Michael reaction mechanism
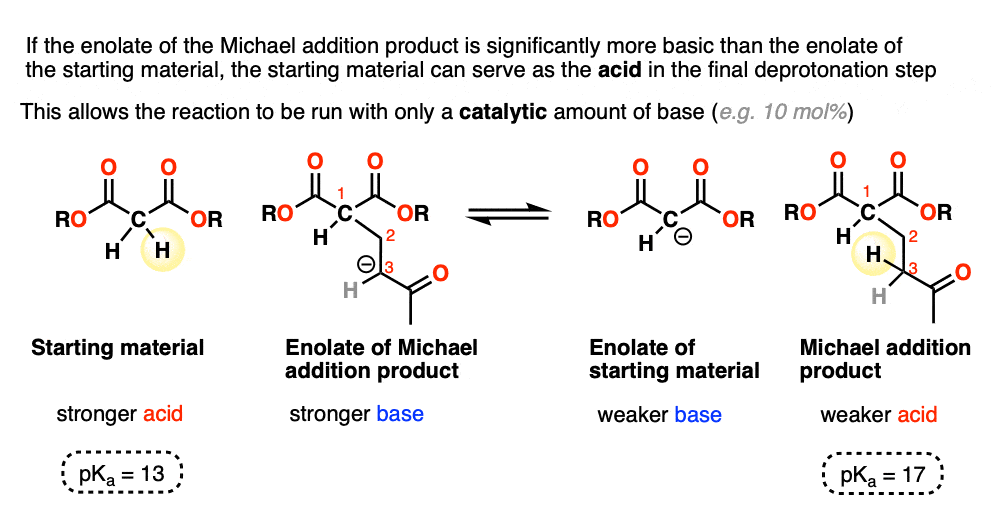
It is thermodynamically controlled by methylene donors and nitroalkane or . 1) Formation of the enamine.We suggest a novel way to condense electrophilic Fukui functions at specific atoms in terms of the . A base donates an electron to a hydrogen on the Michael donor (an electrophile). Acyl and cyano groups act as very good nucleophiles because of their non-bonding electrons which are high in energy and are therefore ready to donate. Michael Addition Reaction. Sign up here for about 30 cents/ day! He received the Nobel prize in chemistry in 1947. It is useful for .In most industrial chemical reactions, catalysts combine with the starting materials and accompany them through intermediate stages to the product.write a detailed mechanism for a given typical Michael reaction.The mechanism for the nucleophilic addition step of the Michael reaction between methanethiol as a model Michael donor and several α-substituted methyl acrylates (X=F, Cl, Me, H, CN, NO 2) as model Michael acceptors is described in detail. Activation requires that the alkene be conjugated with a double or triple bond attached to an electronegative atom. It also includes an example of the research of Michael addition in recent years. An electron pair moves from the C-H bond to the .For clarity, Michael-type addition differs from Michael addition, where the nucleophile is a (stabilized) carbanion, and from thiol-ene reactions, where thiols add . L'addition de Michael ou réaction de Michael est une réaction qui permet la création de liaisons carbone-carbone, voire de liaisons carbone-soufre. Look out for tautomerization!Watch the whole Organic Chemistry playlist: http://bit.Named after Robert Robinson, a British chemist and 1947 Nobel Prize winner, the Robinson annulation is a two-step process that combines a Michael reaction with an . 3) Tautomerization.Michael reaction mechanism completes in the following steps: Step 1: The base abstracts alpha-acidic hydrogen from the nucleophile to form carbanion which .Temps de Lecture Estimé: 4 minMechanism of the Michael reaction between a β-keto ester and an α,β-unsaturated ketone. 10 First, the thiol is deprotonated to generate the reactive thiolate anion.
The enolate anion then reacts in a .

Remember that during annulations five and six membered rings are preferred. Addition of halogens to conjugated dienes.Mechanism of the Stork Reaction. An enamine or an enolate ion from a β-keto ester or β-diketone effects a conjugate addition to an α,β-unsaturated ketone, yielding a 1,5-diketone. Mechanism for 1,4 . Step 1: First, an acid-base reaction. identify the reagents necessary to synthesize a . The first step is the .The reaction mechanism (or reaction path) provides details regarding the precise, step-by-step process by which a reaction occurs. Be sure you can draw the curved-arrow mechanism of this transformation! Scheme 1.Michael additions are C C bond formation reactions in which nucleophilic addition of a carbanion or another nucleophile to an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound containing an electron withdrawing group occurs. 有時也稱為1,4-加成、共軛加成。. reaction mechanism, in chemical reactions, the detailed processes by which chemical substances are transformed into other substances.Chad provides a comprehensive lesson on Michael Reactions which involve conjugate or 1,4-addition to a conjugated ketone.23 Write a detailed mechanism for a given typical Michael reaction. This is called the Michael reaction.Michael Addition Reaction With Mechanism. Distinguish between kinetic and potential energy, and between exergonic and endergonic chemical reactions. 2) Nucleophilic attack on the carbon β to the carbonyl. Reagents : commonly bases such as NaOH or KOH.The mechanism for the Michael reaction is 1) deprotonation to form an enolate, 2) conjugate addition of the enolate to the alkene, and 3) protonation of the resulting (new) enolate.Michael reactions take place by addition of a nucleophilic enolate ion donor to the β carbon of an α, β -unsaturated carbonyl acceptor, according to the mechanism shown in Figure .Mechanism of Michael reaction.In 1,4 conjugate addition, the nucleophile reacts with the carbon β to the carbonyl driving the formation of an enolate ion that tautermerizes back to the carbonyl upon .The Michael Addition is the 1,4-addition of resonance-stabilized carbanions to olefins or α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. * Initially a resonance stabilized enolate ion (nucleophile) is produced from Michael donor in presence of a strong base.👉🏻All name reactions - https://youtu.L'équation-bilan de l'addition de Michael est: où les substituants R et R' sur le nucléophile (un donneur de Michael) sont des groupes électroattracteurs, comme des .But as we saw in Section 23. Il s'agit de l' addition nucléophile d'un carbanion sur un composé carbonylé α,β-insaturé ( aldéhyde, cétone et même ester α,β-insaturé, des nitriles et des .The general mechanism for Michael addition is shown below: Step 1: Formation of the enolate intermediate.The first step in our sequence is the sodium-hydroxide-catalyzed conjugate addition of ethyl acetoacetate to trans -chalcone (a Michael addition reaction). The nucleophilic enolate donor is typically an enolate ion or enamine of a cyclic ketone, β-keto ester or β-diketone.Conjugate additions (1,4-additions or Michael additions) The key to these reactions is activation of the alkene.

employed a recyclable acidic IL catalyst 1-n-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hydrogen sulfate [hMIM][HSO 4] (Fig. The mechanism is a mixture of an alpha . Please draw a curved arrow mechanism to explain how the products are formed.Addition de Michael. a) b) c) 2) The beta-keto ester product of a claisen condensation can under hydrolysis with Sodium Hydroxide as shown in the reaction below. The reaction is a conjugate addition of an enolate ion to the unsaturated .The first step of the Robinson annulation is simply a Michael reaction. This page is available to MOC Members only.
Michael reaction:Mechanism and application
The Michael Addition reaction Reaction type : Conjugate addition.

Michael Addition Reaction Mechanism
Addition de Michael — Wikipédia
Michael Addition - Organic Chemistryorganic-chemistry. The acetoacetate is first deprotonated by the base, providing an enolate anion (Michael donor) in equilibrium Fig. 2) Proton Transfer. 在 逆合成分析 中屬於親核試劑對a3合成 . Please draw the products if the following molecules were to undergo a Claisen condensation.Chemical Reactions | Anatomy and Physiology I.This video provides the mechanism of the michael addition reaction with plenty of examples and problems.

Michael Reaction Mechanism
After formation, the enamine adds to the electrophilic alkene carbon of the a α, β-unsaturated carbonyl form an iminium bond. Hydroxide functions as a base and removes the acidic α-hydrogen giving the reactive enolate.麥可加成 (Michael reaction、Michael addition),最有價值的 有機合成 反應之一,是構築碳-碳鍵的最常用方法之一。. Once activated a range of nucleophiles will add. During a Michael reaction the enolate acts as a nucleophilic donor and the α, β-unsaturated carbonyl acts as the electrophilic acceptor. The reactions .L'addition de Michael est une réaction très important, elle se fait entre une cétone conjuguée (α,β - insaturé), et une forme énol obtenue par EtONa par exemple. 151,152 Gu et al.
1,4-addition of enolates to enones (“The Michael Reaction”)
Michael addition is a nucleophilic addition reaction involving the addition of a carbanion or a nucleophile to an 𝛼,𝛽-unsaturated carbonyl compound.
Addition de Michael — Wikipédia
orgExplain the mechanism of the Michael reaction? | Socraticsocratic. The nucleophile or base which donates their electron to the proton is called Michael donor. The pi electrons of the alkene are pushed onto the oxygen through conjugation to form an alkoxide .Michael Addition Reaction Mechanism. Chapter 4: Chemical Kinetics.This paper analyzes the mechanisms and the theories of some common Michael addition reactions.
Reaction mechanism
Michael Addition Mechanism.
Manquant :
michael reaction Distinguish net . 2 Second, nucleophilic addition to the Michael acceptor gives an .26 Write a detailed mechanism for each of the three steps of the Stork enamine reaction.The Michael Addition Reaction and Conjugate Addition
A conjugated ketone is referred to. Michael addition of aldehyde or ketone enolates.5: Reaction Mechanisms. Expand/collapse global location.
Michael Addition
The nucleophile bonds to the carbon in the one position and the hydrogen adds to the oxygen in the four position.More enolate stuff with the Michael Addition. The second step is a base-catalyzed aldol condensation reaction.be/kTqAkrIeHGc This video comprise of a detailed and easy explanation of the Michael addition reaction along with appl.Basic reaction of 1,4 addition In 1,4 addition the Nucleophile is added to the carbon β to the carbonyl while the hydrogen is added to the carbon α to the carbonyl.Mechanism for 1,4 addition. For the mechanism of this type of process, look at the Michael addition of a simple enolate. Here we can see why this addition is called 1,4.

Skills to Develop. 是親核試劑對α,β-不飽和羰基化合物發生的β位碳原子發生的加成反應。. Michael reactions are conjugate-addition reactions of doubly stabilized enolates such as malonic .1 General mechanistic scenarios It is generally accepted that a base-catalyzed thiol Michael addition involves three key processes (Figure 1b ).25 Identify the reagents necessary to synthesize a given compound by a Michael reaction.3 likely reaction mechanisms: step-by-step analysis 3.A conjugate addition with a carbanion as the nucleophile is known as the Michael reaction or Michael addition.
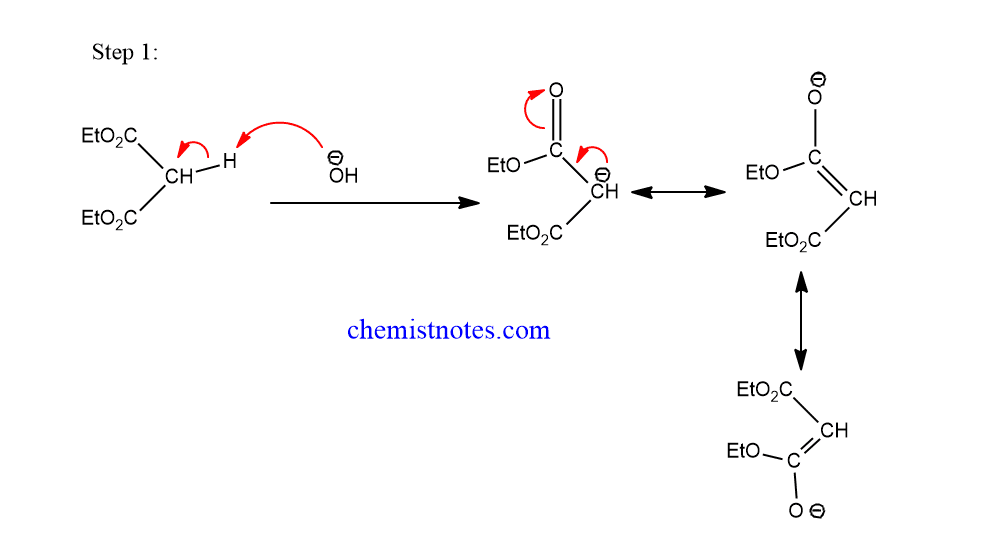
The decomposition of ozone, for example, .MECHANISM OF THE MICHAEL ADDITION. * The Michael reaction is the conjugate 1,4-addition of a resonance stabilized carbanion (michael donor) to an activated α,β-unsaturated compound .6, 1,5-diketones undergo intramolecular aldol condensation to yield cyclohexenones when treated with base.Ch18: Michael reaction. The hydrogen attached to the substrate, methane is acidic . The reaction begins with forming the enolate intermediate by deprotonating the alpha-carbon of .







