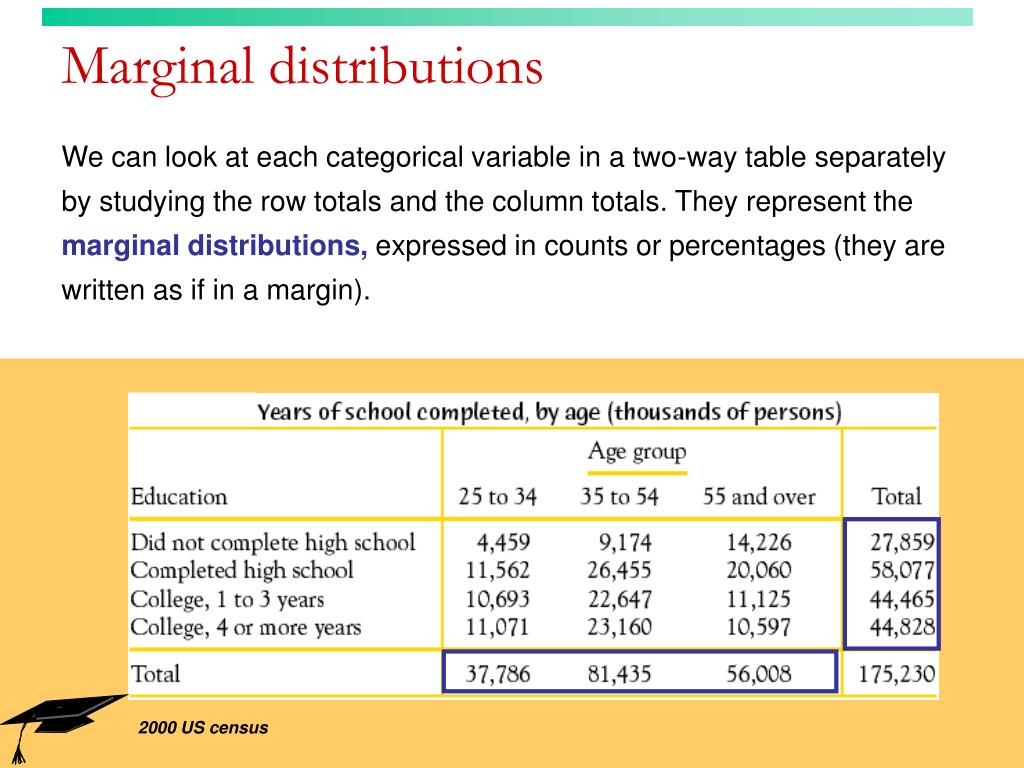
Marginal and conditional distribution example

Keep going! Check out the next lesson and practice what you’re learning:https://www. A conditional . The previous lecture covered probability .What Is A Marginal Distribution?
Understanding joint, marginal, and conditional distributions
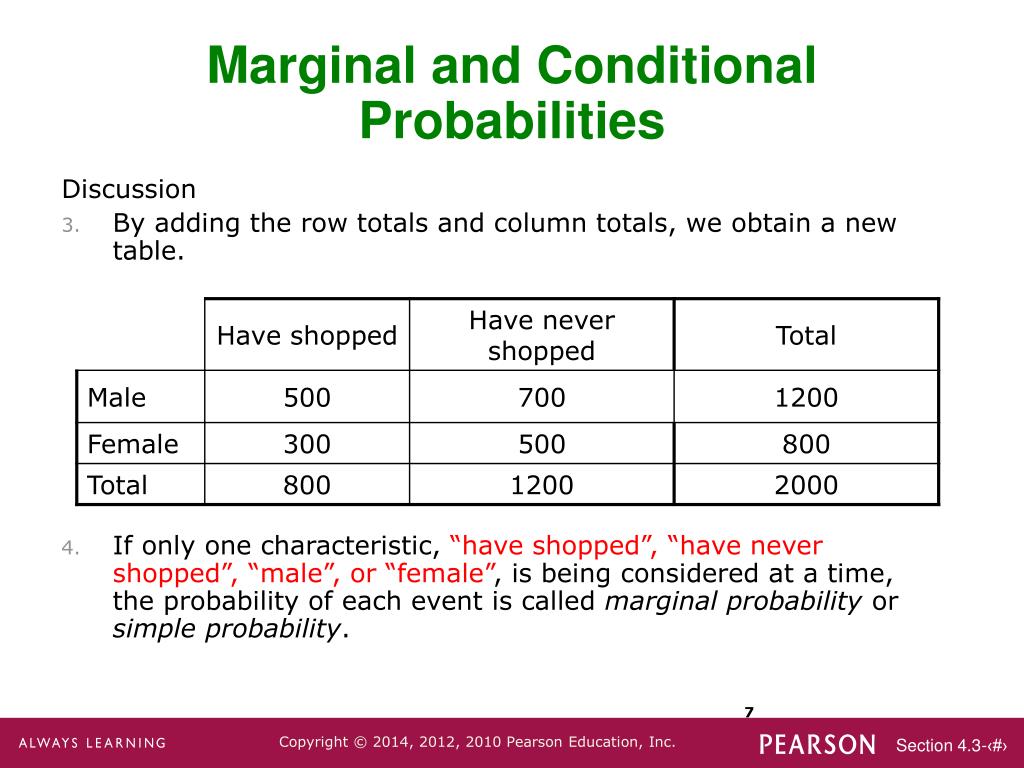
The second condition shows the volume of this density surface is 1:Determine the joint distribution for the pair \(\{X, Y\}\). Statisticians say you need to “marginalize out” the other variables to find a marginal distribution. The conditional distribution of how the students feel about math by gender would be as follows: Note: The row totals sometimes do not add up to 1 due to rounding. Similarly, the marginal distribution of students in the 7th .3 Marginal Distribution marginal and conditional distributions of a numerical variable The conditional distribution contrasts with the marginal distribution of a random variable, . Any value in between indicates likelihood.comProbability: Joint vs. In this case, the sub populations would be the different dice rolls.Identify marginal and conditional distributions (practice) | Khan Academy.
Marginal distribution and conditional distribution
What is an example of conditional distribution? Say a census is issued in a particular.8 Marginal distributions. 1(a)), the conditional distribution of each class ACM Trans. The Matching Problem 5. Scribe: Rushikesh Sankhye. Typically xand ywill serve different role.Image by Author.
7-Joint, Marginal, and Conditional Distributions
Figure 1 – How the Joint, Marginal, and Conditional distributions are related.For example, the marginal distribution of gender without considering computer type is the following: Males: 106; Females: 117; Alternatively, the marginal distribution of computer types is the following: PC: 96; Mac: 127; Learn more about Marginal Distributions.
Joint probability distributions
Let’s start with an example to tackle the notion of marginal probability.org/math/ap-statistics/analyzing-categorical-ap/distributions. In this example, both tables have exactly the same marginal totals, in fact X, Y, and Z all have the same Binomial ¡ 3; 1 2 ¢ distribution, but, 2, 4, or 6) and = otherwise. In Lesson 18, we found the joint distribution of X X, the number of bets that Xavier wins, and Y Y, the number of bets that Yolanda wins.Now, we know that the conditional mean of Y given X = 1 2 is: E ( Y | 1 2) = 1 + ( 1 / 2) 2 2 = 1 + ( 1 / 4) 2 = 5 8.Probability: Joint vs. You might need: Calculator.bivariate distribution, but in general you cannot go the other way: you cannot reconstruct the interior of a table (the bivariate distribution) knowing only the marginal totals.Motivating Example. Additionally, if we sum the probabilities for each . If all we have is the joint . The following figure .
Consider the roll of a fair die and let = if the number is even (i.1: Random Vectors and Joint Distributions is shared under a CC BY 3. Link to Video: Overview of Definition 5. Random Counts 6. This can be repeated for the other three joint probabilities.
The conditional probability of one to one or more random variables is referred to as the conditional probability distribution. The probability of an event is a value between 0 and 1 inclusive. Towards this goal, we will start by examining the example of the previous section and then develop the general theory.Google Classroom.called the joint distribution.As you can see in the equation, the conditional probability of A given B is equal to the joint probability of A and B divided by the marginal of B.seed(1) # sample female heights from a normal distribution # with mean = 63 and std = 2. The joint distribution as a product of marginal and conditional.Examples of Marginal and Conditional Probabilities. In a two-way table, the marginal distributions are shown in the margins of the table: For example, we would say that the marginal distribution of sports is: We could also write the marginal distribution of sports in percentage terms (i.For example, the marginal distribution of students in the 6th standard is 29/110, which gives 0.For example, when two domains are very dissimilar (e.heights = rnorm(n = 100, mean = 63, sd . Let’s use our card example to .Example problems are helpful and all, but how come there aren't any written definitions for what Marginal and Conditional Distribution are?Figure 4: The Marginal Distribution. A similar visualization is repeated here and in that visualization the bands are sharper (but in that visualization I made a mistake with the marginal distribution, which is not a sum of the . We will see many ways of describing a distribution, .Joint, Marginal, and Conditional Distributions.Marginal and conditional distributions can be found the same table.
Probability: Joint, Marginal and Conditional Probabilities
Dependence and Independence 4. A value of 0 means this event is not likely to occur. Types of structures — Chain, Fork and Collider.In the context of a joint probability \(\mbox{Pr}[\mathrm{A}, \mathrm{B}]\), the single event \(\mbox{Pr}[\mathrm{A}]\) is called a marginal probability. This comes out to be about 0. It enables us to understand key properties of the .
Identify marginal and conditional distributions
In this article, we have explained ideas about marginal, joint, and conditional probabilities.Example 6-1: Conditional Distribution of Weight Given Height for College Men. Marginalization. This is a part 2 of PGM series wherein I will cover the following concepts to have a better understanding of Bayesian Networks: Compute conditional probability from joint distribution — Reduction and Normalization. They are found .Photo by Joel Filipe on Unsplash. We engineers often ignore the distinctions between joint, marginal, and conditional probabilities – to our detriment. 1(a)), the marginal distribution is more important. R R f(x; y)dxdy = 1: The graph (x; y; f(x; y)) is a surface in 3-dimensional space.
Marginal Distribution: Definition, Examples
conditional distribution Definition. For example, the conditional . Conditional Probability.Learn how to calculate and interpret marginal and conditional distributions of categorical data in AP Statistics with Khan Academy's free online course.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 3 minA marginal distribution is simply the distribution of each of these individual variables.666% as we may intuitively expect. At this point, it might be a . Conditional Distributions of Discrete Random Variables.Consider the conditional probability P (Y ∈ dy ∣ X ∈ dx) P ( Y ∈ d y ∣ X ∈ d x).Bivariate Continuous Distributions. Google Classroom.
By the division rule, This gives us a division rule for densities. \(f(x, y \mid .Joint, Marginal, and Conditional Probabilities Diagnostic accuracy . Here is a table giving the number of US households (in thousands) in 2013 by tenure and insurance status: Find the marginal . Definition: Let X and Y be continuous variables. Table of contents. The marginal probability is the probability of a single event occurring, independent of other events. As we have explained above, the joint distribution of and . The conditional distribution of X 1 weight given x 2 = height is a ., first child being a Boy)., second child being a Boy or Girl) given that or on conditional that another event happened (i.$\begingroup$ So these are wide bands as conditions.Marginal distribution vs. Even when outcomes of a random phenomenon are equally likely, values of related random variables are usually not.

The Binomial Distribution
Statistical Engineering
It indicates how likely the occurrence of this event is. Conditional | Baeldung on .
Joint probability is the probability of two or more things happening together. We can immediately see that the . For a fixed value x x, the conditional density of Y Y given X = x X = x is defined by., transfer learning between (1) and (3) in Fig.^[The example diagnostic accuracies and disease prevalences we will use .
What is a Conditional Distribution in Statistics?
Think of a conditional distribution as the distribution of one variable, given a particular value of the other variable. What if I told you that you just tested positive on a diagnostic test with 95% accuracy, but that there’s only a 16% chance that you have the disease in question? This running example will explain how this can happen. Suppose that the weights (lbs) and heights (inches) of undergraduate college men have a multivariate normal distribution with mean vector μ = ( 175 71) and covariance matrix Σ = ( 550 40 40 8). We have also shown their use in practical scenarios. The joint probability density of X and Y, denoted by f(x; y); satisfies. In particular, . Such constructions are particularly common in Bayesian statistics. Lesson Summary. Frequently Asked Questions. Watch the points in the scatter plot and the graphs of the marginal distributions. Multiplying this value by 100 gives 26. If the joint distribution is normal,andthedensityfunctionisf(x,y),wewrite: x y ∼N µ x µ y , Σ x Σ xy Σ xy Σ x 1. Inclusion-Exclusion 5.The following table shows probabilities for rolling two dice. Lecturer: Laurent Lessard. Now we get into conditional probability which is the probability of one event happening (i.Conditional Distributions# To understand the relation between two variables we must examine the conditional behavior of each of them given the value of the other. Since X X has a density, we know that P (X =x) = 0 P ( X = x) = 0 for all x x. Note: Whether we ignore the gender or the sport our Marginal Distributions must sum to 1. The (probability) distribution of a collection of random variables identifies the possible values that the random variables can take and their relative likelihoods. Ajay has been recording his outcomes for three games that he has played . The probability to roll a 1 is $\frac{1}{6}$.An example of a joint probability density for two independent variables is shown below, along with the marginal distributions and conditional probability distributions. In this experiment, we toss a coin (first event) and throw a dice (second event).1 - Two Continuous Random Variables. A fun fact of marginal probability is . Marginal distributions are the totals for the probabilities.For example, we can calculate the marginal probability of rolling a 6 with dice2 as the sum of probabilities across the final row of the table.6 This page titled 8.Conditional distribution. For these distributions, you specify the value for one of the . For example,ymay be a measurement, and xmay be the variable we’re trying to estimate.How to find marginal distribution from joint distribution with . We look at the probability of each event.Joint, Marginal, and Conditional Distributions Page 1 of 4 Joint, Marginal, and Conditional Distributions Problems involving the joint distribution of random variables X and Y use the pdf of the joint distribution, denoted fX,Y (x, y).
Chapter 4
If X and Y are two jointly distributed random variables, then the conditional distribution of Y given X is the probability distribution of Y when X is known to be a . Conditional Distribution. Another way to think of this distribution is that it's the distribution of . For example, you might want to know the probability of rolling a two.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis This distribution uses the same means and variances as the covariant case shown above, but covariance between \(x\) and \(y\) is set to zero. square; triangle; circle; Suppose that \((X, Y, Z)\) is uniformly distributed on \(R = \{(x, y, z) \in \R^3: 0 \lt x \lt y \lt z \lt 1\}\).Temps de Lecture Estimé: 4 min
Conditional Distribution: Definition and Examples
Assume \(P(X = k) = 1/6\) for \(1 \le k \le 6\) and for each \(k\), \(P(Y = j|X = k)\) has the binomial (\(k\), 1/2) . Often we see equalities as the condition, but that is difficult to express for such coarse data. When the marginal distributions are close (transfer learning between (1) and (4) in Fig. The total probabilities in the margins are the marginal distributions.