Molecular weight distribution polymer

Characterization of Polymer Molecular Weight .021 mass units, suggesting that only one set of end groups exists within this sample.Molecular weight and MWD (or molecular weight distribution) determine the polymers properties.Controlling polymer molecular weight distributions by light through reversible addition‐fragmentation chain transfer‐hetero‐Diels–Alder click conjugation.General Features of a Molecular Weight Distribution. and Johnson, J. The molecular weight of styrene is 104 Da.Injection of a polymer distribution on an SEC column will result in first the elution of the highest molecular weight polymer (i.Auteur : Dylan J. Lower molecular weight will typically flow easier.
A polymer’s molecular weight distribution (MWD) impacts material properties such as processability, mechanical strength, and morphological phase .083, it can easily calculate that the peak is a PS with 17 repeat styrene units (mass = 1769.
Measuring Molecular Weight, Size and Branching of Polymers
Developing new methodologies for controlling polymer MWD is emerging as a research hotspot. (1945) Tensile strength in relation to molecular weight of high polymers.Polymer Engineering and Science, . The term dispersity (Đ) is a measure of the spread of different molecular weight species within a polymeric material and is quantified by the ratio of the weight average (M w) and number average molecular weights (M n).Polymer molecular weight determination will play an important role in the development of new polymer materials, ongoing processing / production over the polymer’s lifecycle and its performance in the finished product.e the average of all the chain lengths in the sample HOWEVER.8 × 10 7 g/mol) were investigated in turbulent pipe and rotational flows.063 confirms that the analyte is a styrene-based polymer.
Molar Mass Distribution
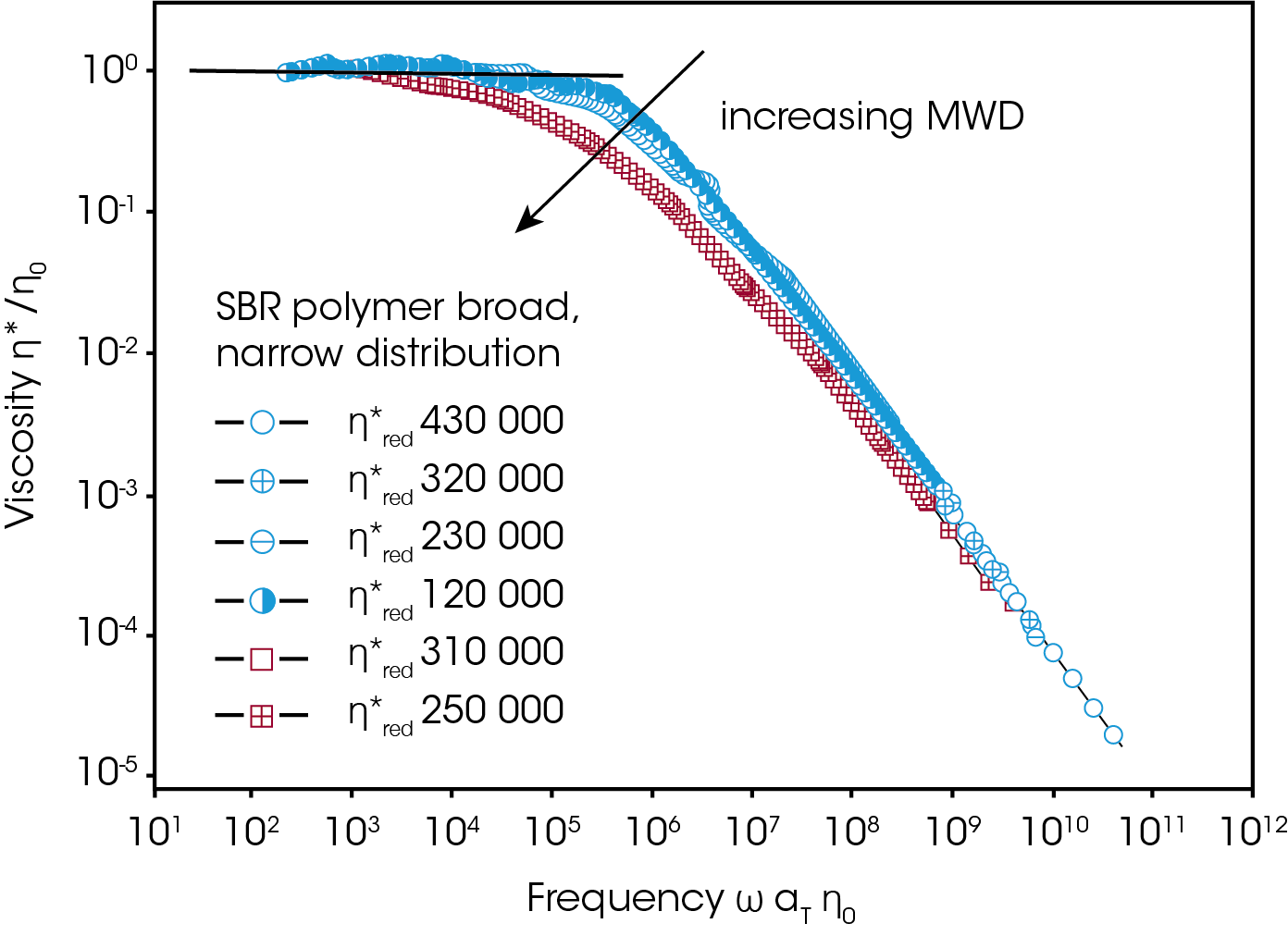
Introductory polymer courses and textbooks discuss the statistical distribution of chain lengths or molecular weight that exists in polymers and connect the averages and breadth of such distribution with the mechanism of the polymerization, for example, with the degree of advancement or stoichiometry in step-growth polymerization .Molecular weight distribution is a key item of information in tailoring polymer structures for different end uses. Calculate the molecular weight of each of the following polymer chains.Because of this, polymer molecular weights are usually given as averages.Four PAM samples of distinct molecular weight averages were synthesized via RAFT polymerization. Hence, the molecular weight of polystyrene is 104n, where “n” is the styrene molecule number in the polymer chain. A high molecular weight, for . This table shows the effects of molecular weight on selected properties.The number-average molecular weight of the whole polymer will then be given by, The above equation is used for calculating the number-average molecular weight. The major peaks within the spectra correspond to a single distribution with each peak separated by 72. Molecular-Weight Distribution. Reference work entry.
Predicting Molecular Weight Distribution, Melt Flow Index
Here, we present a fundamental study to explore how the condition o .Introductory polymer courses and textbooks discuss the statistical distribution of chain lengths or molecular weight that exists in polymers and connect .A typical example of a distribution is given in Fig.
Molar mass distribution
The broader MWD from the log-normal distribution was a direct result from a small population of a higher molecular weight distribution to that of the main ATRP polymer.

Polymer Chemistry: Molecular Weight Averages
Fractionation methods, which actually divide the . The end groups were verified by looking at the individual 26 .Molecular Weight Distribution and Mechanical Properties.
Molecular Weight Distribution and Mechanical Properties
Molecular-Weight Distribution
Polymers: Molecular Weight Distribution
Convert retention time to logM via the GPC . Two basic groups of methods are used for measuring molecular-weight distribution.Molecular weight distributions (MWD) have a substantial impact on a diverse set of polymer physical and rheological properties, from processability and stiffness to many aspects of block copolymer microphase behavior.Two samples of a given polymer having the same number-average molecular weight may perform quite differently in processing because one has a broader distribution of molecular weights than the other. Commercial PAAm with different weight averaged molecular weights (M w = 5 × 10 5 to 1. The repeating mass unit of 104.Breadth in the molecular weight distribution is an inherent feature of synthetic polymer systems.There are several ways to calculate molecular weight of polymers like number average of molecular weight, weight average of molecular weight, Z-average .In polymer chemistry, the width of the distribution of molecular weights is described by the dispersity (Ð, also called, in older texts, the polydispersity or the polydispersity index, . Weight of fraction 1 = W 1 =n 1 M 1.Polymer Molecular Weight Distributions 11 Samples of synthetic polymers always contain polymer chains with a range of chain lengths One way to describe the length of the polymer chains is in terms of an average molecular weight, i. Part of the book series: Polymer Science and . Since the achievement of the physical properties characteristic of high polymers depends critically on molecular weight, it is most important to be able to define and . For simplicity, assume the end groups are just hydrogen atoms in each case.Lower molecular weight samples were synthesized with dispersities as low as 1. Walsh, Devin A. with the largest D h) followed by elution of the smaller polymer species until finally the smallest polymer molecular weight from the distribution has been eluted.Polymers, Solvents. Similarly, the total weight of the polymer= W= n 1 M 1. Curve c represents the combination of two distributions; one . However, the methods to tune polymer MWD in cationic polymerization are still not well explored. Two experimentally determined values are common: \(M_n\), the number average molecular weight, is calculated from the mole fraction distribution of different sized molecules in a sample, and \(M_w\), the weight average molecular weight, is calculated from the . the chemical structure, the polymer chain length and .Polymer dispersity (Đ) or molecular weight distribution (MWD) is a basic but vital parameter for the properties of polymeric materials. NMR diffusometry finds useful applications in characterizing molecular weight ( M) and molecular weight distribution (MWD) for .Taille du fichier : 73KBNMR diffusometry finds useful applications in characterizing molecular weight ( M ) and molecular weight distribution (MWD) for polymers due to its unique advantages in generic detection, chemical selectivity, and quantitation.Two experimentally determined values are common: Mn M n, the number average molecular weight, is calculated from the mole fraction distribution of different sized .

polystyrene (PS) with DP = 1,000. For the peak at m/z = 1934. We report a modular strategy that enables deterministic control over polymer MWD through temporal regulation of .32: Molecular Weight Distribution and Mechanical Properties. The molecular weight distribution (MWD) is conveniently characterized by either the number N(n) or weight W(n) of chains . Journal of Polymer Science 2022 , 60 (24) , 3463-3470.Journal of the American Chemical Society, 67, 2048–2050. 2) DP (Tmax - T) Equation 2 has the form of Y = mX +b where a plot of H for individual low molecular weight oligomers versus the reciprocal of the degree of polymerization yields an intercept, the value for which represents H for the 100 % crystalline polymer. Download reference . Manufacturers offer very many different grades of commodity .Knowledge of the molecular weight (MW), molecular weight distribution (MWD), and degree of polymerization (DP) of a polymeric material is vital to understanding its chemical and physical properties.Depending on the application, MW of polymer materials can encompass an extremely large range extending from several hundreds (paints, coatings, functionalised polymers) to a few million daltons (UHMWPE, .The MWD is probably the single most fundamental property of a polymer (see Molecular Weight Distribution and Mechanical Properties). Another form of the Flory equation is shown in Equation 3. 1 C and D the evolution of molecular weight as a function of polymerization time is shown during the seeded emulsion polymerization of . 1, 2 Both molecular weight distribution (MWD) shape and dispersity can significantly impact polymer .
Overview
Polymers: Molecular Weight and its Distribution

Knowledge of the average length and statistical distribution of polymer chains enables the prediction of numerous physical-chemical and rheological properties [1]. While in the past this was typically considered as an unavoidable consequence of polymer synthesis, multiple recent studies have shown that tailoring the molecular weight distribution can alter the properties of polymer brushes . (1982) Influence of molecular weight and molecular weight distribution on mechanical properties of polymers.Reason for claiming that the average molecular weight (Mn and Mw) and its polydispersity (molecular weight distribution) are the crucial indices in the final product properties and how they affect the physical and mechanical properties of the polymer should be referred to the text course and a lot of articles in this field. It is not necessary to .The molecular weight distributions for this polymer were calculated to be Mn: 2300, Mw: 2350, and Đ =1. T Q Nguyen and H H Kausch.04, but the dispersity increased as the . Weight fraction of fraction 1 = n 1 M 1 /W = n 1 M 1 /n i M i.polymer’s molecular weight distribution (MWD) impacts material properties such as processability, mechanical Astrength, and morphological phase behavior1 –6. The breadth of the molecular weight distributions (MWD) of polymers influences their physical properties; however, no synthetic methods allow precise control of the exact shape and composition of a distribution. This higher molecular weight distribution formed through radical–radical bimolecular termination.Knowledge of the molecular weight (MW), molecular weight distribution (MWD), and degree of polymerization (DP) of a polymeric material is vital to . polypropylene (PP) with DP = 100,000. Schinski, Robert A.Due to the adjustable grain size of the support the morphology as well as the molecular weight distribution [MWD ] of the polymer can be controlled . Molecular weight distribution (MWD) is essential for describing the microstructural quality of a polymer.The effect of molecular weight distribution of polyacrylamide (PAAm) on drag reduction was studied in two flow geometries. The molecular weight averages of each sample are summarized in Table 1, with the full MWD compared in Fig.Several relationships have been proposed .The molecular-weight distributions (MWDs) of polymers have a striking impact over their properties, from processability and mechanical strength to nearly all .The breadth of the molecular weight distributions (MWD) of polymers influences their physical properties; however, no synthetic methods allow precise control . Different samples of the same polymer can have .Comparison of PAAm with different molecular weight . Different methods of measuring the molecular weight yield different types of . 1, 2 These parameters are commonly determined using solvent-heavy gel permeation chromatography (GPC), a variant of size exclusion .A polymer’s molecular weight is related to that of the monomer, and the number of monomers present in the polymer molecule. Cossee and Arlmann [ 14 , 15 , 16 ] described a comprehensive mechanism for the activation and polymerization of olefins with Ziegler–Natta systems, and pictured below (Fig. The precise MWD compositions of these polymers can be modularly controlled through temporal Polymer Chemistry Most . However, most of the studies on MWD are limited .Unless they have been purified, synthetic polymers have a distribution of molecular weights.












