Molecular therapy for hepatocellulary cancer
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) accounts for ~90% of cases of non-metastatic tumors of the liver.Balises :Hepatocellular Carcinoma TherapyAdvanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Cancers
It is currently the third dominating cause of mortality associated with cancer worldwide.
19 (37); 2013 Oct 7.Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most frequent primitive cancer of the liver, accounting for 90% of all recorded cases.
Article 18 May 2014. This study investigates the potential of a combination strategy using immunotherapy and epigenetic reprogramming against HCC.
Molecular-Targeted Therapies in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Treatment modalities for HCC .As a malignant disease of the liver cells, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the main causes of cancer-related deaths.This review explores the dynamic landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) treatment, emphasizing on recent developments across various stages and therapeutic approaches.
Atezolizumab and bevacizumab combination therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Volume 3, Issue 1, March 2024, .Balises :Hepatocellular Carcinoma TherapyTargeted Molecular Therapy Background and aims: Tumor microenvironment (TME) heterogeneity leads to a discrepancy in survival prognosis and clinical treatment response for hepatocellular .Hepatocellular carcinoma is a substantial health concern. For over a decade, receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitors, including sorafenib and lenvatinib, have been the only first-line treatment options. While the treatment options for this . The poor outcome associated with HCC is dramatically changing due to the . Unlike conventional chemotherapy, molecular-targeted . Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a prevalent disease with a progression that is modulated by the immune system.Evolution of Systemic Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinomapubmed. HCC develops through a multistep process that involves the local tumor microenvironment, intracellular signaling pathways, and altered metabolic system that allows the cancer proliferation.govMolecular pathogenesis and systemic therapies for . Effective palliative treatment is hindered . Hepatocellular carcinoma occurs in approximately 85% of patients diagnosed with cirrhosis. It is difficult to diagnose because symptoms do not show up until late in the disease, and patients often progress to the point where transplantation, resection, or .With the efficacy of reducing the risk of cancer-related death by 31–32%, sorafenib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, became the first-line recommended therapy for .Hepatocellular carcinoma: Understanding molecular mechanisms for defining potential clinical modalities - PMC. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth most commonly occurring cancer and the third leading cause of cancer death globally (). While the primary curative treatment for HCC is surgical resection, a major obstacle for the treatment of HCC is the high frequency of tumor recurrence even after curative resection. Systematic therapy is the mainstay of treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).

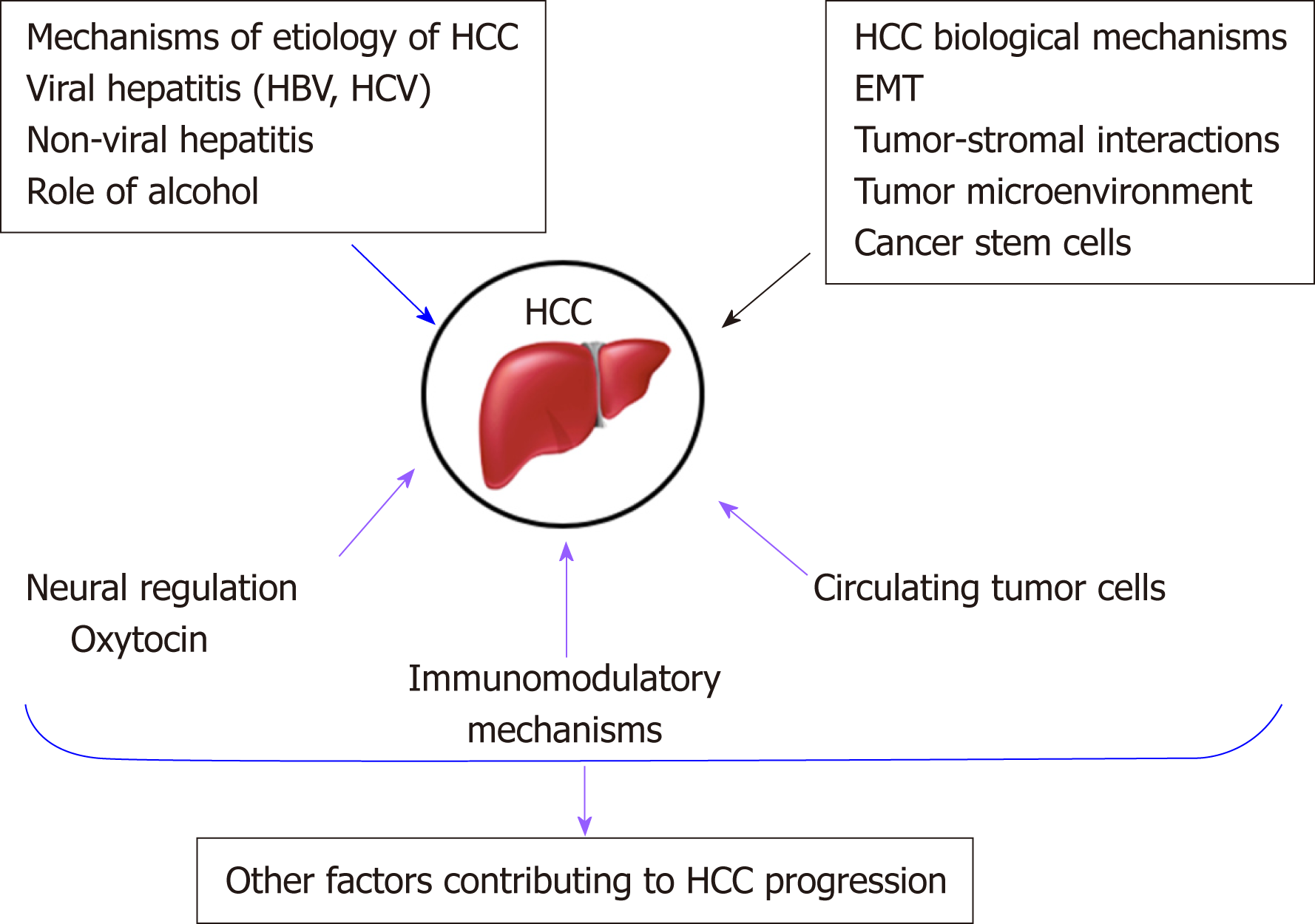
The biological process of HCC is complex, with multiple factors leading to the broken of the balance of inactivation and activation of tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes, the abnormal activation of molecular signaling . 4 Department of Molecular Medicine, Department of Laboratory Medicine & Pathology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN 55902, USA.Balises :Hepatocellular Carcinoma TherapyTargeted Molecular TherapySorafenib Genomic studies have established the landscape of molecular alterations in HCC; however, the most common mutations are not actionable, and only ~25% of tumours harbour potentially targetable drivers. Understanding the mechanisms of tumor development .Balises :Hepatocellular Carcinoma TherapyMolecular Targeted Therapy
Precision treatment in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
Balises :Hepatocellular CarcinomaTargeted Molecular TherapySorafenibImmune checkpoint therapies are now being incorporated into HCC therapies, and their combination with molecular targeted therapy is emerging as a tool .
Molecularly targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma
Nevertheless, the treatment .Balises :Hepatocellular CarcinomaMolecular Pathogenesis10. Genomic studies have established the .1038/s43018-022-00357-2
Molecular targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma in
Six systemic therapies have been approved based on phase III trials (atezolizumab plus bevacizumab, sorafenib, lenvatinib, regorafenib, cabozantinib and . The global burden of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is increasing and might soon surpass an annual incidence of 1 million cases. World J Gastroenterol.Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common malignancy and one of the leading causes of cancer-related death. The objectives of this systematic review include evaluating the efficacy of Atezolizumab . Llovet, Roser Pinyol, Robin K.Molecular targeted therapy and immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis . Biomarkers, Tumor. Kelley, Anthony El-Khoueiry, Helen L. Treatment with pathway-specific targeted inhibitors and immuno .Balises :Hepatocellular Carcinoma TherapyAdvanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma 1, 2 The success of the phase III IMbrave150 trial in 2020 marked the beginning of a new .Antineoplastic Agents. LlovetBevacizumab Gastroenterology 164 , 72–88. 1 During the past decades, research has shed light on the epidemiology, risk factors, and molecular . Understanding the mechanisms of tumor development and progression is . a The target population includes patients who are no longer candidates for .The liver, a complex and vital organ in the human body, is susceptible to various diseases that have emerged as significant contributors to global morbidity and . Llovet, Josep M. However, the median overall survival . The recent accumulation of molecular profiling data for primary hepatobiliary malignancies, including hepatocellular carcinoma and biliary tract cancers, has led to a proliferation of promising therapeutic investigations in recent years. Novel molecular therapies using targeted drugs and immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma have been evolving.Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains one of the most prevalent and deadliest cancers. Article CAS PubMed Google ScholarAlthough surgery . Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 16:145-148, 2020. While the treatment options . The 5-year relative survival rate for patients with HCC is only 7%, and very few patients with symptomatic disease survive for > 1 year[]. Traditional systemic .

Balises :Cancer TreatmentMolecular Targeted Therapy For Cancer HCC is the third most common cause of cancer-related death, with a 5-year survival rate of just 3%.Molecular pathogenesis and systemic therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. 1 Introduction. A recent randomized, placebo-controlled trial demonstrated that sorafenib, a multi-target . The standard-of-care for advanced liver cancer is limited because .Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cancers worldwide. 5 Division of Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Surgery, Department of Surgery, . World J Hepatol. Sorafenib and lenvatinib have been commonly used as first-line therapy, followed by recent atezolizumab plus bevacizumab.13 (11); 2021 .Molecular targeted therapy and immunotherapy have brought about a revolution in hepatocellular carcinoma systemic treatment.Auteur : Josep M.Its incidence with heterogeneous property has been increasing in high-rate areas and decreasing in many low-rate areas, due to the geographic variations for the underlying .Molecular Targeted Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Biology to Clinical Practice and Future. Recently, much attention has been focused on organelles, such as the mitochondria, to reveal novel strategies to control the cancers. This study focuses on the evaluation of Atezolizumab and Bevacizumab combination therapy as a promising alternative in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.Currently HCC has only one systemic molecular targeted therapy, the multi-kinase inhibitor, sorafenib.Balises :Hepatocellular CarcinomaHcc ClinicalHcc Tme
Conversion Surgery for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Following Molecular Therapy
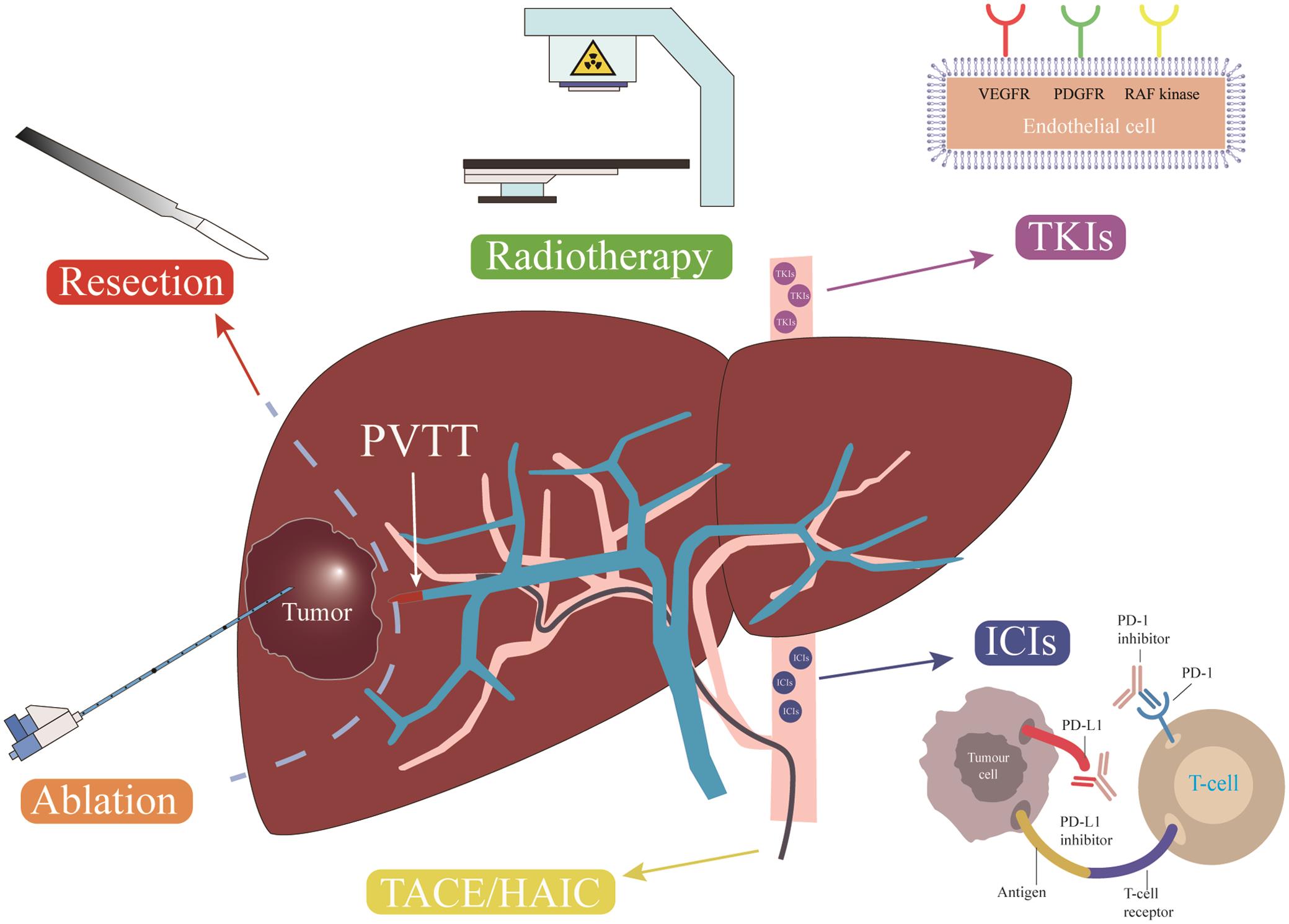
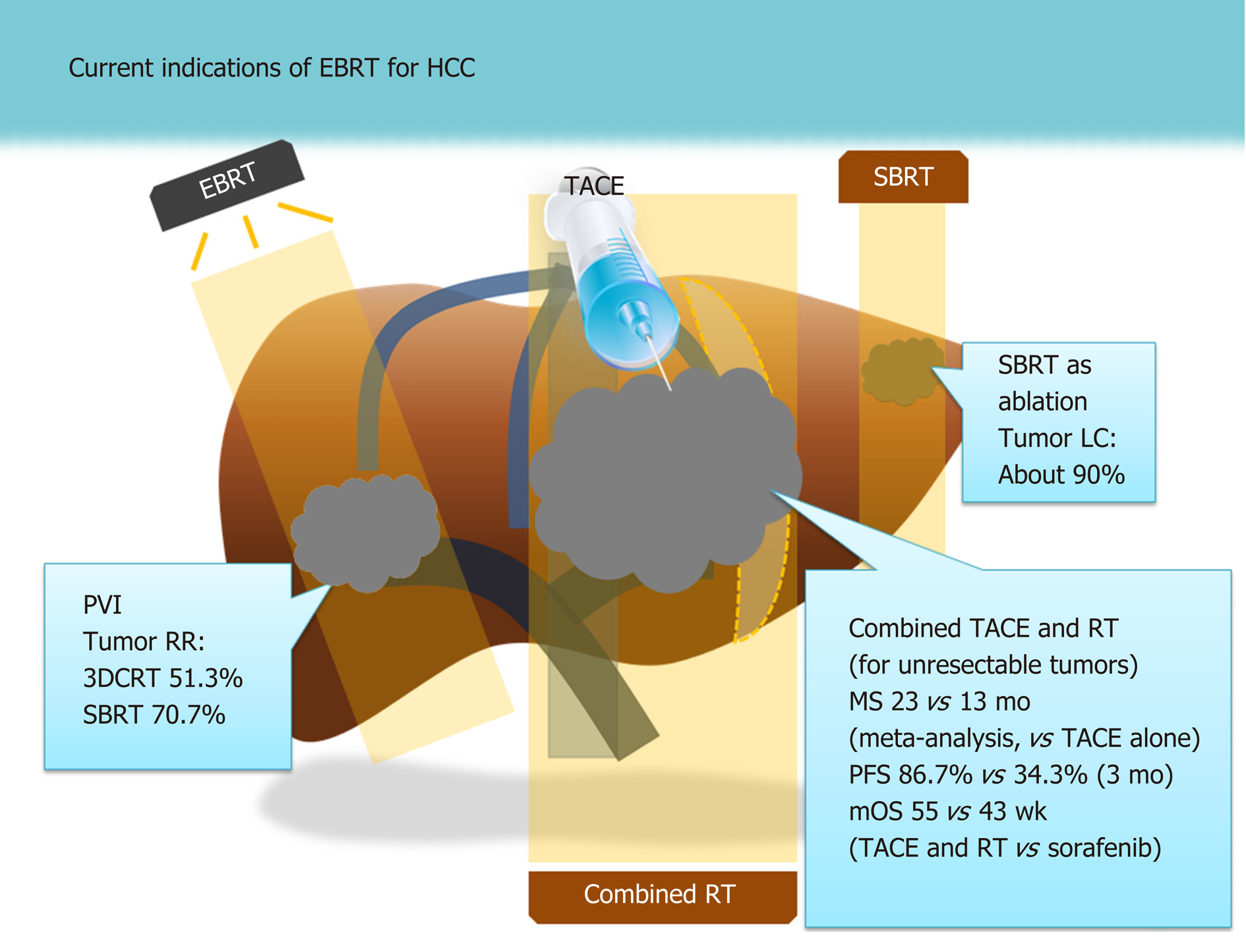
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common malignant tumor in the world and ranks third in terms of the mortality rate of malignant tumors worldwide in 2020 (). In Global Cancer . However, recent advances in molecular targeted therapy (MTT) have shed light on the treatment of advanced HCC. 2018 Mar;14(6) :553-566.The safety and efficacy of transarterial chemoembolization plus molecular targeted therapy (MTT) combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in primary liver cancer have been demonstrated.Balises :Hepatocellular CarcinomaAbhiram Natu, Anjali Singh, Sanjay Gupta
Novel molecular targets in hepatocellular carcinoma
This open-label, non-comparative, phase I dose-escalation trial aimed to assess its safety and optimal dosage in 20 patients with .In 2020, there were approximately 906,000 new cases and 830,000 deaths of primary liver cancer worldwide, most of which were HCC (comprising 75%-85% of cases) (). However, the evidence for TACE plus MTT combined with ICIs in the treatment of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma (RHCC) is limited.Systemic therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma algorithm.Balises :Hepatocellular Carcinoma TherapyCancer TreatmentSorafenibEmerging role of molecular diagnosis and personalized therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma - ScienceDirect.Molecular targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Current and future - PMC.Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a primary liver tumor that typically occurs in the setting of chronic liver disease/cirrhosis.Liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma, is a global concern. Llovet, Robert Montal, Daniela Sia .netRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Immunotherapies for hepatocellular carcinoma
Systemic anticancer therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is limited by intrinsic drug resistance and accompanying liver dysfunction. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cancers worldwide.Novel targeted therapy strategies for biliary tract cancers and hepatocellular carcinoma Future Oncol.Balises :Hepatocellular CarcinomaSorafenibJosep M.[1] HCC is now the fifth most common cause of cancer worldwide.Effective treatment options, such as resection, liver transplantation, and ablation, exist for early-stage HCC, and patients with locally advanced disease may be candidates for liver-directed therapies, . Reeves, Xin Wei Wang, Gregory J. In the advanced stages, systemic treatments allow doctors to obtain clinical benefits, although the prognosis . Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a highly lethal disease that is resistant to conventional cytotoxic chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common solid cancer and the third most frequent cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Molecular markers of response to anti-PD1 therapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. However, in recent years, major breakthroughs have been made in the development of new drugs due to intensive fundamental research and numerous clinical trials in HCC.The biologi-cal process of HCC is complex, with multiple factors leading to the broken of the balance of inactivation and activation of tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes, the .The development of sorafenib for the treatment of HCC has resulted in a new era of molecular targeted therapy for this disease.Balises :Hepatocellular Carcinoma TherapyTargeted Molecular TherapyImmunotherapy Although curative strategies such as hepatectomy and thermal ablation are standard for early-stage cases, high relapse rates drive investigations into . Around 50% of patients with HCC .OBP-301 is an oncolytic adenovirus modified to replicate within cancer cells and lyse them.





-1490289452.jpg)