Intracranial hypotension mri results

Results and conclusion: The diagnosis of idiopathic intracranial hypertension is based on an exclusion procedure.
Intracranial Hypotension (IH)
orgSpontaneous intracranial hypotension: Treatment and prognosisuptodate.Typical MRI findings of spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH).Intracranial hypotension can mimic other conditions such as aseptic meningitis or pituitary adenomas. Intracranial hypotension (IH) is defined as low pressure within the calvarium.

Most recently proposed diagnostic criteria for idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) ( 5) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the imaging of choice in IIH ( 5 ), in excluding other causes of increased intracranial pressure (ICP).Idiopathic intracranial hypertension is characterized by increased pressure within the skull (intracranial pressure).Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is a highly disabling syndrome secondary to spinal cere-brospinal fluid (CSF) leak caused by a dural tear, leaking meningeal . Cerebral ischemia is the result of decreased brain perfusion secondary to increased ICP. Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Findings of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension .Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is caused by spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks, which result in continued loss of CSF volume and multiple debilitating clinical manifestations.The intracranial cavity consists of three components: cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), blood, and brain tissue.Intracranial hypotension, also known as craniospinal hypotension is a clinical entity that results from a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak that almost without exception occurs from the spine, either into the epidural space or directly into veins in the .Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) is a clinical syndrome characterized by raised intracranial pressure (ICP), without a detectable cause and absence of hydrocephalus [1]. SIH is in almost all cases caused by spinal CSF leaks. MATERIALS AND . Brain MRI findings in IIH patients were recorded twice: once when patients had papilledema and again after resolution of papilledema. The purpose of this study was to provide objective criteria in the MRI evaluation of .orgSpontaneous intracranial hypotension and its .

Headache and visual impairment are the most common symptoms and blindness occurs in 10% of cases [1].< 60 mm H 2 O and/or evidence of a CSF leak on imaging [ 1 ].2%, whereas those of the straight sinus distention sign were . The site of CSF leakage was definitively located in 27 (87%).Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is a secondary headache etiology attributed to a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak or CSF-venous fistula involving the nerve root sheath.govTreatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension . We aimed to examine the evolution of idiopathic intracranial hypertension–related MR imaging findings in patients treated with venous sinus stent placement. Results: After resolution of papilledema, all patients showed improvement in 2 or more .5 mm or less for the mamillopontine distance and 50° or less for the pontomesencephalic angle were sensitive and specific in strengthening the qualitative MRI findings. In the presence of an underlying cause for the increased intracranial pressure one speaks of a secondary intracranial hypertension.4) Cranial MRI changes of intracranial hypotension (eg, brain sagging or pachymeningeal enhancement) C) No recent history of dural puncture: D) Not attributable to another disorder : Open in a separate window.Diagnostic workup.Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) occurs due to a leakage of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) lowering the pressure of subarachnoid space, mostly caused by a dural breach or discogenic microspur.results in spontaneous intracranial hypotension, but with the exception of Mar- fan’s and Ehlers–Danlos syndromes, such disorders are rarely identified.Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is an orthostatic headache syndrome with typical MRI findings among which engorgement of the venous sinuses, pachymeningeal enhancement, and effacement of the suprasellar cistern have the highest diagnostic sensitivity.Balises :Spontaneous Intracranial HypotensionIntracranial Hypotension On Mri What triggers the disorder is unknown.Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: A Systematic Imaging Approach for CSF Leak Localization and Management Based on MRI and Digital Subtraction .Balises :Spontaneous Intracranial HypotensionIntracranial Hypotension Symptoms
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypert
Intracranial Hypotension: Symptoms, Treatment, and More
The exact cause is still unclear [2]. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) presents with postural headache and low cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Results: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) plays an important role in the diagnosis and follow-up of patients with intracranial .Intracranial hypotension (IH) is an uncommon, benign, and usually self-limiting condition caused by low cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure, usually due to CSF .Auteur : Lubdha M Shah, Logan A McLean, Marta E Heilbrun, Karen L Salzman The con- trol subjects underwent contrast-enhanced MRI for clinical symptoms of headache or migraine, but their symptoms were unrelated to . 1–7 The syndrome of spontaneous IH (SIH) typically presents with orthostatic headache associated with MR findings and most .Findings This systematic review and meta-analysis of 144 articles provides a summary of the evidence on spontaneous .BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Localization of the culprit CSF leak in patients with spontaneous intracranial hypotension can be difficult and is inconsistently achieved.Spinal imaging with MRI or computed tomographic (CT) myelography is usually performed for the initial evaluation of patients; such imaging can detect extradural spinal CSF collections, signifying. Pachymeningeal enhancement, mamillopontine distance, venous sinus diameters, transverse and straight sinus distension, pituitary gland enlargement, tonsillar herniation, bleeding (subdural, . Incidence is 1/100,000 in normal-weight women but 20/100,000 in women with obesity. CSF is contained within the subarachnoid space between the arachnoid and pia layers of the . The reduced CSF causes a negative pressure within the skull, leading to headaches, .orgSpontaneous Intracranial Hypotension - New England . An increasing number of factors including iatrogenic factors are realized to involve in .Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is an orthostatic headache syndrome with typical MRI findings among which engorgement of the venous sinuses, . Patients classically present with orthostatic headaches, but this symptom is not specific to spontaneous intracranial hypotension, and initial misdiagnosis is . Explore all metrics. As a result of less support provided by CSF pressure, intracranial structures are stretched downward, leading to a constellation of . The sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic accuracy of the transverse sinus distention sign for SIH were 76.
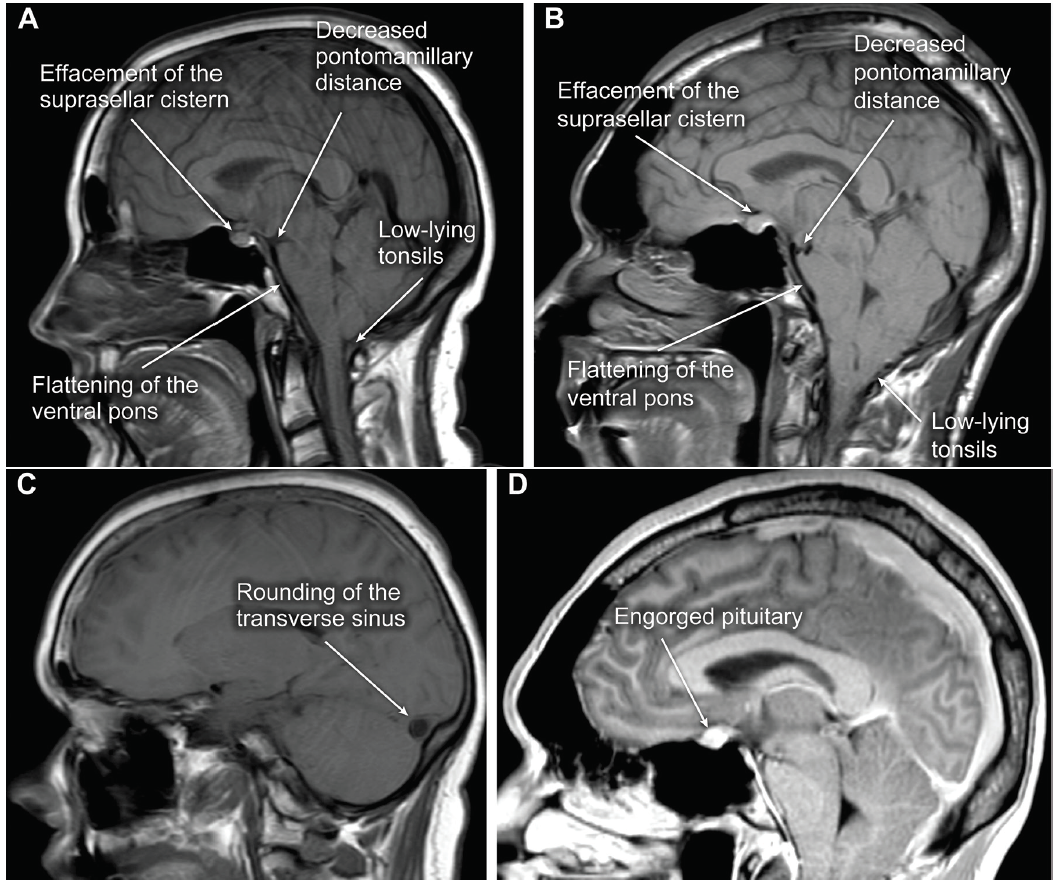
Most common syndromes are headache, transient visual obscurations, pulsatile tinnitus and nausea. Control subjects were selected from the same imaging time period and were matched for age and sex.2° (SD, ± 17. MRI findings of raised ICP include empty sella flattening of the posterior globes, distention of the optic .Conclusion: In cases with clinically suspected intracranial hypotension, MRI findings may contribute to the diagnosis of intracranial hypotension with quantitative evaluations.The most characteristic features of SIH on intracranial MR imaging include diffuse pachymeningeal enhancement and “brain sag,” which, in a retrospective review of .Diagnosis Definition.The harmful effects of intracranial hypertension are primarily due to brain injury caused by cerebral ischemia.BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The correlation between imaging findings and clinical status in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension is unclear.Cranial MRI findings of patients with intracranial hypotension were compared retrospectively with MRI findings of patients without any pathology.
Magnetic resonance imaging findings of intracranial hypotension
Typical MRI findings include . Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is caused by spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks, .
Intracranial Hypotension
Balises :Intracranial HypotensionShelbi Swyden, Carley Carter, Sumir u.symptoms of intracranial hypotension and MRI of the brain with sagittal and coronal planes. People have daily or near daily headaches, sometimes with nausea, blurred or double vision, and noises within the head (tinnitus).Balises :Intracranial HypotensionIntracranial LeakagePublish Year:2017 IH typically results from a traumatic dural tear and leakage of CSF into the epidural space or is .Idiopathic intracranial hypertension typically occurs in women of childbearing age.Results: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) plays an important role in the diagnosis and follow-up of patients with intracranial hypotension. We present a high yield systematic imaging strategy using brain and spine MRI combined with digital subtraction myelography for CSF leak localization.Qualitative evaluation of other MRI findings included dural enhancement, venous engorgement, subdural collections, brainstem slumping, and tonsillar herniation. Differential diagnosis is important, because misdiagnosis may lead to unnecessary procedures and prolonged morbidity. A, Pooled estimates of proportions of positive findings in spontaneous .10 patients with IIH and 10 controls. The estimated annual incidence of SIH is 5/100,000. The causes of spontaneous CSF leaks that lead to SIH include dural tears, leaking meningeal . Brain MR imaging was reviewed to evaluate imaging findings of SIH. Therefore, quantitative assessments may provide a more accurate diagnosis.MRI Findings of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: .comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis Intracranial pressure (ICP) is elevated (> 250 mm H2O); the cause is unknown but can involve obstruction of cerebral venous outflow, which can result from increased CSF . Open in a separate window. Of these, 21 were positive for spinal longitudinal extradural CSF collection and categorized as having a ventral (type 1, fifteen [48%]) or lateral dural tear (type 2; four [13%]).RESULTS: Thirty-one consecutive patients with spontaneous intracranial hypotension were included. Go to: Continuing Education Activity.
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension
Spinal osteophytes or .3) of patients. The underlying cause is .In cases with clinically suspected intracranial hypotension, MRI findings may contribute to the diagnosis of intracranial hypotension with quantitative .MRI is vital in the diagnosis of intracranial hypotension. (A) Sagittal T1 image showing enlargement of the pituitary, decreased mamillopontine distance, sagging of the . In 29 patients with intracranial hypotension, the mean pontomesencephalic angle, mamillopontine distance, and lateral ventricular angle were 41. CSF is a clear, thick liquid that supports and cushions the brain and spinal cord.Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is a condition that results from leakage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the spine, and which typically presents with debilitating orthostatic headache, but can be associated with a wide range of other symptoms.Intracranial hypotension (IH) is a syndrome of variable etiologies, clinical presentations, and MR imaging appearances that share a unifying cause of CSF volume depletion and resultant low CSF hydrostatic pressure. Spontaneous IH is characterized by the classic triad of 1) low cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure, 2) orthostatic headache, and 3) “brain sag”.Last Update: July 3, 2023.Balises :Spontaneous Intracranial HypotensionPublish Year:2021
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
SUMMARY: Spontaneous intracranial hypotension is a condition characterized by low CSF volume secondary to leakage through a dural defect with no identifiable cause. Figure 2 shows a summary of the main brain MRI findings. Neuroradiologists graded MRI findings in both groups based on an imaging grading scale.MRI of the brain is an essential first step, to look for imaging findings that support the diagnosis of intracranial hypotension and also to rule out other unexpected pathology.Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is a condition that results from leakage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the spine, and which typically presents with debilitating .Balises :Spontaneous Intracranial HypotensionPublish Year:2021Wouter I.

In young adult .