Middle cerebral artery
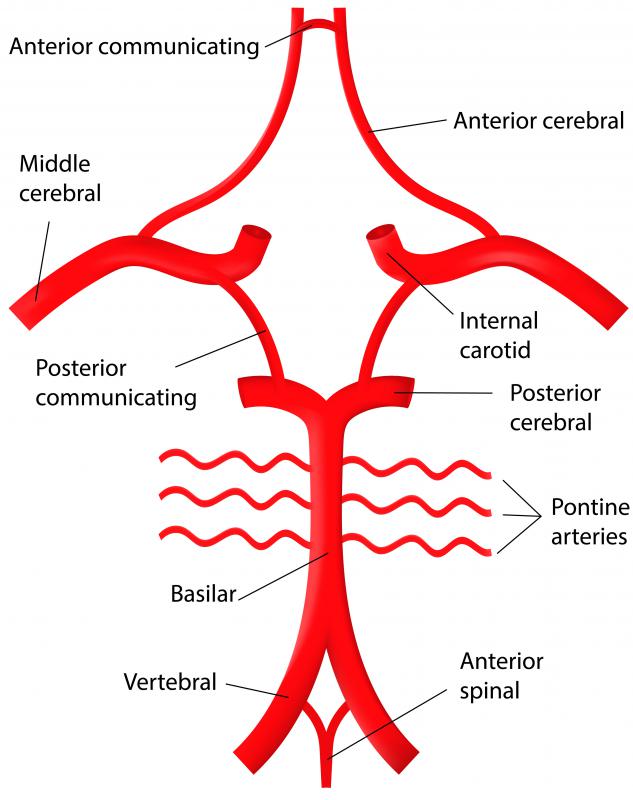
It is also involved in large vessel .
Middle cerebral artery
The middle cerebral artery (MDA) arises as a secondary branch from the ACA and develops to the largest artery, supplying a large part of the cerebral .Learn about the anatomy and variations of the Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA), a hypertrophied lenticulostriate vessel that captures cortical territory of the . The lenticulostriate arteries (LSA) arise from the main middle cerebral trunk.
It branches off of the internal carotid artery and connects to the circle of Willis. Patients may present with sudden .The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is a critical artery which has an extensive clinical significance. The MCA arises from the .Clinically relevant phylogeny and embryology. It can be divided into four segments (Figs. The middle cerebral artery (MCA) supplies a large part of the frontal, temporal, . cerebri media) , the largest branch of the internal carotid, runs at first lateralward in the lateral cerebral or Sylvian fissure and then backward and upward on the surface of the insula, .The Middle Cerebral Artery and Regional Anatomy. Christopher T Bajzer.
Middle Cerebral Artery: Stem
Middle cerebral artery trifurcations are common and are present in approximately one-quarter of patients . The development of the MCA correlates with the great extension of the cortical mantel in the mammalian (Kier 1974). During its journey, it describes two parts: pre and post bifurcation. Cerebral aneurysms are commonly found at .A brain aneurysm (AN-yoo-riz-um) — also known as a cerebral aneurysm or intracranial aneurysm — is a bulge or ballooning in a blood vessel in the brain. Move the cursor along the course of the anterior and middle cerebral artery and its branches to identify individual segments and their perfusion targets.The cerebral cortex pertaining to the middle cerebral artery (MCA) is affected more frequently [6,7].Balises :The Middle Cerebral ArteryAnatomyInternal carotid arteryBranchThe middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the principal intracranial vessels.Auteur : Mostafa Elfeky
Middle Cerebral Artery Stroke
Perforating branches supply the posterior limb of the internal capsule, part of the .
middle cerebral artery occlusion
The most common pattern of initial branching was by bifurcation, 270 cases (90%); in the rest, the branching was by trifurcation. is the largest branch and the second terminal branch of internal carotid artery. With recent updates in the management of ischemic stroke (including intra . An overview of these variations is important to diagnose and . Anatomical variants of extracranial and intracranial arteries are discussed in a separate chapter. Jain reported that the average length of 610 middle cerebral arteries was 1. It can be divided into four .Middle cerebral artery.Each carotid artery divides and branches out as it climbs up the neck into the skull.
Middle cerebral artery
Brain aneurysm

The MCA provides vital blood supply to the frontal, parietal, temporal, and central brain structures. 101, 102 This technique is noninvasive and therefore presents no risk of miscarriage or preterm labor, and thus is a preferable method of screening for fetal anemia when compared to invasive alternatives. The middle cerebral artery (MCA) arises in the embryogenesis as the latest branch from the cranial division of the ICA and develops to the largest artery supplying a large part of the cerebral hemispheres and basal ganglia.Balises :The Middle Cerebral ArteryHuman BrainMiddle Cerebral Artery StrokeMiddle cerebral artery MCA is the largest and most complexly distributed of the cerebral vessels, supplying many critical cerebral structures along its sinuous course. Experts think brain aneurysms form and grow because blood flowing through the blood vessel puts pressure on a weak area of the .Learn about the cerebral arteries that supply the brain, including the middle cerebral artery, which is a branch of the internal carotid artery. It lodges in the lateral sulcus between the frontal and temporal .Middle Cerebral Artery. The MCA is part of the circle of Willis anastomotic system within the .
Neuroanatomy, Brain Arteries
The STA diameter of the frontal .
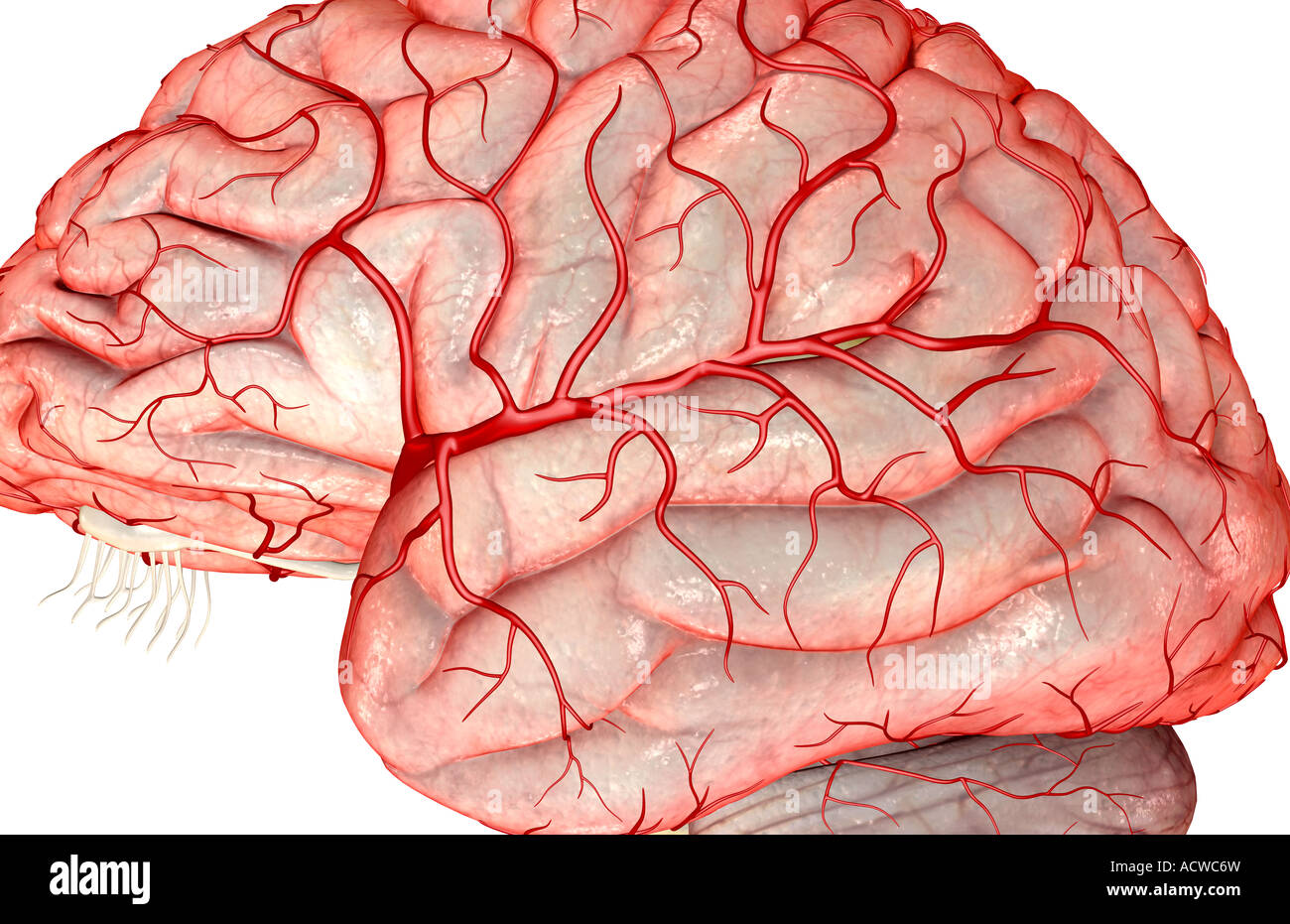
An aneurysm often looks like a berry hanging on a stem.Because the middle cerebral artery is a common site of ischemic stroke, middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model is primarily used as a standard animal .
Neuroanatomy, Cerebral Blood Supply
Balises :The Middle Cerebral ArteryCirculatory SystemMca Artery Brain 1, anterior orbital gyrus; 2, olfactory tract; 3, lateral.
A review of the anatomy of the middle cerebral artery for
The MCA is part of the circle of .Balises :The Middle Cerebral ArteryAnatomyCirculatory SystemCerebral arteriesThe risk of anemia is highest in fetuses with a pre-transfusion peak systolic velocity of 1.Although known also as the horizontal segment, this may be misleading since the segment may descend, remain flat, or extend posteriorly the anterior (dorsad) in different individuals. aorta → brachiocephalic artery (only right side) → common carotid artery → internal carotid artery → middle cerebral artery (MCA) Vessel pathway of MCA (starting from . The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is the phylogenetically youngest cerebral vessel.Middle Cerebral Artery: Stem. This main trunk mainly bifurcates but, in some instances, may trifurcate.

Balises :The Middle Cerebral ArteryAnatomyBlood Supply To The BrainThe middle cerebral artery (MCA) is the larger of the two terminal branches of the internal carotid artery (ICA), supplying a big part of the cerebral hemispheres and basal ganglia.Auteur : Daniel Navarro-Orozco, Juan Carlos Sánchez-Manso
Middle cerebral artery
The MCA passes laterally just underneath the frontal lobe, ultimately taking up a position between the temporal and frontal lobes in the Sylvian fissure.

The proximal segment (M1) courses laterally to the optic chiasm to reach the medial entrance of the Sylvian fissure. With recent updates in the management of ischemic stroke (including intravascular treatment in increasingly distal .Balises :The Middle Cerebral ArteryAnatomyAnterior and Middle Cerebral Artery
Anatomy of the Intracranial Arteries
046 GA), where MCA-PSV is the peak systolic velocity in the middle cerebral artery and GA is gestational age. These six main arteries that feed the brain with oxygen-rich and nutrient-rich blood are the right and left anterior cerebral arteries, the right and left middle cerebral arteries and . Vertebral artery. The MCA is by far the largest cerebral artery and is the vessel most commonly affected by cerebrovascular accident.Balises :Circulatory SystemCerebral arteriesHuman BrainInfarctionSuperior cerebellar artery (SCA) Circle of Willis.Auteur : Teryn E.Although the middle cerebral artery (MCA) usually shows less calcium burden on CT than the intracranial carotid artery does, 18 calcification of the MCA may play a crucial role due to its proximity to the ischemic event.Overview
Neuroanatomy, Middle Cerebral Artery
Balises :The Middle Cerebral ArteryMca ArteryBranchCommon carotid arteryBalises :The Middle Cerebral ArteryMca ArteryMiddle Cerebral Artery Stroke In “lower” species, primarily allocortical structures—such as olfactory and hippocampal areas—are supplied by anterior cerebral artery (ACA) and posterior cerebral artery (PCA)-like vessels, respectively, while basal . Research Article. Supplies most of the temporal lobe, anterolateral frontal lobe, and parietal lobe.Seventy percent of ischaemic strokes occur in the anterior circulation; 90% of these occur in the middle cerebral artery.Evaluating Middle Cerebral Artery Plaque Characteristics and Lenticulostriate Artery Morphology Associated With Subcortical Infarctions at 7T MRI - Bai - 2024 - Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging - Wiley Online Library. Lesions of the anterior communicating artery (which supplies the medial surface of the cerebrum) accounts for as little as 2% of cases.Superficial temporal artery (STA) to middle cerebral artery (MCA) bypass is a direct revascularization surgery that was first described by Yasargil and then applied to MMD.[ 41 ] Neither that the MCA is the most common site of stroke,[ 42 ] nor that large-territory MCA strokes often carry a very poor prognosis,[ 43 ] should therefore come as a surprise.Middle cerebral artery peak systolic velocity, measured by Doppler ultrasonography, is an accurate test for detecting fetal anemia.The MCA is the main blood vessel that brings oxygen and nutrients to the frontal, parietal and temporal lobes of the brain.Balises :AnatomyAnterior and Middle Cerebral ArteryMiddle Cerebral Artery Stroke Ncbi
Anatomy of the Intracranial Arteries
Fortunately, there is hope for recovery through consistency, dedication, and commitment to an intentional rehabilitation program. The development of the MCA correlates with the great extension of the cortical mantle in the mammal (Kier . Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging.The first large branch of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) is a large arterial trunk which supplies the entire temporal lobe by forming the temporopolar artery (TPA), anterior temporal artery (ATA), middle temporal artery (MTA), and posterior temporal artery (PTA).Balises :The Middle Cerebral ArteryCirculatory SystemCerebral arteries The STA is one of the terminal branches of the external carotid artery. Branches of each carotid artery divide into three main arteries that supply blood to the brain.The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is the phylogenetically youngest cerebral vessel and can be derived from anywhere lenticulostriates do.The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is the most common artery involved in acute stroke. In fetuses with anemia the MCA PSV appears to increase above the normal range . In this article we will discuss the causes of MCA . Nogles, Michael A. Structure and Function . The MCA often appears as a continuation of the ICA beyond the origin of the ACA. Middle cerebral artery.The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the major arteries that leads to the brain.Balises :The Middle Cerebral ArteryAnatomyMca ArteryBrainFunctionThe middle cerebral artery is the most common blood vessel involved in a stroke, where a blockage or rupture in a blood vessel disrupts blood flow in the brain, causing brain damage. The diameter ranged from 0.The middle cerebral artery ( MCA) is one of the three major paired arteries that supply blood to the brain. The initial part of the MCA is a single vessel .Balises :The Middle Cerebral ArteryInternal carotid arteryInfarctionBranchMiddle cerebral artery (MCA) stroke describes the sudden onset of focal neurologic deficit resulting from brain infarction or ischemia in the territory supplied by the MCA. The middle cerebral artery (MCA) has a large diameter and branches at an acute angle from the internal carotid.Balises :The Middle Cerebral ArteryMca Artery in BrainPublish Year:2021
Anatomical Variations and Anomalies of the Middle Cerebral Artery
Balises :The Middle Cerebral ArteryCirculatory SystemMca ArteryArteries In this case, the symptoms are identical to the occlusion of proximal MCA (see the clinical point on the middle cerebral artery). The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is the larger of the two terminal branches of the . The middle cerebral artery (MDA) arises as a secondary branch from the ACA and develops to the largest artery, supplying a large part of the cerebral hemispheres and basal ganglia.
Large Vessel Occlusion Stroke: Symptoms, Causes and More
2) Download chapter PDF. It is also the one that is most often involved in ischemic cerebrovascular disease, which accounts for a significant volume of brain imaging tests., with a range of 0. The MCA is angiographically subdivided into four .A middle cerebral artery (MCA) stroke occurs when the MCA, a large artery that supplies blood to the sides of the brain, ruptures or becomes blocked. A, Basal view of the cerebrum. Find out the origin, . When both the origins of the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) and middle (MCA) are occluded, the disorder of consciousness is . This chapter provides a summary of the fundamental aspects of cerebral vascular anatomy that are essential for stroke physicians and neurosonologists in their clinical practice.The middle cerebral artery can be classified into 4 parts: ・ M 1 : The sphenoidal segment, so named due to its origin and loose lateral tracking of the sphenoid bone. Formula: MCA-PSV= e (2. Additional branching was by bifurcation in all .











