the mean of each group.6 Forest Plots.
A Complete Guide to Violin Plots
comMinitab interval plots - YouTubeyoutube.Example: Confidence interval in a graph You may decide to plot the point estimates of the mean number of hours of television watched in the USA and Great Britain, with the 95% confidence interval around the mean.
Contour Plots: Using, Examples, and Interpreting
If a residual plot is deemed “good” then it means we can trust the results of the regression model and it’s safe to interpret the coefficients in the model. September 11, 2019.In the absence of both bias and heterogeneity, 95% of studies would be expected to lie within the diagonal dotted ‘95% Confidence Interval’ lines, as shown in Figure A.library(interactions) interact_plot(fit, pred = wt, modx = cyl, interval = TRUE) The documentation makes clear that interval = TRUE gives 95% confidence intervals by default. Often, the X-axis reflects time, but not always. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of . The logic behind them may be a bit confusing. Step 2: Assess and compare groups. If your one-way ANOVA p-value is less than your .
Survival Analysis Basics
The size of the .In the interval plot, Blend 2 has the lowest mean and Blend 4 has the highest. Assess how the sample size may . The most common way to visualize meta-analyses is through .lm = lm(log(brain) ~ log(body),data=Animals) brain2.comTricks for plotting confidence intervals in Minitabscc. Step 1: Assess the key characteristics.interact_plot(fit, pred = wt, modx = cyl) Looking at this plot alongside the summary() output above, we can see the following: # Effect on mpg of moving from 4 to 6 .Interpreting the box and line plot. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.Contour Plots: Using, Examples, and Interpreting. Analytics Vidhya. First, it always passes through the point of means. Caution when using confidence intervals.
Interpreting a Tukey
To determine statistical significance, assess the confidence intervals for the differences of means.style = “step” to change the style of confidence interval bands. Use contour plots to display the relationship between two independent variables and a dependent variable.
Interpret the key results for One-Way ANOVA
by Zach January 19, 2024. By Jim Frost 3 Comments. Analysts frequently use them during exploratory data analysis because they .The plot may result in weird patterns (e. Use line charts to display a series of data points that are connected by lines. As a rule of thumb, tests for funnel .table = “abs_pct”to show both absolute number and percentage of individuals at risk. Histogram; Box plots; Interaction plots; Bar plot; Scatter plot; Mosaic plot; Histogram shapes; Misleading plots; Exercises E Summary and Analysis .The plot can be further customized using the following arguments: conf. For a single series of data, assess the changes in the line to .boxplot(df['A'],notch= True); Plotting boxplot using seaborn.The extended lines show the 95% confidence intervals. The X and Y values are displayed along the X and Y-axes, while contour lines and bands represent . What I'm not clear on is how to interpret these in the context of the p-values I get from summary() above. xlab to change the x axis label.Complete the following steps to interpret an interval plot.The B&A plot analysis is a simple way to evaluate a bias between the mean differences, and to estimate an agreement interval, within which 95% of the differences of the second method, compared to the first one, fall.
Interval plot
The non-flatness is quite evident with base R plotting, which has much more restricted y-axis scales.In this article, we reaffirm the importance and usefulness of this innovative approach and introduce a graphical summary, predicted interval plots (PIPS), to display . Analysts use line charts to emphasize changes in a metric on the vertical Y-axis by another variable on the horizontal X-axis. It helps us identify the minimum, maximum, median, and quartiles of the data. Prediction Interval: What’s the . All coefficients whose confidence interval (marked by the horizontal lines) does not touch the zero line are significant.Line Charts: Using, Examples, and Interpreting. The graph shows values of the Z variable for combinations of the X and Y variables.Violin plots are used when you want to observe the distribution of numeric data, and are especially useful when you want to make a comparison of distributions between multiple groups. Forest plots show the ratio and confidence interval from each individual study using a box and horizontal line plot. The following step-by-step example shows how to create and interpret a Bland-Altman plot from scratch. A Q-Q plot, short for “quantile-quantile” plot, is used to assess whether or not a set of data potentially came from some theoretical distribution. Examine the center of the distribution.The Johnson-Neyman interval provides the two values of the moderator at which the slope of the predictor goes from non-significant to significant.Interpreting confidence levels and confidence intervals. Logically, if a polynomial term includes an interaction, the lines on the interaction plot will be curvilinear rather than straight.zph object for this data set/model. The shape of the distribution (extremely skinny on each end and wide in the middle) indicates the weights of sunflower-fed chicks are highly concentrated around the median. We now come to a somewhat more pleasant part of meta-analyses, in which we visualize the results we obtained in previous steps. The changing slope of the line segments emphasizes changes, trends, and patterns. When we create a confidence interval, it's important to be able to interpret the meaning of the confidence level we used and the interval that was obtained.5) and compared to N(5, 1).
Calculate Johnson-Neyman intervals for 2-way interactions
You have very wide scales on your y-axes, much wider than in base R plots of the cox.A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number .MINITAB - Interval Plot using Minitab (to calculate .by = 200 break x axis in time intervals by 200. In [3]: coefplot, xline( 0 ) # Notched box plot plt.It is simple: After running a regression analysis, we just type coefplot.
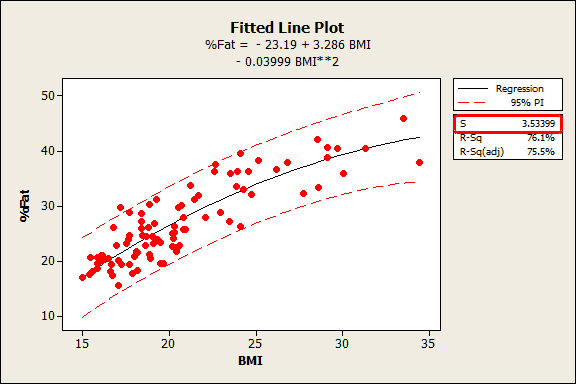
In this case if the confidence interval crosses the 0 point - the difference would not be statistically .comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Tutorial: How to read a forest plot
A partial dependence plot can show whether the relationship between the target and a feature is linear, monotonic or more complex.orgHow to estimate a confidence interval on a box plot?math. Dipanwita Mallick.< 20 values).auRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Interval Plot
Data can be analyzed both as unit differences plot and as percentage differences plot. A box plot displays a ton of information in a simplified format.
Data plots for One-Way ANOVA
Interpretation, Prediction/Confidence Intervals and Added Variable Plots.Interpreting the coefficients becomes even more challenging! However, the interaction plots I highly recommend will show you the big picture. The width of the interval plot provides an indication of the amount of variation that is present in the data.As Demetri Pananos's answer says, this is probably illustrating vertical confidence intervals for conditional means at different values of x x. If ˉx and ˉy are the means of the explanatory and response datasets, respectively, then the point of means is (ˉx, ˉy). So P-P plots are most useful when comparing probability distributions that have a nearby or equal location.
Visualizing regression coefficients with coefplot
Remember that when we're constructing a confidence interval we are estimating a population parameter when we only have data from a sample.
They enable users to extract meaningful insights from intricate patterns and relationships.Regarder la vidéo7:44Interpreting box plots.A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution.
A quick guide to interpreting forest plots
A box and whisker plot is a handy tool to understand the age distribution of students at a party.boxplot function. To create the notch, set notch=True in the plt. A small interval shows more .Interpreting ACF or Auto-correlation plot | by Dipanwita Mallick | Analytics Vidhya | Medium.Clear examples in R. For example, when applied to a linear .2 of the survival vignette for how such plots typically look on these data.Use box plots to illustrate the spread and differences of samples.Funnel plots, and tests for funnel plot asymmetry, have been widely used to examine bias in the results of meta-analyses.Interpreting Scatterplots and Assessing Relationships between Variables.1 - Interpreting Confidence Intervals. To learn more, go to Overview for Interval Plot.
The Complete Guide: How to Interpret Q-Q Plots
In descriptive statistics, a box plot or boxplot (also known as a box and whisker plot) is a type of chart often used in explanatory data analysis. following the axes of the chart) when the distributions are not overlapping. We will also immediately add an option that draws a line at the 0 on the x axis, xline(0). The box plot elements show the median weight for horsebean-fed chicks is lower than for other feed types. A triangular 95% confidence region based on a fixed-effect meta-analysis can be included in the plot, and different plotting symbols allow studies in different subgroups to be identified.