Left bundle branch block ecg findings
Pérez-Riera, Raimundo Barbosa-Barros, Marianne P.
As a result, the finding of left bundle‐branch block (LBBB) in the absence of a well‐defined clinical setting has become relatively frequent and raises questions and often .

12 seconds or greater) · Supraventricular rhythm (ventricular rhythms do not travel via the LBB) · The QRS in V1 is negative, and the QRS . ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest.At both therapeutic and toxic lithium levels, ECG changes such as T‐wave inversions, sinus bradycardia, sinoatrial blocks, PR prolongation, incomplete bundle branch block, QTc prolongation, increased QT dispersion ratio, the Brugada pattern, and ventricular tachyarrhythmias have been observed.
Left Bundle Branch Block
6K subscribers. Pre‐2015 patients formed the derivation cohort (n=163, 61 with AMI); patients between 2015 and 2018 formed the .Correctly diagnosing left bundle branch block (LBBB) is fundamental, as LBBB occurs frequently in heart failure and may trigger a vicious cycle of progressive left .A left bundle branch block (LBBB) is an abnormal finding on an ECG (electrocardiogram). If sinus bradycardia is likely due to drug side effects, it is necessary to weigh the risk . Left Axis Deviation (LAD): Leads II, III and aVF are NEGATIVE; Leads I and aVL are POSITIVE.Left and right bundle branch blocks may occur in up to 12% of patients at the time of admission or during hospitalization [32,39].This video lecture provides detailed explanations of the ECG findings associated with left bundle branch block (LBBB) and right bundle branch block (RBBB). The pathway includes two branches the left and the right bundles. This allows both ventricles to contract at the same time.Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is a common electrocardiographic (ECG) abnormality seen in patients whose normal .Background: Complete left bundle branch block (CLBBB) is an electrocardiographic (ECG) dromotropic disorder seen in patients with various structural heart diseases and sometimes is associated with poor prognosis. de Rezende Barbosa, Rodrigo Daminello. This ECG shows a “classic” left bundle branch block pattern. Digoxin should be . This does not preclude lithium use, but .
Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB) ECG Review
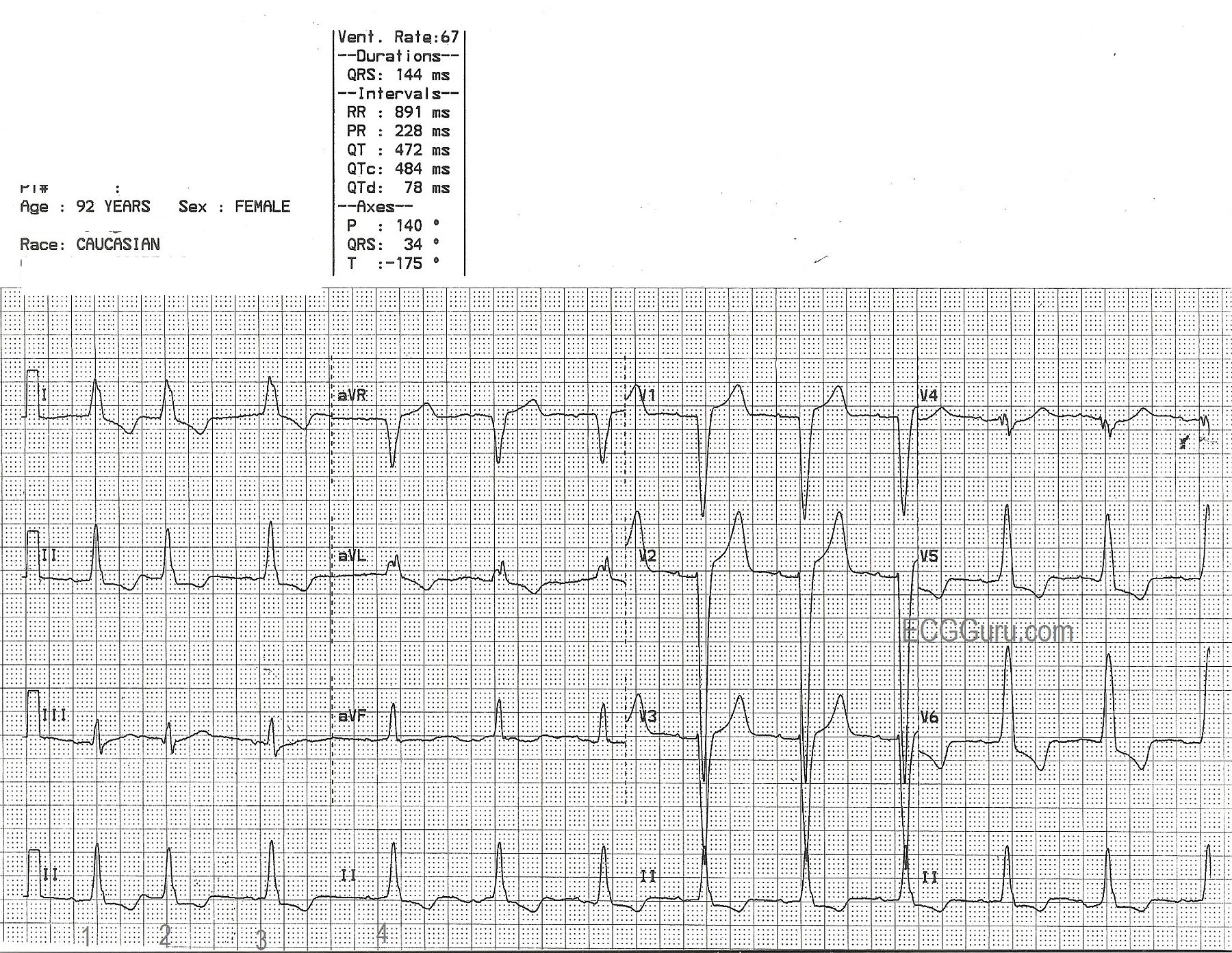
In bundle branch block, the pathway these impulses follow is delayed or blocked. This detour means that . But when there’s a “block” in one of the branches, electrical signals have to take a different path through the ventricle.Using a multivariable logistic regression model that included age, ECG, and clinical characteristics, they found that the presence of one or more atrial premature contractions, a right bundle branch block or intraventricular block, ischemic T-wave inversion and nonspecific repolarization increased the odds of death .Methods and Results.Correctly diagnosing left bundle branch block (LBBB) is fundamental, as LBBB occurs frequently in heart failure and may trigger a vicious cycle of progressive left ventricular dysfunction. Left bundle branch block widens the entire QRS, and in most cases shifts the heart's electrical axis .This topic reviews our approach to the management of patients whose baseline ECG is abnormal. A multicenter retrospective cohort study including consecutive patients with suspected AMI and left bundle branch block, referred for primary percutaneous coronary intervention between 2009 and 2018.ECG changes in left bundle branch block (LBBB) ECG findings: there is a Q in V1 and an R wave in V6 - there is depolarization of the right ventricle before the left. Inferior infarction.ECG (EKG) in acute STEMI (ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction) The ECG is the key to diagnosing STEMI.
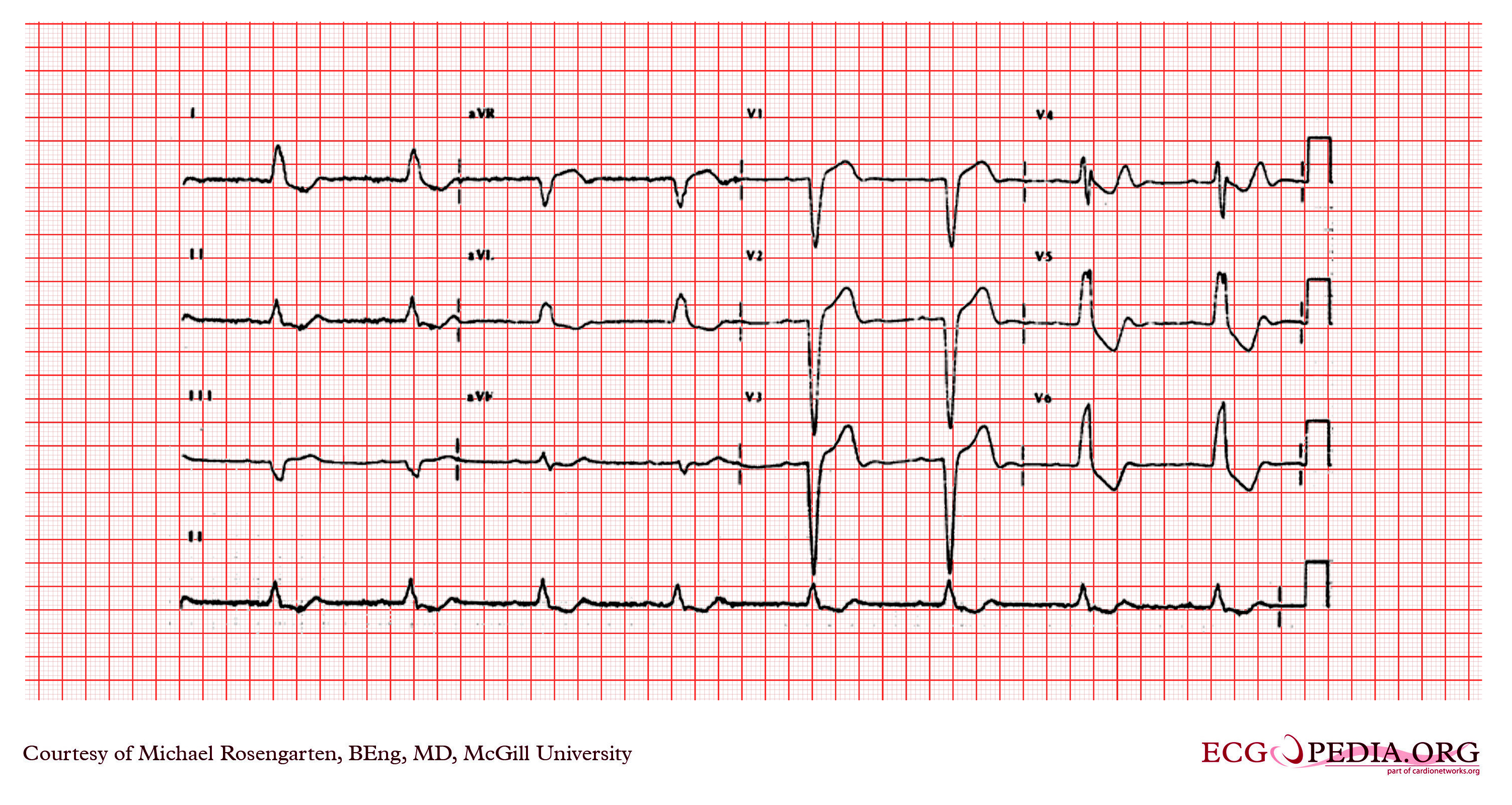
Auteur : Dmitriy Scherbak, Gregory J.The hallmark of right bundle branch block is QRS duration ≥0,12 seconds, large R’-wave in V1/V2 and a broad and deep S-wave in V5/V6. ECG criteria for STEMI are not used in the presence of left bundle branch block or left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) because these conditions cause secondary ST-T changes which may mask or simulate ischemic ST-T changes.
Atrial flutter: classification, causes, ECG diagnosis & management
A recent study correlating ECG and . This quick and painless test measures the electrical activity of the heart. Left anterior fascicular block is diagnosed if the axis is between -45° and 90° with qR-complex in aVL and QRS .Left Bundle Branch Block ECG Explained - YouTube.

Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is not a simple and generalized electrocardiogram (ECG) alteration in QRS pattern.FindingsIn this diagnostic study of 75 patients, LBBB pattern on surface electrocardiography (ECG) was categorized as being due to complete conduction . It is considered an . Medical Education for Visual Learners.

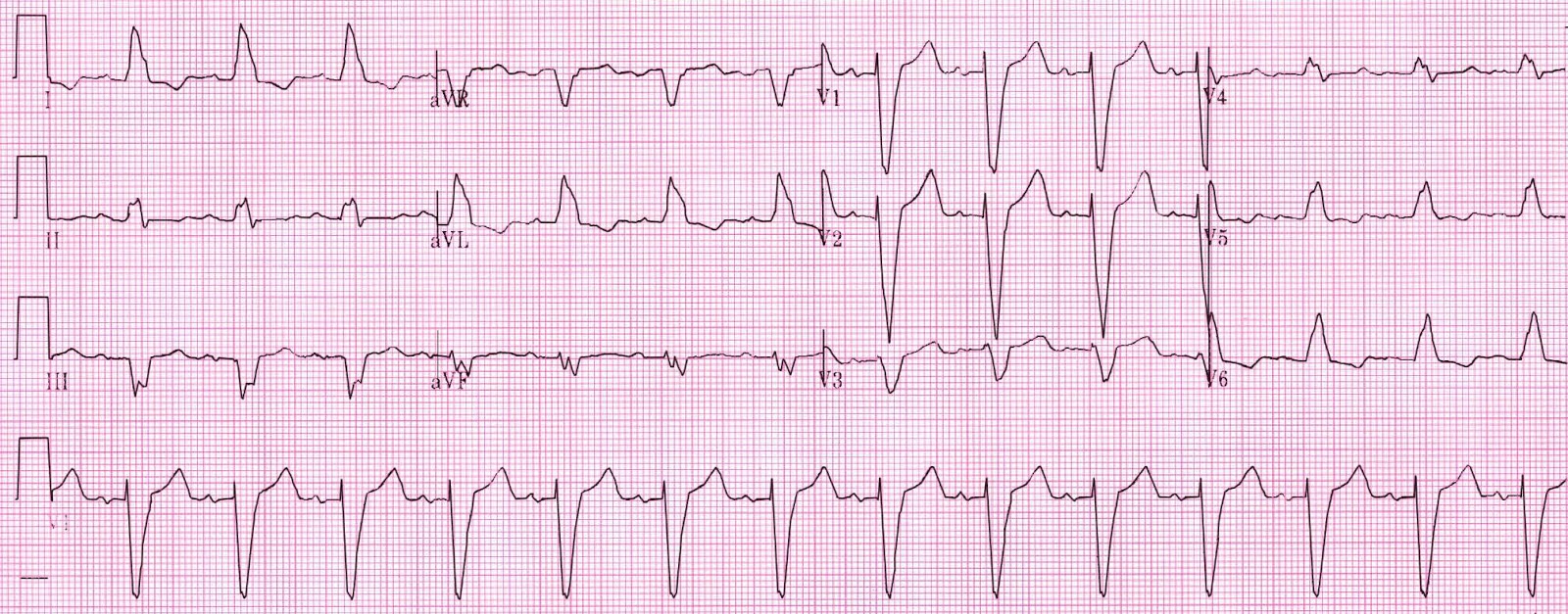
Submitted by Dawn on Tue, 02/17/2015 - 21:54.The most common non-reversible causes of sinus bradycardia are sinus node dysfunction, side effects of medications and acute myocardial infarction.Bundle branch block. Left ventricular hypertrophy. Such ST depressions are usually generalized, meaning that they are evident in most ECG leads.Left bundle branch block may be due to conduction system degeneration or a reflection of myocardial pathology. Pre-excitation. Learn the ECG criteria, causes, and . ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context. The exact appearance of the flutter . In our patient, the frontal plane QRS axis is superiorly directed (negative QRS complexes in the inferior leads and positive ones in leads aVR and aVL), indicating additional RV disease. It is associated with advanced conduction system and structural heart disease, and has .Left bundle branch block (LBBB) pattern on the electrocardiogram includes patients with both complete conduction block in the His-Purkinje system as well as .Left bundle-branch block completely modifies the electrical acti-vation of the left ventricle and QRS complex on ECG.Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is a cardiac conduction abnormality that can affect the diagnosis and treatment of various heart conditions. Its presence confounds the application of standard ECG criteria for the diagnosis of left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), myocardial . A LBBB can be caused by problems with the electrical conduction of the heart, the heart muscle, or the shape of the heart. If a normal atrial impulse is conducted to the ventricles approximately simultaneously as a premature ventricular impulse is discharged, the ventricles might be depolarized by both these . This is clinically important as the patient may intermittently go into complete heart block as they are solely relying . 3 is the ECG of a patient with COVID-19-related myocarditis; the ECG reveals atrial fibrillation with a mean rate of approximately 100 bpm, .Fascicular block (hemiblock) An anatomical or functional block in a fascicle causes a fascicular block. ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases.If the morphology in lead V1 is similar to a left bundle branch block (i.Several ECG patterns confound the diagnosis of AMI, including left bundle branch block (LBBB), ventricular paced rhythms (VPR), and left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH). Flutter waves are typically best seen in leads II, III aVF, V1, V2 and V3. qR complexes in leads I, aVL, with small Q waves and tall R waves.Given its broad use as a screening tool, the electrocardiogram (ECG) has largely become one of the most common diagnostic tests performed in routine clinical practice. Significant QT interval prolongation may lead to torsade des pointes.Scroll to annotate: Left Anterior Fascicular Block (LAFB) Typical ECG of LAFB, demonstrating: rS complexes in leads II, III, aVF, with small R waves and deep S waves. Block in the anterior fascicle is termed left anterior fascicular block (LAFB), and . The ECG criteria for left bundle branch block are: · Wide QRS (.Left bundle branch block (LBBB) occurs when something blocks or disrupts the electrical impulse that causes your heart to beat. Since the LBBB diagnostic criteria were recently updated by . If you have a newly diagnosed LBBB, .
Left Bundle Branch Block
Moreover, a correct diagnosis of LBBB is pivotal to guide cardiac resynchronisation therapy. Tests that can be used to diagnose a bundle branch block or its causes include: Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). The flutter waves (on the contrary to f-waves in atrial fibrillation) have identical morphology (in each ECG lead).
Left bundle branch block
Patients using digoxin (digitalis) may also display significant ST-T changes, particularly ST depressions, on the resting ECG. Left bundle branch block ( LBBB) is a conduction abnormality in the heart that can be seen on an electrocardiogram (ECG). It occurs from a change in the way the heartbeat travels down the left side of the heart. Normally, electrical impulses travel down the right and left bundle branches of the ventricles at the same speed. Figure 2 illustrates a normal ECG, a right . Left bundle branch block may also develop following aortic valve disease or cardiac procedures. Electrical impulses that cause your heart to beat (contract) start in the heart's upper right chamber (right atrium) and travel to the lower chambers (ventricles). These changes may only appear as notches on the ECG.On the contrary to right bundle branch block, left bundle branch block is always a pathological finding which affects cardiovascular and total mortality.Auteur : Andrés R. This topic will not discuss the pathophysiology of ECG .If the left anterior fascicle (or left posterior fascicle but this is much less common) and the right bundle are blocked you will see both right bundle branch block and left axis deviation, this is known as bifascicular block.
As a result, the finding of left bundle‐branch block (LBBB) in the absence of a well‐defined clinical setting has become relatively frequent and raises questions and . During an electrocardiogram (ECG), sensors (electrodes) are .Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is an electrocardiographic (ECG) QRS pattern that aims to identify patients with conduction block along the left His-Purkinje .Atrial flutter is the only diagnosis causing this baseline appearance, which is why it must be recognized on the ECG. The ac-tivation of the interventricular septum, .
Left Bundle Branch Block: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice.ECG = electrocardiogram; LBBB = left bundle branch block; LV = left ventricle/ventricular; RV = right ventricle/ventricular.Left axis deviation: Left bundle branch block.












