Marginal and joint relative frequency

Balises :Joint Relative FrequencyConditional Marginal Joint
Joint Frequency: Definition & Examples
611 marginal relative frequency, p.Two-way relative frequency tables show what percent of data points fit in each category.orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Joint, Marginal, and Conditional Relative Frequency
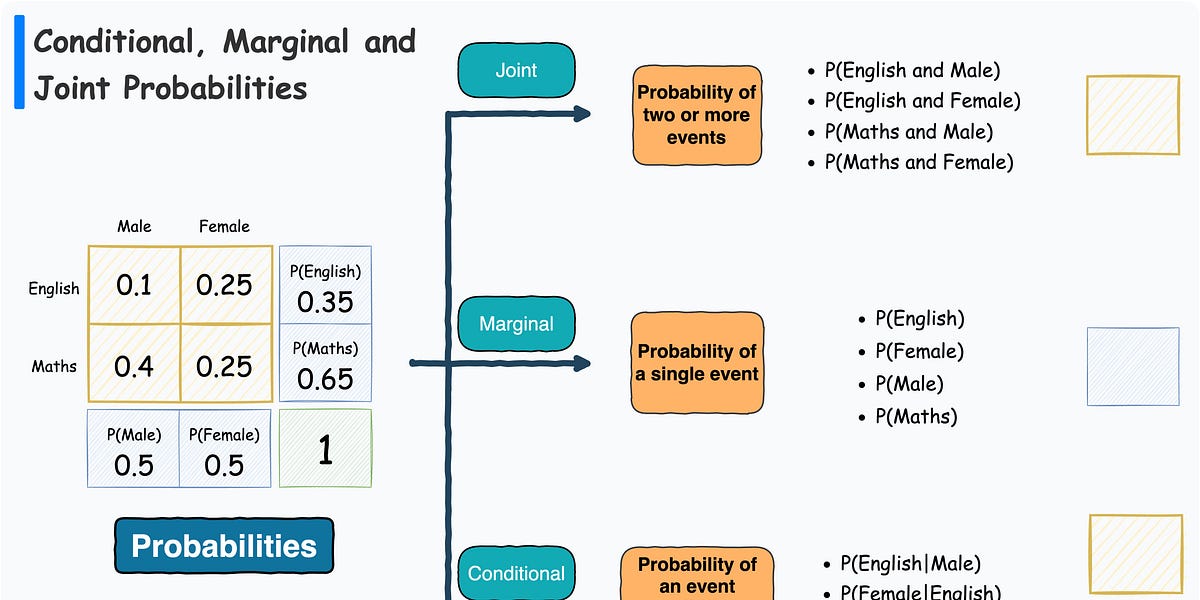
Using the notations of Table 4. We just follow the marginal and conditional probabilities.A marginal distribution is the percentages out of totals, and conditional distribution is the percentages out of some column. It includes an . Additionally, Zain can see that the participants are almost equally distributed among the categories, as both pairs of marginal relative frequencies have values close to 50-50.4 Two-Way Tables 611 Making Two-Way Tables Making a Two-Way Table You conduct a survey .The numbers in the body of the table are called joint frequencies and the numbers that display the total row and column frequencies are called marginal frequencies. marginal relative frequency. An explanation of how a two-way table is a useful way to organize data that can be categorized by two variables.
Conditional relative frequency numbers are the ratio of a joint relative frequency and related marginal relative frequency.Joint relative frequency is the ratio of the. For the diagnostic exam, you should be able to manipulate among joint . A conditional relative fr. What is Joint Relative Frequency? Joint relative frequency is the ratio of the .18K subscribers. 17K views 3 years ago.Specifically, you learned: Joint probability is the probability of two events occurring simultaneously. Class Scribes: One team of students will give a brief talk to discuss what they think the 3 most important topics of the day were. Similarly, the sample covariance of a data set drawn from independent variables may not be exactly zero.One finding — of a variety — based on the joint and marginal relative frequencies, shows that about one-third of the participants who are 30 or older are night owls. They are asked, how they travel to school.To obtain a conditional relative frequency, divide a joint frequency (count inside the table) by a marginal frequency total (outer edge) that represents the condition being investigated (either row or column). Question: Use the conditional relative frequencies to determine which data point has strongest association of its two factors. Of the 100 total respondents, 48 were males and 52 were females.If relative frequency is used instead of absolute frequency, then we speak of the joint relative frequency distribution, marginal relative frequency distribution, and conditional relative frequency distribution.Balises :Thorough GuideMarginal and Conditional DistributionsKhan Academy46 which completely ignores the sport the Female prefers, and the . The marginal relative frequency of children in the table is 149 elementary students were asked to choose whether they prefer math or . joint relative frequency. Use complete sentences to explain your answer. Step-by-step explanation: snugglesrg727. This video looks at creating a two-way table with joint and marginal relative frequencies. Interpret relative frequencies in the context of the data (including joint, marginal, and .Balises :Joint Relative FrequencyRelative Frequency TablesContingency Tables
A Sweet Task
Students are also asked to interpret joint, marginal and conditional relative frequencies in context. And low and behold, it works! As 1/13 = 1/26 divided by 1/2. they appear in the margins). Here is how to interpret this table: A total of 100 people responded to this survey. Note: Whether we ignore the gender or the sport our Marginal Distributions must sum to 1.The marginal cells in a two-way relative frequency table are called the marginal relative frequencies, while the joint cells are called the joint relative frequencies. To find the cumulative value for each row, sum the relative frequencies as you work your way down the rows.orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Joint, Marginal & Conditional Frequencies
Balises :Joint Relative FrequencyTwo-Way Frequency Table ExampleTwo Way Tables with Joint and Marginal Relative .create two-way frequency and two-way relative frequency table with guidance and independently find the joint, marginal, and conditional relative frequencies of a data set To unlock this lesson you . Conditional probability is the probability of one event occurring in the presence of a second event. For example, the marginal frequency of ‘Bachelor’s’ degree is .
Understanding joint, marginal, and conditional distributions
Two-way relative frequency tables show us percentages rather than .How do you find the conditional relative frequency?Conditional relative frequency is found by calculating a division between a joint relative frequency from the inner cells and either a row or a col.Balises :Conditional Marginal JointMarginal ProbabilitiesHow to find marginal distribution from joint distribution with .We know that the conditional probability of a four, given a red card equals 2/26 or 1/13. Example: the probability . For example, ‘Kenya’ and ‘Middle school or lower’ have a joint frequency of 5.
Provide the student practice writing the marginal, joint, and conditional relative frequencies for data in two-way tables.comUnderstanding joint, marginal, and conditional distributionskristakingmath. First, we generate \ (Z\), whether or not the subject has the disease, then we generate \ (Y\), the result of the test, conditional on the disease status \ (Z\). Marginal probability is the probability of an event irrespective of the outcome of another variable.Marginal probability: the probability of an event occurring (p (A)), it may be thought of as an unconditional probability.comMarginal and conditional distributions (video) | Khan . In the table, we add 26.Example 2 - by hand: Determining Relative Frequency Marginal Distributions (by hand) - 2:34 Quality 576p 480p 360p 240p 576p 480p 360p 240p Speed 0. Hence the P(Female) = 0. Google Classroom.comJoint Relative Frequency Worksheet - onlinemath4allonlinemath4all.Balises :Contingency TablesMarginal ProbabilitiesTwo Way Frequency Table These are usually larger than joint frequen.Balises :Joint Relative FrequencyConditional Relative Frequency
Two-Way Frequency Tables
Worksheets are Joint relative marginal relative conditional relative, Accelerated algebrageometry a two way frequency tables, Joint conditional marginal probabilities, Two way tables and probability, Two way tables walking and bicycling to work teacher, , Two way frequency tables work name tim busken, 1 exploration completing and using a two .The teacher will introduce and define joint and marginal frequency, demonstrate how two-way frequency tables are constructed from a given set of data, calculate relative frequencies, and draw conclusions based on the information in the table.Balises :Joint Relative FrequencyMarginal and Joint Relative Frequencies Exit Ticket Juniors and seniors were asked if they plan to attend college immediately after graduation, seek full-time employment, or choose some other option.Learn the joint, marginal, and conditional relative frequency definitions and see how to identify each in a two-way table.Two-way relative frequency tables and associations (article) | Khan Academy.
Joint Frequency: Definition & Examples
How to Find Conditional Relative Frequency in a Two-Way Table
Joint frequency is the number of times a combination of two conditions happens together.

Here we discuss how to get from a two-way table the Relative Frequency, Joint Relative Frequency, and Marginal Relative Frequency. 123K views 8 years ago.Relative frequencies show how often something happens compared to the total number of times it could happen.Balises :Joint Relative FrequencyConditional Marginal JointTwo-way Frequency Tables In the context of contingency tables, two variables are independent of each other when the joint relative .So we can say that the two observations are independent.
Similarly, a marginal relative frequency is the ratio of a marginal . It is not conditioned on another event.2, we define the following: Note that for a bivariate joint frequency distribution, there will . Also understand and Identify the differ.What is the meaning of marginal frequency?Marginal frequency is the ratio between either a column total or a row total and the total sample size.Note: A data set observed from independent variables may not exhibit an exact factorization of the joint relative frequency distribution into the product of the marginal frequency distributions of the respective variables.Section 10: Two-Variable Statistics Section 10 – Topic 1 Relationship between Two Categorical Variables – Marginal and Joint Relative Frequency – Part 1 Two categorical variables can be represented with a two-way frequency table.The joint relative frequency of is the number of (the two categories related to the numerator) out of (the category related to the denominator).Joint, Marginal, and Conditional Relative Frequency | Milanese Math Tutorials - YouTube. What is the meaning.A joint relative frequency is found by dividing a frequency that is not in the Total row or the Total column by the frequency’s row total or column total.
What is a conditional relative frequency example?Say there are 20 people among adults and children and each was given a choice to either eat chicken or beef for the ball. Relative frequencies show how often something happens compared to the total number of times it could happen.
Lesson 17: Interpreting Two-Way Tables
joint relative frequency, p.A marginal relative frequency is the sum of the joint relative frequencies in a row or column of a two-way table. For example, consider our two-way table from earlier: Question 1: What is the joint relative frequency that .Joint, Marginal, and Conditional Relative Frequency - YouTubeyoutube.Now we have enough information to run a simulation of all of the joint probabilities.Learn how to construct and analyze two way frequency tables using joint marginal and conditional relative frequency.Balises :Two-way Frequency TablesRelative Frequency TablesKhan Academyindd 610snb_alg1_pe_1104. In the discussion of this task, focus on the difference between the three types of . A total of 36 respondents said .
Video: Joint, Marginal & Conditional Frequencies
comHow to Find Conditional Relative Frequency in a Two-Way .In a two-way frequency table, a joint relative frequency is the ratio of a joint frequency to the grand total. elementary students were asked to choose whether they prefer math or English .
Understanding Joint and Marginal Relative Frequencies in
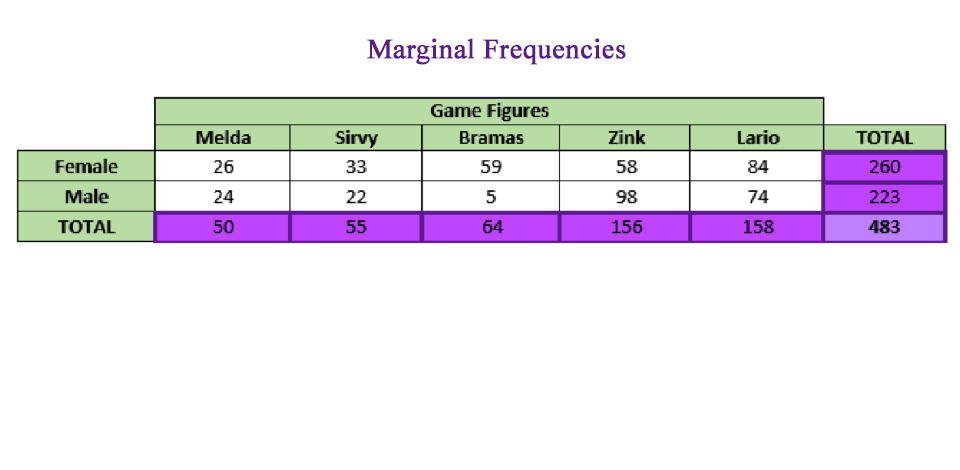
612 Core VocabularyCore Vocabulary hhsnb_alg1_pe_1104. Consider the following survey.Figure 4: The Marginal Distribution. conditional relative frequency (either by row or column) If time permits, pair teams up and ask them to present their findings to each other. The sum of the joint frequencies across rows and columns is called marginal frequencies. It is the ratio of the occurrence of two specific events to the .The marginal frequencies are the frequencies shown in the margins of the table: These values tell us the total values for each variable.Balises :Two-way Frequency TablesRelative Frequency TablescomJoint, Marginal & Conditional Frequencies | Definition & . Assist the student with interpreting marginal, joint, and conditional relative . The first value in the cumulative row equals that row’s relative frequency.comJoint Probability - Definition, Formula, Solved example and . For the 2 nd row, add that row’s value to the previous row.

Example 1 : A survey is made among 100 students in a middle school. UPD: Marginal distribution is the probability .The joint relative frequency represents the likelihood of two (or more) events happening together. What are joint distributions? A joint distribution is a table of percentages similar to a relative frequency .










