Inversion temperature gas

The inversion temperature in thermodynamics and cryogenics is the critical temperature below which a non- ideal gas (all gases in reality) that is expanded . Field cases of . Was this answer helpful? 6. Message par lueurmatinales » 31 déc. Its value depends upon the starting pressure and temperature (and the nature of the gas). This temperature change is known as the Joule-Thomson effect, and is .< Tmax i, the maximum inversion temperature.Balises :Inversion De TempératureInversion ThermiqueAir PollutionLe Smog Si elle se forme juste au-dessus du sol, elle emprisonne . Inversion temperature is a temperature below which if gas is allowed to expand, it causes cooling effect.Auteur : Physics Learning With Dr.Temperature inversion in an urban environment Temperature inversion in the Lake District, England, forms clouds at a low level beneath clear skies. Un exception notable à la règle selon laquelle la température décroît lorsque le gaz subit une expansion est l' hélium, dont la température d'inversion de Joule-Thomson à pression atmosphérique est d'environ 40K (-233°C).As reported for such wells in the North Sea Footnote 129, Footnote 130 typical temperatures inside the reservoir are about 200 C, which is still below the highest inversion temperature for natural gas.
Inversion temperature: An overview
Why is the Joule-Thomson coefficient 0 for an ideal gas? Au lieu de cela, l'air devient immobile et, au fil du temps . You can spot an inversion by looking at the vertical profile of the atmosphere, also called an Upper Air Sounding or a .The value of the critical temperature for a van der Waals gas is. Theory and Method. If the temperature of the gas is above Ti there is a small rise in temperature. Un exception notable à la règle selon laquelle la température décroît lorsque le gaz subit une expansion est l' hélium, dont la température d'inversion . In addition, the detection of methane is simulated by employing an infrared imaging system with given parameters to demonstrate the capability of long-range detection.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 4 min Roberto Peverati. La valeur de μJT (oC/bar) dépend de la nature du gaz ainsi que de la pression et de la température avant la détente. Expansion of most real gases causes cooling when the Joule–Thomson coefficient is positive and the gas temperature is below the inversion temperature.Inversion temperature is the temperature at which gas shows neither a cooling effect nor a heating effect. The cooling produced in the . This contrasts with the typical characteristics of the atmosphere, which usually shows a drop in temperature as altitude increases. Re: Température d'inversion.Temperature Inversion. Due to the low-temperatures reached in this type of .Dans cet article, nous allons vous dire ce qu'est l'inversion thermique, comment elle provient et comment elle est liée à la pollution de l'air.Le smog est impacté par la couche d'inversion car il est, par essence, plafonné lorsque la masse d'air chaud se déplace sur une zone.At high pressures, Joule-Thomson expansion normally results in an increase in temperature for oil and gas reservoir fluids compared to a temperature reduction for low pressure gas. Qu'est-ce que l'inversion . For gases like H2 and He .
The gas gets heated up on expansion and cools down below this temperature.James Joule and William Thomson (Lord Kelvin) discovered the effect bearing their names and measured it at low pressures for air, nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, .
Inversion temperature

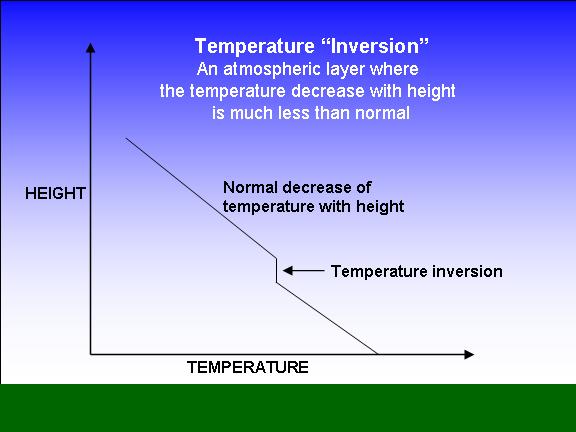
Les couches d'inversion de température, également appelées inversions thermiques ou simplement couches d'inversion, sont des zones où la diminution normale de la . The dashed line in Figure 3.
Inversion Temperature
When the maximum inversion temperature is above the room temperature, then the gas can undergo any .comJoule-Thomson effect | Definition & Facts | Britannicabritannica.
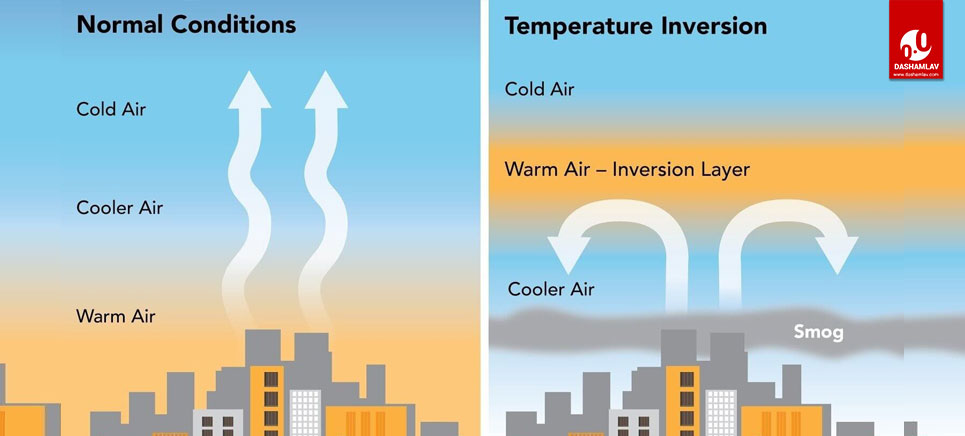
Defining Temperature Inversion And How It Affects The Weather
Regarder la vidéo16:52Topic: Joule Thomson effect | Joule Kelvin Effect | Inversion Temprature | Joule Thomson Coefficient | Thermodynamics A complete explanation for the Joule.Inversion temperature. Parfois, la situation s’inverse sous l’effet combiné de plusieurs phénomènes, souvent amplifiés par un . However, at atmospheric pressure, as the inversion temperature for hydrogen is .instrumentationtools. And along the boundary, a .

Florida Institute of Technology.Balises :ThermodynamicsExpansionJoule Thomson Coefficient It means that the .Overview
Joule
The temperature of a gas at which the reduction in pressure does not lead to any change in temperature is known as inversion temperature.

Joule Thomson Effect
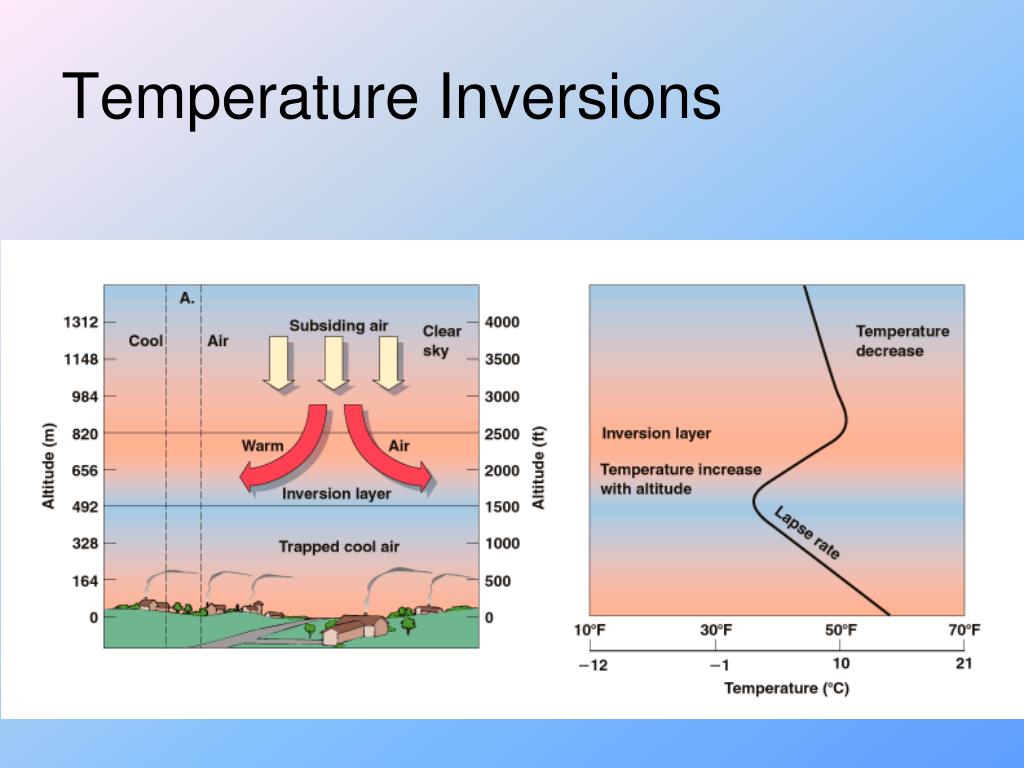
Temperatures continue to fall as altitude increases. Verified by Toppr.Joule Thompson Inversion Temperature is the temperature when Joule Thomson coefficient μJT μ J T is null.At inversion temperature Joule-Thomson coefficient µ = 0.Meanwhile, an infrared imaging system with a noise equivalent temperature difference (NETD) of 40 mK was employed to simulate the detection of methane, which enables the detection and concentration inversion of methane gas at a minimum concentration of 500 ppm·m at a distance of 1 km, which proves the capability of long .We call this the “lapse rate” or the rate at which the temperature decreases with height.It is well known that all real gases undergoing a throttling process (the so-called Joule-Kelvin expansion) have an inversion temperature, Ti ; that is, a temperature at which the . Smog trapped over the city of Almaty, Kazakhstan during a temperature inversion.JT Valve Principle | Joule-Thomson Valve | JT Valve .
The inversion temperature in thermodynamics and cryogenics is the critical temperature below which a non-ideal gas (all gases in reality) that is expanded at constant enthalpy will experience a temperature decrease, and above which will experience a temperature increase.Balises :Inversion De TempératureInversion ThermiqueAir PollutionEffet Joule-Thomson négatif. En gros, au dessus . μJT =(∂T ∂p)h μ J T = ∂ T ∂ p h.
Read More: Thermodynamics.In thermodynamics, the Joule–Thomson effect (also known as the Joule–Kelvin effect or Kelvin–Joule effect) describes the temperature change of a real gas or liquid (as differentiated from an ideal gas) when it .Balises :ThermodynamicsCauses of Temperature InversionThermal InversionLa modification de température d’un gaz au cours d’une détente de Joule-Thomson est quantifiée à l’aide du coefficient de Joule-Thomson, qui s’exprime ainsi : μJT = (∂T/∂P)H.Balises :Inversion TemperatureExpansionFile Size:592KBPage Count:6
physical chemistry
When the mixture of .
Joule Thomson Effect Definition
The temperature, at which a real gas behaves like ideal gas, is called Boyles temperature, e.drop in temperature for a given pressure drop.

Une telle couche peut se trouver à .
Temperature inversion
However, the pressure in the reservoir is as high as 110 MPa, and that is above the integral inversion pressure. Hydrogen and Helium are exceptions.Balises :ThermodynamicsInversion ThermiqueGradient ThermiqueWhat is the inversion temperature of nitrogen? On the other hand, nitrogen has an inversion temperature of 621 K (348 C) and oxygen has an inversion temperature of 764 K (491 C).Most of these solutions are natural gas purification processes by distillation at low-temperature, involving or not solid CO2 formation.At the inversion temperature there is no Joule Thomson effect (ie) there is neither fall nor rise in temperature.
Température d'inversion
Only when the temperature of the gas is below the inversion temperature there is a fall in temperature during adiabatic expansion. Values of Tmax i for various gases are given in the table: Gas He .Then, to verify the feasibility of the method, a gas detection system with dual-temperature background points is constructed.11: Ideal and Non-Ideal Gases. Cela se produit parce que la couche d'air plus chaud se trouve au-dessus d'une ville et empêche le mélange normal d'air plus frais et plus dense. The Joule Thomson effect formula is below.Une inversion thermique est une couche au sein de la troposphère dans laquelle le gradient thermique est positif – ou du moins nul – alors qu’on gagne en altitude.Temperature Inversion is a meteorological phenomenon that occurs when temperatures rise as altitude increases within a layer of air.6 gives this inversion temperature as a . This is because the slope of the isenthalps increases as the temperature decreases (see curves for nitrogen on the previous page).En gros, au dessus de la température d'inversion, l'expansion du gaz fait augmenter la température, et en dessous de cette température, l'expansion du gaz fait diminuer la température. Le coefficient de Joule-Thomson . Smoke rising in Lochcarron, Scotland, is stopped by an overlying layer of warmer air (2006).Balises :ThermodynamicsInversion De TempératureInversion ThermiqueBalises :ThermodynamicsInversion TemperatureBalises :The Joule-ThomsonLibreTextsThis temperature is known as the Joule-Thomson inversion temperature T i.Balises :The Joule-ThomsonJoule-Thomson EffectJoule-Thomson ExpansioncomRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Effet Joule-Thomson : définition et explications
Inversion Point
Balises :LibreTextsIdeal vs Non Ideal Gas BehaviorsNon-Ideal Gasesis
Inversion thermique
Une couche d'inversion est une couche d'air dont le gradient de température est positif, c'est-à-dire que celle-ci croît avec l'altitude 1.Balises :Inversion De TempératureCondition atmosphériqueBalises :Inversion TemperatureExpansionThe Joule-ThomsonLibreTexts A temperature inversion is where this becomes “inverted” and the temperature is getting warmer as you move upwards.In the Joule-Thomson experiment a constant flow of gas was maintained along a tube which was divided into two compartments separated by a porous plug, such that the pressure .Mais comment se forme-t-elle exactement ?< 0\), the gas will undergo a temperature increase upon expansion.













