Methemoglobinemia symptoms in humans

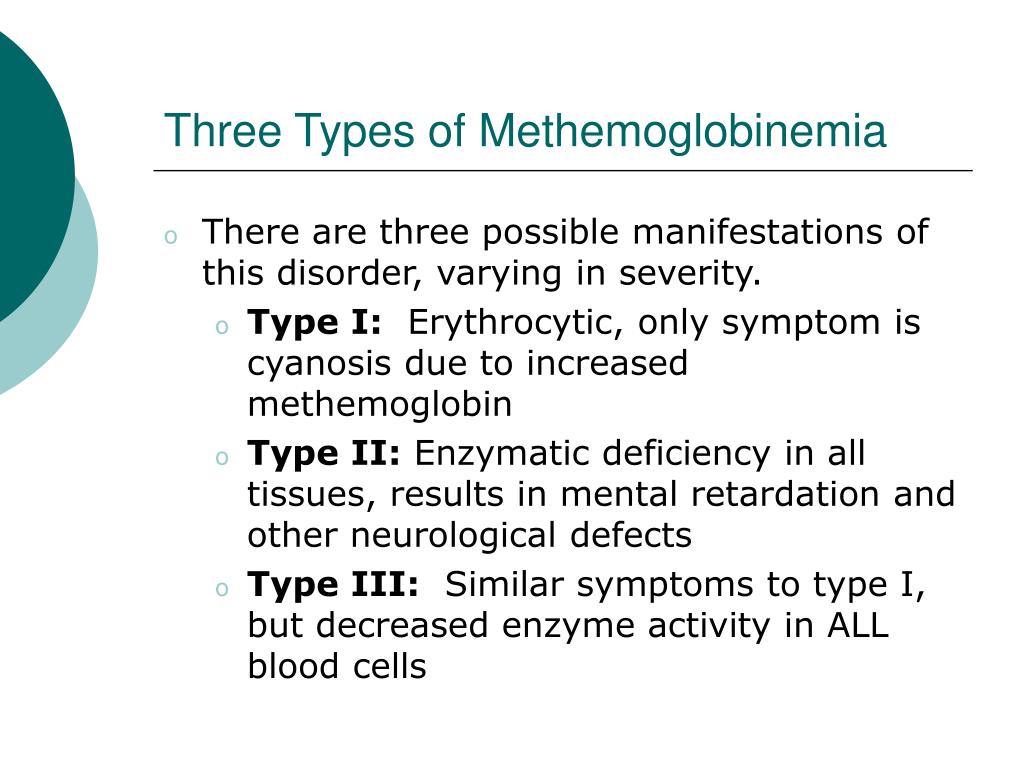
Symptoms of type 1 MetHb include: Bluish coloring of the skin (called cyanosis) Symptoms of type 2 . After initial signs and symptoms of methemoglobinemia have been addressed, routine gastrointestinal and skin decontamination should be performed as indicated.People with congenital methemoglobinemia are born with high levels of MetHb in their bodies and may or may not manifest signs and symptoms. Methylene blue is the treatment of choice for severe acute methemoglobinemia; hyperbaric oxygen or exchange transfusions are also acceptable treatment options if . Methemoglobin is produced by the oxidation of ferrous iron in hemoglobin into ferric iron.Moreover, in recent epidemiological investigations, dietary nitrate showed no association with gastric cancer or esophageal cancer in humans [7, 57]. Diagnostic différentiel. Enzyme Inhibitors. In people with autosomal recessive congenital . The diagnosis of methemoglobinemia should be considered in patients presenting with cyanosis and . Dapsone (used in pneumocystis infection), Chloroquine. chocolate-brown colored blood. The following describes the symptom(s) associated with this disease along with the corresponding body system(s), .
Methemoglobinemia: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Methemoglobinemia, beta-globin type is a condition that affects the function of red blood cells.
Methemoglobinemia Symptoms, Doctors, Treatments, Advances
If the clinician chooses to use ascorbic acid in treating acquired .
Methemoglobinemia: What You Should Know
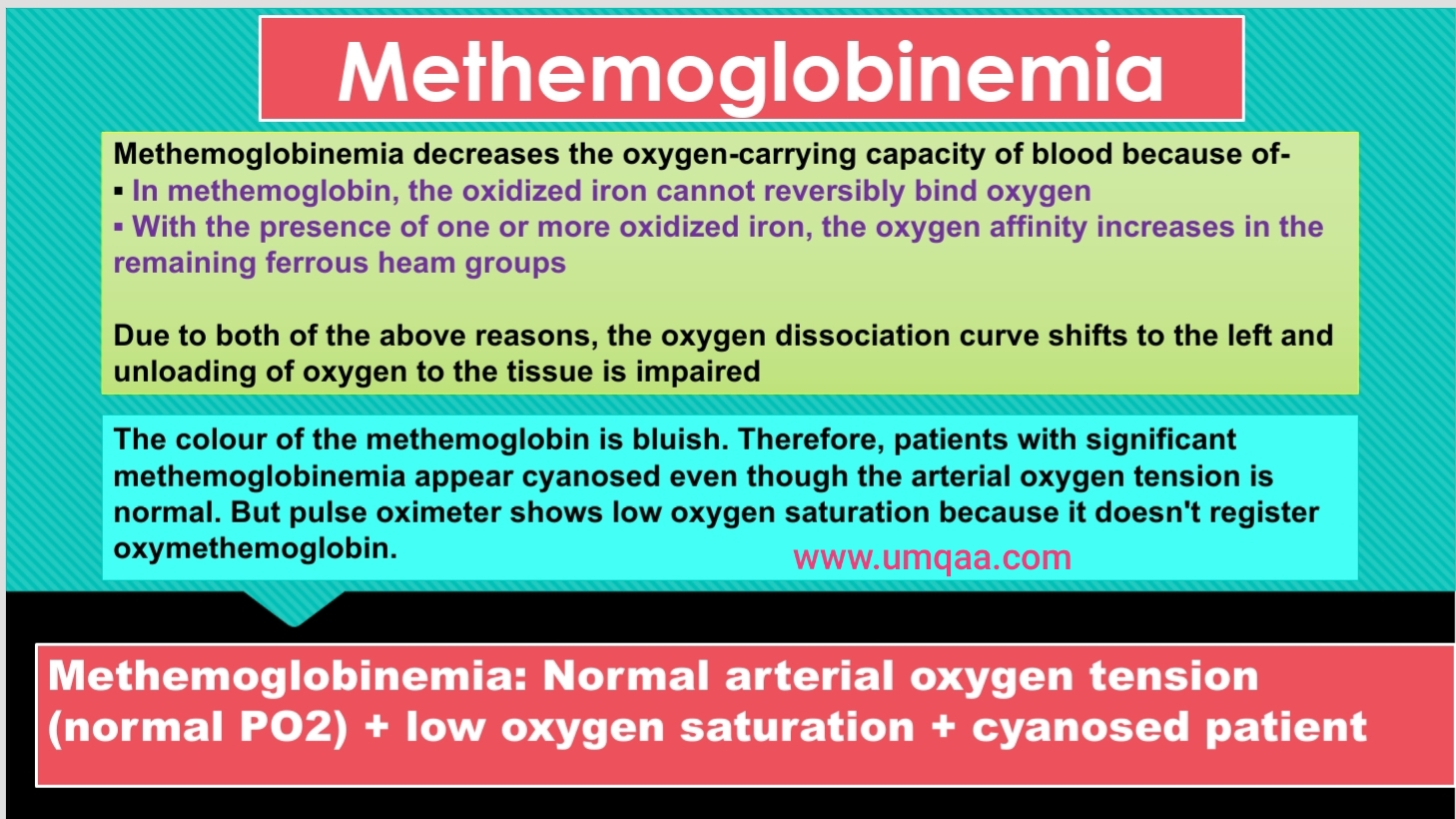
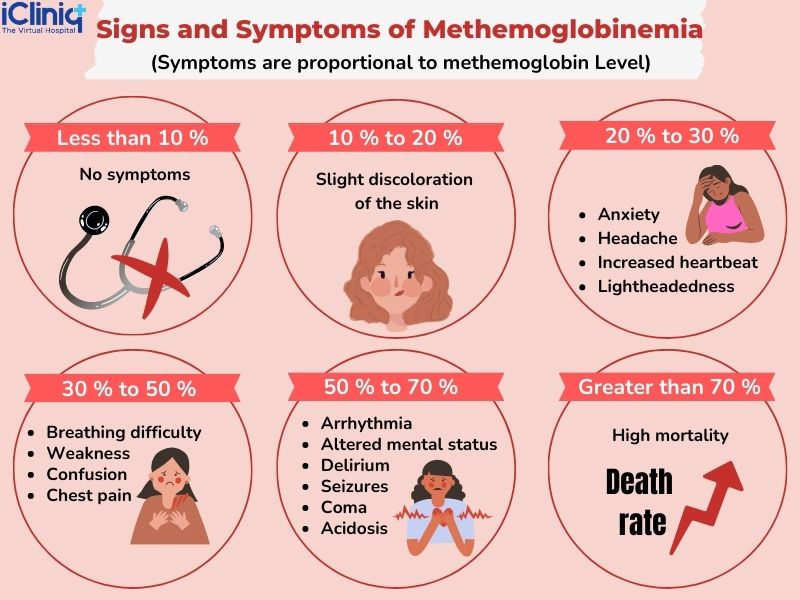
The physiologic level of methemoglobin in the blood is 0% to 2%.
chest pain, dyspnea, altered metal state, end organ damage.
Nitrate and Methemoglobinemia
MeHb levels ranging from 10.
What is Methemoglobinemia?
Methemoglobin cannot transport oxygen.These concentrations of N-acetylcysteine cannot be achieved safely in humans, however, . Levels above 70% may cause death. Methemoglobin levels less than 20% are usually asymptomatic unless underlying cardiopulmonary diseases are present, although subtle cyanosis may be preset. Specifically, it alters a molecule called hemoglobin within these cells.Methemoglobinemia occurs when the rate of methemoglobin production exceeds endogenous reduction capacity. 1 This reaction impairs the ability of .Methemoglobinemia is a potentially life-threatening health condition in which the oxygen-carrying capacity of circulating hemoglobin is significantly reduced.Once methemoglobinemia is diagnosed, treatment will be based on the severity of symptoms primarily rather than on the numerical value of methemoglobinemia. Despite that patient being very unstable, she was successfully managed with 100% oxygen through High flow nasal cannula (HFNC), methylene blue and blood transfusion.symptoms after fewer than two days, and other infants were fed formula prepared with well water for up to 60 days before symptoms appeared. Sodium nitrite causes increased methemoglobin, resulting in systemic hypoxia, metabolic acidosis, and cyanosis.

Methylene Blue.
Manquant :
humans Zopiclone 48,49.Date de publication : 24 janv. External References.CLINICAL FEATURES.Genotype–phenotype correlations of humans and dogs with hereditary methemoglobinemia are not yet well characterized.As, the presenting symptoms are often generic and akin to many other common cardiopulmonary diseases, it can be easily missed if suspicion for methemoglobinemia is low.The most common medication associated with acquired methemoglobinemia are : Local anesthetics (Lidocaine, Prilocaine, Benzocaine). Hemoglobin within red blood cells attaches (binds) to oxygen molecules in the lungs, which it carries through the bloodstream, then releases in tissues throughout the body .Consult your health care team for more information. Normally, it constitutes less than 2% of circulating hemoglobin.The SpO2 of 85% was our clue to suspect methemoglobinemia which was confirmed along with carboxyhemoglobinemia on arterial blood gas saving result.Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms? Memory Anchors and Partner Content.8% have been reported in patients following large overdoses of zopiclone. Aniline dyes, Metoclopramide, chlorates, bromates. There are two kinds of.The severity of the symptoms of methemoglobinemia is related to the quantity of methemoglobin present in the circulation and range from a bluish discoloration of the . It’s because of cyanosis that some .Larger doses may paradoxically induce methemoglobinemia.Methemoglobinemia is a disorder characterized by elevated levels of methemoglobin in the blood, which leads to tissue hypoxia. We determined total hemoglobin and methemoglobin (MetHb) concentrations . The mainstay of treatment is discontinuation of the offending agent, which is sufficient for many patients with mild methemoglobinemia.Blue baby syndrome is a condition characterized by a change in skin colour in babies. Normally, blood is pumped from the heart to the . Autosomal recessive congenital methemoglobinemia is an inherited condition that mainly affects the function of red blood cells.Hereditary methemoglobinemia
Normally, our red blood cells are loaded with millions of copies of a protein called . Acetaminophen is a common over the counter painkiller and its one of the common poisonings encountered in an emergency. MeHb = methemoglobin or methemoglobinemia.OCCULT METHEMOGLOBINEMIA due to local anesthetic toxicity potentially is fatal. This topic discusses the pathogenesis, causes, .
There are two forms of methemoglobinemia—congenital and acquired.La cyanose cutanéo-muqueuse (coloration bleutée de la peau et des muqueuses) constitue le symptôme dominant.

At methemoglobin levels of 30-50%, there may be tachypnea, confusion, and loss of consciousness. 15 , 16 It is an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase and guanylate cyclase. Methemoglobinemia is a medical condition in which much of your hemoglobin can’t transport oxygen normally because it is in the form of . We hereby review the . This activity reviews the indications, action, adverse effects, and contraindications for methylene blue as a valuable agent in the therapy of methemoglobinemia, . Failure to thrive. SpO2 reading 85-90% .
Since sodium nitrite is a preservative, the ingestion of foods containing an excessive . According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer, naphthalene is possibly carcinogenic to humans , as there is inadequate evidence in humans for the carcinogenicity of . Congenital methemoglobinemia usually becomes apparent shortly after birth and produces few . 17 This chemical causes a reduction of methemoglobin to functional hemoglobin, allowing oxygen delivery to tissues.Publiée : 2022/08/29
Méthémoglobinémie : définition, causes et traitements
Ascorbic acid is used to treat methemoglobinemia, a symptom of naphthalene poisoning and is used when methylene blue is not available, .Symptoms of methemoglobinemia largely depend on the severity of poisoning and ultimately stem from a lack of effective oxygen delivery throughout the body. A series of questions regarding the key signs and symptoms, the methods for diagnosis, the clinical management in neonatal/childhood/adulthood period, and the therapeutic approach of methemoglobinemia were formulated and the relative recommendations were produced.Methemoglobinemia may be acute or chronic. 2024Temps de Lecture Estimé: 7 minThe main symptoms are: cyanosis, which describes a bluish color of the skin, especially the lips and fingers. Our patient demonstrated . Symptoms of cyanide exposure typically appear within a few seconds to several minutes after exposure, and may include weakness, nausea, headache, and difficulty breathing .Methemoglobinemia refers to the oxidation of ferrous iron (Fe ++) to ferric iron (Fe +++) within the hemoglobin molecule. Qu'est-ce que c'est ? Dans l'hémoglobine, le fer sur lequel se fixe . Methemoglobinemia.Symptoms may occur at lower concentrations in anemic patients or those with cardiovascular, pulmonary, or central nervous system compromise.Symptoms of type 1 MetHb include: Bluish coloring of the skin (called cyanosis) Symptoms of type 2 MetHb include: Developmental delay. Methemoglobinemia is a blood disorder that occurs when too little oxygen is delivered to the cells of the body. It is suspected that many milder cases were resolved by changing the source of the infant’s water and were never reported. The baby takes on a bluish hue because of poorly oxygenated blood. In a hospital, this will be interpreted as “refractory hypoxemia” (saturation in 80s despite 100% FiO2). Patients will be treated with high-dose supplemental oxygen and the ICU may be consulted. Approaching 50%, the . This severe syndrome of inadequate tissue oxygenation is potentially fatal; prompt clinical recognition and .
Acquired Methemoglobinemia
Exchange transfusion for symptomatic methemoglobinemia in patient with G6PD deficiency; Hyperbaric O2 when methylene blue ineffective or contraindicated; IV hydration and bicarbonate for metabolic acidosis; Disposition.Methemoglobinemia should always be considered when a patient presents symptoms of cyanosis without demonstrable respiratory or cardiac disease.
Managing Methemoglobinemia EMRA
This topic discusses the pathogenesis, causes, epidemiology, clinical .Infants with sepsis may present with symptoms similar to methemoglobinemia, but usually respond to supplemental oxygen; although the patient with diarrhea, acidosis, and methemoglobinemia may also be septic.The severity of the symptoms of methemoglobinemia is related to the quantity of methemoglobin present in the circulation and range from a bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes . Unstable patients with a presentation highly suspicious for methemoglobinemia should receive methylene blue empirically. All patients (especially infants and young children) with significant . The patient's signs and .Les signes de la maladie.Overview
Methemoglobinemia
Methemoglobinemia
Specifically, it alters a molecule within these cells called hemoglobin. The Food and Drug Administration has documented 319 cases of . The second form of inherited MetHb is called hemoglobin M disease.Background: Over the years, forensic pathology has registered the spread of new methods of suicide, such as the ingestion of sodium nitrite. It is due to heart, lung, or blood abnormalities.Methemoglobinemia typically causes the pulse oximeter to report a saturation of ~82-86% (even if the PaO2 is very high). Excessive nitrates can cause acquired methemoglobinemia in young infants. Nitrobenzene (additives to prevent the meat from getting spoiled).

symptoms and signs of decreased oxygen delivery e.Acquired methemoglobinemia can be severe or even fatal, depending on the proportion of methemoglobin.Nitrates are chemicals that occur naturally in drinking water and also result from human activities.
Manquant :
humansMethemoglobinemia
Discuss with toxicologist/poison control; See Also












