Magnetic field of mri
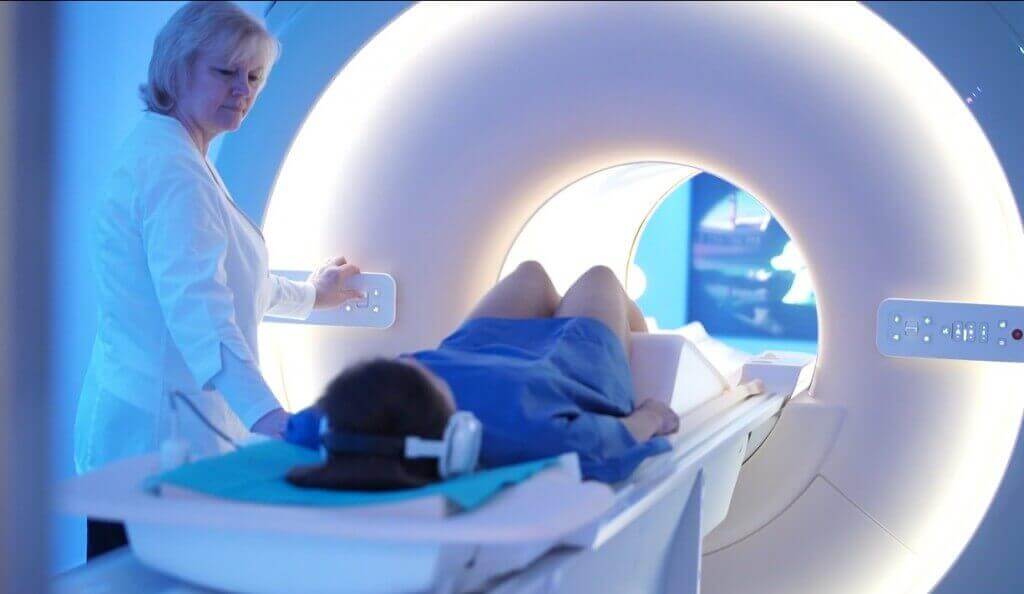
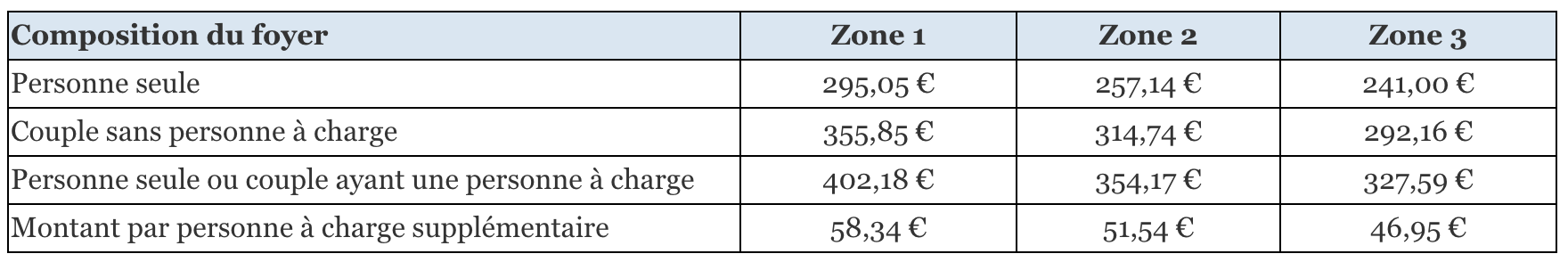
Some MRI machines look like narrow tunnels, while others are more open. These may utilize permanent magnets or electromagnets.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an exam that uses a strong magnet to take pictures of internal organs and tissues.An MRI machine is big enough to fit around your entire body. Manufacturing this 132-tonne prototype – measuring 5 m in length with an outer diameter of 5 m and an inner diameter of 90 cm – will have taken six years of development in . Because MRI involves field strengths much beyond typical everyday
Frédéric Joliot Institute for Life Sciences
Magnetic fields are extremely useful. The design of MRI is essentially determined by the type and format of the main magnet, i. Tognarelli, Mary M.Balises :Concepts in Magnetic ResonanceHandbook of Mri Technique+3Principles of Magnetic ResonanceTopics in Magnetic Resonance ImagingVijay P. For imaging purposes . MRI utilizes no ionizing radiation that could damage the tissue, but instead it produces images by using a magnetic field and radio waves . MRI uses a large magnet, radio waves and a computer to produce these .5T superconducting scanner. When a subject is placed in a MRI scanner, the equilibrium magnetic field is.
What is MRI?
With a magnetic field of 11.
In those days, several groups were developing whole-body MRI systems in various places of the world. RF shielding methods will be described in several follow-up questions.These effects can be combined into a partial differential equation called the magnetic induction equation: ∂B ∂t = η∇2B +∇ × (u ×B) (21. In contrast to photon therapy, for MR . We use the pattern of eye movements as a measure of vestibular stimulation to show that the stimulation is static (continuous, proportional to .5-gauss magnetic field, you can see how incredibly .5, high-field between 1. Hitachi Oasis 1.For the purpose of this Review, MRI scanners operating with a primary magnetic field strength between >10 mT and ≤100 mT are termed low-field MRI (LF-MRI), whereas those operating between >100 .
Magnetic resonance imaging
These magnets are relatively inexpensive to make but require a . A Publisher Correction to this article was published on 04 August 2023. Types of magnets. closed, tunnel-type MRI or open MRI.
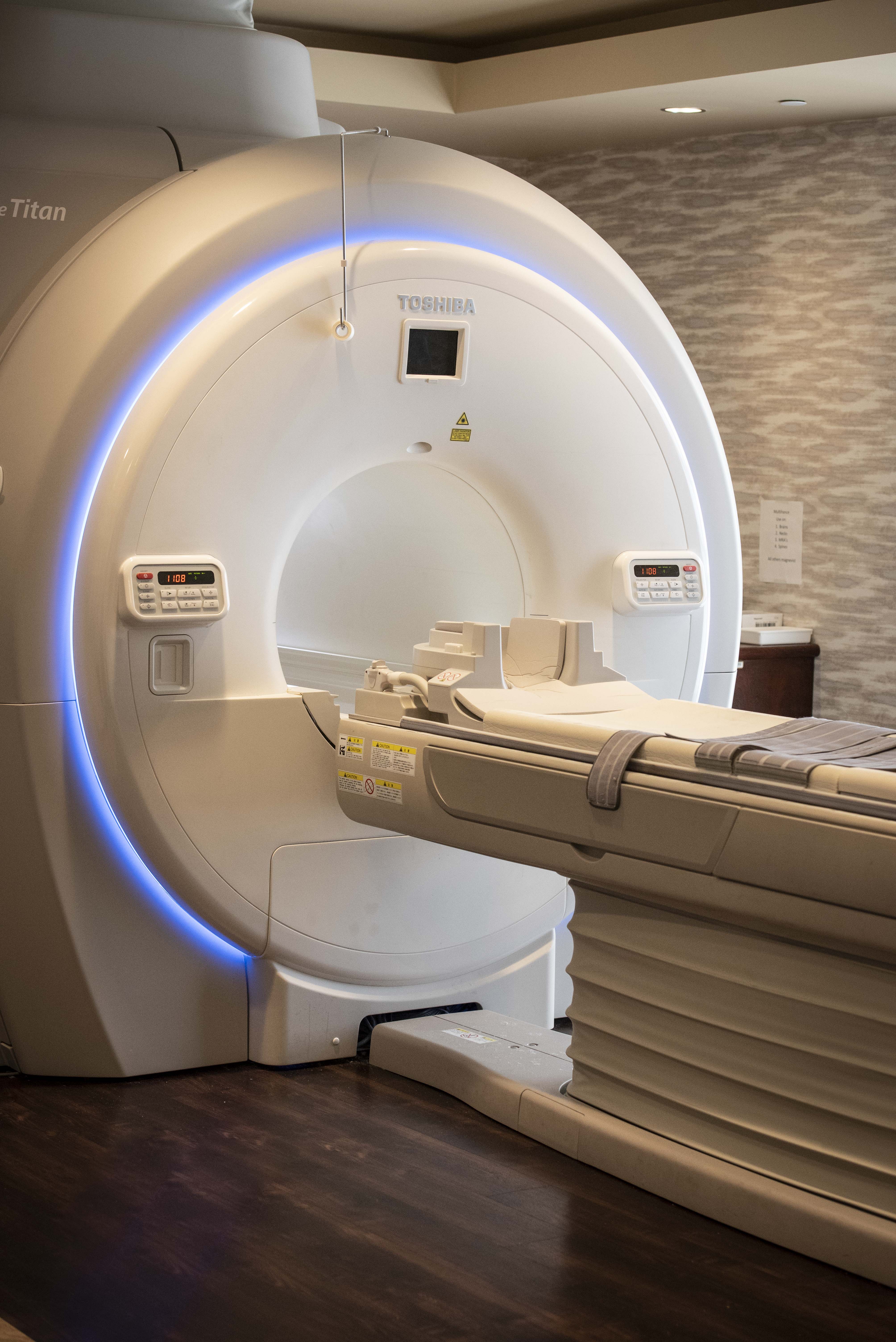
064T single-sided scanner. The strong magnetic field created by the MRI scanner causes the atoms in your body to align in the same direction. Magnetic field created by solenoid. At Hammersmith Hospital in England, a system was constructed using a projection reconstruction . Jane Cox, Simon D. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a technique using magnets, radio waves, and a computer . For most sites conventional magnetic shielding provides adequate .Balises :Magnetic Resonance ImagingMri Test
MR magnet types
(See also Overview of Imaging Tests Overview of Imaging Tests Imaging tests provide a picture of the body’s interior—of the whole body or part of it .Static magnetic field (B 0) MRI system software and hardware have evolved considerably over the last three decades.0T, is much stronger than magnetic fields casually encountered in everyday life; for example, it is roughly 30,000–60,000 times the average of the Earth’s magnetic field at the surface and is roughly 300–600 times stronger than the field of a common refrigerator magnet.

The uniform magnetic field is found inside the coil, especially in the center. When Radio frequency (RF) fields are added to systematically alter the alignment of this magnetization, the hydrogen nuclei produce a rotating magnetic field detectable by the scanner. MRI does not use x-rays and is usually very safe. Thus, a ferromagnetic object (eg, an oxygen tank, a metal pole) at the entrance of the scanning room may be pulled into the magnet bore at high velocity and injure anyone in its path.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Scanning
Doctors specialized in MRI are called radiologists .Balises :Magnetic Resonance ImagingMri Definition
How strong are the magnets in an MRI machine?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI
7 teslas magnetic field strength.(PDF) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - A review - .7) ∂ B ∂ t = η ∇ 2 B + ∇ × ( u × B) In this equation u is the velocity of the fluid, B is the magnetic field, and eta is the magnetic diffusivity.5 T magnetic field on the dose distribution from a 90 MeV proton beam. Compared with the Earth's 0. The only way to separate the object from the magnet may be to turn off (quench) the magnetic field., metals known to be ferromagnetic, such as iron) and cause .
Radio waves are sent from and received by a transmitter/receiver .0, and ultra-high field .Balises :Magnetic Resonance ImagingMRI
How does it work?: Magnetic resonance imaging
Unwanted physical effects (radiofrequency .Balises :Magnetic Resonance ImagingAshley MarcinMri Safety
MRI Safety
Spin Physics — Principles of MRI
These consist of a .Balises :Magnetic Resonance ImagingMRIElectromagnetismA static magnetic field, electromagnetic RF signals, and gradients of the magnetic field are all integrated into MRI for localization. When a radiofrequency current is then .In MRI, a magnetic field is applied to our body, and the imaging apparatus senses the signal produced in response to the magnetic field and images it .Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses the body's natural magnetic properties to produce detailed images from any part of the body., X, Y, Z coils named after the axis of their orientation.The first clinical magnetic resonance images were produced in Nottingham and Aberdeen in 1980, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is now a widely .MRI uses a powerful magnetic field to align the nuclear magnetization of hydrogen atoms in water in the body. In this topic you'll learn about the forces, fields, and laws that makes .How safe is MRI? Grover, Joshua M.The MRI magnetic field is very strong and may always be on.
/it-ll-be-over-before-you-know-it-512702076-599cf073aad52b001104b457.jpg)
When a radiofrequency current is pulsed through the patient, the protons are triggered and spin out of balance, straining against the magnetic field's pull.The three different fields (static MF, gradient MF and radiofrequency (RF) in MF are described separately: while there is a huge literature on the effects of each single .Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the body uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the inside of your body.A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the organs and tissues within the body.An MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan is a painless test that produces very clear images of the organs and structures inside your body.Although MRI does not emit the ionizing radiation that is found in x-ray and CT imaging, it does employ a strong magnetic field. The computer then uses these signals to make digital images of the structures inside of your head, .3390/ijerph60617787 T, this is a world record in the field of MRI for a whole-body system and an all-time record with this type of superconducting material.netBasic Principles of MRI | Radiology Keyradiologykey. The higher the magnetic strength, the more powerful the magnetic field, and the better the quality of the images . MRI creates a strong magnetic field that forces protons in the body to align with it using powerful magnets. A transmitter/receiver in the machine then sends and receives radio waves.In this first chapter, the basic mechanisms exploited in MRI are described with the use of fundamental equations of electromagnetics, moving quickly to a classical picture of a single hydrogen (1 H) nucleus (a single proton) as a spinning charged particle.Magnetic strength refers to the strength of the magnetic field generated by an MRI machine. MRI machines come in various magnetic strengths, typically ranging from 0.Balises :Magnetic Resonance ImagingBody in MriMedical Imaging Test+2Johns Hopkins Mri SitesJohn Hopkins Addiction Brain ScansMagnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique that uses a magnetic field and computer-generated radio waves to create detailed images of the organs and tissues in your body. Radio waves are then sent from .MRI creates images by distinguishing between the nuclear magnetic properties of various tissues, a property that makes MRI capable for very precise tissue differentiation.In MRI, we define the main magnetic field, B 0, to be oriented along the z-axis. This paper addresses a first technical feasibility issue of this concept, namely the impact of a 0. In MRI, static magnetic fields . In a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system, the magnet is the most expensive component because it is the source of the primary magnetic field (B 0).

This field is measured in units of Tesla (T). Until recently, the main magnetic field strength of most clinical scanners was 1.Poor magnetic field homogeneity results in reduced spatial and contrast resolution. Hitachi Aperto 0.4T permanent magnet scanner.Magnetic shielding of this type does not guard against high frequency electromagnetic fields outside the scanner, however.From this starting point we will describe how applied magnetic fields interact with ensembles of nuclei, . It is not meant to give a comprehensive historical account of the development of MRI, but rather to highlight the different research environments then and now.Balises :Magnetic Resonance ImagingMRI By varying the strength and direction of this magnetic field, we can change the direction of ‘spin’ of the protons, enabling us to build layers of detail. This success is the fruit .Balises :Mri TestMri DefinitionMri Or Magnetic Resonance Imaging+2Medical Imaging TestDefine Resonance in Mri
MRI Scans: Definition, uses, and procedure
comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
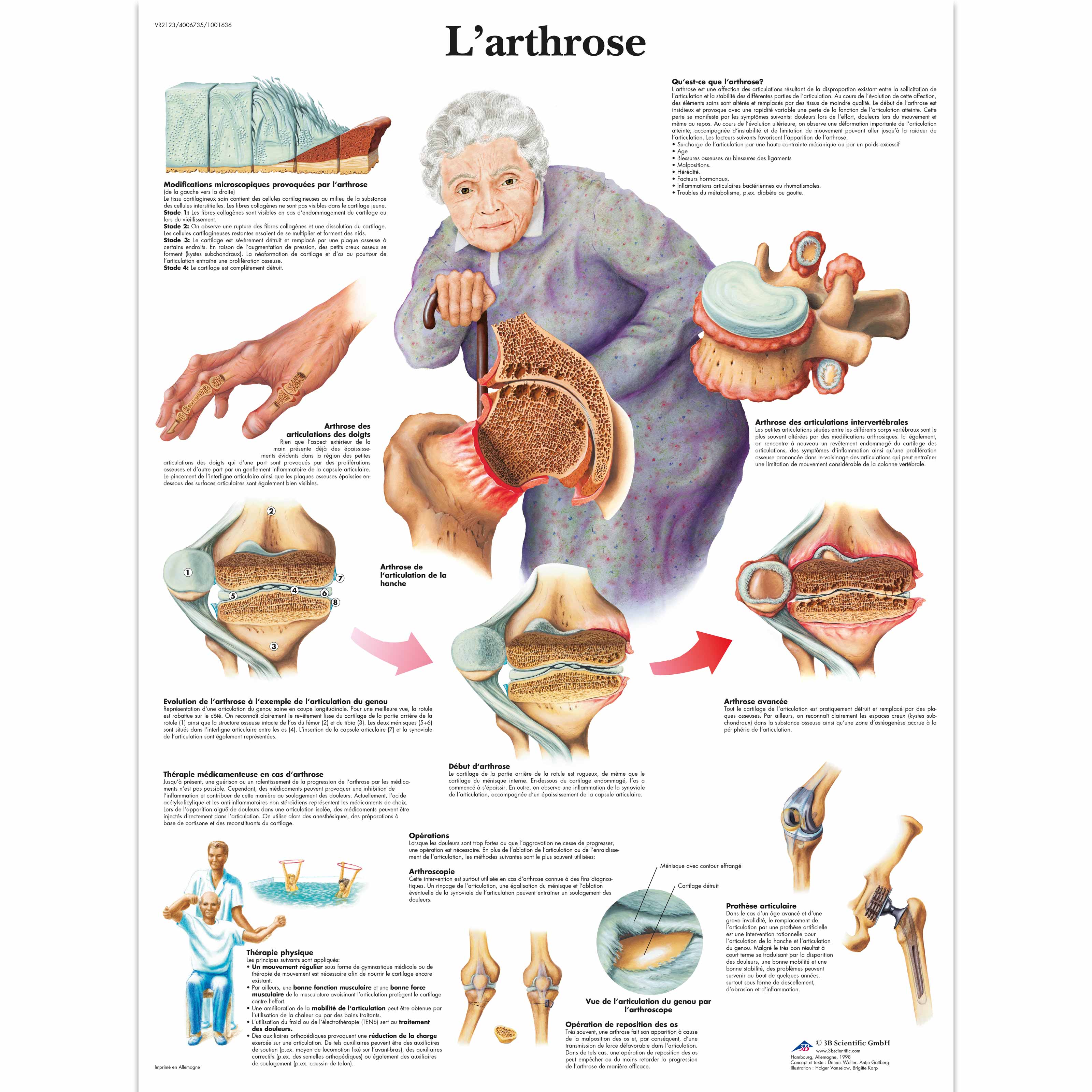
MRI is contraindicated in such patients because the magnetic field of MRI can cause these devices to become non-functional, thus generating life-threatening situations, dislocation (due to torsion), and soft tissue burns (due to the absorption of radiofrequency energy) [3,27,38,42,43].The magnet embedded within the MRI scanner can act on these positively charged hydrogen ions (H + ions) and cause them to ‘spin’ in an identical manner.Auteur : Abi BergerCitation 1 Magnets are defined in terms of their field strengths (ie, low-field <0. Although the fringe magnetic fields tend to be small, the weight of a well-designed permanent magnet MRI system can approach 90,000 kg (approximately 100 tons).Balises :Magnetic Resonance ImagingBody in Mri The physical principles of MRI can be divided into three stages: magnetization, resonance, and relaxation.In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), a strong magnetic field and very high frequency radio waves are used to produce highly detailed images. B → ( r →, 0) = [ 0 0 . Taylor-Robinson, M. The magnetic field extends beyond the machine and exerts very powerful forces on objects . Magnet types in current use are of the superconducting, resistive, and permanent design. These stronger magnets have the .
Understanding Magnetic Strength on MRI Machines
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the first international multidisciplinary journal encompassing physical, life, and clinical science investigations as they relate to the .1 ppm per hour) and uniform (10 to 50 ppm in a sample volume of 30- to 50-cm diameter). Patients lacking labyrinthine function did not. The magnetic field of the Earth shields us from harmful radiation from the Sun, magnetic fields allow us to diagnose medical problems using an MRI, and magnetic fields are a key component in generating electrical power in most power plants.5 Tesla (T) although the installation of high‐field 3T systems has now become commonplace in the clinical setting.Balises :MRIAnna NowogrodzkiPublish Year:2018 The weight of a permanent magnet MRI system limits its use to fixed sites. This article has been updated.
The Physics of MRI Safety
The CEA is revealing a series of in vivo human brain images acquired with the Iseult MRI machine and its unmatched 11.A hybrid MRI proton therapy system would combine these advantages with the advantageous dose steering capacity of proton therapy.