Ischemic vb stroke
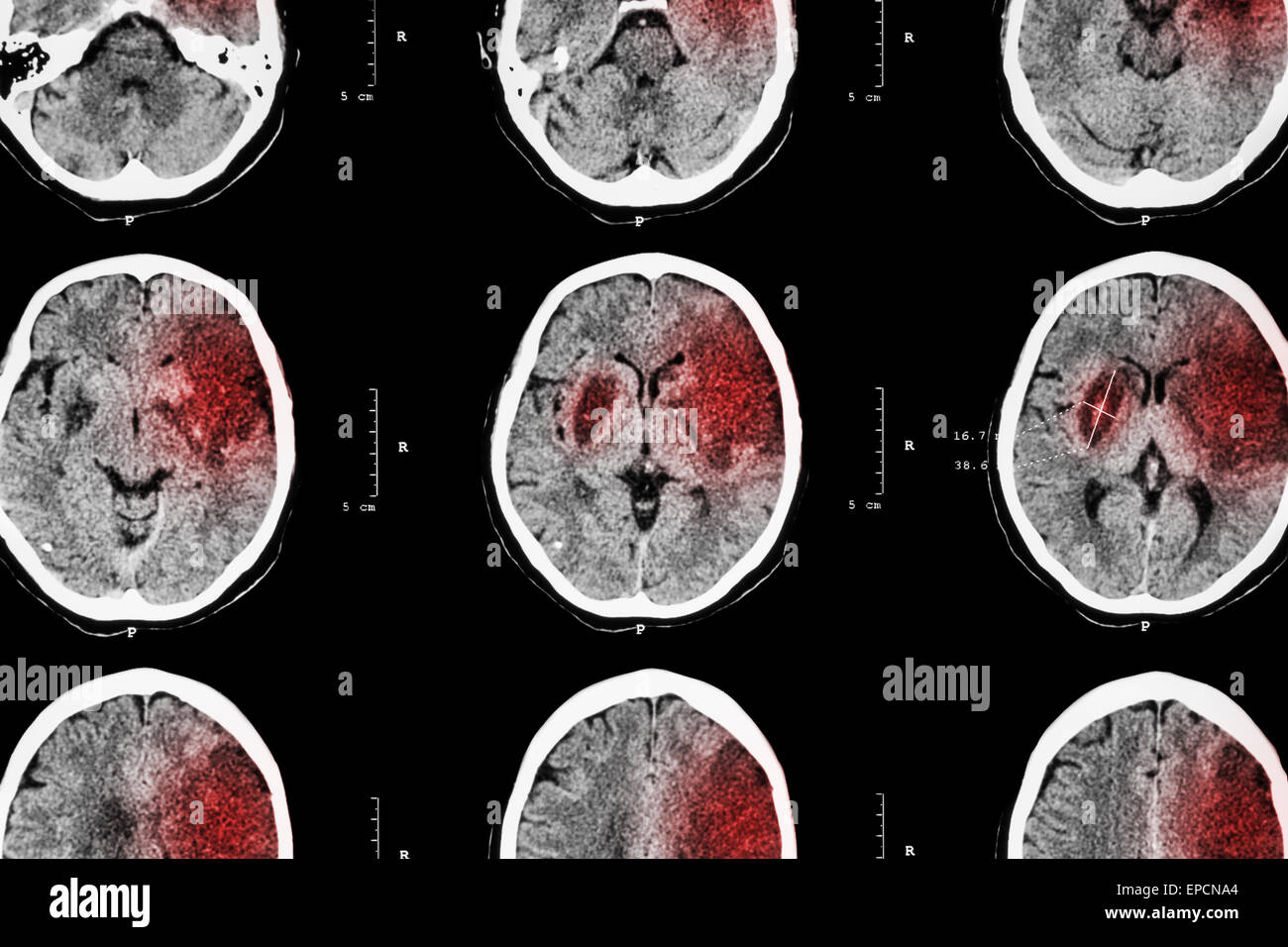
Using these stroke registries, we retrospectively identified patients with: (1) acute ischemic stroke [defined as acute-onset focal neurological deficits with .[1] Knowledge pertaining to brainstem stroke syndromes is .3% for brainstem compression, 10. After a thalamic stroke, it’s common for survivors to experience sensory issues such as numbness, tingling, pins-and-needles sensations, or pain. Ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes have different causes. Primary Care; Urgent Care; COVID-19 services ; Women’s health; Nutrition Counseling; Corporate health & Occupational medicine . Patients eligible for IV alteplase should .Brainstem stroke is the most lethal form of all strokes. Often introduced by an occupational therapist, sensory retraining is a technique involving various exercises to stimulate the tactile sensory system. A systematic review of . Acute coronary syndrome; ischemic heart disease (chronic) NOS (I25.Emboli may cause lacunar infarcts. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I24.This hospital-based study included 214 consecutive patients with acute ischemic VB stroke. Practice Essentials.Vertebrobasilar (VB) stroke is responsible for 20% of all strokes and transient ischemic attacks.6% for ischemic stroke, 10.Background and Purpose—20% of ischemic stroke is in the posterior circulation, but there is little prospective data on early recurrent stroke risk and whether vertebrobasilar stenosis predicts a high recurrence risk. Hemorrhagic stroke. We defined transient neurological attacks (TNAs) as temporary (< 24 h) episodes .Vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia (VBD) has been associated with stroke and all-cause mortality []. Acute ischemic stroke is caused by thrombotic or embolic occlusion of a cerebral artery and is more common than hemorrhagic stroke. Most strokes are ischemic strokes.Transient isolated dizziness/vertigo is one of the most common premonitory symptoms of vertebrobasilar transient ischemic attack (VB-TIA) from days to weeks before posterior circulation stroke (PCOS). Author: Vladimir Kaye, MD; Chief Editor: Stephen Kishner, MD, MHA more.
144 results found. These are strokes caused by blockage of an artery (or, in rare instances, a vein). Eagle looks at a scientific statement from the American Heart Association on the diagnosis and management of cardiac sarcoidosis. The estimated 5-year complications in VBD is 17.Intracranial atherosclerosis is one of the primary causes of posterior circulation stroke and transient ischemic attack (TIA), particularly in people of South and .1161/STROKEAHA.
Search Page 1/6: THALAMIC STROKE
Ischemic stroke is caused by a narrowing or blockage in a blood vessel that carries oxygen-rich blood to the brain. Due to the vast cerebral territory it supplies, VB ischemia can present with a .This review describes the impacts of aging on each NVU component and discusses the mechanisms by which aging increases NVU sensitivity to stroke and neurodegenerative diseases.Stroke outcomes also vary greatly, from no .Although magnetic resonance imagings (MRIs) with DWI remain the standard modality to confirm acute ischemic lesions, MRIs can be falsely negative in .
Search Page 1/20: acute ischemic stroke
369 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Vertebrobasilar (VB) stroke is responsible for 20% of all strokes and transient ischemic attacks.
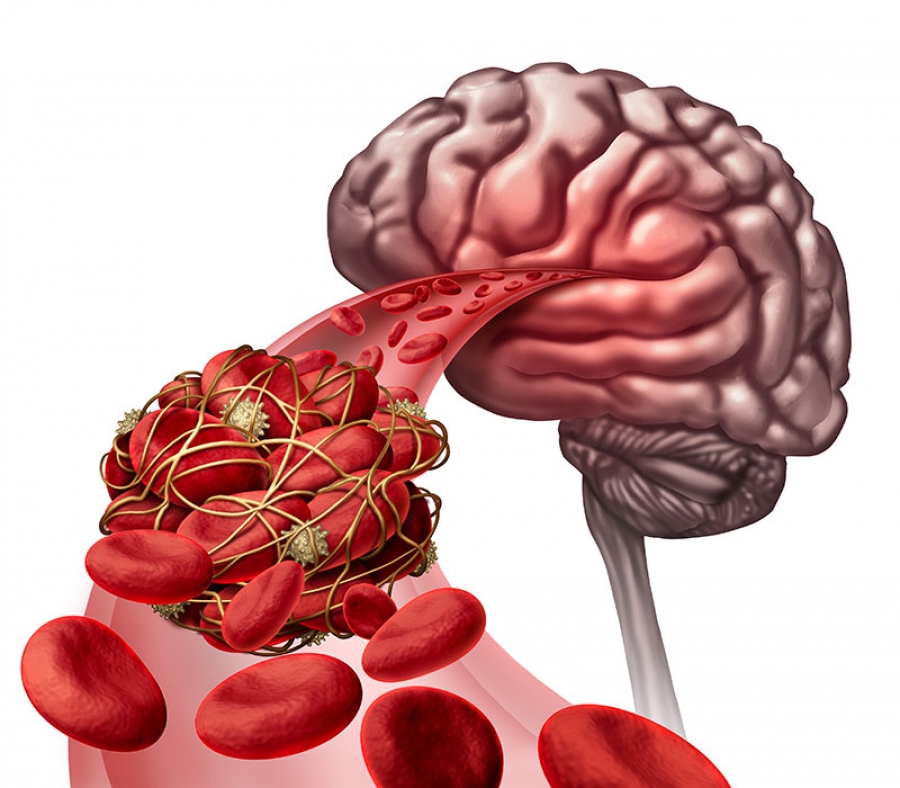
When a blood clot or other debris blocks a blood vessel leading to part of the brain, it causes an ischemic stroke. Subsequent stroke risk is also higher in patients with VBD, with . speech difficulties.
Clinical presentation of vertebrobasilar stroke
This natural history data are important as it is technically possible to stent such lesions.VA benefits for ischemic stroke.

Acute fulminant ischemic colitis; Subacute ischemic colitis.Patients with vertebrobasilar (VB) circulation ischemia can present with nonspecific symptoms, which complicate the distinction of transient ischemic attack (TIA) . These small (≤ 1. vision loss or disturbance.An ischemic stroke is the most common type of stroke. Head pain, especially from a hemorrhagic stroke. It occurs when a blood clot or fatty plaque lodges in a blood vessel within the brain, blocking blood flow.Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography, or computed tomography angiogram, and clinical follow-up were available in 323 patients.
Clinical presentation of vertebrobasilar stroke
Subsequent stroke risk is also higher in patients with VBD, with ischemic stroke (IS) and transient ischemic attack (TIA) being the most common types of recurrence [2, 3]. 1,2 Symptomatic atherosclerotic VB occlusive disease is associated with a high risk of recurrent stroke despite medical . RIC is a form of preconditioning with similarities to physical exercise.Eight hundred seventy-five patients with acute ischemic stroke in any brain area who had magnetic resonance imaging with diffusion-weighted imaging were included for analysis and split 80/20 for training/testing.
Due to the vast cerebral territory it.5 cm) infarcts result from nonatherothrombotic obstruction of small, perforating arteries that supply deep cortical structures; the usual cause is lipohyalinosis (degeneration of the media of small arteries and replacement by lipids and collagen).

Ischemic stroke.While there are well-known risk factors, there is often a complex interplay of known factors with new ones that places one person at a higher stroke risk compared to another or suggests one mechanistic cause rather than another [].Vertebrobasilar (VB) territory transient ischaemic attacks (TIAs) and minor strokes are perceived to have a better prognosis than carotid territory events, and are .Computerized tomography (CT) scan. These are strokes caused by bleeding. Because brain cells begin to die within minutes of the interruption of blood flow, it’s crucial for an ischemic stroke to be diagnosed and treated as quickly as possible. Advances in medical therapy have decreased the rate of .
Thalamic Stroke: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, Recovery, Prognosis
About 13% of all strokes are hemorrhagic. While ischemic .The results showed a significant association between migraine and ischemic stroke (HR 1. Background and purpose: Recent prospective studies have shown vertebrobasilar (VB) stenosis predicts stroke risk in . Updated: Mar 20, 2024. Prophylactic or therapeutic perspectives that may delay or diminish aging and thus prevent the incidence of these neurological disorders will also be reviewed.PubReaderIschemic Stroke
Vertebrobasilar stroke: Causes, treatment, and outlook
When the brain can’t get enough oxygen and nutrients, a stroke can occur.Ischemic stroke can also result from lacunar infarcts. Comprehensive Overview of Nursing and Interdisciplinary Care of the Acute Ischemic Stroke Patient. • IV alteplase within 4.In acute ischemic stroke, the primary therapeutic goal of reperfusion therapy, including intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (IV TPA) and/or . An ischemic form has a higher incidence compared to its hemorrhagic brainstem counterpart. 1–3 The diagnosis of transient dizziness/vertigo originating from VB-TIA is challenging since about half of patients with VB-TIA presented . You might have a dye injected into your bloodstream to view the blood vessels in the neck and brain in greater detail. Severe dizziness, balance problems, and difficulty walking. Skip to content. It is applied with a blood pressure cuff on the limbs and is ideal for the prehospital setting. Vertebrobasilar (VB) territory transient ischaemic attacks (TIAs) and minor strokes are perceived to have a better prognosis than carotid territory events, and are sometimes managed less aggressively.Transient isolated dizziness/vertigo is one of the most common premonitory symptoms of vertebrobasilar transient ischemic attack (VB-TIA) from days to weeks .Strokes can be divided into ischemic and hemorrhagic, while ischemic strokes can be further delineated into thrombotic, embolic, and lacunar subtypes. Contrast enhanced MRA (CE .In this week’s View, Dr.
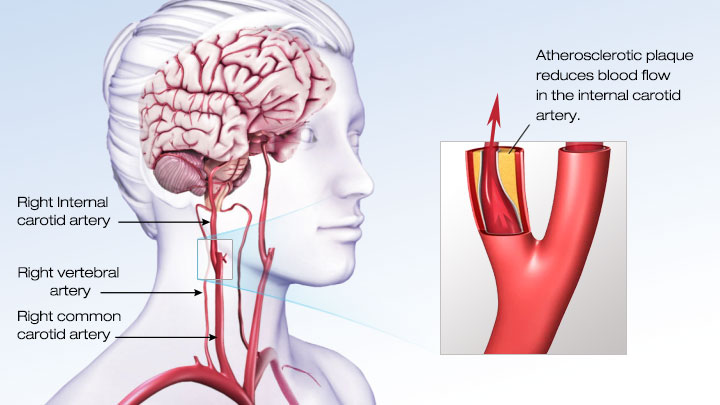
In the United States, about .Basilar artery curvature may result from congenital asymmetric blood flow to the VB junction causing asymmetric vessel wall . Acute (reversible) ischemia of large intestine. Showing 1-25: ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z82. 1, 2 Although ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke is perhaps the best known end-organ effects, diseases of the cerebral circulation are a major contributor to hemorrhagic stroke, dementias (Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia) and other .
Overview of Acute Ischemic Stroke Evaluation and Management
Like the other types of stroke, ischemic stroke can be caused by a number of risk factors that are especially common .
Acute Ischemic Stroke
[1] Lacunar strokes are caused by uncontrolled . difficulties with movement or maintaining balance.
Stroke
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I69.However, some general symptoms of a thalamic stroke include: loss of sensation. A CT scan can show bleeding in the brain, an ischemic stroke, a tumor or other conditions. Some blood clots travel to the brain from the heart.Auteur : Vanessa Carvalho, Vitor Tedim Cruz
Vertebrobasilar Stroke
500 results found. The exact mechanism of stroke caused by . However, this notion stems mainly from a few small studies in the 1960s and 1970s, and has not been systematically tested.

Family history of aneurysm of brain and stroke; Family history of stroke due to brain aneurysm (artery dilation); Conditions classifiable to I60-I64.A look at ischemic stroke, including the main mechanisms and causes of ischemic stroke, as well as the signs and symptoms of ischemic stroke (Bamford classif.This is a retrospective study of patients with ischemic stroke with intra‐ or extracranial vertebrobasilar atherosclerotic stenosis, who underwent magnetic resonance .1% for TIAs, 4.
GUIDELINES FOR THE EARLY MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE
Infarct volumes were manually segmented by consensus of 3 independent clinical experts and cross-referenced against radiology .In addition to the classical etiologies of stroke as atherosclerosis and cardioembolism there are many unusual, rare causes, which require a high level of .Learn about the signs and symptoms of acute ischemic VBA thalamic stroke and how Nao Medical can provide cost-effective, high-quality care to help you recover.6% for subarachnoid hemorrhage .A right-sided stroke can occur suddenly, and it can cause: Sudden weakness of the face, arm, or leg.Posterior circulation strokes account for up to 30% of all ischemic strokes, and atherosclerotic occlusive disease of the vertebrobasilar (VB) system is an important etiology, responsible for approximately one-third of the cases.