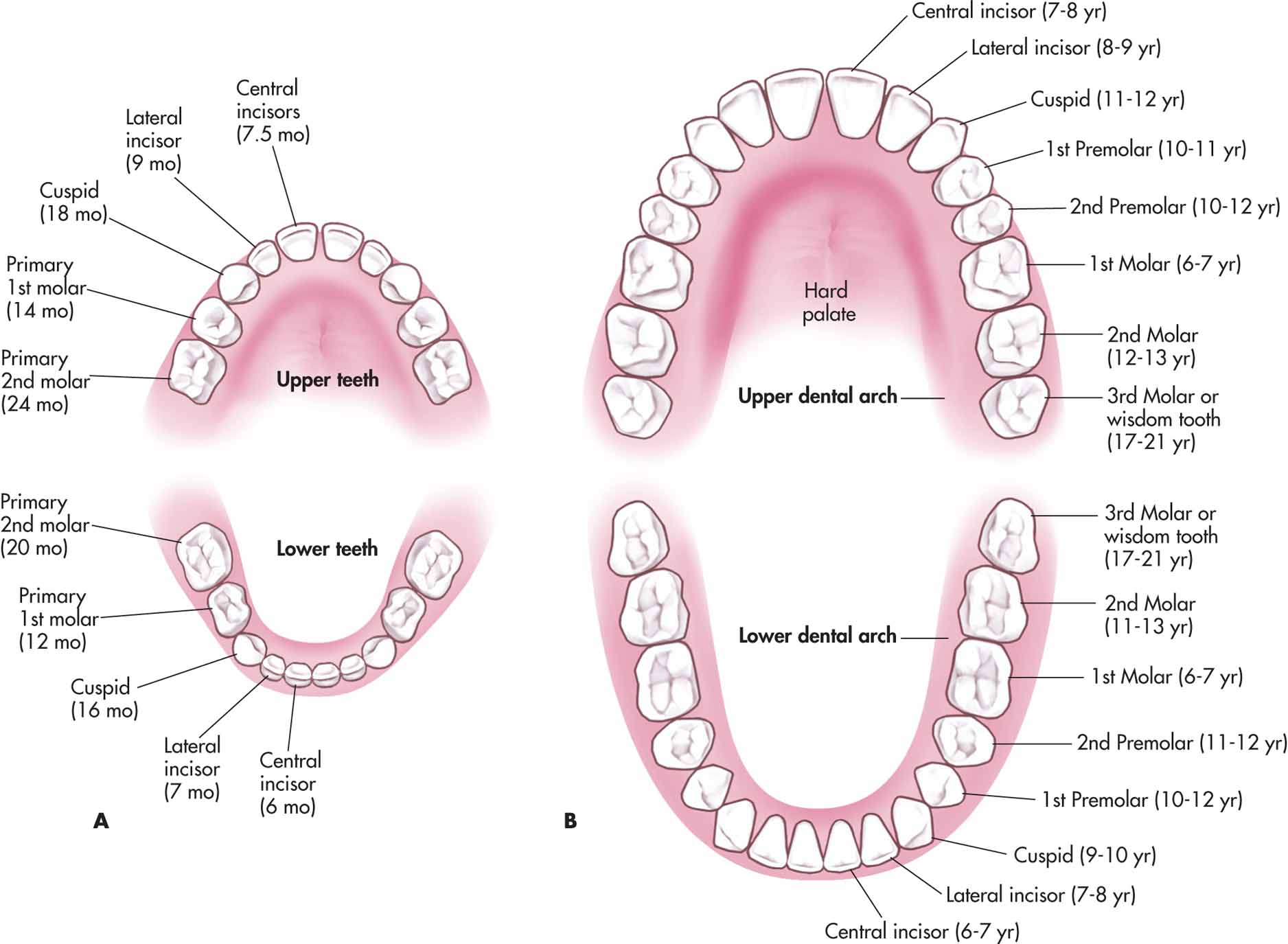
Maxillary teeth labeled
There are subtle differences between these two types of teeth. Each maxillary bone has the shape of a pyramid, it's base adjacent to the nasal cavity, its apex being the zygomatic process, and its body constituting the maxillary sinus. The name of teeth on each arcade .The maxillary nerve, which is the second division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V/II) carries sensory fibers teeth of the maxillary dental arch. Each maxilla consists of a maxillary sinus and includes . Adult teeth are called permanent or secondary teeth: 8 incisors. The maxilla connects with surrounding facial structures through four . The maxillary .The maxillary central incisor is a human tooth in the front upper jaw, or maxilla, and is usually the most visible of all teeth in the mouth.Types Of Teeth- Types of Teeth In Humans, Diagram and . Usually the extra dimension .The maxillary dental arcade (upper dental arcade; superior dental arch) is larger than the mandibular dental arcade (lower dental arcade; inferior dental arch), so that -in normal conditions- the teeth of the maxillae slightly overlap those of the mandible both in front and on the sides.
Teeth Names: Shape and Function of Four Types of Teeth
comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Anatomy, Head and Neck, Teeth
First maxillary molar (part 1)
5/5(20)
Maxilla: Anatomy, function and clinical notes
In this video lecture we have described the timeline of . In radiographs acquired with nonideal angulation, the corticated sinus floor may superimpose on the apical third of the roots of the maxillary molar teeth.There are thirty-two teeth in total in the oral cavity of an adult dentition. Each tooth is mainly composed of dentin and is made up of . The crown of the maxillary third molar is smaller than the maxillary first and second molar.Maxillary Teeth: The teeth on the upper jaw; Sources. The crown of this tooth is wider buccolingually than mesiodistally.The five surfaces are labial, palatal, mesial, distal and incisal surfaces.The maxillary second molar is the tooth located laterally from both the maxillary first molars of the mouth but mesially from both maxillary third molars. Molars are the most specialized of the teeth for grinding of food due to their broad crowns and rounded tips. Ash M M, Stanley JN. If you get the chance to see their maxillary teeth, you will notice a cone-like set along the edges of their mouth.
11: The Permanent Maxillary Molars
The maxillae (or upper jaw bones) are a pair of large bones found along the anterior aspect of the cranium.Auteur : Alyssa L. So, you will find 30 teeth in the cat’s mouth cavity.The oral cavity contains six maxillary molars, and every side of the upper jaw has three maxillary molars.Teeth are organised into two opposing arches – maxillary (upper) and mandibular (lower). Each maxilla forms the floor of the nasal cavity and parts of its lateral wall and roof, the roof of the oral cavity, contains the maxillary sinus, and contributes most of the inferior rim and floor of the orbit.0, modification of images from Anatomy Standard . The lower portion of the maxilla is connected to the upper teeth . There are 8 molars in the primary dentition: 4 maxillary and 4 mandibular. In the maxillary arch, there are three molars in each quadrant. The maxillary bone forms the upper jaw and supports the upper teeth. The maxillae are the two facial bones that form the upper jaw. The esophagus then passes the food into the stomach, where enzymes start to break down .The top teeth, numbered 1-16, are on the upper jaw, which is also known as the maxillary arch. C: Right maxillary canine. To begin, the human jaw consists of two parts: the maxillary, referring to the upper jaw, and the mandibular, referring to the lower jaw (see Figure 1) [].5K subscribers. There are 12 molars in the permanent dentition: 6 maxillary and 6 mandibular. Maxillary third molar varies considerably in size, shape, and position in the dental arch.
The roots are short, and usually, they are fused.The permanent maxillary first molar help in the grinding of food.The tooth is made up of a crown and either single or multiple roots.
Maxillary dental arch
Maxillary central incisor
Auteur : Dental Education Hub

In order to understand tooth morphology, it is important to understand both the nomenclature and the associated anatomy. They are the teeth most visible to the others during eating, . Humans have four types of teeth: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars, which each have a specific function. Dental Anthropology: Fundamentals, Limits and Prospects. One half, or sixteen, are embedded in the maxilla, while the lower half are situated within the mandible.

Permanent maxillary first premolar. Morris, Prasanna Tadi
Tooth anatomy: Structure, parts, types and functions
Dental anatomy
Wheeler’s dental anatomy, physiology, and occlusion. 1 Intraoral left molar bitewing radiograph labeled showing enamel (1), dentin (2), cementum (3), pulp (4), lamina dura (short white arrow), periodontal ligament . It is involved in the formation of the orbit, nose and palate, holds the upper .The third molars are also known as wisdom teeth. The cat’s dental formula shows incisor, canine, premolar, and molar types of teeth present in the upper and lower jaws of a cat. It has a rhomboid shape, and its mesiodistal length is slightly smaller than the buccolingual length. This video lecture includes timeline of tooth.There are four primary categories of human teeth: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars.The first maxillary molar is the most significant tooth of all maxillary molar teeth. The buccal mesiodistal length of the first maxillary molar is narrower than the same palatal length. The deciduous (primary) teeth start erupting at six months (lower central incisor) .
Anatomy, Head and Neck, Primary Dentition
Tooth Numbering Systems. External anatomy. A frog’s maxillary (upper jaw) teeth are not typically visible to humans. Rösing, Maria Teschler-Nicola.The maxillary teeth and the vomerine teeth located on the roof of its mouth do not chew: a frog swallows its meal whole. As such, they are considered part of the human digestive system.

Each maxilla attaches laterally to the zygomatic bones (cheek bones).The occlusal surface usually .
Child and Adult Dentition (Teeth)
In adult dentition, the molar teeth are the big, flat teeth located posterior to the pre-molars. The tooth sits in alveolar processes of the upper jaw ( maxilla) or lower jaw ( mandible ). It runs laterally to the .In addition to helping you chew through even the toughest foods, they also help you speak clearly. For example, in posterior teeth, mandibular molar, the five surfaces are buccal, occlusal, lingual, mesial, and distal surfaces. -----CONTENTS OF THIS .
Maxillary Third Molar: Morphology of tooth
The shape of the crown, in . They are classified as irregular bones, lodge the maxillary (upper) teeth, and contribute to the formation of the orbits, nasal cavities, bony hard palate, and the viscerocranium. Alt, Friedrich W. The sinus has a thin wall that separates it from the oral cavity, and it is lined with a thin layer of mucous membrane. In most adults, there will be a total of twelve molars: six maxillary and six mandibular (three on each side of each jaw). The maxilla is centrally located within the skull and makes up the center of the face. It has a central location and provides structural support to the viscerocranium. Understanding the role of the upper teeth and caring for them properly is important in the fight against bacteria and .In the maxilla, permanent adult teeth are numbered 1 through 16 from right to left, and primary teeth are labeled with letters A . UWBM-71908a and 71908b have a single, large tooth with a .
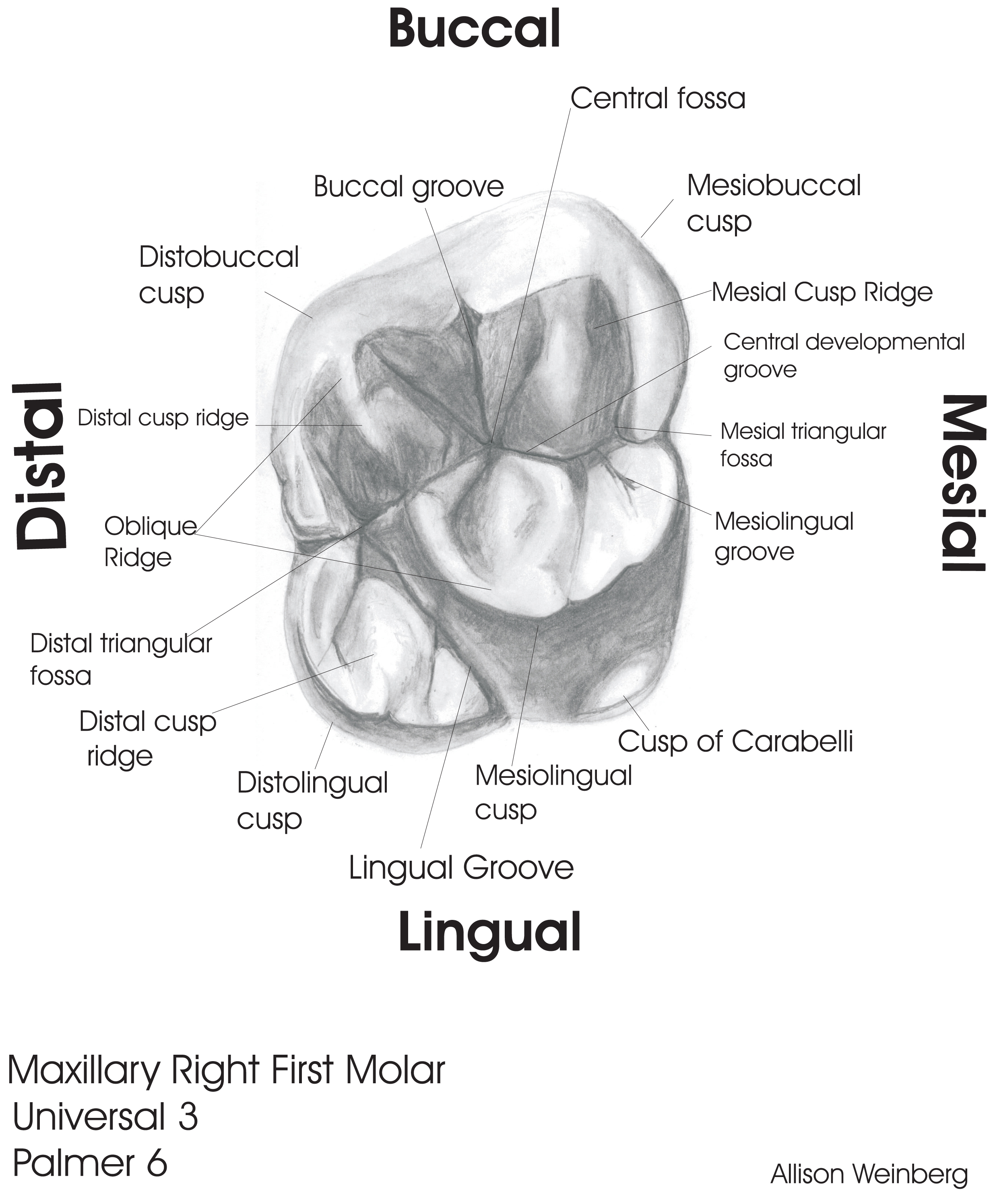
The floor of the maxillary sinuses (see Fig.Maxillary refers to the teeth on the upper jaw.The upper arch is the maxillary arch, with the teeth embedded in the maxilla, and the lower arch is the mandibular arch, with the teeth embedded in the mandible. 6) appears as a thin radiopaque partially curved line in the superior aspect of the PA radiograph in the maxillary molar teeth regions. Each maxilla also forms the lateral floor of each orbit and the majority of the hard palate. When the frog swallows, it passes food from the oral cavity and pharynx into the esophagus.The maxillary sinus is located within the body of the maxilla, which forms the upper jaw and the roof of the oral cavity. The cervical distobuccal line angle is concave and rounded, and it is a common . They enable the frog to catch and consume prey, which is necessary for maintaining its energy levels and staying alive. The anterior teeth in both the upper and the lower jaws, from the right first premolar to the left . Following is a brief description of this topic. The tooth has four well-developed cusps and one accessory or supplementary cusp called the cusp of Carabelli. Maxillary and vomerine teeth are essential for a frog’s survival. It is located mesial (closer to the midline . B: Right maxillary 1st molar.Regarder la vidéo17:05In this video lecture we have briefly described the timeline of development of the maxillary first molar tooth. The cusp of Carabelli . Kenny and Sarrah Zamora shares more information about maxillary teeth below. It has functional and aesthetic significance as it has a fundamental role . Age of primary tooth eruption. Instead, the teeth hold prey still.]
First maxillary molar (part 1)
To calculate the total number of teeth, let’s multiply the teeth in each half of the jaw by 2. (Image credit: Maxillary Bone by Sofia Elizondo is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.The incisors cut the food, the canines . They are eight in number, four upper and four lower, two centrals and two laterals. 1st edition Jan 1, 1998. It is a pyramid-shaped cavity that extends from the cheekbone (zygomatic bone) to the upper molars.
Maxilla: Anatomy, Function and Treatment
Since the upper central incisors are wider than the lower, the other teeth in .

The fusion of the right forms the maxilla and left maxillary bones at the midline.

In the maxillary arch, the permanent first molar is the largest tooth. This means that the teeth on your upper jaw – at the back of your mouth – towards your right hand are your first tooth, your . The names are given to these surfaces according to their position and use. Article Media (16) The maxilla (or maxillary bone, upper jaw bone, Latin: maxilla) is a paired bone of the facial skeleton, and it has a body and four processes.The importance of maxillary and vomerine teeth in a frog’s survival.Primary teeth are labeled in the following classification system and are designated in a clockwise direction: A: Right maxillary 2nd molar. They are classified as irregular bones, lodge the maxillary (upper) teeth, .
Open Wide: A Guide to Dental Anatomy
These can be divided down the midline .
Teeth anatomy: Blood supply and innervation
The maxillary first molar is the largest tooth in the maxillary dental arch.Synonyms: none.
![Schematic drawing of the oral cavity [97]. | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Javier-Sotres/publication/259357833/figure/fig5/AS:297123783430169@1447851238813/Schematic-drawing-of-the-oral-cavity-97.png)
These teeth of the cat are highly adapted for a carnivorous diet.The maxilla is the most important bone of the midface. Image from Visible Body Suite. This is true only in . All four categories have a specific function to aid in chewing food. 44K views 3 years ago #dentaleducation #dentaleducationhub. Saunders Elsevier 8th ed 2005.Human teeth function to mechanically break down items of food by cutting and crushing them in preparation for swallowing and digesting. The two maxillary bones (maxillae) are fused in the midline . They have sharp biting surfaces designed for shearing and cutting of food materials into small chewable pieces.
Physiology, Tooth
1 Crown morphology.The maxillae (or maxillary bones) are a pair of symmetrical bones joined at the midline, which form the middle third of the face. The third molars are the most variable [.The maxilla, also known as the upper jaw, is a vital viscerocranium structure of the skull.The alveolar process of the maxillae holds the upper teeth, and is referred to as the maxillary arch.