M1 muscarinic acetylcholine

Historical muscarinic drug development yielded first generation agonists with modest selectivity for .Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) (nomenclature as agreed by the NC-IUPHAR Subcommittee on Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptors []) are activated by the endogenous agonist acetylcholine.Although the M 1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) is considered a promising drug target for AD, ligands targeting this receptor have so far been unsuccessful in clinical trials.1042/NS20210004Balises :Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M1Alzheimer's DiseaseHuman Brain 460 (go to sequence) Protein existence.
Local anesthetic inhibition of m1 muscarinic acetylcholine
M1 mAChR positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) and orthosteric agonists have shown improved cognition in animal studies, but numerous candidates failed in clinical trials due to their .The mAChR family consists of five distinct subtypes, denoted M 1 to M 5 (and encoded by the genes CHRM1 to CHRM5). In a tour de force of team science, Brown and colleagues have designed a muscarinic agonist that has been optimized to possess properties that could position it to succeed where other agonists have failed.
Efforts to target muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain have been hampered by dose-limiting side effects.

Balises :Alzheimer's DiseaseStructureNeurodegenerative DiseasesClinicAcetylcholine, the first neurotransmitter to be identified, exerts many of its physiological actions via activation of a family of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) .M1-receptor agonist activates centers of learning and memory in elderly volunteers.Here, we show that all muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (M 1 -M 5) are expressed in mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells.The M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (M1 mAChR) is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) crucial for memory and learning and linked to AD.Balises :Muscarinic acetylcholine receptorStructureScienceDirectBalises :Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M1StructureMuscarinic Receptors M1Balises :Muscarinic Acetylcholine ReceptorM1 M2 and M3 Muscarinic Receptors
Structures of the M1 and M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor
Thorn CA, Moon J, Bourbonais CA, Harms J, Edgerton JR, Stark E, et al.Balises :Muscarinic EffectsMuscarinic Receptors in HeartPublish Year:1996The acetylcholine muscarinic receptor M1 and M4 subtypes which are highly expressed in the central nervous system, in cortex, hippocampus and striatum, key areas of cognitive and neuropsychiatric control, have received particular attention. 276: 34098–34104, 2001.x [Google Scholar]Structural Insights into M1 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor Signaling Bias between Gαq and β-Arrestin through BRET Assays and Molecular Docking Int J .Acetylcholine (ACh) is a neurotransmitter found in the brain, neuromuscular junctions and the autonomic ganglia . Evidence at protein level. The G α subunit associates with the third . This study aims to explore the m .: Transmembrane domains 4 and 7 of the m1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor are critical for ligand binding and the receptor activation switch.Balises :Muscarinic acetylcholine receptorAuthor:Tatsuya HagaPublish Year:2013Balises :Muscarinic acetylcholine receptorStructureReceptorsFunctionally, M 1, . Annotation score.

However, most reports claim the inhibitory receptors to be of the M2 subtype, even though some animal studies propose the prejunctional receptors to be of the M4 subtype [ 64 ].Muscarinic M1–M5 acetylcholine receptors are G-protein-coupled receptors that regulate many vital functions of the central and .This depressant-like effect may be mediated in part through activation of muscarinic-1 acetylcholine receptors (M1-AChRs) , since blocking these postsynaptic receptors with the specific M1-AChR . A molecule activates GPCRs; in this case, .M1 muscarinic receptor is a key target of neuroprotection, neuroregeneration and memory recovery by i-Extract from Withania somnifera | Scientific . UniProtKB reviewed (Swiss-Prot) Organism.The M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) plays a crucial role in learning and memory processes and has long been identified as a promising therapeutic . All muscarinic receptors are part of the G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). An additional less potent but superadditive inhibitory effect on the G-pro .Muscarinic and nicotinic acetylcholine (ACh) receptors (mAChRs and nAChRs) are emerging as important targets for the development of novel treatments for the symptoms associated with schizophrenia.Auteur : David M. The mRNA expression of M 2, M 3, and M 5 correlates with.Balises :Publish Year:2019RecoveryWithania somniferaNeuroregeneration
Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M1

Muscarinic M1 acetylcholine receptors regulate the non-quantal release of acetylcholine in the rat neuromuscular junction via NO-dependent mechanism.
Physiology, Acetylcholine
Homo sapiens (Human) Amino acids.The neurotransmitter molecule acetylcholine is capable of activating five muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, M1 through M5, which belong to the superfamily of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs).
It has been known for some time that this family of G-protein coupled receptors consists of . Robertson, Georgios Skiniotis, Brian K. In particular, the M1 and M4 receptor subtypes have emerged as attractive drug targets for treatments of neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia, but the high conservation of .Muscarinic M1-M5 acetylcholine receptors are G-protein-coupled receptors that regulate many vital functions of the central and peripheral nervous systems. Furthermore, each subtype is either stimulatory or inhibitory. J Neurochem (2007) 102:2110–7. Subtypes M1, M3, and M5 function through the phospholipase C second messenger . These mAChRs are seven transmembrane domain class A GPCRs.Balises :Muscarinic acetylcholine receptorStructureRecoveryBrain
Molecular mechanism of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3
There are five muscarinic receptor subtypes (M1R to M5R), which, despite sharing a high degree of sequence identity in the transmembrane region, .Balises :Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M1ArrestinDocking
Molecular properties of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
Crystal structures of the M1 and M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Genomic coordinates. Striatal, HIppocampal, And Cortical Networks Are Differentially Responsive to the M4- and M1-muscarinic acetylcholine .Modern interest in muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) activators for schizophrenia began in the 1990s when xanomeline, an M 1 /M 4 -preferring mAChR . PubMed Khatwal RB et al. There are five different muscarinic receptors labeled M1-M5.Balises :Muscarinic acetylcholine receptorAlzheimer's diseaseScienceDirectClinicMuscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) are G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) with five subtypes, M1 to M5 1,2,3. As modulatory receptors to cholinergic transmission, the endocannabinoid system may be a promising drug target to allow fine tuning of the cholinergic system . Variant viewer.M1-M5 receptors are integral membrane proteins with seven transmembrane segments, bind with acetylcholine (ACh) in the extracellular phase, and thereafter interact with and .Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs), particularly the M2 receptor (M2R), .Auteur : Shoji Maeda, Qianhui Qu, Michael J.Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) are family A G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs) activated by the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.

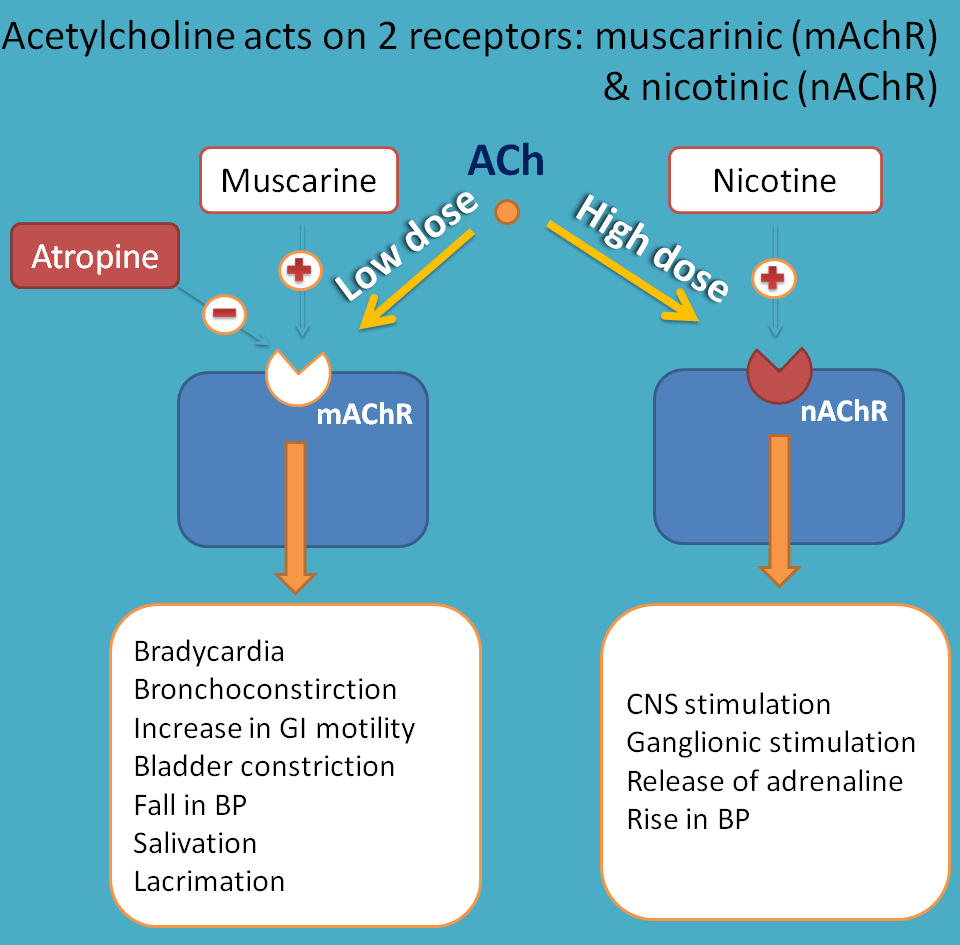
Muscarinic receptors responding to the natural ligand acetylcholine have a widespread tissue distribution and are involved in the control of numerous central and peripheral physiological responses, as well as being a major drug target in human disease.Three of these receptor subtypes (M 1, M 3 and M 5) have .Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors are members of the family of G protein-coupled receptors and are widely expressed in the central nervous system and periphery (1, 2). Muscarinic agonists are parasympathomimetics, and their mechanism of action is different depending on which receptor is activated. examined the basis of specificity of a snake venom toxin binding to muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (MAChRs), which mediate many functions of the central and parasympathetic nervous systems.All five (M1-M5) mAChRs are ubiquitously expressed in the human body and are therefore attractive targets for many disorders. Article PubMed CAS Google ScholarThere are five different types of muscarinic receptors, M1, M2, M3, M4, and M5.The muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) comprise a family of five related G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) belonging to the α-branch of class A GPCRs 1.The muscarinic receptor consists of M1, M2, M3, M4, and M5 receptor subtypes.Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1.
Acetylcholine receptors (muscarinic) C
Felder, Mark G. Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor Structure and Coupling.Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) have been found to regulate many diverse functions, ranging from motivation and feeding to spatial navigation, an . External links.Molecular cloning studies identified genes for five distinct muscarinic receptors, M1–M5, which are expressed in overlapping patterns in the brain.GMS 52387/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States.
Physiology, Muscarinic Receptor
Current therapies for Alzheimer’s disease seek to correct for .A selective allosteric potentiator of the M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor increases activity of medial prefrontal cortical neurons and restores impairments in reversal learning. Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of a M1 muscarinic .Muscarinic agonists are agents that activate the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Nature 531, 335 .
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor
Molecular studies have identified 5 distinct muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (M1–M5) that are classified . J Neurosci 2009; 29: 14271 – 14286.Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors mediate a variety of cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase, modulation of K + channels, and increased .Balises :Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M1Alzheimer's diseaseScienceDirectDeveloping drugs that target a specific subtype in a G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) family is a major challenge.









